Abstract
The problem of stable wage growth of medical workers has been in the focus of state attention for the last few years and nevertheless does not lose its relevance, despite payments and emergency measures in connection with work during the pandemic period. Periodically carried out reorganizations of payment systems in health care are local, which does not lead to the formation of decent wages for medical workers. The authors' attention is focused on the analysis of the structure of wages and the results of the application of the coefficient of labor participation in health care on the example of a state medical institution – a blood transfusion station of regional significance. The authors of the article conducted study on the structure of wages before and after the introduction of an effective contract using the method of calculating the labor participation rate. The analysis of the calculation methodology and the practice of applying the labor participation coefficient revealed its shortcomings, which consist in the lack of connection of the indicators taken into account when calculating the coefficient with the results of work of medical workers. This situation does not contribute to increasing the confidence of medical workers in the stability of wages, and has signs of subjectivism and practically does not depend on the results of labor activity. However, this does not solve the existing problems with an inefficient wage structure and requires additional studies to develop new approaches to the formation of remuneration of medical workers.
Keywords: Effective contractlabor participation coefficientmedical personnelmotivationremuneration
Introduction
Decent remuneration for health care workers is a priority in the system of effective public health protection. The strategic goal of the state health policy is to increase life expectancy and improve the health of the population. To do this, it is necessary to create a system that will ensure the availability of medical care, increase the efficiency of medical services provided, establish a correspondence between the volume, types, quality of these services and the level of morbidity, the needs of the population, while using advanced achievements in the field of medicine. The key link in achieving the set goal and the main performers of time-consuming and responsible work is the medical staff. Thus, the state, the leadership of medical institutions and the population are interested in attracting qualified labor resources and in obtaining the maximum return from the use of available personnel. However, the real situation is significantly different from the required level and the insufficient level of salaries of medical workers is one of the significant reasons for the reduction in the number of doctors in our country.
Research conducted in Russia and abroad shows that the most effective tool for evaluating employee performance is an open and understandable stimulation system for employees, one of the tools of which is the monthly calculation of the labor participation coefficient, the principles of which are fixed in the effective contract system. The use of this coefficient in the remuneration system implies fair remuneration, which should encourage employees to work more efficiently, bring the efficiency of the organization's activities into line with the individual efficiency of its employees, objectivity in assessing the results of work, which supports the interest of employees in the effectiveness of their activities; accessibility, simplicity and economy. However, the practice of applying an effective contract in medical institutions shows ambiguous results, which may be a result of both the imperfection of the effective contract system itself and the principles of determining the effectiveness of employees' work, which determines the relevance of the research topic.
To analyze the availability of medical workers in the Russian Federation, we considered the dynamics of the number of doctors and mid-level health professionals for 2013-2018. As can be seen in Figure
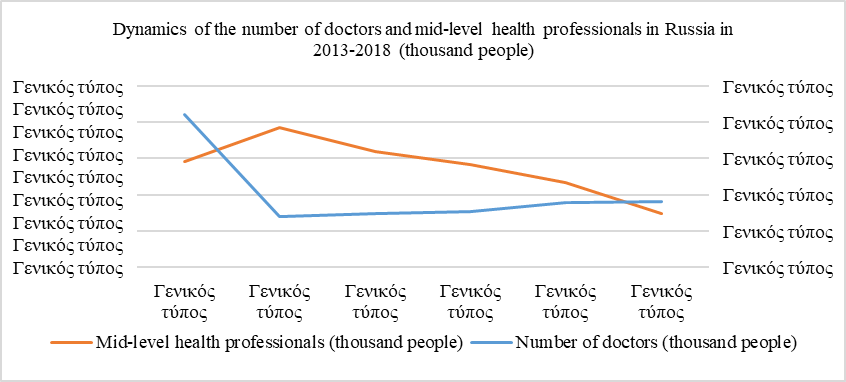
Source: authors based on (Rosstat, 2019)
This trend among medical professionals may be due, among other things, to unsatisfactory working conditions and insufficient remuneration of staff. In conditions of critically low growth rates or reduction in the number of staff in medical institutions, it is necessary to take all possible measures to increase the motivation of medical workers and attract new specialists (Kulakov et al., 2020). It is worth noting that the most important factor in motivating any employee is remuneration for his work, and the most stimulating effect is provided by remuneration, especially linked to the results of labor activity (Cheng et al., 2019). According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 2190-R of 26.11.2012, one of the ways to solve these problems is the mandatory reconstruction of the remuneration system for all budget medical institutions based on the introduction of an effective contract. An effective contract is a labour contract with an employee that specifies the employee's job responsibilities, payment terms, performance indicators and performance evaluation criteria for assigning stimulation payments depending on the results and quality of services provided, as well as social support measures (Kuchits, 2020). Thus, as a result of the introduction of an effective contract, health care workers have the opportunity to establish a direct relationship between the efficiency and quality of work and the size of their wages through the use of the labor participation coefficient.
