Abstract
Increasing of personnel services role in the enterprise activity is due to transformation of the socio-economic sphere, the development of the labor market. The human factor is becoming increasingly more important in solving problems and improving the competitiveness of an organization. People who work in the organization are the key element of the management system. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that all of the employees are effectively included in organizational processes. Responsibility for solving this problem rests largely on the personnel department. As a result, the work of the staff of the personnel department should be more efficient, multifaceted and operational. Consequently, the question of its performance assessment arises. Efficiency assessment of the enterprise personnel department work is a complex and important task. On the one hand, the assessment is needed to ensure the management of the information necessary for control and decision-making; on the other hand, the assessment process often causes serious difficulties associated with selecting the necessary assessment methodology adapted to the conditions of a particular enterprise. Organization and improvement of personnel services performance is the most important direction of an enterprise's development. The basis for the development of directions for improving the performance of personnel service as a whole and of its individual employees is a planned systematic assessment of the results of the work of the personnel service and an individual assessment of its employees. Therefore, the choice of methods and evaluation criteria is the most important task of management.
Keywords: Efficiency assessmentpersonnel managementpersonnel service
Introduction
Approaches to efficiency assessment of personnel service performance
Nowadays there are a variety of approaches to efficiency assessment of personnel service performance.
Bilorus (2018) suggests to approach the issue of personnel strategy formation on the basis of the GE/McKinsey model, changing the coordinates of the matrix to the attractiveness of the state personnel policy and the competitiveness index of the personnel management system, correspondingly. The competitiveness index of the personnel management system is determined on the basis of evaluation of the effectiveness of the subsystems of motivation, selection, personnel assessment, level of workplace organization, state of the moral and psychological climate, etc. (Bilorus, 2018).
A number of authors, such as Saeed, Wall, Roberts, Riahi, & Bury (2017) and others consider the issue of assessing the effectiveness of the personnel management system taking into account the specifics of the activity of the object of research, its industry sector.
However, in these cases the authors pay attention to the issues of the personnel management system evaluation, while the evaluation of the personnel service effectiveness in these cases can be carried out indirectly, in the context of the effectiveness of personnel management.
Whereas Kibanov (Kibanov, Mitrofanova, & Esaulova, 2016) considers the following foreign approaches to assessing the personnel service efficiency (Figure
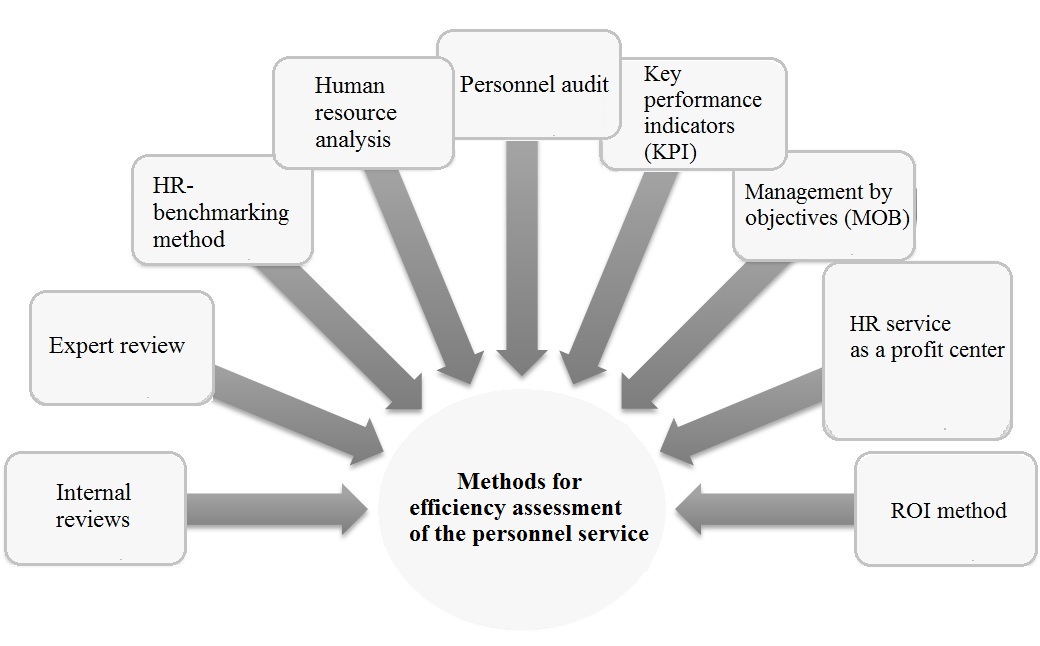
Internal reviews are carried out through surveys, interviews, questionnaires. As for expert review, surveys are conducted among the heads of structural divisions in order to reveal their opinion on the effectiveness of the personnel service. The HR-benchmarking method is a comparative assessment of the key performance indicators of the enterprise’s personnel service and its competitors. Human resources analysis implies not necessarily an assessment of the personnel service activity, but an assessment of the labor potential as a whole, evaluation of the value and contribution of all employees in the activities of the organization.
