Abstract
The paper presents the methodology to assess sustainable development in agriculture. First basic principles of sustainable development concept are presented. Main features of agriculture sustainable development were defined, by its specific areas. According to them, agriculture sustainable development indicators from Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations database were chosen and modified. By using mathematical metric and standardization methods, the algorithm was constructed, which allows to evaluate the current level of national agriculture sustainable development, by calculating rating for each sphere of sustainable development and for all spheres at ones. Presented algorithm is tested on database of Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. At the end, results are presented. Dynamics chart of calculated rating is presented with box-whisker plot of world rating distribution. Specified Russian dynamics of agriculture level of sustainable development and rank place in global agriculture, according to the main domains concept of sustainable development.
Keywords: Agricultureindicatorsmetric methodsRussiasustainabilitysustainable development
Introduction
Agriculture is a vital industry for every country. Moreover, agriculture alows to achieve one of the main goals of sustainable development “Zero Hunger” (Hák, Janoušková, & Moldan, 2016; Barbier & Burgess, 2017). This is why sustainable development of agriculture is so important.
Many studies are dedicated to the sustainable development of agriculture (Jeníček, 2013; Madu & Kuei, 2012; Martinet, 2011). They define basic of agriculture sustainable development in three main areas:
Economic;
Social;
Ecological.
The economic area of agriculture sustainable development implies the optimal use of limited resources, i.e. achieving economic viability by maximizing revenue while minimizing costs.
The social area of agriculture sustainable development is expressed in its main social function, namely, in providing people with food in the quantities necessary to meet their needs.
The ecological area of agriculture sustainable development ensures the integrity of biological and physical natural systems in the production activities of agriculture (Glazovsky & Sdasyuk, 2005; Gnezdova et al., 2016; Gur'eva, 2016; Ugol'nickij, 2016; Ushakova, 2015).
Problem Statement
Nowadays when many countries try to reach the goals of sustainable development, agriculture gets one of the main positions in achieving them. This is why it is valuable to find out the current level of sustainable development before finding the best development pattern of agriculture.
Research Questions
The main questions of the research are below:
What are the trends of world agriculture sustainable development?
What is Russia’s position in world agriculture development?
Purpose of the Study
The paper aims at developing an algorithm, with the help of mathematical methods, that allows to evaluate national level of sustainable development in agriculture.
Research Methods
Summarizing international experience in evaluating the level of sustainable development, two approaches can be distinguished (Heink & Kowarik, 2010; Muthu, 2019; Sakalauskas, 2010; Danilov-Danil'yan & Losev, 2000; Bobylev, Zubarevich, Solov'eva, & Vlasov, 2008; Waas et al., 2014) :
the construction of an integral, aggregated indicator based on the degree of sustainability can be defined. Aggregation is usually based on three groups of indicators: economic, social and ecological ones;
working out the system of indicators, each reflecting three areas of sustainable development.
The first approach was used in this study.
Research database
The main source of indicators was a database of Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Indicators were divided into three groups by domains of sustainable development:
Economic;
Social;
Ecological.
Main indicators presented by FAO were modified into the following ones (Table
Indicators from FAO database are presented for different periods of time. Using moving average, indicators were evaluated for identical time periods. However, some indicators presented in FAO database have significant lag (Table
Algorithm
The rating was evaluated with metric methods calculating distance from the ideal object (country). A country that has ideal indicators value was referred to as an ideal country. The distance was calculated for each country from the ideal country for all time periods. The algorithm is presented in Figure
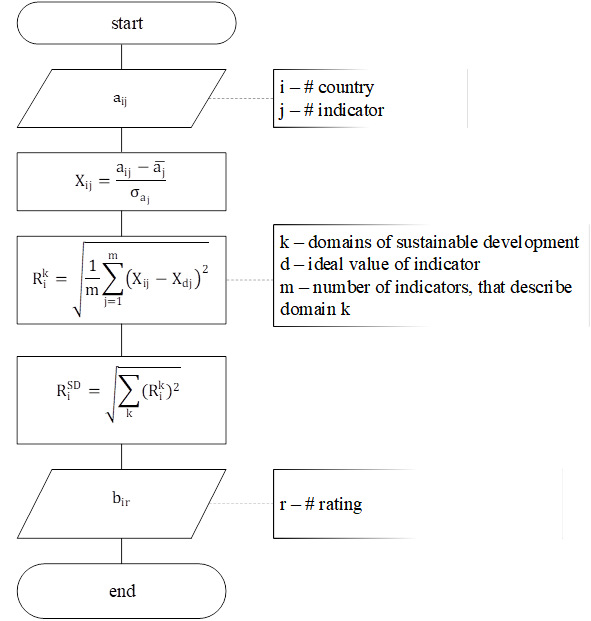
Before applying the algorithm, some indicators (see Table
The algorithm was produced in the following sequence:
Indicators values (aij) were standardized.
