Abstract
Every day we encounter such an irreversible reality as inscriptions and prints on our casual clothes. People buy garments sometimes even not understanding or reading what is written on them. Those who speak English are motivated to purchase clothes with English inscriptions understanding the meaning of the printed phrases, words and word-combinations. There always stands a native speaker between a language and a real world, who perceives and classifies the world in his own way. Therefore, for some people it is the brand which is really important, for others – the meaning plays the most significant role in their buying decision. The article presents a study of the T-shirt inscriptions as new urban media. More and more people wear T-shirts with slogans and prints. The article considers this phenomenon in the context of communicative linguistics. There is investigated the communicative significance of the semantic structure of elements, which is manifested in the certain media discourse. There were analysed approximately 5 thousand T-shirt inscriptions. Depending on the semantics carried by the inscriptions, there are singled out a number of thematic groups. The study is aimed at identifying features of linguistic and cultural concepts, crystallizing popular wisdom and value orientations. The results of the study reveal the most frequently occurred concepts in the new media text.
Keywords: English inscriptionsinscriptions on T-shirtsprintsurban mediasemantic componentsconcept
Introduction
People cannot live without communication. The development of our society is impossible without the development of language. Language is a means of expressing thoughts, feelings and various emotions. It is an endless process of human creativity. Language is one of the most complex and mysterious phenomena, although the ability to speak and to use the language is as natural as the ability to walk, see and breathe (Gorbachevskii, 2009). And it is natural that changes in society and consciousness of people are all reflected in the language. From a cultural point of view, language is a cultural and historical phenomenon that forms a nation. Reflecting on the nature of language, Puzyrev (1996) says that language beyond its reality is a dead language. It is communication that demonstrates the reality of language (ontological aspect). The level of communication is the realm of subjectivity, where everyone is right: there are as many truths as there are people in the world (Puzyrev, 1996). Between a language and a real world there always stays a speaker of a certain language, perceiving and classifying the world in his own way (e.g. so where a Russian person sees two colours – grey and black, the Englishman sees only one – grey, although they both look at the same part of the colour spectrum). Language is a mirror of culture, it reflects not only the real world of a human, not only the real conditions of his life, but also social consciousness of people, their mentality, national character, their way of life, traditions, customs, morality, value system, attitude, vision of the world (Ter-Minasova, 2016). The language embodies the results of the practical and intellectual activity - both of an individual and of the whole nation. Today, having freedom of speech, everyone is free to express his thoughts and ideas in the form he likes. Every day we meet such an irreversible reality as some inscriptions on our casual clothes. People buy them sometimes without even realizing what's written on them. The article presents the study of the English T-shirt inscriptions as new urban media. T-shirt illustrates functional duality in the subject attributes of a modern man. The primary utilitarian purpose (protection of the body) competes here with the socio-symbolic, semiotic in its basis, functionality (translation of culturally significant meanings) (Khalikov, 2015). Nowadays, more and more people chooseT-shirts with inscriptions. T-shirt today has become an essential garment of our casual outfit. This garment appeared thanks to the entrepreneurial spirit of the American military men in the First World War (Golovanov & Orlova, 2018). At first, it was a part of a military uniform, but quickly appeared on the rack of the ordinary people. In 60-ies there were made the first inscriptions on the T-shirts. And such T-shirts have become part and parcel of our live as banners to express our attitude to any problem, mood, emotions, motivation, famous cites etc. Today there are offered to the customers huge designer collections of the T-shirts with various inscriptions, prints, photos that provide a wide choice of ideas to promote.
Problem Statement
We use various channels in our everyday communication. We are surrounded by the powerful information flows. It is becoming more and more difficult to filter and percept different data. The English inscriptions and slogan are presented on clothes, billboards, adverts etc. Knowing the language you stay tuned for more news. The purpose of our work is to study the inscriptions on clothing as new urban media translating and promoting certain ideas, thoughts, motivating on something. The relevance of this study is due to the lack of knowledge of this phenomenon, its novelty, frequent use of the inscriptions on the casual clothes.
Research Questions
The research questions for this study are the following:
What types of the T-shirt inscriptions are commonly used in the English language?
What criteria should we rely on to classify them?
What are the most frequent concepts of the T-shirt inscriptions?
This study gives the classification of the T-shirt inscriptions and results of the statistical analysis.
