Abstract
In the contemporary constantly changing context, a person becomes a key player of economic development. The person's activity is aimed at achieving corporate objectives by means of his or her potential. The issue of employees’ competitive growth and application of resource efficient technologies in the human resources management field as a method of its solution are growing more urgent. In order to evaluate the level of competitiveness, the employees working at the oil and gas industry enterprises were surveyed as part of the study. As a result of gathered data analysis, factors having a strong influence on the employees’ competitiveness were identified and ranked; the assessment of individual competitiveness of the employees at the domestic and foreign labor markets was taken. The identified issues of the employees’ competitive growth require the employer to change approaches to human resources management, especially in the field of development of performance potential of the enterprise’s employees. The authors consider introduction of humanistic human resources management the potential solution of the identified issues. The articles suggests a mechanism of humanistic management, defines its structure: sub-processes, implementation tools, effectiveness assessment criteria. Introduction of the humanistic management mechanism will allow the enterprises to use human resources rationally and to increase competitive advantage of the employees and the enterprise in general.
Keywords: The employee’s competitivenesshumanistic management
Introduction
In the contemporary context, the key resource of economic development of an enterprise is a person, being an idea provider and a capital source. Application of resource efficient technologies in management of this type of resources will certainly lead to an improvement of enterprise performance efficiency.
Problem Statement
New approach to human resources management is humanistic management (Kondratev & Novikov, 2016; Krainov, 2011; Zhuravlev & Kupreichenko, 2007), which prioritizes creation of environment for production system development, on the one hand, and competitive growth of the enterprise’s employees, on the other hand.
Research Questions
In the authors’ opinion, the employee’s competitiveness is a complex attribute and one cannot express it monosyllabically, in the form of just one indicator, since it is based on a combination of various performance potential components having different degree of development at any particular time and depending on organizational and technical conditions of the enterprise (Khadasevich, 2011).
The enterprises need an assessment of the level of employees’ competitiveness in order to strategize their development, as well as to create efficient staff policy (especially related to training, development, motivation etc.).
The level of individual competitiveness of an employee allows him or her to take a certain position at the domestic and foreign labor markets (Miliaeva, 2017; Miliaeva & Bavykina, 2014; Ozernikova & Kravtsevich, 2008; Riazantseva, 2013, 2018; Stepus, 2007).
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to study the factors having influence on competitiveness of the enterprise’s employees and to define resource-saving technologies in human resources management for the employees’ competitive growth.
Research Methods
The questionnaire-based survey results were used as the data for assessment of internal and external competitiveness, as well as factors influencing on the competitiveness of enterprises’ employees.
Findings
Oil and gas industry enterprises were selected as the subject of the study: Mamontovskiy KRS, LLC (hereinafter MKRS), Pyt-Yakhavtotrans-3, LLC (hereinafter PAT-3), PYAUAT, LLC (hereinafter PYAUAT).
For the survey of values-based orientations related to professional life and competitiveness, the employees of the enterprises under survey had to answer the question: “What does work mean in your life?” (see in Figure
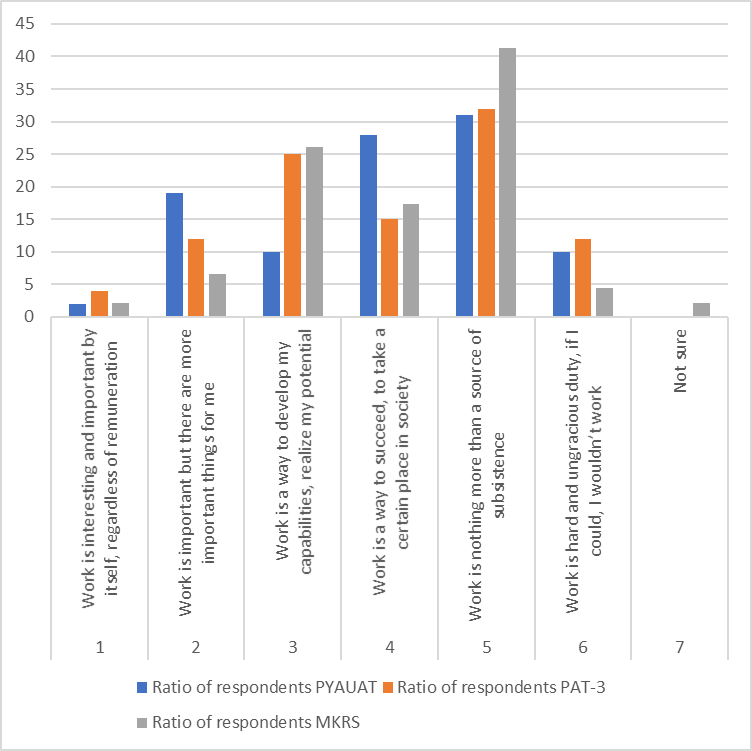
Gathered data analysis shows that more than 34.7 % of the employees take work only as a source of subsistence. It should be noted that 54 % of them were the employees aged 40 to 50 years. The employees aged under 30 years are more ambitious and take work as means of self-actualization, development, achievement of a certain social status. Assessment of own competitiveness defines behavior of the employees both at the domestic and foreign labor markets. In the course of the study, we asked the employees: “How do you assess the competitiveness of your profession in the event of a corporate restructuring?” (Figure
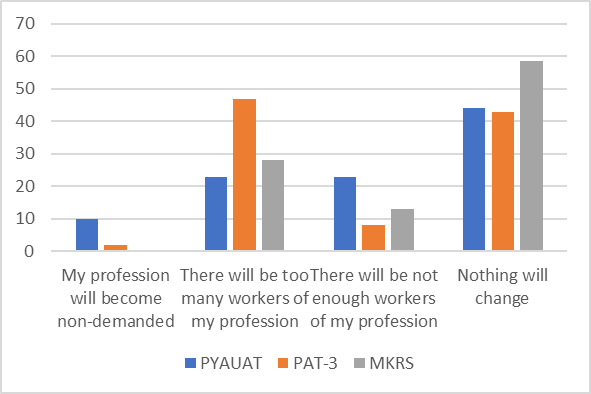
Analysis of survey findings shows that only 25% of respondents are not sure that they can withstand professional competition. More than half of respondents think that in the event of a corporate restructuring nothing will change and their profession is competitive.