For each country rating ( ) was calculated, by each sustainable development area.
For each country rating ( ) was calculated.
Countries were ranked by rating ( ).
The lower value of ( ) the higher level of agriculture sustainable development.
Findings
The algorithm was applied to every country that has information for those time periods (Table
Economic area
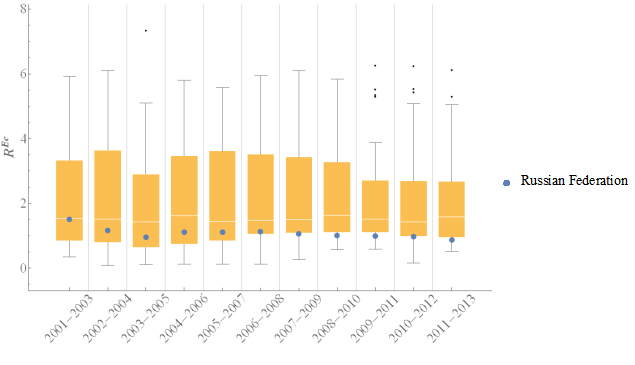
For most of the time periods value of
for Russia was less then 50% of other countries. In the last periods of time (2007-2013) Russian value of
was going outside of the interquartile interval. For all time periods under analysis,
became smaller by 40% (Table
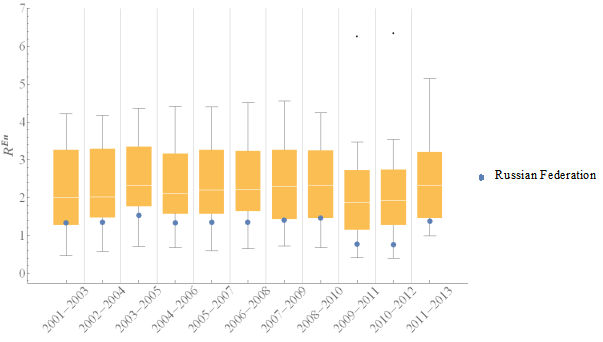
Social area
In the context of social area, the median value of is increasing. Most of all it means that food production is growing slower than people population in most countries.
For most time periods value of
for Russia was less than 50% of the countries had. There was not so much of fluctuation of
over the past time periods. This fluctuation can also be viewed by the growth rate and rank number # (Table
Ecological area
Agriculture sustainable development had no dramatical change in ecological area. An exception has only 2 time periods (2009-2011 and 2010-2012), when the distribution of
changed by a much lower value. Russian dynamics of
doesn’t differ strongly from world dynamics (Table
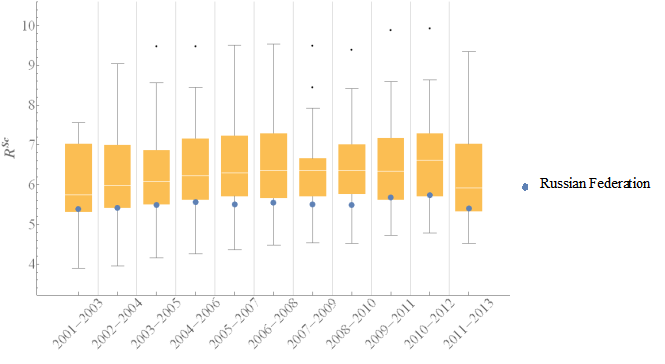
Sustainable development
Considering all three domains of sustainable development was calculated. In first time periods median value of was near to 3-rd quartile, then to the first one. That fact means there were more countries were concentrated then in the last periods of time periods.
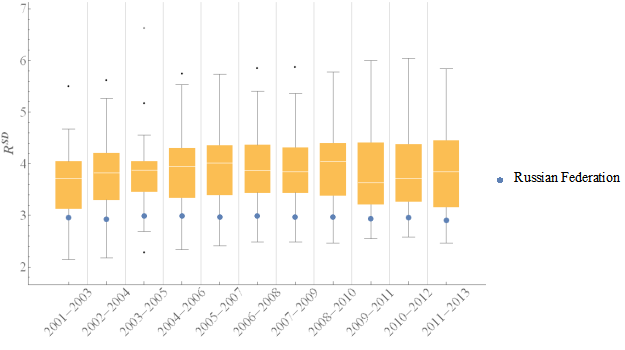
According to all time periods, Russian level of agriculture sustainable development was high. Russian level of was lower then the first quartile, it mean that Russia was in 25% of countries with hightes level of agriculture sustainadble development. That fact also comfirms with dynamics of growth rate and rank number # in table 07. The rank number of Russian changed from 11 to 7.