Purpose of the Study
Currently the world and its conceptualization are changing (Mamonova & Yukhmina, 2018). T-shirt inscriptions are exciting and creative. The scientific novelty of this study is that for the first time T-shirt inscriptions are studied as new urban media and there is offered the thematic classification of the T-shirt inscriptions, done a linguo-structural analysis of the inscriptions. The purpose of our research is to study T-shirt inscriptions, their systematization and classification. For this purpose, the following tasks were set: to compilate the material (about 5 thousand T-shirt inscriptions); to conduct a linguistic and structural analysis of the English T-shirt inscriptions; to identify the key themes of the T-shirt inscriptions; to make up a classification of them.
Research Methods
The methodology of the work is based on a number of linguistic methods (component analysis, linguistic-structural analysis) and methods of related sciences (statistical analysis). The theoretical basis of this work relies on the works of Van Dijk (2015), Bart (2003), Zhilavskaya (2016), Bouchev (2014), Gorbachevskii (2009), Olausson (2014), Wohlwend and Medina (2012), Cherednjakova and Sknarev (2014) etc. and others who are dedicated to the study of the advertising and media discourse and its peculiarities from the point of the structural-semantic approach. The study is based on the principles of the semantic structure analysis. There are also used other methods such as descriptive (material compilation, its processing, interpretation and generalization), contextual analysis and semantic analysis.
Findings
In all variety of similar messages the dominating semantic components of a discourse system illustrate modern valuable ethnic reference points, common wisdom in a brief and informative way. Messages on clothes represent and broadcast some experience to a wider public. It can be a piece of advice, a bright idea, a motto, a guideline to follow. Cultural, spiritual and material values of these or those social groups of the population influence considerably the human behavior. Today, we often observe a rough rejection of the traditional values, a search for the new orientations. Actually it is a measure of responsibility of every person himself. The polarization of values makes him choose his own vital life approaches. In other words, the time we live is considered to be an era of resolute break with the traditional and time-honored valuable orientations. In this conceptual piece, Wohlwend and Medina (2012) examine modern media and their pervasive and educational power on children. The researchers also place emphasis on a deeper understanding of the complexities of using media in the educational contexts. Bouchev (2014) pays special attention to the importance of the estimated connotations in the context of mass information. So many scientists are interested in investigating the media discourse from various angles.
Our modern culture is subject to globalization processes. The identity of our national culture is gradually erased, coming under powerful influence of the English-speaking culture. It can be illustrated on the example of the integrated mass media discourse. This type of a discourse allows people to interact actively which can begin with a simple exchange of views and living positions and eventually is actively getting into all spheres of life, forming new collective values. This type of media so to say provides an integrated view, incorporating all types of means of communication and creating a convergent media sphere in which there is a modern person (Zhilavskaya, 2016).
English clothes inscriptions are quite popular in Russia. Therefore, choosing this or that T-shirt, you should know the meaning of the inscription, a phrase or a word (if it is given in a foreign language). As the inscription gives the image a new value. And this value can emphasize all your beauty or spoil your image, despite its perfection and originality.
Thematic classification of the T-shirt inscriptions:
Language exists in various forms. Media texts are the most common among them, being the main units of the media stream. Due to the fact that the media discourse is characterized by unlimited themes and originality of genres, it is able to penetrate into all kinds of communication, both everyday and institutional. Media discourse is the most "globalized" and relevant, i.e. reflecting the latest trends and phenomena of the social reality (Ostapenko, 2008).
Among the language features peculiar to media texts, it is necessary to distinguish the following ones: 1) an average language norm and a rejection of the author's means of expression; 2) the reality of facts, ideas, thoughts contained in the media texts, the documentary nature of media; 3) the presence of a special text modality, which is reflected in the expression of the author's assessments, feelings to the described events and facts. Olausson (2014) noticed that digitalization processes of mass media allow cross-boarder exchange of different types of information, so the media do not necessarily produce global knowledge among individuals.
Media discourse can be interpreted in the light of the idea of nonlinearity, inconsistency, lack of causality (Mamonova & Yukhmina, 2017). Among media texts, that are distributed on a daily basis, certain functional and genre types can be clearly distinguished. They all have a set of certain parameters at all levels: at the format level, at the content level, at the linguistic level. There are traditional media texts such as news, information analytics, text-essays, in other words, any thematic materials that are called "features”, advertising. But due to the new advertising space there appeared new urban media types: graffiti, street advertising, inscriptions on clothes etc. This new media types differ from the traditional ones not only in location of their distribution, but also in linguistic structure and themes.
