Information Component Of The Business Strategy Development By Modern Russian Manufacturing Companies
Abstract
The article deals with a research assistant of developing business strategies due to the developmental characteristics of Modern Russian pharmaceutical companies. A number of approach of establishing a strategic planning process were identified, including: corporate planning, logical incrementalism, muddling through, garbage can, with a focus on corporate planning. For the objective of study of the characteristics and develop recommendations to information management of corporate planning process, Expert interviews and questionnaire survey were held in 43 Modern Russian pharmaceutical companies. On the basis of the analysis of the results has been developed a schematic diagram of the business strategy development process including such phases as: a vision for the future strategic process; process visualization (which involves a description of the creating process, types and volumes of information which would be used in the context of the different stages of the process and a method of processing); a development team - building and the diffusion of authority and responsibility among departments/managers/employees; a common structure to support the implementation of the strategic plan, procedure for establishment of strategy and implementing regulations; the collection and processing of information with utilizing policy instruments; in conclusion - a final version of the strategy and testing. Based on results of the study, recommendations were made regarding phasing of the strategy development process, the general principles of the strategic process building and the use of the most effective policy instruments in the process of strategy developing which had provided information for process enforcement and implementation.
Keywords: Methods for strategic planningbusiness strategyinformation componentstrategic planning phase
Introduction
On approaches to organizing the strategic planning process
Strategic management methods are successfully applied in the management of modern organizations (Bartkus, Glassman, & McAfee, 2006; Buzzell, 2004; Sazonenka, Towhid, & Siemieniako, 2018). Strategic planning of the organization involves the use of a various kind of information (Pasichnyi, Levihn, Shahrokni, Wallin, & Kordas, 2019; Springmier, Edwards, & Bass, 2018), while strategic plans based on a well-established process of collecting and processing information can improve the efficiency of commercial organizations (Enad, 2019).
Experts have identified several different approaches to the establishing of a strategic planning process (Richardson & Richardson, 1992; Engle, Schlaegel, Dimitriadi, Tatoglu, & Ljubica 2015; Mishurova, Nikolaev, Nikolaeva, Sinyuk, & Nesterova, 2019). As founders of the first approach (corporate planning) (McCaskill, 1973; Timofeeva & Vinnitckaia, 2017) can be mentioned Andrews (1987) and Chandler (1962) who formulated strategic management in general. In organizations implementing this approach, top management creates detailed instructions for organizing the strategic process, which is a sequence of well-established procedures, the main component of which is the collection of verified information and its processing using specific tools. The main goal of establishment of such a process is to select the most reasonable and rational version of the strategy, while the management of the Organization plays a key role in managing both the process of developing the strategy and choosing its final version.
The second approach, iterative planning (logical incrementalism) differs from the first in the lower level of orderly process (Andrews, Beynon, & Genc, 2017; Goldsmith, Salvador, Knipe, & Kendall, 2002). In this case, the company's management acts as the organizer of the strategic process, consolidating the components of the overall strategy developed in the functional departments. At the same time the management of the Organization formulates the fundamental guidance for the development of the Organization (on which actions should be focused), teaches accordingly the personnel involved in the strategic process and forms the information base which should be used. The iterative nature of the process is formed by periodically providing to the management with strategies created in the departments and receiving instructions for its improvement (and subsequently submit to senior management).
The third approach, intuitive planning (muddling through) (Hanney, 2016) is characterized by specialists as a way to achieve a less rational result (Richardson & Richardson, 1992). This approach uses the experience and intuition of top management, that enable management to guide employees into chain of small tasks, the implementation of which should help to concretize the way of developing.
The fourth approach, garbade can (Cohen, March, & Olsen, 1972; Fioretti & Lomi, 2008; Lai, 2006), is difficult to associate with planning due to the chaotic nature of the underlying model and related activities. The adoption of that model, the strategic choice is based on an intensive assessment of unrelated problems that attract the attention of senior management (Richardson & Richardson, 1992).
The authors are proponents of the first approach (corporate planning) taking into account the need to use characteristic elements of other approaches, first of all, a comprehensive assessment of various problems, the successful solution of which can positively affect the level of efficiency of the strategies to be developed (Richardson & Richardson, 1992; Timofeeva &Vinnitckaia, 2017).
