Abstract
In this article, existing methods are analyzed of state regulation and its effectiveness using the example of international road transport. A special feature of these transportations is the dual responsibility of the regulatory body. The article examines the mechanism of state regulation through the prism of public, industrial and individual enterprises. The tendencies are revealed of lobbying interests increasing for large enterprises and tendencies of small businesses displacement from the international road transport market. The conclusions are made about the balance violation of all market participants' interests and the impact on the quality of services provided to participants in foreign economic activity. In this article, there are also conclusions about the need to develop a mechanism to regulate the international road transport market that will allow to use transport resources effectively, to improve the economic performance of enterprises, to reduce transport costs and to increase tax revenues to the budget.
Keywords: State regulation, international road transport, small business, international economy, market
Introduction
Market relations development implies a reduction of state interference in the activity of economic entities: market entry procedures, regulatory and supervisory regimes are simplified. At the same time, there are areas of activity that are regulated by the state not only in the Russian Federation, but also in all European countries. International road transport is such an activity, since its operation is classified as a high-risk area.
Problem Statement
Russian transport companies should have access to international road transport (IRT). The IRT market is characterized by high level of Russian carriers and foreign companies. The market includes large companies with hundreds of vehicles, medium-sized enterprises, small and even micro-enterprises. The market has constantly been evolving despite the existing difficulties and problems – small business turns into medium-sized ones and medium-sized ones turn into large ones. At the international level, certain results have been achieved in national carriers' protecting: according to the Association of international road carriers of Russia (ASMAP), the market share of Russian carriers has increased to 44-45%. Unfortunately, these figures have been obtained not by increasing the competitiveness of Russian companies, but by reducing the licensing quotas for foreign carriers.
Research Questions
However, the introduction of restrictions led to retaliatory measures from other countries and a lack of permits for Russian companies. Every year the number of countries with fewer permits increases, and it means that market access of Russian carriers is limited. The situation has become particularly acute in the context of the crisis and pandemic, when the demand for transport companies' services is falling catastrophically, and transportation rates are decreasing. Many companies are forced to leave the market because they do not have the technical ability to realize transportation (because of permits lack), and new companies are almost closed for market entry (no access to distribute) (Lyashuk et al., 2016).
Consequently, improving the state regulation mechanism (Bryukhov & Kovalenko, 2018) in the conditions of permits shortage is an urgent task.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of this research is to develop a methodological approach to the creation of an innovative transport resource and its effective usage.
Research Methods
State regulation is measures set of administrative, regulatory and legal influence of the state on various spheres of the economy and society in order to achieve socially significant goals (Asyaeva et al., 2018).
Public interests in international transport are defined as road safety ensuring and transport quality. For this purpose, in many countries general requirements for companies engaged in road freight and passenger transportation have been developed and applied. The main criteria are reputation, financial position and professional competence. This approach has had a positive impact on the international road transport market in Europe. Thus, the establishment of uniform rules in the European Union directives has led to increasing the quality of transport services in Eastern European countries compared to the founding countries of the Union. Similar results are observed in Russia and other countries of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).
However, a special feature of IRT in Russia is the "dual regulation" related with lack of provision ability of transport resources (Wang, 2017) available to enterprises with foreign permits. More and more countries are becoming inaccessible to Russian carriers. The permits deficit to such countries as Poland, the Czech Republic, and Hungary makes it impossible to realize transportation not only to these countries, but also to many others, as routes pass through their territories. The absence of Polish permits actually closes transportation to Germany, Belgium, France, and the Netherlands, while the lack of Hungarian transit permits blocks transportation to Bulgaria, Slovenia, Serbia, Italy, and Greece.
The analysis revealed the following reasons for dissatisfaction with the demand for foreign permits:
- retaliatory measures to the actions of the competent authority to reduce the quota for the number of countries;
- traffic routes changes caused by the risks of passing through the territories of a number of transit states in relation to the unstable political situation that increased the burden on directions that have a short supply of permits;
- inefficient use of permits by enterprises due to control failure over performed transportation.
Table 01 shows the methods of state regulation on IRT and the main purposes that should be set by the regulator.
The excess demand for foreign permits from the Russian carriers leads to the need to develop transparent common rules for allocation of these permits. The task is to find a balance between public and private interests represented by enterprises or groups of enterprises. At the centre there should be taken the task of effective usage of transport resources available to carriers and also the formation of competitive potential of transport companies (Mikhailushkin et al., 2018; Ryazantsev et al., 2018). For this purpose, it is necessary to create conditions where the transport company can be freely available to plan its road freights instead of "just in case" stating permits needs with unsecured orders while these needs are creating a new deficit. It should be a flexible system that allows transport companies to hand over or exchange permits freely, without any sanctions from the regulator. If this process is not stopped, the negative trends of market loss by Russian carriers will continue and also tax revenues to the budget will decrease (Table 02, Figure 01).
