Abstract
A well-built system of motivation can become a source of long-term competitiveness of the enterprise development. The article presents an overview of the main stages of the KPI motivation development and its deployment process. The purpose of this research paper is to reveal the fundamental aspects of building a motivation system based on KPI. The general theoretical basis of this study is the concept of methodology «Management by Objectives», method of «Performance management». It is proposed to integrate the KPI's system into the enterprise management system. It has been proven that the KPI system is a tool for specifying and bringing business strategy to each department and employee through the mechanism of motivating each employee to achieve this goal. The article identifies the place of the KPI system in the structure of business processes. A typology of KPI system options is based on the resources required to develop and implement such system. It has been proven that the system of motivation based on the KPI is a tool for achieving long-term and short-term company goals and is not just a monetary and non-monetary incentive system.
Keywords: Employees remunerationimprovement of compensation efficiencykey performance indicatormotivationcompetitiveness
Introduction
The transition to a knowledge-based economy requires new management tools from both the state (Rozhdestvenskaya, 2016) and the enterprises (Ewenstein, et al., 2016). Remuneration is the key element of the relationships between the staff and the owner of the business. Both sides are interested in a fair remuneration for work, but have a different perspective on the "justice" of the distribution system. The most progressive method of the remuneration system is considered to be a system of KPI bonuses. The owner and staff interests are different. The owner is interested in the amount of profit the organization makes as a whole, and the employee interest is his final monthly salary. Connection of profit organization and the individual employee's contribution is very illusory.
Methodological basis of motivation system by KPI
KPI concept enables us to reconcile the different interests through a system of measurable indicators. Accomplishing planned KPI values will lead to the achievement of the objectives of the owner, on the one hand, and to a fair remuneration, on the other hand. Thus, KPI system capabilities are a management tool of the owner. Centralized manual control is not always possible, especially in highly specialized issues. It is extremely difficult for the head to delve into every situation in the company, and it requires considerable effort (The Segal Group, 2010).
KPI’s are a good alternative, reforming the business management system as a whole. KPI binding to the target wage level allows employees to express goals of the owner in a simple and understandable way - in salary (Srimannarayana, 2010). Enterprise Management System involves a chain of "goal-strategy-tactics-business processes." Levels can be both formal (typical for a company with a high level of internal organization), and formalized (Gabcanova, 2012). First, let us define the purpose of the enterprise. For example, the goal is to retain current position in the market. Then depending on the goals, the main directions of the goal (its strategy) are being outlined. According to the planned direction, a work plan is being developed - a tactical level of management. Further, at the operational level, the work plan is adopted by members of stuff to their work (Fig.
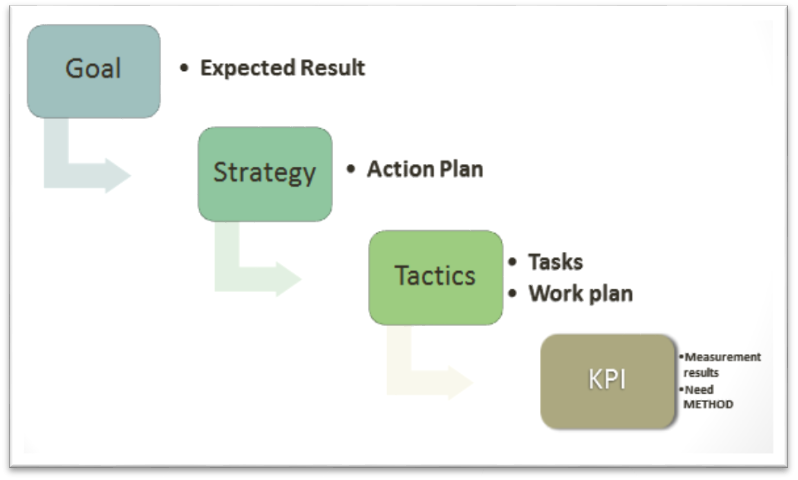
KPI allows establishing some indicators at each stage of management that allow evaluating the quality of the results, i.e., consistency with the objectives of the owner.
The main conclusion is that the system requires a clear objective of the owner. Without goals there is no object for measurement at any level.
