Abstract
Employment of the population may vary depending on the region, while not only the geographical location and climatic conditions of regions can affect indicators of employment. The economic development of neighboring regions often varies significantly for other reasons. The authors conducted a study of indicators of employment, the state of labor potential depending on economic factors of neighboring regions to identify the most significant reasons for each region. The relevance of the study is the analysis of factors influencing effective employment of the population, which is crucial for the development of labor potential and improving living standards. The authors analyzed indicators of employment, the level of education and wages depending on age and the most significant economic factors of two neighboring regions located in the Volga Federal District to identify and compare factors that have the greatest impact on employment in each region and compare results. As a result of the correlation analysis, it was determined that the economic development is most strongly affected by the size of wages in the Samara region, and it is affected by the value of the gross regional product in the Nizhny Novgorod region. A decrease in wage growth rates was revealed. When developing programs for the development of employment and labor potential, it is necessary to take into account the results obtained.
Keywords: Labor potentialemploymentlabor force qualityqualified specialistslabor market
Introduction
Labor potential of regions is largely determined by the types of economic activity that are priority in a given territory. Therefore, the level of employment in regions even located in the same climatic zone can differ significantly due to different effects of socio-economic factors. To form effective employment promotion programs, it is necessary to take into account the influence of the human factor, which is forming both at the individual and regional levels ( Lavrikov, 2017). At the same time, Russian scientists note the increasing influence of administrative tools for regulating the labor market that do not consider digital changes in the technological sphere and are in conflict with the requirements of innovative development ( Maslov, Dmitriev, & Krapil, 2018). At the same time, more and more digital jobs are being created that require appropriate training from users ( Dittes, Richter, Richter, & Smolnik, 2019). The period of the demographic decline that our country is entering will affect the change in the age structure of the labor market, and a decrease in the share of young specialists is forecasted ( Liadova & Loginova, 2018). Under conditions of the labor-deficit market for qualified specialists, cross-cutting competencies that make it possible to combine specialties and professions become especially demanded ( Kibanov et al., 2017). An increase in social guarantees to the population increases trust in society, but it can also have a negative effect, reducing motivation for employment ( Vakhtina & Simonova, 2019). At the same time, competition among specialists is an incentive to develop labor potential ( Kottaridi, Louloudi, & Karkalakos, 2019). The problematic issue is the employment of graduates of vocational and higher education not in the specialty gained at the educational institution. In this case, the structural imbalance of the labor market is increasing, the employee is disqualified, and the employer receives an employee with low qualifications ( Simonova, Kolesnikov, & Karakova, 2018). State regulation of employment and creation of new jobs has some positive impact on reducing unemployment, but this relationship is not linear, since effective jobs attract residents of other settlements ( Jofre-Monseny, Silva, & Vázquez-Grenn, 2018). Our previous studies of regional labor markets allow determining some aspects of regional differences in employment, but the question of assessing the impact of socio-economic factors on differences in employment of neighboring regions located in the same climate zone remains unresolved ( Simonova, Mirzabalaeva, & Sankova, 2019).
Problem Statement
The relationship between the level of development of the regional labor potential and effective employment must be confirmed by a study of socio-economic regional factors, such as the level of education of the population in various professional groups, the development of agglomerations, and transport relationships ( Li, Wei, & Wu, 2019). Priority studies are employment mobility, especially in problematic employment sectors, such as older workers and low-skilled personnel, which show significant differences depending on regional characteristics ( Böckerman, Skedinger, & Uusitalo, 2018). The youth employment segment is a source of job instability and to a large extent depends on the degree of adaptation of employment assistance programs to local conditions, which justifies the need to study the regional specifics of employment ( Kluve et al., 2019). International practice shows that the regional specifics reflected in employment promotion programs have a greater impact on large and medium-sized companies than on small businesses ( Epstein & Shapiro, 2017)
Research Questions
Based on the identified employment problems, we can conclude that it is necessary to conduct additional research on the impact of regional socio-economic factors on population employment. We can distinguish the following indicators that can have a significant impact on the level of employment in the region - educational characteristics, the level of the gross regional product, average wages, investments in fixed assets, and the number of enterprises in the region. The differences in values of these indicators for different regions can be a justification for making adjustments to existing regional employment programs. Studies were conducted in neighboring regions of the Volga Federal District (VFD) with the same climatic characteristics - Samara, Nizhny Novgorod and Ulyanovsk regions.
Purpose of the Study
In view of the increase in the pace of creating jobs for innovative activities that impose rather high requirements on qualifications of workers ( Van Roy, Vértesy, & Vivarelli, 2018), it is necessary to analyze the state of education, the growth rate of wages of the population of the studied territories, and it will give grounds for developing long-term employment programs and areas for the development of vocational education in regions. We will assess the impact of socio-economic factors using correlation calculations. We assume that in different regions such indicators as the level of the gross regional product, average wages, investments in fixed assets, the number of enterprises in the region have different effects on employment, and it is also interesting to assess changes in the influence of these indicators in different periods.