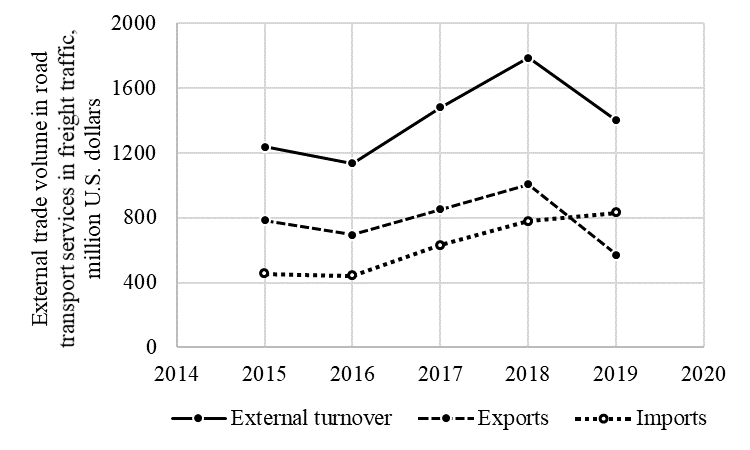
As can be seen from Table 02 and Figure 01 (according statistics from corresponding Yearbooks of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on External Trade of the Russian Federation in Services), there is a general decline in external trade volume in road transport services, while decline rate in exports of transport services outstrips reduction in imports that led to a negative balance.
Findings
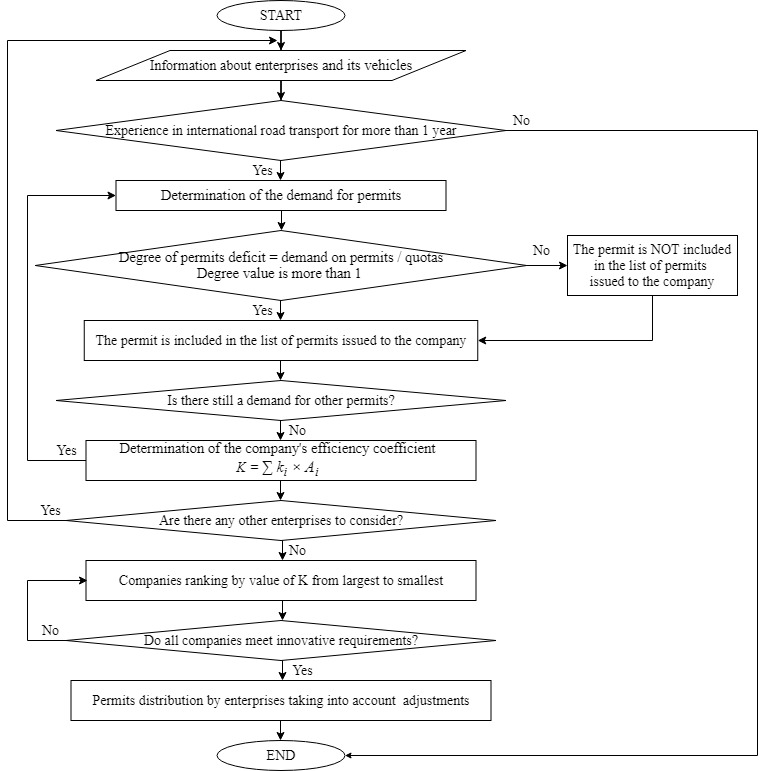
The purpose of offered in this paper concept is to create an innovative transport resource and to use it effectively (Figure 02).
Stage 1. Selection of enterprises based on binary decision indicators (indicators with value of either "Yes" or "No")
Enterprises give information about:
- availability of access to IRT,
- availability of vehicles with indication of the environmental standard.
The authority responsible for issuing permits verifies the accuracy of data provided.
Companies that satisfy the requirements of stage 1 and have at least 1, 3, 5 years of experience in international transportation are allowed.
Stage 2. Determination of the demand for permits
Enterprises apply for each type of permit that based on the forecast of work with the regular and potential customers.
Stage 3. The countries rankings according to the degree of permits deficit
The degree of deficit is determined by the ratio of demand (declared permits needs) and quotas agreed for the next period.
Ranks are defined for each type of permits.
Stage 4. Determination of the company's efficiency coefficient for the previous period
where – comprehensive indicator of the company's efficiency;
– indicator of each type of violation;
– the weight value of this violation.
Deviations from set rules for working with permits are considered as indicators. For example, the lack of confirmation of the permit use or late permit delivery can be referred to such deviations.
Stage 5. Additional or innovative requirements
5.1 Assessment of the company's vehicles fleet by the progressivity index that shows technical lag behind the market leaders.
5.2 Equipping the vehicles fleet with a tracking system.
There is determined the share of the vehicles fleet equipped with a tracking system.
5.3. Application of technological solutions.
Availability to use two drivers for transportation, to realize mixed transport and to couple / uncouple trucks and trailers.
Stage 6. Determination of the number of permits for each enterprise, taking into account adjustments to multilateral permits received.