Problem Statement
According to the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 07.05.2012 No. 597 until the beginning of 2019, employees of state and municipal organizations have to increase their salaries and bring them to a certain socially normal level (Sakhno, 2019). This process of changing wages in the public sector is controversial and has not been fully resolved (Chirikova, 2019). Therefore, the study of wages as an economic category and concept is relevant for modern economic science and practice. In this regard, there is a need to study the practice of using an effective contract system, evaluate labor results and analyze the impact of these results on the amount of wages.
The economic value of the labor force based on the economic result obtained can be differentiated through the labor participation coefficient or the qualification coefficient. Therefore, wage as an economic category is a monetary form of expression of the value of the labor force of an employee, which he receives from the employer for the created and realized economic result (Doljenkova, 2019). To approve such an economic form of salary, the employer must provide the employee with socially normal working conditions, the corresponding socially normal level of production technology and the implementation of the economic result. Wage as an economic concept is a monetary form of expression of the value of the labor force of an employee, which he receives from the employer, depending on the actual result created, mediated by the planned economic result. In the regulatory documents of the Russian government, there is no clear division of remuneration at state-owned enterprises into basic and premium (additional). In our opinion, the division of wages into basic and premium is associated with the allocation of its statistics and dynamics in the economic result.
If we turn to the state regulatory documents that should contribute to more reasonable remuneration in the transition of state organizations to the system of "effective contract", they have, in our opinion, a number of significant shortcomings. Firstly, there is no clear division of payment into basic and premium from the point of view of the obtained economic result. And the proposed division of labor remuneration into salary, compensation and stimulation payments is not justified from an economic point of view. In fact, the salary (basic wage) is lower, and stimulation payments are updated, becoming decisive in remuneration.
The introduced system of remuneration on the basis of an effective contract for the employee and for leadership is complicated. Many people that conclude an "effective contract" do not understand the components of both basic and stimulation remuneration. The wage is distorted as an economic concept, does not work effectively for the economic result, because the socially normal reproductive aspect of the wage and its stimulating function for the actual development of the employee disappears and, ultimately, the concluded labor contract ceases to work effectively. In our opinion, the "effective contract" should be used not only as a tool for preserving human resources, but also as a system for justifying the economic results of activities, as well as the reproduction of employees themselves as limited economic resources of organizations and their development.