Personnel audit is a method of integrated assessment of the personnel service, which is usually conducted by external auditors. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are based on the identification of key indicators of enterprise personnel management, which are linked to the organizational goals and objectives. Management by objectives is about setting goals and evaluating their achievement. HR service as a profit center. The cost of services can be determined based on market prices. The method of ROI is the evaluation of personnel service projects of the enterprise by comparing the benefits that these projects give to the enterprise with the costs of their implementation.
Therefore, it can be noted that the choice of approaches to assessing the effectiveness of the personnel service is determined by a set of specific management tasks, and also depends on the resources the organization has.
Practical aspects of efficiency assessment of personnel service performance
In our opinion, to assess the efficiency of the personnel service of an enterprise, the method of expert estimates of performance indicators is preferable, since this method can be implemented on its own, that is, without the involvement of third-party experts, which ensures its availability and low cost.
At the first stage the expert method implies the construction of a hierarchical system of performance indicators (table
The presented system of indicators consists of three levels. On the first level of the hierarchical system stands the comprehensive indicator of the personnel service efficiency. The second level is the indicators that assess the integrated functional groups of the personnel management system. And the third level consists of indicators that describe functional subsystems.
The second stage is the formation of an expert group. It is advisable to include in the expert group employees from among the managers and specialists of the personnel service and other functional divisions of the organization.
At the third stage, it is necessary to familiarize the members of the expert group with the task of evaluating the effectiveness of the personnel service, to present a system of indicators for evaluation.
The fourth stage is related to the determination of the coefficient of the expert’s confidence. The maximum value of the coefficient is one.
The fifth stage is where the experts determine the actual values of the indicators of the third level of the model. For this each expert gives an assessment of the state of the functional subsystem on a ten-point scale. Then the generalized expert opinion is calculated by the formula (1):
(1)
where
Herewith, the assessment of compliance with the appropriate level of a specific parameter was carried out as follows:
10 points – complete compliance,
8-9 points – acceptable compliance,
6-7 points – admissible compliance,
3-5 points – partial compliance,
Less than 3 points – complete discrepancy
The expert assessment of the third level indicators, reflecting the state of the subsystems of the personnel management system, is presented in table
As follows from the data of Table
In a similar way, experts evaluate all individual performance indicators shown in table
Thus, the analysis of expert opinions allows us to characterize the functioning of all subsystems of the personnel management system. We see that the opinions of experts differ, which is a consequence of the subjectivity of judgments. Differences in opinions are due to position, different work experience, education and other personal characteristics. However, in aggregate, these opinions provide an opportunity for a fairly objective assessment of the personnel management system.
A comparative assessment of the enterprise personnel management subsystems is reflected in the diagram (Figure
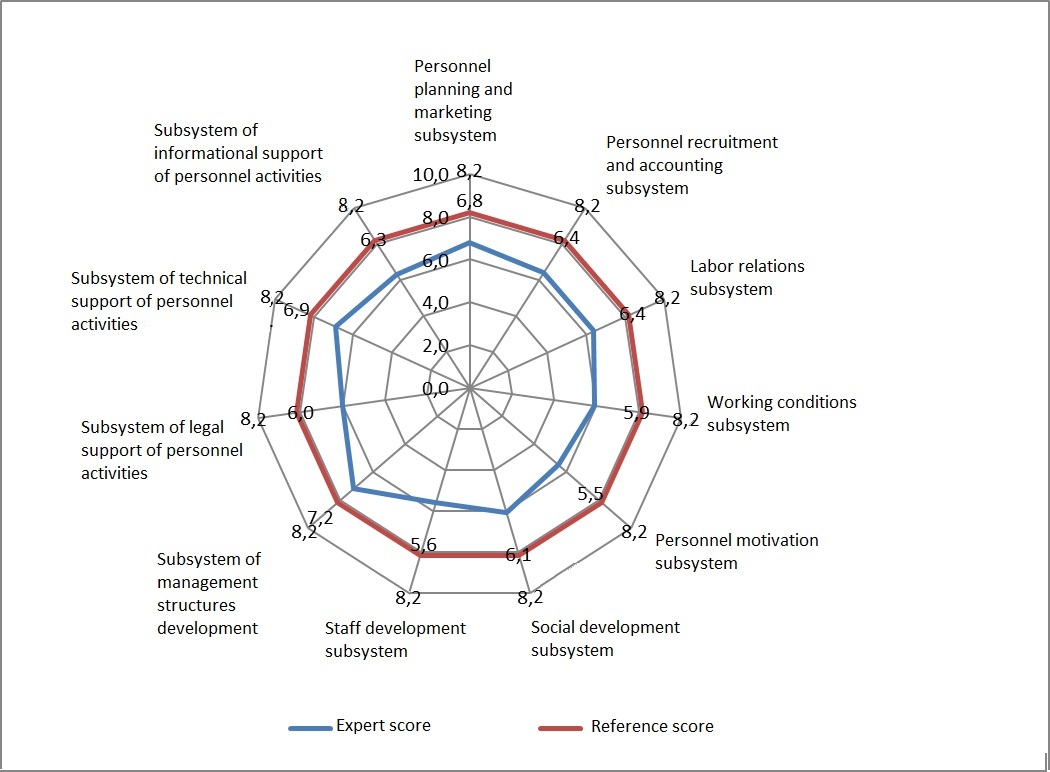
