Abstract
SMEs are one of the sectors that play an important role in the economy, but in reality, there are still many problems facing their development. The problems that arise in SMEs are related to finance, sources of capital, and the limited use of information. These problems are the main factors that can affect business sustainability in the face of the global market. This study aims to investigate the factors that influence the increase in business sustainability in the SMEs sector in Indonesia post-COVID-19 pandemic. These factors are financial literacy, use of accounting information, working capital, and use of technology. The population and sample in this study were SMEs in Indonesia, and the technique of collecting data used a questionnaire. This study uses the Suctural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis technique to test all hypotheses. The results of this study state that there is no influence between financial literacy, the use of accounting information, and working capital on the business success of SMEs. However, the use of technology by SMEs is able to increase the success of their businesses. Furthermore, this research can be used as a guideline to ensure the level of business sustainability in SMEs.
Keywords: Accounting information, Capital, Technology, Financial literacy, SMEs
Introduction
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) have long been trusted as an important unit to support the Indonesian economy. One of the roles of SMEs is to reduce poverty through providing employment opportunities (Wibowo & Kurniawati, 2016). In addition, SMEs also have a very important role for the national economy. Data from the Central Bureau of Statistics in Indonesia in 2018 shows that SMEs absorb up to 97% of the total workforce, contribute 60.34% of the total national GDP, and contribute 15.80% to national exports (Umami et al., 2020). Similarly, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) located in Semarang have demonstrated a consistent growth trend, with an annual average increase of around 1.97%. Between 2015 and 2019, approximately 14,893 small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) were registered with the Semarang City Cooperatives and SMEs Office, as documented. It is hoped that with the increasing number of SMEs in Semarang City, it will increase the amount of local government revenue, improve the regional economy, and absorb a large number of workers.
Although SMEs are one of the sectors that play an important role in the economy, in reality there are still many problems facing its development, including SMEs in Semarang. Increasing business competition, especially competition against large and modern competitors, has put SMEs in a vulnerable position (easily attacked). Most of the SMEs in Semarang City still operate in the traditional way in terms of production and marketing. Lack of capital, skills, and problems in business development are problems faced by SMEs (Noviani Hanum & Sinarasri, 2018).
Other problems that arise in SMEs are related to finance, sources of capital and limited use of information. These problems are the main factors that can affect business success in the midst of facing the global market. Seeing the potential of SMEs, these problems should be overcome with the government considering that currently SMEs are the main agenda in national development (Firdarini & Prasetyo, 2020). Moreover, it has been almost 2 years since Indonesia has experienced the Covid-19 pandemic which will certainly have an impact on the success of SMEs in maintaining their business. The Covid-19 pandemic has resulted in a reduction in revenue for numerous businesses as a consequence of limitations on social gatherings and a decrease in consumers' buying capacity. The impact of this pandemic is enormous, especially in the SME sector. Although the government has provided a lot of capital assistance to the SME sector, if from an internal perspective, SMEs themselves do not have innovation, their business will also experience bankruptcy.
Therefore, increasing the success of SMEs is an important factor because the increase in the income of SMEs will also affect the increase in government revenue through taxes paid by SMEs (Wadesango et al., 2018). In addition, business success is also able to improve the welfare of SME owners and employees.
Business sustainability is success in achieving its business goals. SMEs are said to experience business success if there is an increase in capital, income, sales, total production, and number of workers (Fitriyani et al., 2020). There exist multiple variables that can enhance the efficacy of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). First, financial literacy, namely knowledge possessed by someone in managing or planning their business finances. SME owners who are able to manage and plan their business finances well will be able to achieve their business goals (Widayanti et al., 2017). The business objectives achieved indicate that SMEs are able to increase income, total production, capital, and labor. According to (Ye & Kulathunga, 2019), individuals possessing financial literacy are capable of effectively managing economic information, devising financial strategies, and making informed decisions regarding the acquisition of assets, retirement planning, and debt management. In order to survive during this pandemic, SME owners must be able to have good financial literacy, namely by managing and planning SME capital effectively and efficiently, and being able to make the right decisions regarding the use of wealth and debt. Enhancing financial literacy can potentially reduce the incidence of erroneous decisions pertaining to economic and financial matters (Widayanti et al., 2017).