Problem Statement
The content of the strategic planning process implemented by domestic manufacturing companies has not been adequately studied, in particular, the approaches to working with information implemented by Russian managers have not been adequately covered.
Research Questions
The research subject is a clearing house mechanism for the strategic process of corporate planning, the object of research is Russian pharmaceutical companies.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is a study of the characteristics and developing of recommendations to information management of corporate planning process for Russian pharmaceutical companies.
Research Methods
Methodological settings for this study
Expert interviews (EIs) and questionnaire surveys (QSs) were held. The purpose of EIs – identification of the main phases of the modern process of developing a business strategy by manufacturers, as well as the forms of implementation of each phase that the most commonly used in practice. The purpose of QSs – to detect frequency of use of the implementation forms of each phase of the developing process of a business strategy identified during the EIs. 12 highly qualified specialists who developed business strategies participated in the expert interviews, 9 men and 3 women aged 31 to 45 years with work experience in the field from 4 to 17 years among them.
The questionnaire surveys have involved 43 top managers (one from each company): 26 men and 17 women with work experience in senior positions from 3 to 17.5 years, age - from 30 to 49 years among them.
The respondents were requested to evaluate frequency of use of the implementation forms of each phase of the developing process of a business strategy identified during the EIs using the rating scale presented in Table
Research Methods for strategic planning organization
The questionnaire results were processed using spreadsheet tools. The processing allowed the methodology for calculating relative weighting coefficients and ranking their values in descending order of the frequency of using individual forms of implementation of the phases of developing a business strategy and the frequency of applying specific characteristics of approaches to organizing strategic planning.
Findings
Implementation of the stages of the strategic process in manufacturing companies
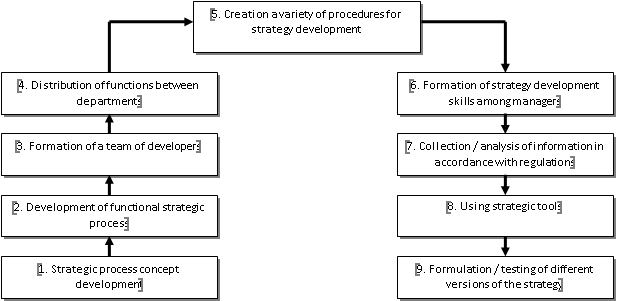
A diagram of the main phases of the business strategy development based on the analysis of the results is presented in Figure
First of all, senior management develops the concept of a strategic process that must be formed. In the next phase, the functional of the strategic process is developed, which includes a description of the phases of strategy creating, a specification of the types and volumes of information that will be used during the process, as well as methods for processing it.
Then, a group of strategy developers is formed, focused on the implementation of the strategic process, and functional elements are distributed among departments / managers / employees. After that, management forms the general structure of the strategic process, the procedures for creating a strategy and a set of relevant regulations.
The transition to the practical implementation of the developed procedures requires the formation of managers involved in the strategic process, both modern ideas about the specifics of strategic management and the skills to execute the developed procedures; this goal is achieved with the use of corporate training programs in conjunction with internships at the workplace, followed by coaching sessions.
At phases 7 and 8, information is collected and processed using strategic tools. At the final phase, the final version of the strategy is selected, as well as its testing.