The proposed approach will allow:
- for foreign trade participants – to get a high-quality service at a market price;
- for the state – to increase transport services exports and budget revenues;
- for companies – to use truck fleet effectively and to improve the economic performance.
The results of the study are compared with methodological approaches for selecting enterprises to work in the road freight transport market at the international level, using the instance of the European conference of Ministers of transport (ECMT), as well as approaches for permits allocation at the national level, for example of Russia and Belarus.
ECMT system
The main purpose of the distribution system of the ECMT permits is to use green and safe vehicles. Increasing coefficients are being introduced for vehicles that meet environmental standards. This approach is aimed at stimulating fleet renewal. According to International transport forum 2015 the practical results of this approach indicate that vehicles are constantly being upgraded and it is in the ECMT system that the most modern vehicles operate.
The second factor that affects permits allocation is the efficiency of its using. To assess the efficiency there are used indicators such as general vehicle kilometres travelled and vehicle kilometres travelled with the load.
Monitoring is carried out using the logbook that is entered information about transport operations performed under this permit in chronological order in.
The Republic of Belarus
In Belarus, international road transport is a dynamically developing activity. This is largely due to the country's transit position. Exports of road transport services occupies an important place in the country's economy. The problem of distribution of permits between transport companies is also relevant for this country, especially in the context of falling demand for transportation.
Conceptual approaches to the allocation of deficit permits are:
1) Access restrictions to deficit markets for new carriers, for one year after obtaining international cargo transportation license, the company can not participate in permits distribution.
2) As a criterion for selecting enterprises, revenue per vehicle is used and compared with the industry average.
3) Control over the use of permits (confirmed by the realization of transportation and the availability of goods and transport documents).
The accepted practice of quarterly permits exchange between countries and, accordingly, every three months permits allocation limit the planning horizon of transport companies.
Consideration of applications under the quota apart for multilateral and bilateral road haulage permits gives advantages to separate companies in obtaining two types of permits for one vehicle.
The regulator's requirement for the company to provide certain revenue and budget payments, accordingly, corresponds to the purpose of state regulation.
Russian Federation
The terms of foreign carriers distribution developed in the Russian Federation are aimed at large, experienced market players.
For these purposes, restrictive measures have been introduced to allow new carriers to enter the IRT market, so "if the carrier has not made road freights using foreign permits during five years preceding the year, that the distribution was made in, or has not made such freights every year, then the work experience coefficient is 0", that means that it is impossible to work in the market.
The lack of control over the use of permits allows carriers to declare the permits need in all directions of transportations.
As a result, carriers get permits, do not use them, but do not allow others to perform transportations. This is a good example when regulation realizes the function of permits redistribution.
Each approach to permits allocation has positive and negative aspects and can be taken into account when forming a new approach to carriers selecting.
Conclusion
1. A special feature of international road transport is the dual state regulation of business entities in the Russian Federation that is associated with an increasing shortage of permits to travel to foreign countries territories.
2. The current approach to permits distribution does not take into account the economic and innovative market requirements.
3. Developed concept of selecting enterprises for work is based on setup depending on the degree of deficit of permits type.
4. Innovative orientation of the proposed approach is a stimulating factor for updating the vehicle fleet and introducing new technological solutions.
5. Account and control of the use of permits will increase the number of road freights realized and provide additional tax budget revenues.
References
Asyaeva, E. A., Shichiyakh, R. A., Petrov, I. V., Dovtaev, S. A. S., & Listopad, E. E. (2018). External economic activity of enterprises: competitive advantages, state regulation. ESPACIOS, 39(31), 1.
Bryukhov, R. B., & Kovalenko, K. E. (2018). International legal regulation of road transportation (features of the legal consciousness of legislators). MATEC Web of Conferences, 239, 1–7.
Lyashuk, O., Kuzmych, V., & Lototska, V. (2016). The role of legal regulation and place of international organisations in transport companies’ development at foreign market. Journal of Sustainable Development of Transport and Logistics, 1(1), 49–55.
Mikhailushkin, P. V., Novoselova, N. N., Shulga, K. V., Kolpak, E. P., & Kabrits, S. A. (2018). Study of the forms and conditions of economic crises in the regional economies of developing countries. ESPACIOS, 39(31), 26.
Ryazantsev, S. V., Bogdanov, I. Ya., Gusakov, N. P., Moseikin, Yu. N., & Sholudko, A. N. (2018). Analysis of the implementation of the investment policy at the state level in the unstable geopolitics. ESPACIOS, 39(31), 12.
Wang, X. (2017). Static and dynamic resource allocation models for single-leg transportation markets with service disruptions. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 103, 87–108.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 December 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-118-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
119
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-819
Subjects
Uncertainty, global challenges, digital transformation, cognitive science
Cite this article as:
Domnin, I. V., Lutsenko, E. A., & Moroz, D. G. (2021). State Regulation Of International Road Transport In Conditions Of Restrictions. In E. Bakshutova, V. Dobrova, & Y. Lopukhova (Eds.), Humanity in the Era of Uncertainty, vol 119. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 793-800). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.12.02.99