Research Questions
Of interest is the question of the practice of applying the labor participation coefficient, the assessment of the impact of its introduction on the size and structure of wages, the perception of its introduction by employees of medical institutions. As an example for the study, the regional state medical institution the Blood Transfusion Station was chosen, in which, as in other state medical institutions of Russia, the transition to an effective contract was made in order to improve the remuneration system. To assess the results and prospects for the development of an effective contract, we conducted a SWOT analysis of the new remuneration system based on indicators and criteria for the performance of employees (Table
In the process, analysts identified weaknesses and threats that may hamper achievement of the objectives of the introduction of an effective contract and involve the development and implementation of a number of measures on their elimination and prevention, namely: definition of the mechanism to increase wages (source of funding); establishment of a system of performance indicators, the relevant duties of the employee and taking into account the actual labour contribution and specifics of work; informing all employees about the implementation of effective contract with a detailed explanation of the principles of calculation of stimulation payments; creation of conditions for carrying out independent expert evaluation of workers. As a result of the analysis, it was determined that the most effective tool for evaluating employee performance should be an open and understandable stimulation system for employees, one of the tools of which is the monthly calculation of the labour participation coefficient.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of study is to identify characteristics of transition of the state medical institutions on the use of the effective contract in system of social and labor relations in providing a stimulating effect on the workers' labor activity on the example of doctors of main blood sampling department. To achieve this goal, tasks were solved that allow to identify the main stages and systematize the results. In the course of the study, the staff schedule of the blood sampling department was analyzed according to the professional and official structure and the structure of cash payments. Analysis of the content of the personnel employment contract in terms of remuneration allowed us to determine the principles of remuneration and mutual responsibility of the parties in social and labor relations. In order to detail the principles and methods of calculating wages in the institution, an analysis of local regulations governing the payment of labor in the institution was carried out. A survey of blood sampling department employees was conducted, and the results of the survey were analyzed.
Research Methods
The study uses such methods of economic research as: modeling, the method of scientific abstractions, analysis and synthesis, system and functional approaches; special research methods: sociological and comparative methods. The coefficient of labor participation (CLP) is a differentiated remuneration of employees of a medical institution, taking into account the quality and volume of total individual labor invested in the overall result of the team. The use of this coefficient in the remuneration system implies fair remuneration, which should encourage employees to work more efficiently; bringing the efficiency of the organization's activities into line with the individual effectiveness of its employees; objectivity in assessing the results of labour, which supports the interest of employees in the effectiveness of their activities; accessibility, simplicity and economy.
Findings
Awarding of medical workers based on the results of work for a month is made taking into account the indicators (criteria) of the quality of work of each employee, developed jointly with the heads of structural divisions.
As an example, let's consider the criteria for the appointment of CLP in the Samara medical institution:
working conditions (physical activities), where the doctor and the head of the department can get from 1 to 3 points;
ability to work with equipment-a 5-point rating system (5 points for the most difficult work and then in descending order) for the head of the department and 1 point for the ability to work on each type of equipment for doctors (there are 4 equipment in the organization);
ability to set up equipment: the head of the department and doctors are awarded 2 points for setting up each equipment;
the intensity of work, which is evaluated by a 3-point system for both the head of the department and the doctors;
implementation of quality control – a 3-point evaluation system for the head of the department and doctors;
responsibility - assessment on a 3-point system, where 3 points are awarded for the most responsible work and then in descending order.
The personalized calculation of the CLP and the amount of the award is reflected in the work evaluation sheets filled in by the heads of structural divisions with the approval of the directors deputy for the medical part, for production, for economic issues. We analyzed one of these sheets for evaluating the work of employees of one of the departments of the Samara medical institution in 2019. The stimulation effect that is expected from the introduction of an effective contract system largely depends on the validity of the CLP, the principles of calculation, and its connection with the results of the entire Institution's activities. The system of local regulations describing the principles of remuneration should be confirmed by the facts of accrued wages in settlements with employees, which will be carried out by us later when assessing the parameters of accrued wages before the introduction of the effective contract system and after it.
The principle of calculating the CLP is specified in the Regulation on monthly award and is established depending on the criteria for evaluating the work of medical personnel for awarding within the framework of the state task of heads of structural divisions (doctors). The analysis of the criteria used to evaluate labor allows to conclude that they are poorly related to the parameters of the state task and the evaluation criteria of the entire Institution and do not show the results of the employee's work. The nature of the criteria is more related to the skills and abilities of working with equipment, rather than to the results of work, which does not allow the organization to encourage employees to work productively.
Judging by the calculation parameters, we can say that, most likely, the CLP is affected by what equipment a particular doctor works on, his skills and abilities to work on this equipment, which is of course important, but not related to the results of the work of doctors and mid-level health professionals. This does not take into account the effectiveness of the doctor's work, his communication with patients, the presence of positive or negative reviews, etc. The validity of the criteria "Intensity" and "Responsibility" and the principles by which their significance is determined raise questions. Thus, despite the presence of such an indicator as CLP in the labor remuneration system, its effectiveness cannot be high due to insufficient elaboration of the criteria for evaluating the results of work.