Approaches to the development of KPI systems differ depending on the measurement level of management - strategic, tactical or operational KPI (Figure
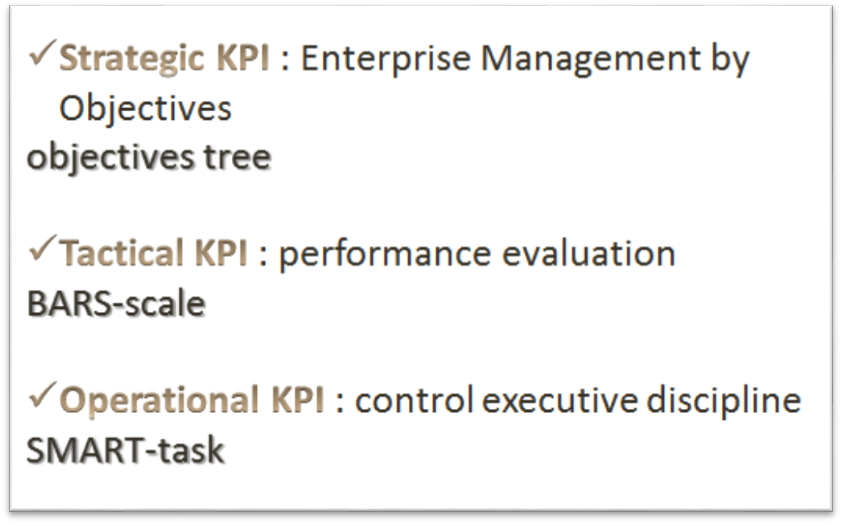
Let us consider the first level - a strategic one. A recognizable example is the owner's desire to increase his operating profit. Depending on the purpose, KPI is developing in absolute terms, as well as relative – in profitability. The operating profit level depends ultimately on the management decisions of the CEO, but the level of sales profitability depends on the commercial director‘s decisions (Toulson, & Dewe, 2004).
On the one hand, the figures are as simple and clear before the procedure begins its decomposition into simpler performance. After the operating profit, this level begins to depend on the work of the entire enterprise.
A simple measure "the amount of operating income" is broken down into a number of indicators of the tasks that must be performed to ensure that the desired volume is achieved. Plans are being made on the company budget. Depending on this, developing a work plan forms tasks registry (Harvey, 2005).
For example, an increase in operating profit involves working as part of the cost reduction. Much will depend on the quality of the production process and implementation. It is the competence of the chief engineer and the commercial director.
Ensuring prerequisites for reducing the cost depends on the reliability of accounting information - accounting and management. It is important to obtain data (instrument) and not to reason (some rough calculations) on the development process. Thus, a simple measure requires a systematic approach to the development and data collection.
Results. Technology of KPI system implementation
The more complex the system of indicators is, the higher the level of automation should be, skills and organization: the KPI system on motivation requires collecting and processing of a large flow of information, which is unthinkable without the appropriate level of automation. Everything is interconnected (Skibniewski & Ghosh, 2009). The more complicated the automation system is, the higher the required level of personnel qualification is. In other words, the motivation KPI system must be balanced relatively the level of organization of management of the company (Figure
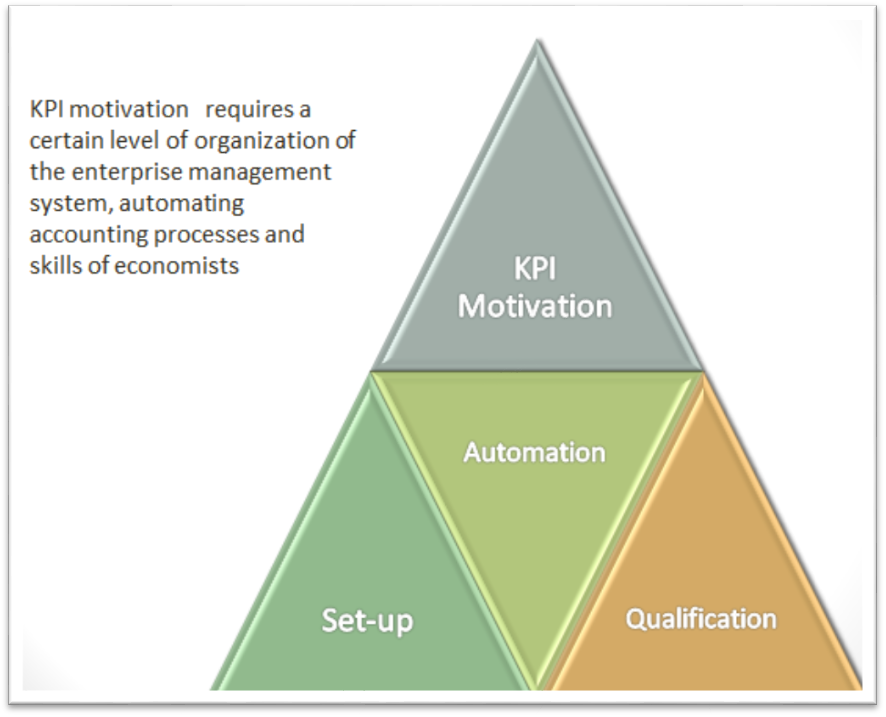
KPI motivation can help to achieve the desired level of automation, but it happens over time. If a qualification and set-up system is clear, the level of automation requires comment.