Bart (2003) notes that at any semantic creativity the problem consists not only in how to invent a sense, but also in how to master it. The problem of interpretation is closely connected with the phenomenon of understanding. Understanding is not based only on rational components, it demands personal sincere efforts, reconstruction of other reality which is behind the studied subject. Foregrounding of these or those semantic interpretations depends not only on the author, but also on the language consciousness of the reader. The readiness to percept this or that message takes an important part in the process of interpretation.
The linguistic and structural analysis of the English T-shirt inscriptions allows us to assume that there are a number of peculiarities in their representation. Among them we have noticed the zigzag structure of sentences, elliptical constructions, language games, intertextuality, absence of subject, changes in the word order, substitution of some parts of speech and whole sentences, the predominance of the imperative constructions, etc. T-shirt inscriptions are also rich in acronyms and other abbreviations. In addition, they can be brightly highlighted graphically, accompanied by a variety of prints, unusual colours (Figure

New urban media are rich in the English inscriptions. We analyzed 5 thousand English T-shirts inscriptions. The research data was taken from the sites of popular online stores Wildberries.ru, AliExpress.ru, Amazon.ru. Depending on the semantic loading of inscriptions, we single out the following thematic groups:
Brand naming and advertising: Reebok, Puma, Brekka, Levi’s, GAP, PINK ROCK produce, BLACK FRIDAY SALE.
Numerical combinations: YOUR NAME 00, 0:1 act while others watch acting, NYC 1624, I’m LIKE 2019% Done!, WE’RE KIND OF A B 19 DEAL!, PROBLEMS 99.
Expressions about nature and animals: Be kind of animals or I’ll kill you, Of course I talk to my DOG who else can I trust?, Anime LIFE is the best life, The human spirit needs places where nature has not been rearranged by the hand of man, NERDY by NATURE, Keep me safe I will keep you WILD!, Is not the mountain we conquer but ourselves.
Musical groups: The Beatles, LINKIN PARK, Queen, Mdna skin (Madonna), All you need is love (The Beatles), Rock'n'Roll.
Sport: Just do it (Nike), I like sport!, UNITED ATHLETE, NUMBER 7, HUSTLE, COMBAT SPORTS, Air Force I (Nike Air).
Space: I need more space, NASA, THANOS, I’m going to be A BIG BROTHER, space CAMP, СОЮЗ-9, VOYAGER 1.
Geographical names: Miami, New York, Barcelona, West coast.
Jokes, funny statements: Redskins, Two Beers, or Not Two Beers…is it a question?, The pig is full of many cats; Please let there be someone behind me to read this! (Figure
Joy exclamations: Hello weekend, bye Friday!, WHAM, I wonder what my job description says today?, CAREER development DIRECTOR only because FULL TIME multitasking NINJA is not an actual job title.
Negative emotions: Stupid, Queen, Bad + Mad, It’s cute how stupid you are, Free for all, Always unique – never boring.
Encouragement: It could be worse, You’re doing amazing SWEETIE, Don’t stop when you’re TIRED stop when you’re DONE, project ENCOURAGEMENT, HANG IN there BABY.
Provocative inscriptions: Search and destroy, Back to Nature, Get rich or drunk trying, Catch me if you can, Don’t stop the party!, Will drink for peace , Want to be rich, Back to school.
Job inscriptions: Career development DIRECTOR, COOKING is not a career, More work, FBI; I love my work with so much passion, Work hard so YOU can SHOP HARDER, ALLERGIC TO WORK, Work hard dream BIG, WILL WORK for HOT DOGS.
Famous proverbs and sayings: EXCUSE ME WHILE I SUCCED, PERFECTLY IMPERFECT, Take it easy, The future is female, If I say “FIRST OF ALL” run away because I have prepared charts, data, research and will destroy you, I can’t adult today tomorrow doesn’t look good either.