Confirmation of the conclusions made is the analysis of the job descriptions of the doctor, senior nurse and nurse, whose job responsibilities, respectively, and performance indicators are not reflected in the calculations of the CLP. Consequently, employees cannot influence the amount of the stimulation part of wages, even if they perform their duties in a high-quality and conscientious manner.
To assess the results of implementing an effective contract in practice, we also conducted a survey that confirmed the results of the analysis of the stimulation system. 27 people took part in the survey. The main contingent of employees has more than 15 years of experience and is over the age of 45 years. As a result of the survey, it turned out that only 11.11% of the surveyed employees understand the point of an effective contract and its fundamental difference from the previous employment contract. The remaining 88.89% of respondents either do not know about its existence, or believe that the names of the documents are different, but the point is the same (Table
More than 60% of all employees do not understand the salary structure, and therefore cannot influence its value. Among them, 70% of employees of mid-level health professionals and 61.5% of employees of other personnel consider the remuneration system as too complex. However, three-quarters of doctors and a third of employees of other and mid-level health professionals can check what their salary consists of, which indicates the applicability of such complex stimulation systems only for qualified personnel who have the necessary competencies to perceive it.
For doctors priority factors influencing wages rate are skills (25%) and organization incomes (25%), for mid-level health professionals – qualifications (of 28.57%) and Government Decree of the Russian Federation (23,81%), for other staff – number and quality of the performed work (46,47%) and the income of the organization (26,67%). However, despite the fact that most employees do not understand the essence of an effective contract and the structure of wages, 45.5% of all respondents noted the quantity and quality of work, qualifications, experience, and ability to work with equipment as factors that influence wages, which are very similar to performance indicators.
A third of the surveyed doctors and employees of other personnel claim that the amount of their bonuses is not related to the actual results of work, which confirms our conclusion about the need for changes in the principles of calculating CLP and forming wages for different categories of employees. Almost 40% of mid-level health professionals associate the amount of rewards with their qualifications and position. 50% of respondents believe that the distribution of stimulation payments in their organization does not depend on the results of the work of a particular employee and allow the possibility of excluding personification in favor of avoiding conflicts in the team. Such contradictory results of the survey can be both a consequence of insufficient awareness of employees about the principles of distribution of stimulation payments, and the result of a transparent and subjective assessment of the management of employees' activities. The majority of employees (85.19%) believe that they are underestimated and consider the assessment of their work as subjective. And only 14.81% of all employees are confident in the objectivity of the assessment of their work. At the same time, employees would like to be able to influence their wages through more efficient work - 58% of all employees said that the ability to manage their wages encourages better work. Among them, this opinion is shared by half of the surveyed doctors and employees of other personnel, as well as 64.3% of mid-level health professionals. The rest of the respondents do not consider this possibility as a stimulation tool.
Thus, the analysis of the calculation of the labor participation coefficient and the analysis of the survey results showed the weaknesses of applying an effective contract in practice and confirmed the threats identified by us in the SWOT analysis. The first problem is that most employees do not understand what an effective contract is all about. In this regard, there is no understanding of the order of distribution of stimulation payments, the relationship between performance indicators and wages. At the same time, the staff is aware that the quality and quantity of work performed affects the amount of remuneration, but they do not understand the principles of this influence. Another problem lies in the subjective evaluation of employees work by leadership, in connection with which health staff can't tie the actual results of labour to the wage rate. Because of this, there may be conflicts in the team, a decrease in motivation, an increase in the level of staff turnover. However, the results confirmed the need to introduce effective stimulation systems for employees of budgetary institutions to increase motivation and retain employees in the team. An effective contract as a way to introduce an innovative form of remuneration and the use of CLP in this system can really become a powerful tool for stimulating labor and securing personnel. However, to achieve the expected result, it is necessary to use the experience gained as a result of implementation, to use grading systems and attract highly qualified personnel who will be able to develop and implement new remuneration systems that will increase the level of monetary remuneration of medical personnel, taking into account objective performance indicators.