Conclusion
Sustainable development of agriculture is impossible without an objective statistical evaluation of its current level of development. Presented methodology allows to estimate current level of sustainable development of agriculture in general and in the context of areas.
This methodology has some disadvantages. Because most of indicators has ideal values maximized (+∞), there is no much variation between countries by rating values.
Nevertheless, the results of presented methodology facilitate management decisions for countries agriculture sustainable development.
References
- Barbier, E. B., & Burgess, J. C. (2017). The sustainable development goals and the systems approach to sustainability. Economics, 11.
- Bobylev, S. N., Zubarevich, N. V., Solov'eva, S. V., & Vlasov, Yu. S. (2008). Indikatory ustojchivogo razvitiya: ehkonomika, obshchestvo, priroda. Moskva: MAKS Press.
- Danilov-Danil'yan, V. I., & Losev, K. S. (2000). Ehkologicheskij vyzov i ustojchivoe razvitie. Мoscow: Progress-Tradiciya.
- Glazovsky, N. F., & Sdasyuk, G.V. (2005). Ustojchivoe razvitie sel'skogo hozyajstva i sel'skih territorij: Zarubezhnyj opyt i problemy Rossii. Мoscow: T-vo nauch. izd. KMK.
- Gnezdova, Yu. V., Vypryazhkina, I. B., Galij, E. A., Goloveckij, N. Ya., Anisimov, E. Ya., Medvedeva, I. A... Kondrashov, K. A. (2016). Problemy ustojchivogo sbalansirovannogo razvitiya regionov v sovremennyh usloviyah. Moskow: Nauchnyi konsultant.
- Gur'eva, M. A. (2016). Vzaimoobuslovlennost' ponyatij "zelenaya ehkonomika", ustojchivoe razvitie, ehkologicheskoe razvitie ehkonomicheskogo prostranstva. Global'nyj Nauchnyj Potencial, 5(62), 46–55.
- Hák, T., Janoušková, S., & Moldan, B. (2016). Sustainable Development Goals: A need for relevant indicators. Ecological Indicators, 60, 565–573.
- Heink, U., & Kowarik, I. (2010). What are indicators? On the definition of indicators in ecology and environmental planning. Ecological Indicators, 10(3), 584–593.
- Jeníček, V. (2013). Sustainable development - Indicators. Agricultural Economics (Czech Republic), 59 (2), 74–80. Available online at https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84875104409&partnerID=40&md5=9cf9c08d8a90ac16fed286c3d78308c2.
- Madu, C.N., & Kuei, C, (2012). Handbook of sustainability management. Singapore, Hackensack, NJ: World Scientific.
- Martinet, V. (2011). A characterization of sustainability with indicators. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 61(2), 183–197.
- Muthu, S. S. (2019). Quantification of sustainability indicators in the food sector. Singapore: Springer (Environmental footprints and eco-design of products and processes, 2345-7651).
- Sakalauskas, L. (2010). Sustainability models and indicators. Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 16(4), 567–577.
- Ugol'nickij, G. V. (2016). Upravlenie ustojchivym razvitiem aktivnyh sistem. Rostov-na-Don: Izdatel'stvo YUFU.
- Ushakova, N. B. (2015). Napravleniya ustojchivogo razvitiya ehkonomiki sel'skogo hozyajstva regiona. Mezhdunarodnye nauchnye issledovaniya, 1-2(22-23), 44–48.
- Waas, T., Hugé, J., Block, T., Wright, T., Benitez-Capistros, F., & Verbruggen, A. (2014). Sustainability assessment and indicators: Tools in a decision-making strategy for sustainable development. Sustainability (Switzerland), 6(9), 5512–5534.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
02 April 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-058-7
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
59
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1083
Subjects
Business, innovation, science, technology, society, organizational theory,organizational behaviour
Cite this article as:
Timofeev, A., Telyuk, M., & Lebedinskaya, O. (2019). Evaluation Of Agriculture Sustainable Development. In V. A. Trifonov (Ed.), Contemporary Issues of Economic Development of Russia: Challenges and Opportunities, vol 59. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1033-1041). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.04.112