Research Methods
The Volga Federal District is located in rather favorable natural and climatic conditions and the studied areas are in close proximity to each other, which allows us to conditionally accept this factor as insignificant and analyze factors that affect employment by such socio-economic indicators as the level of education, average wages, the gross regional product, investment in fixed assets, the number of enterprises in the region. Considering the structure of employed and unemployed by the level of education in the Volga Federal District, there is a tendency toward an increase in employed with higher and secondary vocational education with a slight increase in unemployed with secondary, compulsory education, as well as those without education (see Table
The data for the Volga Federal District as a whole are confirmed by the characteristics of the population structure by regions. However, significant differences are observed in the structure of employed by the level of education in the studied regions - in the Samara region, the employed population with higher education has been growing steadily over the past decade and it is 38.4%, which is significantly higher than the average for the region. At the same time, a fairly stable share of employees with secondary vocational education is observed, while in the Ulyanovsk region the share of specialists with higher and secondary vocational education is lower than the average for the region and these indicators do not tend to change significantly with a fairly high share of employees without vocational education. The indicators of the Nizhny Novgorod region in terms of the structure of employed are approximately at the level of the average for the Volga Federal District. A similar situation with the heterogeneous distribution of employees by educational level in neighboring regions indicates the absence of considering the influence of other socio-economic factors on employment of the population.
The level of education is closely connected with the structure of the region’s workplaces and wage growth opportunities, which are closely correlated. The transformation in the world of work is associated both with changes in the content of labor caused by digitalization and increased requirements for product quality, as well as with the growth of informal employment, the emergence of new forms of precarious work, and increased demands on the flexibility and mobility of employment, which modern Russian employer cannot always offer under a fairly tough administrative regulation. Differences in the structure of employment are a reflection of the policies of the regional leadership, which form local conditions for doing business with varying degrees of consideration of existing socio-economic factors. Economic development trends and population sentiment are often in contradictions, which must be coordinated with the maximum consideration of factors specific to a particular territory. The reduction of traditional industries, the growth of the sphere of intangible production, the desire of people for higher mobility and the optimal balance between working time and personal put forward a new level of requirements for regional management of the employment sector. The growing regional imbalance of vacancies and job seekers indicates the presence of structural problems in employment management due to the following reasons:
A high proportion of inefficient jobs with unattractive working conditions: low pay, difficult or harmful working conditions;
Underdeveloped employment regulation systems, a high degree of application of administrative management tools, lack of flexibility in the use of various forms of employment;
Ineffective regional management, which does not allow realizing available natural, economic and human resources;
Lack of flexibility in the education system, which does not allow gaining qualifications necessary for employment;
Increasing population requirements for working conditions and quality.
At the same time, when solving these problems, it is necessary to consider emerging long-term risks:
With the development of non-standard forms of employment, the stability of employment decreases, the uncertainty in employment time increases, the social function of labor is alienated, the value of collective forms of labor decreases;
Reduced opportunities for using social and corporate benefits and guarantees;
The threat of rising unemployment due to a reduction in inefficient jobs and increased qualifications in new jobs.The solution of these problems requires an analysis of the influence of socio-economic factors considering regional specifics. We will use one of econometric methods - correlation analysis to assess the degree of influence of some of the most significant factors on employment in the region. The following factors have been used for the assessment - the level of the gross regional product, average wages, investments in fixed assets, the number of enterprises in the region. One of the most common and resulting indicators affecting employment in the region is the regional gross product, which shows the value added produced to end users. Other factors are related to the gross regional product, but they characterize important economic indicators that affect the level of employment. The level of employment was adopted as the determining factor in relation to which the influence of other indicators was calculated. According to the results of calculations for a 10-year period from 2007 to 2017, correlation values were determined for the Samara and Nizhny Novgorod regions, according to which a graph was constructed (Fig. 01).
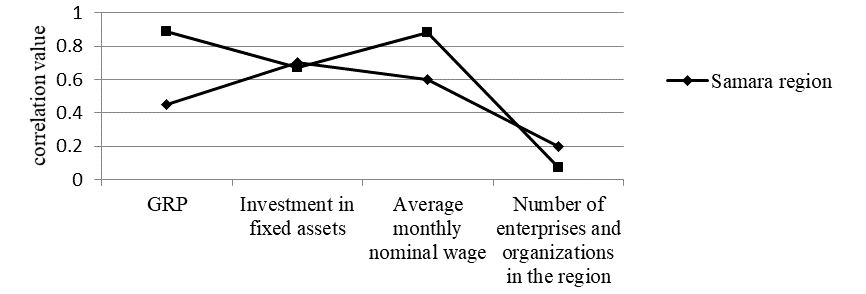
The data obtained characterize the different correlation dependence of the same factors on employment in different regions, in addition, the influence of factors varies in different periods. So, in the Samara region, wages have the greatest impact on employment, but it has a much smaller impact in the Nizhny Novgorod region. The gross regional product has the opposite effect on employment in the studied areas – there is a significantly larger impact in the Nizhny Novgorod region than in the Samara region. At the same time, investments in fixed assets have approximately the same effect in both areas. The least impact on employment is exerted by the number of enterprises located in this region, which is explained by different scales of activity of enterprises and the level of automation in production, when small-sized production personnel produce a product with high added value.