Conclusion
As a result of conducting studies on the example of one of the structural divisions of the state medical institution blood transfusion station, systemic inconsistencies in the salary structure were identified for the purposes of introducing an effective contract, which allowed to determine the principles of forming criteria for evaluating labor. Thus, the analysis of the calculation of the labor participation rate and the analysis of the survey results showed the weaknesses of the application of an effective contract in practice and confirmed the threats identified by us. The results of the study are applicable for the development of new criteria for evaluating the work of employees of the studied institution, other medical institutions, as well as for the formation of a new system of motivation of employees of the medical field of activity.
Based on the results of the study, it is recommended to change the principles of labor evaluation for use in the effective contract system. As a result of the use of research materials in practical activities, an improved system of employee motivation can be developed, which will lead to an improvement in performance indicators. The materials of the study are necessary for making a decision on the development of a new system of motivation of employees of a medical institution and evaluating the results of the implementation of an effective contract system. If a decision is made to develop a new system of motivation for employees of an institution, new criteria for evaluating work related to the performance parameters of the entire institution and individual structural units can be developed for use in the motivation system and fixing the main provisions of this system in the structure of an effective contract. The implementation of an improved effective contract system can lead to an increase in the efficiency of the institution as a whole. The obtained results can be used in the health care system in other medical institutions.
References
- Cheng, Y., Mohanty, A. F., Ogunyemi, O. I., Smith, C. A., Leroy, G., & Zeng, Q. T. (2019). 2018 salary survey of AMIA members: Factors associated with higher salaries. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32308820/
- Chirikova, A. Sh. (2019). Effective contract and motivation: Can reforms improve the work of Russian doctors? Sociological Studies, 5, 36-44.
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 07.05.2012 No. 597. https://mintrud.gov.ru/docs/president/ukaz/37
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 2190-R of 26.11.2012. https://mintrud.gov.ru/docs/government/91
- Doljenkova, Y.V. (2019). The new system of remuneration of labor in budget health care: Analysis of practice and problems of implementation. Problemy Sotsial’noi Gigieny, Zdravookhraneniia i Istorii Meditsiny, 27(4), 452-458.
- Kashtanova, E. A. (2020). Russian labour market outlook. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 753(7), 082026.
- Kostyrin, E. V. (2020). Economic and mathematical models of financial incentives for the personnel at medical organization departments. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 12(4), 1769-1780.
- Kuchits, S. G. (2020). The organizational legal and methodological foundations of implementation of effective contract in functioning of medical organizations Problems of Social Hygiene, Public Health and History of Medicine, 28(1), 94-94.
- Kulakov, A. A., Butova, V. G., Andreeva, S. N., & Tarasva, I. P. (2020). Regulatory framework of the new system of wage payment in research institutions. Stomatologiia, 99(4), 57-63.
- Rosstat (2019). Russian statistical yearbook. https://rosstat.gov.ru/folder/210/document/13204
- Sakhno, N. (2019). Effective contract in a medical facility. Chief Medical Officer, 5, 32-34.
- Sang, T. Z. (2020). Investigation of the differences between the medical personnel’s and general population’s view on the doctor-patient relationship in China by a cross-sectional survey. Globalization and Health, 16(1), 99.
- Simonova, M. V., Mirzabalaeva, F. I., & Sankova, L. V. (2019). Differentiation of regional labor markets: New risks and opportunities for smoothing. In S. Ashmarina & M. Vochozka (Eds.), Sustainable Growth and Development of Economic Systems. Contributions to Economics (pp. 259–274). Springer.
- Ulumbekova, G. E. (2019). A system approach to achieving the national goal of increasing life expectancy to 78 years by 2024. Economics, Taxes & Law, 12(2), 19-30.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Simonova, M. V., Kuskov, V. M., & Kolesnikov, S. A. (2021). Issues Of Applying The Labor Participation Coefficient For Remuneration In Health Care. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1598-1607). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.191