Second, the use of accounting information is one of the factors that can affect business success. The utilization of accounting information enables management to execute strategies and operational activities aimed at attaining the overarching objectives of the organization (Firdarini & Prasetyo, 2020). Accounting information is used as the basis for making business decisions in planning, managing and evaluating businesses. The use of good accounting information will lead to good management of business activities, so that it can support business success (Suhendi et al., 2022). During the Covid-19 pandemic, SME players must be able to use accounting information in order to evaluate their business, so they can manage their business well and plan activities for the success of their business.
The third factor that can increase business success is working capital. The adequacy of working capital is a crucial determinant of business success. The greater the business capital owned, the greater the possibility that the business can be successful (Siswanti & Nawangsari, 2023). An increase in working capital can affect income, sales volume, production volume, and labor (Olowookere et al., 2021; Romus et al., 2020). Thus, business success can be determined from the size of the working capital owned by each SME. The government provides a working capital assistance program for SMEs, however, SMEs must be able to use this capital wisely so that it can be used to increase the amount of production, so that sales are expected to increase and business success is achieved.
Furthermore, the use of technology can also be a determining factor for business success. Utilization of technology can be interpreted as the use or mastery of technology by someone to achieve business goals. The presence of technology, especially the internet in the business world can provide different opportunities and challenges. The existence of technology will help business actors, especially SMEs, increase sales, income, production, and be able to provide job opportunities (Yanti et al., 2018). Thus, good use of technology will increase efficiency, product, and service quality, which can have an impact on business success (Marfuah & Hartiyah, 2019). The Covid-19 pandemic has made people experience limitations in carrying out their activities. Therefore, SMEs must be able to take advantage of technology in order to improve innovation, product and service quality, such as online sales so that income can increase, and business success can be achieved.
This research needs to be done because SMEs still need to make improvements to their businesses post-COVID-19 pandemic, including in the city of Semarang, due to the large effect on the economy due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Even though the government has supported and provided assistance to SMEs players, if SMEs are unable to manage their businesses, they are unable to maintain them. In addition, the number of SMEs is increasing every year, so the increasing success of businesses in the SMEs sector will have an impact on increasing government revenues. Therefore, it is necessary to know what factors can increase business success in the SMEs sector.
Based on this, the problem in this research is focused on does financial literacy, the use of accounting information, working capital, and the use of technology affect the success of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Semarang City, Indonesia?
Literature Review
Capacity Building
Capacity building refers to the systematic enhancement of an individual, group, institution, or system's ability to attain superior objectives or outcomes (Brown et al., 2001). In the business context, an individual or business actor is required to continuously improve his skills and abilities by making continuous improvements both in the financial and non-financial fields.
Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is the ability that a person has to understand how to manage and plan his finances. Acquiring knowledge is advantageous as it enables individuals to engage in effective financial planning and circumvent potential financial predicaments (Widayanti et al., 2017). Furthermore, according to Ningsih and Tasman (2020), financial literacy refers to an individual's capacity to effectively manage economic information, develop financial strategies, and make informed decisions regarding the acquisition of assets, retirement planning, and debt management.
Enhanced financial literacy has the potential to reduce errors in decision-making pertaining to economic and financial matters. From the perspective of a financial service provider, proficient financial literacy can furnish insights into products, enable comprehension of risks to clients, and enhance cost-effectiveness. Moreover, proficient financial literacy among small and medium enterprises (SMEs) can facilitate the government in acquiring optimal tax revenue (Dwitya Aribawa, 2016).
Financial literacy is one of the key factors that can affect the performance of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) because it enables SMEs to evaluate the financial implications of their business decisions. Financial literacy contributes to organizational decision-making and enables organizations to acclimate to change and capitalize on the opportunities presented by these changes. Thus, enhancing the understanding of financial literacy is highly significant and essential for the performance of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) (Kulathunga et al., 2020). Thus, if SMEs have good financial knowledge, they will be able to manage, plan, and make decisions related to financial aspects and understand what is more prioritized in business development, so that business sustainability will be achieved. This is in accordance with research conducted by Kulathunga et al. (2020), that SMEs who have financial literacy are able to increase success in their businesses. Thus, hypothesis 1 in this study is:
H1: Financial literacy has a positive effect on the business sustainability of SMEs.