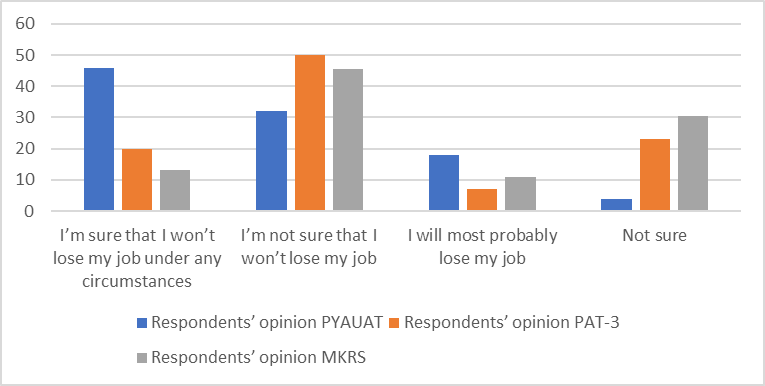
For the assessment of internal individual competitiveness, the respondents had to answer the following question during the survey: “How do you assess the possibility of employment in the event of a slowdown in economic growth?” (Figure
For the assessment of external individual competitiveness, the employees had to answer the question: “What are the prospects of your employment within the city?”, results are shown on Figure
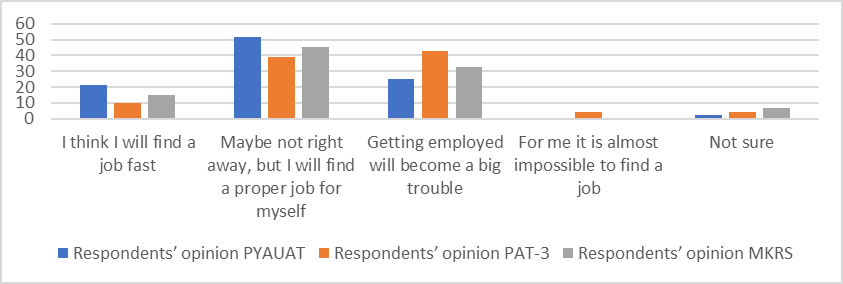
Gathered data show that 50 % of the employees of the enterprises under survey are afraid of being in low demand at the labor market in the event of a slowdown in economic growth. However, the higher the level of internal competitiveness, the higher the employees assess the possibility of employment at the external labor market.
The employees of the enterprises under survey recognize the importance of development, advanced training for competitive growth. In the course of the study, factors determining the employees’ pursuance of development and skill enhancement were ranked (table
As can be seen from table
When analyzing the reasons for skill enhancement, the dependence of importance of factors on the age and experience of the employees was found: the older the employees are, the lower the motivation for self-development and opportunity for growth of the wage level, and the higher the influence of the factor related to potential unemployment. Ratio of the employees, whose activities in the field of skill enhancement can be attributed to the opportunity for growth of the wage level, increases as work experience increases. Consequently, professional life is an integral part of a person’s life and the level of competitiveness at the labor market defines the quality of human resources.
As a result of the undertaken study, it was found that the employees of the enterprises under study think that their competitiveness is insufficient, are afraid of professional competition and insecure of the opportunity for employment in the event of termination of employment. But at the same time, they note the importance of professional development for competitive growth at the internal and external labor markets.