The experts identified three implementation models at every stage, which differ in the level of manufacturability and the degree of direct involvement of the head in the process. In Table
A graphical interpretation of the questionnaire data of QS-1 shown in Table
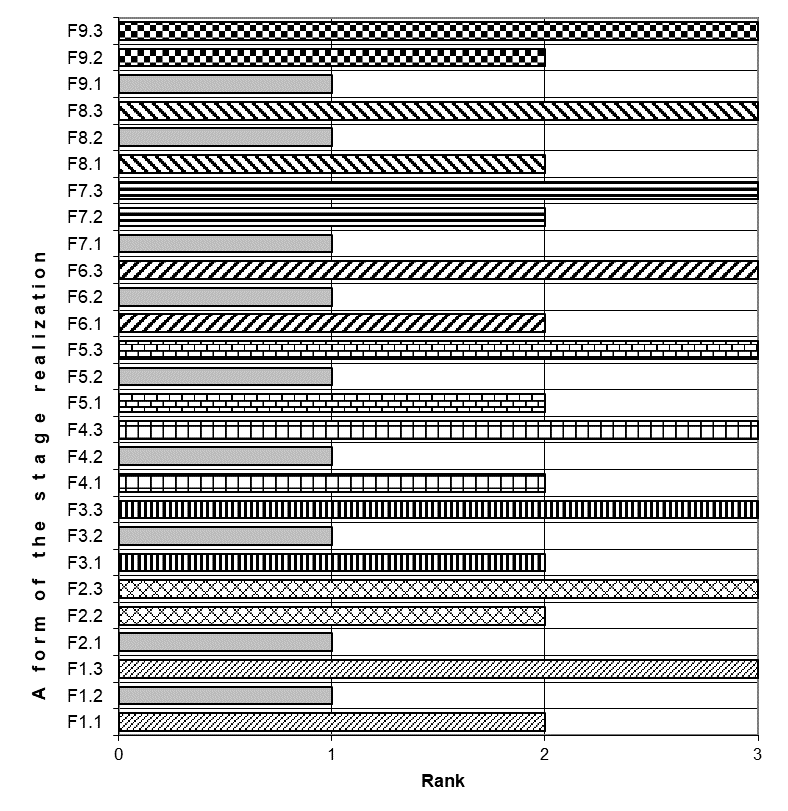
An analysis of the graphical interpretation of the questionnaire data of QS-1 presented in Table
1) The most technologically advanced implementation model of the business strategy development stages Fi3 with the maximum participation of the top management is used extremely rarely or never in the companies;
2) The implementation model Fi2 with moderate participation of the top management and, therefore, with sufficient independence in the adoption of decisions by the personnel in the implementation process of the stage, with an average level of manufacturability is applied at most stages such as:
F1. Strategic process concept development,
F3. Formation of a team of developers,
F4. Distribution of functions between departments,
F5. Creation of a variety of procedures for strategy development,
F6. Formation of strategy development skills among managers,
F8. Using of strategic tools;
3) The most non-technological implementation model of stages Фi1 with a low degree of participation of the top management/high level of participation of employees and low technological level is used by top managers of the studied companies at the next stages:
F2. Development of functional strategic process,
F7. Collection / analysis of information in accordance with regulations,
F9. Formulation / testing of different versions of the strategy.
Conclusion
Thus in the majority of the studied companies, the groups formed by the top manager for the development of the strategy from pre-trained department heads (which group is not fixed by a separate order / document) receive from top management a list of the main stages for the strategy development process, the general principles developed by the senior manager and the scheme of use in the process of developing a strategy of the most effective strategic tools which is used by developers as a guideline. As a task they receive a list of questions (tasks) that are important for receiving answers, the responsibility for solving each of which the managers distribute among themselves, control over the development process is assigned to the heads of departments, who in the process of work independently find the most important blocks of information to use when developing a strategy. During the implementation of the development process, the top management of the company adjusts the actions of the managers involved in the development of the strategy, and as a result of the work carried out by the developers, the main version of the developed strategy is formed. The authors believe that in order to improve the informational component of the strategic process and to increase the effectivity of the developed strategies in general, it is advisable for management to transform the content of the sequence of actions of personnel [8] by introducing the 3rd form of implementation of steps 1, 2, 5, 7, and 8. This approach will optimize collection and processing of information for the process of developing a business strategy by modern Russian manufacturing companies and will serve as the basis for improving the strategic planning system.
References
- Andrews, K. (1987). The concept of corporate strategy. Irwin: Homewood.