The outer circle of the diagram represents the highest possible assessment value for each subsystem, which, taking into account the coefficients of experts, is 8.2 points. The diagram shows that the subsystem of management organizational structure development (7.2 points), the technical support subsystem (6.9 points) and the personnel planning and marketing subsystem (6.8 points) received the highest marks. At the same time, according to experts, the subsystem of personnel motivation (5.5 points), the staff development subsystem (5.6 points) and the subsystem of working conditions (5.9 points) are the weakest.
Next the value of group indicators for functional subsystems should be calculated (6):
(2)
where
m is the number of indicators of the third level of the model, which are a part of the second group.
Let us calculate the average group value for each functional subsystem:
I. Personnel recruitment: Р2э = (6.8+6.4)/2 = 6.6 points,
II. Use of personnel: Р2э = (6.4+5.9+5.5+6.1)/4 = 5.98 points,
III. Staff development: Р2э = (5.6+7.2)/2 = 6.4 points,
IV. Provision of personnel management system
Thus, the scores of functional subsystems are approximately at the same level due to the fact that they contain particular performance indicators with relatively high and low values, and as a result of calculating the arithmetic average, the averaging of estimates within functional groups has occurred.
Let us calculate the value of a comprehensive performance indicator according to the following formula (7):
(3)
where
m is the number of indicators of the second level of the model
Consequently, it can be concluded that the value of the integrated performance indicator of the enterprise’s personnel service, which equals to 6.3 points, is less than the maximum possible value (8.2 points) by 1.9 points. That is, the efficiency of the personnel service is at an acceptable level, but individual areas of work need to be improved.
Problem Statement
Improving the assessment of personnel service’s work
Human capital is the most important economic resource of a modern enterprise in all areas of its activity. The role of personnel service in the formation of human capital in most modern enterprises comes down to documentary support of work with personnel and staffing activities. It is necessary to engage the capabilities of the personnel service to a fuller extent, but for this it is necessary, first of all, to provide the enterprise's personnel service with appropriately qualified staff with the required knowledge and skills.
Assessment of the efficiency of the personnel service performance on the basis of a comprehensive indicator of the effectiveness of the personnel management system does not provide an assessment of an important component of the personnel service's work – that is of its employees. For an objective assessment of personnel service’s staff, it is advisable to use professional standards. The professional standard “Personnel Management Specialist” was approved by the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation on October 6, 2015 Order No. 691n (Professional standard Personnel Management Specialist, 2015).
The proposed method makes it possible to evaluate the personnel service’s staff taking into account the content of labor functions stipulated by professional standards. The estimated coefficient of a specialist’s activity is calculated on the basis of the significance of generalized labor functions, the significance of labor functions and the degree of their fulfillment. The coefficients of significance and gradation of the coefficients of the level achieved should be determined by the management of the analyzed enterprise, taking into account the existing priorities in the development of the enterprise.
In the professional standard there are eight generalized labor functions:
A - documentary support of work with the staff;
B - staffing activity;
C - staff assessment and certification activities;
D - staff development activity;
E - work organization and labor remuneration activity;
F - activity of corporate social policy organization;
G - operational management of personnel and department of the organization;
H - strategic management of the enterprise’s staff.