Use of Accounting Information
Accounting information pertains to numerical data regarding economic entities and serves as a valuable resource for making economic decisions by evaluating various options (Firdarini & Prasetyo, 2020). Accounting information is very useful for the SMEs sector, because it can be used as a tool to measure and communicate financial information needed in the process of solving problems at hand, so that the use of accounting information allows SMEs to make strategic operational activities needed to achieve their business goals (Umami et al., 2020). Accounting information is also able to provide risk measurement for the sustainability of a firm through better disclosure in financial reporting (Selahudin et al., 2014).
Accounting information can serve as a fundamental framework for formulating business decisions, which helps in planning, managing, and evaluating businesses. Accounting information that is managed properly can support business success, so that accounting information has a very important influence on the achievement of the success of SMEs. Accounting information can be a good basis for making business decisions in the SME sector, such as decisions in developing markets, pricing and others (Firdarini & Prasetyo, 2020). Thus, hypothesis 2 in this study is:
H2: The use of accounting information has a positive effect on the business sustainability of SMEs.
Working Capital
Capital is something important for SMEs to run their business (Dhiana et al., 2021). Business will not be realized without capital (Arilani et al., 2019). SMEs must have accuracy regarding the use of working capital to ensure smooth operational activities. Insufficient working capital will result in delays in the production process, while excessive working capital can hinder SMEs from obtaining investment opportunities.
Lack of working capital will cause delays in the production process and conversely an excessive amount of working capital will prevent companies from obtaining investment opportunities because working capital only revolves around business operations. SMEs need to determine the right amount of working capital to ensure that operational activities run smoothly and can capture investment opportunities to increase profitability so that they can achieve business success. Thus, hypothesis 3 in this study is:
H3 : Working capital has a positive effect on business sustainability of SMEs.
Use of Technology
Technology pertains to the utilization and comprehension of tools and techniques, and their impact on humanity's capacity to manipulate and alter their surroundings (Marfuah & Hartiyah, 2019). Use of technology is a crucial instrument for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to guarantee their efficacy in a digital commercial setting. Moreover, it facilitates small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to gather, assess, and analyze pertinent and effective data. In addition, the utilization of technology holds significance in terms of organizational strategizing, communication and cooperation, provision of customer service, and management of business operations. Researchers have also identified the use of technology as a key driver in the success of SMEs (Kulathunga et al., 2020). Thus, hypothesis 4 in this study is:
H4: The use of technology has a positive effect on business sustainability of SMEs.
Research Methods
The study focused on Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) located in Semarang, Indonesia. The sample is determined through the utilization of the convenience sampling method. If the minimum sample size uses the Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimation model, then a minimum sample of 100 is required (Hair et al., 2019). Furthermore, data collection was carried out using a survey method. The data for this research is primary data, namely by using a questionnaire distributed to SMEs in Semarang, via a Google form and directly distributed to SMEs.
The present research employs Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) as a means of hypothesis testing, given its capacity to effectively and concurrently integrate measurement models with structural models, in comparison to alternative multivariate techniques.
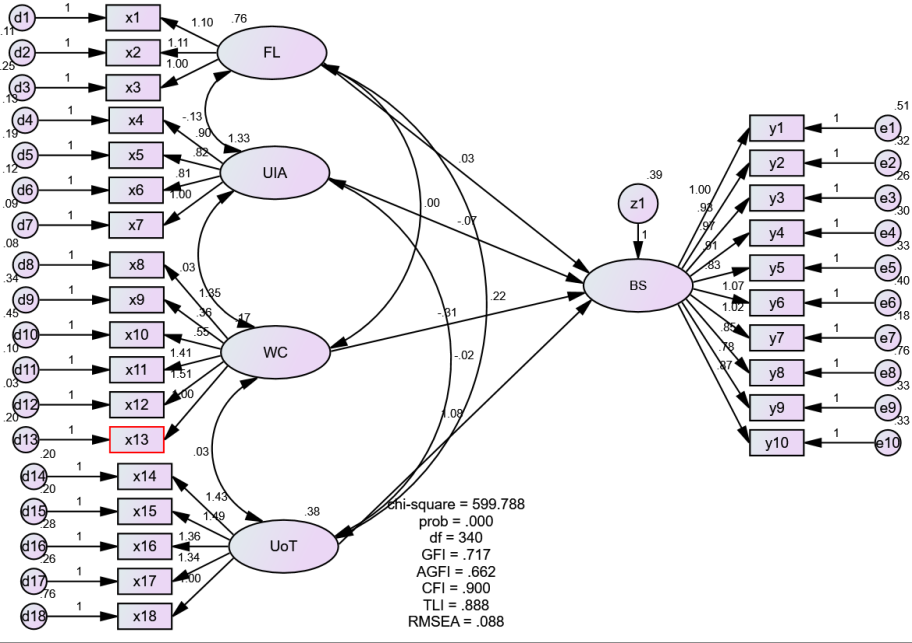
Result and Discussion
Validity and Reliability Test
Table 2 below is the results of the validity and reliability tests of all constructs in this study. Based on the table, all values of the validity test are more than the value of r table (5%), which is 0.1966. So it can be concluded that all the questions in this study are valid. Furthermore, the results of the reliability test for all constructs in this study showed results of more than 0.60, so it was concluded that all questions in this study were reliable.