Words about love: I love you, Love is…, Love forever, Love is the world!, Angel, Happy Queen, Only you, We are sailing in a love story; I live I love for myself (Figure
Conclusion
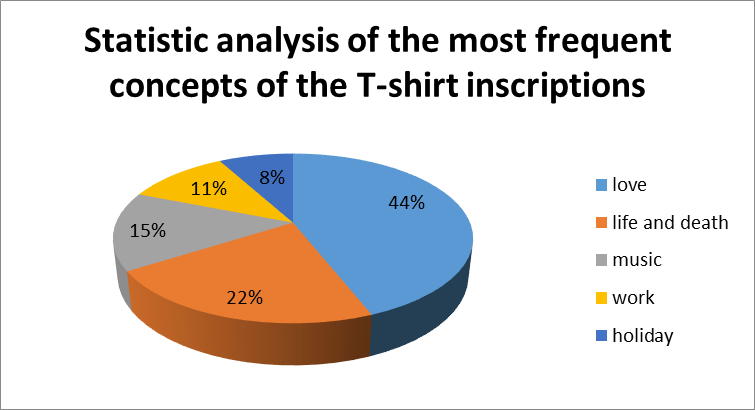
In this media discourse, the most frequent concepts are:
References
- Bart, R. (2003). Sistema mody. Stati po semiotike kultury [System of fashion. Articles on semiotics of culture]. Moscow: Izdatel'stvo im. Sabashnikovyh.
- Bouchev, A. B. (2014). Media discourse studies: generalities and specifics in political discourse. YAzyk i kul'tura. Prilozhenie, 3, 6-11. Retrieved from https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/media-discourse-studies-generalities-and-specifics-in-political-discourse
- Cherednjakova, A. B., & Sknarev, D. S. (2014). Nemedijnye kommunikacii: monografija [Non-media communication: a monograph]. Chelyabinsk: South Ural State University.
- Golovanov, R. А., & Orlova Е. М. (2018). Sravnitelno-sopostavitelnyy analiz soderzhaniya angliyskikh i russkikh nadpisey na futbolkakh [Comparative analysis of the content of English and Russian inscriptions on T-shirts]. Yuniy ucheniy, 2, 20-24. Retrieved from http://yun.moluch.ru/archive/16/1121/
- Gorbachevskii, А.А. (2009). Teoriya yazyka [Theory of language]. Chelyabinsk: Chelyabinsk State Pedagogical University.
- Khalikov, М. М. (2015). Tekstil i teksty: semiotika nadpisey na futbolkakh [Textiles and texts: semiotics of T-shirt inscriptions]. Retrieved from https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/tekstil-i-teksty-semiotika-nadpisey-na-futbolkah.
- Mamonova, N. V., & Yukhmina E. A. (2018). Instagram network folklore in the light of the linguosynergetics. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, XXXIX, 146-150.
- Mamonova, N. V., & Yukhmina, E. A. (2017). Lineynyy i nelineynyy teksty v globalnoy seti internet [Linear and non-linear texts in the global network Internet]. In Aktual'nye problemy nauki i obrazovaniya v sovremennom vuze (pp. 33-38). Sterlitamak: Sterlitamakskij filial BashGU.
- Olausson, U. (2014). The Concept of Culture in Media Studies: A Critical Review of Academic Literature. Retrieved from: https://journals.openedition.org/inmedia/768
- Ostapenko, T. A. (2008). Kommunikativno-pragmaticheskiy potentsial nechlenimykh predlozheniy v sovremennom russkom yazyke [Communicative and pragmatic potential of non-verbal sentences in the modern Russian language] (Doctoral Dissertation). Belgorod.
- Puzyrev, A. V. (1996). Substratnyy podkhod k yazyku i cheloveku [Substrate approach to language and human]. In Ehtnokul'turnaya specifika yazykovogo soznaniya (pp. 55-66). Moscow: In-t yazykoznaniya RAN.
- Ter-Minasova, S. G. (2016). Russian English: History, functions, and features. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Van Dijk, T. A. (2015). Yazyk. Poznanie. Kommunikaciya [Language. Knowledge. Communication]. Moscow: LENAND.
- Wohlwend, K. E., & Medina, C. L (2012). Media as Nexus of Practice: Remaking identities in What Not to Wear. Discourse Studies in the Cultural Politics of Education, 33, 1-16. DOI:
- Zhilavskaya, I. V. (2016). Klassifikatsiya media. Problemy, ponyatiya, kriterii [Classification of media. Problems, notions, criteria]. Vestnik Volzhskogo universiteta im. V.N. Tatishcheva, 2(4), 169-175.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
07 August 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-065-5
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
66
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-783
Subjects
Communication studies, press, journalism, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Yukhmina*, E., Mamonova, N., & Mingazheva, E. (2019). Linguo-Structural Analysis Of The English T-Shirt Inscriptions As New Urban Media. In Z. Marina Viktorovna (Ed.), Journalistic Text in a New Technological Environment: Achievements and Problems, vol 66. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 424-431). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.08.02.49