Assessment of personnel service's staff should be carried out on the basis of the data contained in the professional standard on generalized labor functions, labor functions, labor actions, skills and knowledge. During the assessment it is necessary to determine the significance of the considered evaluation parameters in relation to a specific position, since the standard imposes requirements on the labor functionality of various positions in the field of personnel management. It is obvious that employees and managers of various services cannot possess all this set of qualities, therefore it is necessary to differentiate the requirements depending on the department and position.
In order to assess the personnel service staff, it is advisable to use the formula for calculating the coefficient of quality of activity (4):
(4)
When assessing the degree of fulfillment of the labor action, it is necessary to determine the scale of assessment (in fractions of one):
1 – high degree of fulfillment;
0.7 – medium degree of fulfillment;
0.3 – middling degree of fulfillment;
0.1 – inadequate degree of fulfillment.
It is advisable to carry out the assessment within the framework of a specific generalized labor function, since it is within the framework of generalized labor functions that the standard determines the requirements for the level of qualifications, position, level of education and training, as well as labor knowledge, skills and actions.
Assessment of the personnel service's staff work quality
Let us consider the use of methods for assessing the quality of the personnel services work on the basis of the professional standard on the example of an employee of the department of documentation support - document specialist.
Analyzing the data of the professional standard "Personnel Management Specialist" one can note that the specialist occupying this position should have the fifth level of qualification, and that the requirements for his or her knowledge, skills and actions are described in the framework of the generalized work function A - "Documentary support for working with personnel." Document specialist must have secondary vocational education.
Within the framework of this generalized labor function three labor functions are distinguished, and for each of them there are labor actions, skills and knowledge. Within the confines of this methodology we are interested in labor activity, although the assessment of knowledge and skills must also be present, but for this, in our opinion, a separate study is necessary.
Table
The assessment of the significance of labor functions for this position varies. Such labor functions as “Maintaining organizational and administrative documentation on personnel” and “Maintaining records on personnel accounting and staff movement” have a weighting factor equal to 0.4 units, while the labor function “Administration of processes and document flow for personnel accounting and staff movement, submission of personnel documents to state bodies" - only 0.2 units. The labor actions considered within the framework of these labor functions also have a different assessment of significance.
The assessment of the degree of fulfillment of labor actions given by the experts of the documentation specialists’ activities revealed that the document specialist A has shown much higher level of performance of official duties, since in almost all the compared indicators his or her score is higher than that of his or her colleague.
Next one needs to calculate the quality factors of work for these employees. In order to do that let us construct an auxiliary table
On the basis of the data of table
KFj(А) = 0.4*0.94 + 0.4*0.81 + 0.2*0.85 = 0.87 points,
KFj(А) = 0.4*0.7 + 0.4*0.68 + 0.2*0.38 = 0.63 points.
Thus, the calculated data affirm the high level of quality of document specialist A’s work and the average (and even lower than average) level of quality of work of document specialist B.
In the future the results of the personnel department's staff assessment may be useful for developing a training plan (identifying areas of study), developing programs for motivation and stimulation of the employees' work. That is, an objective basis will be created for planning out the work with the personnel services staff and improving the quality of their performance.
Research Questions
Approaches to efficiency assessment of personnel service performance.
Practical aspects of efficiency assessment of personnel service performance.
Improving the assessment of personnel service’s work.
Assessment of the personnel service's staff work quality.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to develop recommendations for improving the assessment of the enterprise's personnel service. The objectives of the study are:
the research of approaches to assessing the efficiency of the enterprise's personnel service;
the analysis of the method of conducting an expert assessment of the personnel services work based on the formation of a hierarchical system of indicators;
consideration of the method of conducting an individual assessment of a personnel services employee's performance;
exploring the possibility of using a professional standard for assessing the quality of personnel services staff work.
Research Methods
To achieve the objectives set in the scientific article, the following methods were used: comparative-analytical, sociological, expert assessments, system analysis, economical and mathematical modeling, graphic modelling (Karabasevic, Zavadskas, Stanujkic, Popovic, & Brzakovic, 2018; Pogodina, 2004; Rogozhin, 2014).
Findings
Currently, the authors offer a variety of approaches to assessing the efficiency of the personnel service. In particular, there are methods aimed at assessing the efficiency of the personnel management system as a whole, methods that allow to evaluate the personnel management system in the context of a specific field of work, as well as approaches aimed at evaluating the work of the personnel department itself.