Descriptive Statistics
This study uses a population of SMEs in Semarang, where the number of samples taken is 100 respondents, using the convenience sampling method. The results of the descriptive statistics can be seen in Table 3. Based on the table above, it can be seen that all the variables in the study, namely financial literacy, use of accounting information, working capital, use of technology, and the success of SMEs have a real average value that is greater than the theoretical average value. This indicates that the respondent's assessment of each question in the research variable is high.
4.3 Normality Test
The normality test in the Structural Equation Model (SEM) is seen from the critical skewness value for each variable and the total multivariate value. Based on a univariate analysis, it can be inferred that the data exhibits a normal distribution. This conclusion is drawn by examining the critical skewness value of each indicator, which indicates a value below ± 2.58. However, the data used multivariately has an abnormal distribution, with a kurtosis value of 199.643 and a critical skewness value of 24.354 > ± 2.58. However, according to Kline (2011), multivariate abnormal data conditions can be accepted on the condition that the data are univariately distributed normally.
4.4 Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) Analysis Techniques
From Figure 1, it can then be seen that the value of the goodness of fit indices criteria for the full structural model is described in Table 4.
According to Table 4, the Chi-Square value is 599.788 with probability = 0.000; GFI = 0.717; AGFI = 0.662; TLI = 0.888; CFI = 0.90 and RMSEA = 0.08 indicate that some of the criteria for the suitability of the model are fit and some of the other criteria are accepted at a marginal level. GFI and AGFI criteria which are measures of R2 and adjust R2 in multiple regression analysis. Ghozali (2018) states that the Chi-square value exhibits a high degree of sensitivity to sample size, which may result in a consistent tendency for the Chi-square value to yield significant results. AMOS 22 output results for other parsimony fit measures such as PNFI = 0.718, PGFI = 0.601 and PCFI = 0.809 are above 0.50 which indicates that this model is accepted at the fit level.
In addition, the results of the confirmatory factor analysis also show that the indicators that measure the construct have good convergent validity. This is shown through the loading factor indicator value of each construct which is above 0.50 (Ghozali, 2018). Furthermore, the results of the reliability and construct validity calculations also show that all constructs have good convergent validity. Therefore, it can be inferred that the comprehensive model utilized in this investigation may serve as a foundation for evaluating research hypotheses, given that the constructed model is sound despite not being flawless.
Hypothesis Test
Based on Table 5, it is observable that the variables of financial literacy, use of accounting information, and working capital have a critical ratio value is < ± 1.96 and the probability is > 0.05. This explains that the level of financial knowledge possessed by SMEs will not affect the business sustainability. The COVID-19 pandemic, which emerged in 2019, has resulted in certain small and medium enterprises (SMEs) being unable to sustain their operations. Therefore, promotion and marketing through e-commerce can be a more important alternative in order to maintain SMEs (Puspitaningtyas et al., 2021). This study's findings align with prior research conducted by (Kusumadewi, 2017) that financial literacy is not the main factor that can affect the business sustainability of SMEs.
In addition, it is described that the use of accounting information has no effect on the business sustainability of SMEs. In fact, many small and medium enterprises (SMEs) lack an understanding of how accounting data can benefit their operations. This is evidenced by the average score of 3.56, which indicates that the majority of respondents continue to provide neutral responses. The findings of this investigation are consistent with studies conducted by Rakhmawati (2018).
In the working capital variable, it can be seen that the size of the working capital owned by SMEs does not affect the business sustainability. During the Covid-19 pandemic, some products from SMEs were not sold, so they chose to prioritize marketing so that their products were sold by Puspitaningtyas et al. (2021), compared to increasing working capital. Dhiana et al. (2021) said that working capital has no effect on the business sustainability of SMEs.