Findings
In the course of the study, it was revealed that employment in regions is determined by a combination of factors that have different effects depending on the territory and characterize the performance of management in the region. It is determined that one and the same factor in different regions can show both strong and weak correlation dependence on employment of the population, which should influence managerial decisions when developing regional employment programs. The main causes of the imbalance of supply and demand in the labor market are identified, risks of the development of flexible forms of employment that can arise in the process of solving employment problems are identified.
Conclusion
As for today, employment of the population is transforming due to significant technological and structural changes in the economy. The study of the dependence of employment on socio-economic factors that have features of mutual influence in each region allows us to take these results into account when developing programs to promote employment in the face of new forms of employment. The structure of the employed population by the level of education characterizes the trends in the regional employment, determines the possible long-term changes in employment, and it is one of the main reasons for the increase in wages. It is necessary to continue research on the impact of socio-economic factors on employment in the regional context to develop effective solutions to stabilize employment in the context of digital changes in the economy.
References
- Böckerman, P., Skedinger, P., & Uusitalo, R. (2018). Seniority rules, worker mobility and wages: Evidence from multi-country linked employer-employee. Labour Economics, 51, 48-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2017.11.006
- Dittes, S., Richter, S., Richter, A., & Smolnik, S. (2019). Toward the workplace of the future: How organizations can facilitate digital work. Business Horizons, 62(5), 649-661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2019.05.004
- Epstein, B., & Shapiro, A. F. (2017). Employment and firm heterogeneity, capital allocation, and countercyclical labor market policies. Journal of Development Economics, 127, 25-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2017.02.006
- Federal Service of State Statistics (2018). Region of Russia: Socio-economic indicators. Moscow: Rosstat. Retrived from: https://www.gks.ru/free_doc/doc_2018/region/reg-pok18.pdf Accessed: 13.11.2019. [in Rus.].
- Jofre-Monseny, J., Silva, J. I., & Vázquez-Grenn, J. (2018). Local labor market effects of public employment. Regional Science and Urban Economics. In Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2018.11.001
- Kibanov, A. Ya., Mitrofanova, E. A., Dolzhenkova, Yu. V., Pugach, S. P., Mikhailov, F. B., Esaulova, I. A., . …& Durakova, I. B. (2017). Personnel management in Russia: New functions and new in functions. Moscow: INFRA-M. [in Rus.].
- Kluve, J., Puerto, S., Robalino, D., Romero, J. M., Rother, F., Stöterau, J., ... & Witte, M. (2019). Do youth employment programs improve labor market outcomes? A quantitative review. World Development, 114, 237-253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.10.004
- Kottaridi, C., Louloudi, K., & Karkalakos, S. (2019). Human capital, skills and competencies: Varying effects on inward FDI in the EU. International Business Review, 28(2), 375-390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2018.10.008
- Lavrikov, V. V. (2017). The role of the human factor in achieving competitiveness and efficiency of enterprises and organizations. Economy and Society: Modern Models of Development, 17, 56-65. [in Rus.].
- Li, H., Wei, Y. D., & Wu, Y. (2019). Urban amenity, human capital and employment distribution in Shanghai. Habitat International, 91, 102025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.102025
- Liadova, E. V., & Loginova, T. P. (2018). Institutional mechanisms for the regulation of the shortage of labour resources in the Russian industry. Economics and Entrepreneurship, 1(90), 890-894. [in Rus.].
- Maslov, D. V., Dmitriev, M. E., & Krapil, V. B. (2018). Public administration at the new stage of administrative reform: Horizontal business methods in vertical state structures. Finance and Business, 1, 6-27. [in Rus.].
- Simonova, M., Kolesnikov, S., & Karakova, T. (2018). Assessment of labor potential on the regional level by the index method. In I. Ilin, O. Kaldina (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Science Conference SPbWOSCE-2017 “Business Technologies for Sustainable Urban Development”. MATEC Web of Conferences, 170, 01069. Les Ulis: EDP Science. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201817001069
- Simonova, M. V., Mirzabalaeva, F. I., & Sankova, L. V. (2019). Differentiation of regional labor markets: New risks and opportunities for smoothing. In S. Ashmarina, M. Vochozka (Eds.), Sustainable Growth and Development of Economic Systems. Contributions to Economics (pp. 259-274). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11754-2_20
- Vakhtina, M. A., & Simonova, M. V. (2019). Development issues of an institute of an independent assessment of service quality in the social sector of Russia. Bulletin of Perm University, Series: Economics, 14(1), 5-19. https://doi.org/10.17072/1994-9960-2019-1-5-19 [in Rus.].
- Van Roy, V., Vértesy, D., & Vivarelli, M. (2018). Technology and employment: Mass unemployment or job creation? Empirical evidence from European patenting firms. Research Policy, 47(9), 1762-1776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.06.008
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
09 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-078-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
79
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1576
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Simonova*, M. V., Spravchikova, N. A., & Vagin, S. G. (2020). The Impact Of Regional Socio-Economic Factors On Employment. In S. I. Ashmarina, & V. V. Mantulenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 79. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1319-1325). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.189