The analysis allows us to conclude that to assess the efficiency of the enterprise's personnel service, the method of expert assessment of personnel service's performance indicators is preferable, since this method can be implemented on its own, that is, without the involvement of third-party experts, which ensures its availability and low cost. Formation of a hierarchical assessment model allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the work of the personnel service, which covers all relevant areas of activity.
Analysis of expert opinions allowed us to characterize the functioning of all subsystems of the personnel management system. The expert opinions differ, which is a consequence of the subjectivity of judgments (Wang, Hou, & Cullinane, 2015). Subjectivity is due to position, various work experience, education and other personal characteristics. However, in aggregate, these opinions provide an opportunity for a fairly objective assessment of the personnel management system.
Conducting an assessment of the personnel service should include not only results, but also an individual evaluation of the labor functions fulfillment by the service staff. For this purpose, it is preferable to use the requirements for a specialist in the field of personnel management specified in the professional standard “Personnel Management Specialist”.
The professional standard is structured based on the allocation of generalized labor functions, which are arranged in order of increasing complexity. Accordingly, the higher are the requirements in the framework of the generalized labor function, the higher is the level of qualification corresponding to this function.
The use of a professional standard as a basis for evaluating an employee of the personnel management service ensures an objective assessment and differentiates the requirements for specialists in a given functional area depending on their position (Oh, Blau, Han, & Kim, 2017).
In addition, the considered method allows to take into account the specifics of the enterprise’s activity and the role of personnel service specialists in the implementation of the goals and objectives of the enterprise due to the assignment of significance coefficients to labor functions and labor activities.
Conclusion
Thus, the assessment of the efficiency of the personnel service should consist of two stages:
I. Evaluation of the results of the personnel service’s work;
II. Evaluation of the personnel service’s staff performance quality.
The assessment of the personnel service's work from the whole to the particular case allows not only to draw conclusions about the current state of affairs, but also to form the basis for planning out the future development of this unit and, as a result, for the improvement of the personnel management system.
Individual assessment of the personnel service staff has several goals:
stimulation and motivation;
education and development;
control of the work.
At the same time, the goal associated with education is of primary importance, since individual assessment is the basis for forming plans for training personnel in the personnel department and choosing the direction of training depending on the individual needs of employees.
References
- Bilorus, T. V. (2018). Development strategy formation of the personnel management system of the enterprise based on portfolio analysis. Marketing and Management of Innovations, 1, 184-195.
- Karabasevic, D., Zavadskas, E. K., Stanujkic, D., Popovic, G., & Brzakovic, M. (2018). An approach to personnel selection in the it industry based on the edas method. Transformations in Business & Economics, 17(2), 54-65.
- Kibanov, A. Y., Mitrofanova E. A., & Esaulova, I. A. (2016). Economics of personnel management. Moscow, VS: INFRA-M.
- Oh, I. S., Blau, G., Han, J. H., & Kim, S. (2017). Human capital factors affecting human resource (hr) managers' commitment to hr and the mediating role of perceived organizational value on hr. Human Resource Management, 56(2), 353-368.
- Pogodina, G. V. (2004). Compulsory course for a professional of personnel work. Received April 1, 2018, from https://biblioclub.ru/index.php?page=book_view_red&book_id=57311&page_id=23#
- Professional standard Personnel Management Specialist (2015). Received August 10, 2018, from http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_187770/8d97991911697adbb3993f17fc9875f0115604ce/
- Rogozhin, M. U. (2014). Organization of enterprise’s personnel work. Received August 10, 2018, from from https://biblioclub.ru/index.php?page=book_view_red&book_id=253710&page_id=22.
- Saeed, F., Wall, A., Roberts C., Riahi, R., & Bury, A. (2017). A proposed quantitative methodology for the evaluation of the effectiveness of human element, leadership and management (helm) training in the uk. Wmu Journal of Maritime Affairs, 16(1), 115-138.
- Wang, X. L., Hou, Y. Z., & Cullinane, N. (2015). How does the human resource department's client relationship management impact on organizational performance in China? Mediate effect of human capital. South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences, 18(3), 291-307.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
02 April 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-058-7
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
59
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1083
Subjects
Business, innovation, science, technology, society, organizational theory,organizational behaviour
Cite this article as:
Legostaeva, S., Alekhina, L., Troshina, E., Zakharkina, N., & Ilin, I. (2019). Formation Of A Criteria Base For Efficiency Assessment Of The Personnel Service. In V. A. Trifonov (Ed.), Contemporary Issues of Economic Development of Russia: Challenges and Opportunities, vol 59. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 803-816). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.04.87