Business Process Automation assumes that the data does not depend on people and on the testimony of metering devices. The individual in this case is not in a position to have a significant impact on the calculation of indicators. The system assumes impartiality.
Requirements for the automation of business processes are not limited to the introduction of accounting documents in the program payroll and assumption that there is the automatic processing of data on all key transactions in the company - the formation of orders, execution of orders of clients, production, planning and budgeting, logistics, etc., as well as other simple, but numerous and routine processes - forming documents from templates, the unification of directories, electronic documents, etc.
The budgeting system in the enterprise requires a certain procedure for collecting operational data, their primary accounting, processing of analysis. To avoid doubling for functions or data gaps, the document management system is developed.
Initial accounting is management accounting. Planning for the Enterprise occurs in two main ways - conditional planning based on the average actual costs and on the basis of standard costs (Eckerson, 2009).
The KPI system involves motivating employees to achieve the target values of reference. A positive motivation effect is possible when planning on the basis of certain standard cost values, otherwise the system will contribute to the reproduction of the results that have been already achieved, and in its turn stimulate the motivation "to do as it was", and not "reach".
In the absence of standards on the automated budgeting system, motivation for KPI methodology will encourage to blow the budget, because the new budget is based on the current flow without regard to efficiency. To complete KPI, based on the fact that the previous years is not difficult, is to repeat the fact that we can do it without any additional effort. Salaries will suit all, but the goals of the owner will not be achieved.
Automation of management accounting involves the collection of operational accounting data primarily via metering devices - counters, scales, satellite navigation systems and other devices for determination of physical indicators.
Defining indicators "by eye", and keeping records on paper allows us to adjust the data for the performance of any KPI. Binding physical indicators to wage without automation of management accounting is to motivate the "Extra" in the data, rather than the result that the owner would like.
Automation of accounting involves communication with management for the purpose of monitoring data. Otherwise, figuring out the financial result would allow filling with KPI and getting wages, but would not contribute to the achievement of the objectives of the owner
Thus, without the automation of a budgeting process, management, accounting and a planning process, strategic KPI turns into an entertaining way to spend money on the development and implementation, but the goal will remain unattained.
The KPI system is not limited to operating profit, volumes of production, costs and other economic indicators.
Let us consider the tactical level indicators. It is not necessary to build a system of any indicators solely for getting the system of KPI. Performance standards require a certain level of organization of the administrative process only in relation to staff. This is an easier level.
Techniques of BARS-scale are represented as the tactical level, which stands for behaviorally anchored rating scales or behavioral rating scales. A Chief Manager describes three situations of performance ― good, average and poor performance. If desired, it is added to the level of labor feat or is set as the parameters of performance at each level.
Then it is estimated and it is entered into the database. Each event is characterized by a small comment. Implementation of KPI is calculated as the average of the facts. Depending on the level of bonuses, in general, execution is a certain percentage of the planned premium.
If it is planned award of 10,000, then if the KPI is 37%, it is obtained award of 3700.
To avoid turning the system to the tool for faultfinding and misunderstandings, the company must have a system of labor regulation - work schedules, job descriptions, etc.
The system requires the maintenance of a database for each employee and then to use the final salary, which implies the presence of computer processing power - the system of entry and expansion of personnel documents in the relevant analysts, the use of standardized forms of assessment, the possibility of rapid communication - electronic document.
Do not be upset, and in a hurry to develop standards for labor resources, it is better to use for this system of incentives on KPI.
Operational KPI, such as SMART-task, just contribute to the development of consistent standards and lay the foundations for the transition to the tactical level on KPI management.
We will understand the term: S- specific - specific, that is, clearly describes what needs to be done and why, M- measurable - measured in order to be able to accurately assess the extent of the task. A- agreed - agreed and accepted for execution by all parties concerned, R- realistic - attainable, realistic, T- time bound - with a time-bound, that is, by what date, or to any intermediate deadlines task to execute.
The bottom line - control task execution, assessment of the extent to which the formation of orders flow through the analysis of which is possible to develop relevant job description with required officers functions.
Each employee can see his results through the system-task execution.
To lay down a clear view of employees required work function. The system allows to accumulate information over time to establish objective indicators of performance evaluation functions of labor (labor force ratios).
Why a task execution control. We are talking about problems that solve business process problems as a whole, rather than household level. The system allows to motivate the artist to execute decisions made problems that hinder business process. In the absence of failure to control priority does not involve an employee of the Executive's risk of loss in the RFP, he quietly pulls the rubber.
An employee is interested to maintain wages, therefore making efforts to fulfill tasks in the required time.
Control execution of instructions SMART-objectives will enhance the credibility of management solutions, will promote quality performance within the required time, which will increase the efficiency of labor costs.
The total calculation principle is very simple and convenient (an employee can himself calculate the premium) - transparency of the calculation increases in comparison with, for example, payments for seniority, or percentage of salary.