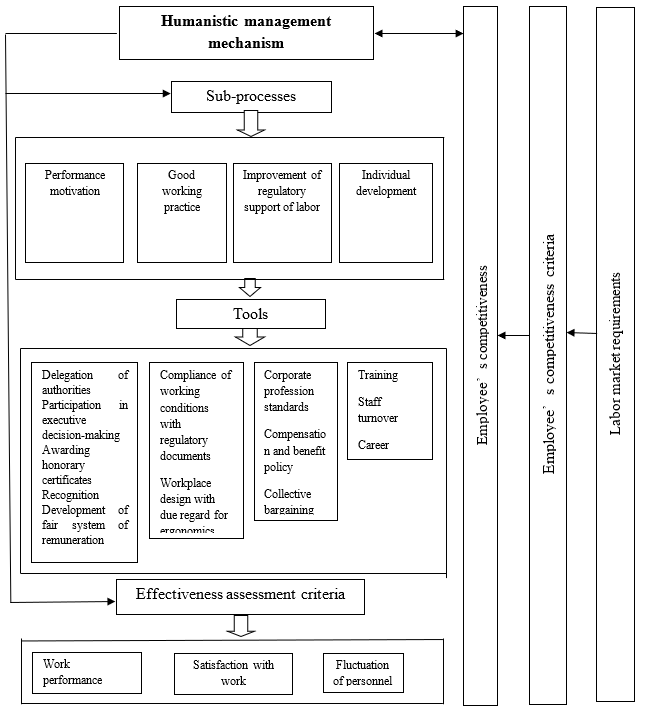
The authors regard introduction of humanistic management, focused on creation of conditions for development of the employees, into human resources management practice as the solution of the identified issue of the employees’ competitive growth (Riazantseva & Samoiliuk, 2016; Safonov, 2015, 2016; Shaburova & Samoiliuk, 2016). For optimum use of this approach to management, it is required to create a mechanism of humanistic management in the human resources management system (Figure
Humanistic management mechanism is based on performance motivation, good working practice, improvement of regulatory support of labor, individual approach to development of the enterprises’ employees that increases the competitiveness of the employees.
Conclusion
Introduction of the humanistic management mechanism to the human resources management practice will provide for competitive growth of the employees and the enterprise in general thanks to more efficient utilization of performance potential of the personnel.
References
- Khadasevich, N. R. (2011). Regarding some special aspects of labor potential of an enterprise. Topical Issues of Economic Science, 21-2, 222.
- Kondratev, E. V., & Novikov, K. V. (2016). Humanistic approach in management – “careful” approach to people. Drucker’s Bulletin 2(10), 7–16.
- Krainov, N. N. (2011). Economic substance and principles of humanization of social and labor relations at the enterprises. Social policy and social, 4(70), 303–311.
- Miliaeva, L. G. (2017). Comprehensive review of competitiveness of corporate staff. International Journal of Economic and Education, 1(3), 33–54.
- Miliaeva, L. G., & Bavykina, E. N. (2014). Competency-based approach to corporate staff competitiveness management. Bulletin of Eastern Economic and Law Academic for the Humanity, 6(74), 52.
- Ozernikova, T. G., & Kravtsevich, S. V. (2008). Estimation and assessment of a worker’s competitiveness at the labor market. Modern Competition, 2(8), 97.
- Riazantseva, I. V. (2013). Assessment of competitiveness of skilled professionals. Modern Issues of Science and Education, 6, 479.
- Riazantseva, I. V. (2018). Current trends in management of competence-based competitiveness of specialists. Society: politics, economic, law, 3, 56–59.
- Riazantseva, I. V., & Samoiliuk, T. A. (2016). Humanistic approach to human resources management. Theory and Practical of Social Development, 6, 76–78.
- Safonov, K. B. (2015). Humanistic paradigm of social management. Theory and Practice of Social Development, 15, 14.
- Safonov, K. B. (2016). Humanization of administrative relations: foreign and domestic experience. Society: social, psychological, pedagogical, 1, 33–35.
- Shaburova, A. V., & Samoiliuk, T. A. (2016). Modern approaches to human resources management. Theory and Practice of Social Development, 2, 47–48.
- Stepus, A. F. (2007). Theoretical background of a term “employees’ competitiveness”. Bulletin of the University of Udmurtia Economic and Law, Series 2, 239.
- Zhuravlev, A. L., & Kupreichenko, A. B. (2007). Conception of humanization of administrative relations and principal directions of its study within an enterprise. Human factor: issues of psychological and ergonomic, 4(42), 97–102.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
07 December 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-095-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
96
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-833
Subjects
Management, human resources, resource efficiency, investment, infrastructure, research and development
Cite this article as:
Shaburova, A. V., & Samoiliuk, T. A. (2020). Resource Efficient Technologies For Competitive Growth Of The Enterprise’s Employees. In A. S. Nechaev, V. I. Bunkovsky, G. M. Beregova, P. A. Lontsikh, & A. S. Bovkun (Eds.), Trends and Innovations in Economic Studies, Science on Baikal Session, vol 96. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 534-540). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.12.70