- Andrews, R., Beynon, M. J., & Genc, E. (2017). Strategy Implementation Style and Public Service Effectiveness, Efficiency, and Equity. Adm. Sci., 7, 4. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/admsci7010004
- Bartkus, B., Glassman, M., & McAfee, B. (2006). Mission Statement Quality and Financial Performance. European Management Journal, 24(1), 86-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2005.12.010
- Buzzell, R. D. (2004). The PIMS program of strategy research: A retrospective appraisal. Journal of Business Research, 57(5), 478-483. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0148-2963(02)00314-4
- Chandler, A. D. (1962). Strategy and structure - Chapters in the History of the Industrial Enterprise. Cambridge, Mass.: M. I. T. Press.
- Cohen, M. D., March, J. G., & Olsen, J. P. (1972). A Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice. Administrative Science Quarterly, 17(1), 1-25.
- Enad, O. M. A. (2019). The Impact of Generated Information on the Banks Efficiency: Strategic Planning as a Mediator: A Case Study on Al-Tadamon Islamic Bank in Sudan. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 9(5), 130-134.
- Engle, R. L., Schlägel, C., Dimitriadi, N., Tatoglu, E., & Ljubica, J. (2015). The intention to become an expatriate: A multinational application of the theory of planned behaviour. European Journal of International Management, 9(1), 108-137. https://doi.org/10.1504/EJIM.2015.066623
- Fioretti, G., & Lomi, A. (2008). The garbage can model of organizational choice: An agent-based reconstruction. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 16(2), 192–217. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2007.11.010
- Goldsmith, P., Salvador, A., Knipe, D., & Kendall, E. (2002). Structural Change or Logical Incrementalism? Turbulence in the Global Meat System. Journal on Chain and Network Science, 2(2). http://dx.doi.org/10.3920/JCNS2002.x022
- Hanney, R. (2016). Taking a stance: resistance, faking and Muddling Through, Journal of Media Practice, 17(1), 4-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14682753.2016.1159437
- Lai, S. K. (2006). A spatial garbage-can model. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 33(1), 141-156.http://dx.doi.org/10.1068/b31111
- McCaskill, D. B. (1973). Comment: Corporate Planning that Works. Management Science, 20(4-part-ii), 570-571. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.20.4.570
- Mishurova, I. V., Nikolaev, D. V., Nikolaeva, N. V., Sinyuk, T. Y., & Nesterova, O. S. (2019). Communicative technologies in crisis management of corporate structures. International Conference on Communicative Strategies of the Information Society (CSIS 2018). Advances in Social Sciences, Education, and Humanitarian Studies, 289, 79-83. https://doi.org/10.2991/csis-18.2019.16
- Pasichnyi, O., Levihn, F., Shahrokni, H., Wallin, Jö., & Kordas, O. (2019). Data-driven strategic planning of building energy retrofitting: The case of Stockholm. Journal of Cleaner Production, 233, 546-560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.373
- Richardson, В., & Richardson, R. (1992). Business Planning. Art Aproach to Strategic Management. Pitman: London.
- Sazonenka, Y., Towhid, Y., & Siemieniako, D. (2018). One-page strategic plan: the case of Aarong company from Bangladesh. Engineering Management in Production and Services, 10(2), 57-65. Retrieved 20 Oct. 2019, from http://dx.doi.org/10.2478/emj-2018-0011
- Springmier, K., Edwards, E., & Bass, M. (2018). Sharing Success: A Review of Strategic Planning, Annual Reports, and Publicly Available Information from Academic Libraries. Evidence Based Library and Information Practice, 13(2), 70-82. https://doi.org/10.18438/eblip29316
- Timofeeva, T., & Vinnitckaia, N. (2017). Applying corporate planning system for the companies with a state participation, in the view of the regulatory documents of strategy planning. Bulletin of Science and Practice, 2, 208–214. Retrieved from http://www.bulletennauki.com/timofeeva, accessed 15.02.2017 (in Rus.).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
12 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-079-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
80
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-483
Subjects
Information technology, communication studies, artificial intelligence
Cite this article as:
Dimitriadi*, N. A., Dzhukha, V. M., Mishurova, I. V., & Chernenko, O. B. (2020). Information Component Of The Business Strategy Development By Modern Russian Manufacturing Companies. In O. D. Shipunova, V. N. Volkova, A. Nordmann, & L. Moccozet (Eds.), Communicative Strategies of Information Society, vol 80. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 68-76). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.02.9