Implementation of KPI is calculated as the ratio of the tasks to be executed.
Employee assessment sheet looks something like this. This is a table with a set of parameters - firstly, with the description of the tasks expected result, secondly, the status of the task - performed / not been performed, thirdly, calculation of the execution plan for each day.
For the first time reasonable to include in the list of priority tasks only (from the annual work plan, for example), and then gradually expanded to a list of direct orders, instructions.
First, the system is implemented in the control unit and then transmitted to the production services. Otherwise, motivate production workers will not be able to find understanding in the control unit.
The system requires a certain level of automation - at least doing registry maintenance tasks - tasks and delivery of the performance report.
Perhaps management system in Excel, this is the cheapest method, but time-consuming. For enterprises with the number 1,300 is required department of 13 people for calculations in Excel.
Better to do additional processing to the program payroll. For Russia, the most common program is the calculation of 1C, especially if the company payroll is carried out in this program, the system will be easier to spread. The very process of reform at the coordination of the project will take - 3 months.
By law, you must notify the employee of the change in the calculation of wages for two months. Therefore it will be necessary to rely on the old two months. The first month is to pay the old - time for system improvement. Second month - to pay on more employees to become accustomed to the new system and were able to adapt. Third month is needed to calculate KPI (The Labour Code of The Russian Federation, 2001).
KPI system implies that the company is only one incentive system - the result. All other systems which do not depend directly on the result of the labor, will be perceived by employees more preferred.
Conclusion
To motivate employees to binding monetary reward is not necessary, especially in the early stages of implementation. It depends on the mood of the owner - liberalism or radicalism in the approach to change. Motivation based on clear indicators such as the KPI, allows operational staff to translate objectives of the owner through clear them with the tools - salaries and disciplinary promotion / recovery. In the beginning, you need to determine the scale of use on KPI system:
Right-on enterprises and activities,
Right-on implementation of labor functions of some posts,
As a lever of labor and performance discipline.
Introduction to the KPI-based motivation system requires a high level of skills, business process automation, besides development and implementation involve imposing costs in the early stages.
KPI system in addition to motivating employees qualitatively improves the entire spectrum of business processes and the organization of the enterprise. The process becomes more transparent, the owner receives information faster, increasing business agility, maneuverability. All these aspects are developing the overall competitiveness of the enterprise, endurance to market volatility, political factors, and other externalities. Tool motivation becomes the locomotive of the development of all economic activities, with the core competitiveness of well-built methodology and implementation of the technology. Based on the methodology it becomes apparent that there is no universal recipe development and implementation of KPI. Each enterprise should be decided individually. In other words, the initial costs of research, systems analysis and design, even on the basis of methodological development will take time and distract finances, as well as any other projects aimed at the development, the KPI requires investment.
References
- Eckerson, W.W. (2009). Performance Management Strategies. Business Intelligence Journal, 14(1), 24-27
- Ewenstein, B., Hancock, B., & Komm, A. (2016). Ahead of the curve: The future of performance management. McKinsey Quarterly, Retrieved from http://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/organization/our-insights/ahead-of-the-curve-the-future-of-performance-management
- Gabcanova, I. (2012). Human Resources Key Performance Indicators Journal of Competitiveness,4 (1), 117-128,
- Harvey, J. (2005). KPIs – The Broader strategic context Credit Control, 26 (4), 65-66
- Skibniewski, M. J. & Ghosh, S. (2009). Determination of Key Performance Indicators with Enterprise Resource Planning Systems in Engineering Construction Firms. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 135 (10), 965-978.
- Srimannarayana, M. (2010). Status of HR measurement in India VISION – The journal of business perspective, 14 (4),295-307
- Rozhdestvenskaya E. M. (2016). A pro-competitive order as an institute of the economy based on knowledge
- SHS Web of Conferences,28.
- The Labour Code of The Russian Federation (2001) No. 197-FZ of December 30, 2001. Retrieved from http://www.ilo.org/dyn/natlex/docs/WEBTEXT/60535/65252/E01RUS01.htm
- The Segal Group. (2010). Study on The State of Performance Management Retrieved from http://www.sibson.com/ publications/surveysandstudies/2010SPM.pdf.
- Toulson, P. & Dewe, P. (2004). HR accounting as a measurement tool. Human Resource Management, 14 (2), 75-90.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 July 2017
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-025-9
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
26
Print ISBN (optional)
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1055
Subjects
Business, public relations, innovation, competition
Cite this article as:
Rozhdestvenskaya, E., Ermushko, Z., Zhavoronok, A., & Polunina, S. (2017). Methodological Basis of KPI Motivation. In K. Anna Yurevna, A. Igor Borisovich, W. Martin de Jong, & M. Nikita Vladimirovich (Eds.), Responsible Research and Innovation, vol 26. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 830-837). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2017.07.02.107