While for the use of technology variable, it can be seen that the critical ratio value is > ±1.96 and the probability is < 0.05. These results illustrate that the technology used by SMEs will increase the percentage of success of SMEs. The Covid-19 pandemic has significantly restricted people's mobility, thereby necessitating the utilization of technology to enhance the sale of products by small and medium enterprises (SMEs). This approach can potentially lead to the attainment of success by SMEs. After the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of technology has become commonplace and is always used to improve SME businesses (Rudiatin et al., 2021). The results of this study are in line with the research of Yanti et al. (2018), Marfuah and Hartiyah (2019), and Kulathunga et al. (2020) that the use of good technology increases the business sustainability of SMEs.
Conclusion and Suggestion
The objective of this research is to ascertain the impact of financial literacy, use of accounting information, working capital, and use of technology on the sustainability of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The present study is grounded on the theoretical framework of capacity building. The results of the study explain that SME actors who use technology well are able to increase the business sustainability of SME. However, other factors, such as financial literacy, use of accounting information, and working capital do not affect the business sustainability of SMEs.
Further research is expected to add other variables that can affect the business sustainability of SMEs, such as locus of control, e-commerce, and so on. In addition, further research can add samples to further generalize the results of the study.
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to the Accounting Research Institute, (ARI- HICoE), Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia, and the Ministry of Higher Education for providing research funding.
References
Arilani, L., Indrayani, L., & Endah, T. L. (2019). The Effect of Business Actor Behavior and Business Capital on the Success of MSMEs in Tukad Sumaga Village, Gerokgak District, Buleleng Regency. Jurnal Pendidikan Ekonom, 11(2), 427–436. https://ejournal.undiksha.ac.id/index.php/JJPE/article/viewFile/21520/13994
Brown, L., LaFond, A., & Macintyre, K. (2001). Measuring Capacity Building (Issue March, pp. 919–966). http://www.heart-intl.net/HEART/Financial/comp/MeasuringCapacityBuilg.pdf
Dhiana, P., Gagah, E., & Purwanti, D. (2021). The Effect of Business Capability, Business Capital and Marketing Strategy on Business Success with Business Development as Intervening Variables. Journal of Management.
Dwitya Aribawa. (2016). The Influence of Financial Literacy on the Performance and Sustainability of MSMEs in Central Java. Jurnal Siasat Bisnis, 20(1), 1–13.
Firdarini, K. C., & Prasetyo, A. S. (2020). The Effect of Using Accounting Information and Working Capital Management of MSME Actors on Business Success with Age as a Moderating Variable (Case Study in Creative Industries in Yogyakarta). Jurnal Stie Semarang, 12(1), 19–32. DOI:
Fitriyani, I., Sudiryati, N., & Fietroh, M. N. (2020). Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Business Management Strategy. Indonesian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 1(2), 87–95. https://journal.publication-center.com/index.php/ijssh/article/view/106
Ghozali, I. (2018). Structural Equation Modeling Konsep dan Aplikasi dengan Program Amos 24. Undip Press.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., Black, W. C., & Anderson, R. E. (2019). Multivariate data analysis (Eighth). Cengage Learning EMEA.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling (3rd ed.). The Guilford Press.
Kulathunga, K. M. M. C. B., Ye, J., Sharma, S., & Weerathunga, P. R. (2020). How Does Technological and Financial Literacy Influence SME Performance: Mediating Role of ERM Practices. Information, 11(6), 297. DOI:
Kusumadewi, N. R. (2017). The Influence of Locus of Control and Financial Literacy on the Performance of SMEs in SME Actors in Rawa Village. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Dan Call for Papers, 5(November), 915–924.
Marfuah, S. T., & Hartiyah, S. (2019). The Influence of Own Capital, People's Business Credit (KUR), Technology, Length of Business, and Business Location on Business Income. Journal of Economic, 1(1), 183–195.
Ningsih, T. N., & Tasman, A. (2020). Pengaruh financial literacy dan financial inclusion terhadap kinerja UMKM [Pengaruh financial literacy dan financial inclusion terhadap kinerja UMKM]. Jurnal Kajian Manajemen dan Wirausaha, 2(4), 151. DOI:
Noviani Hanum, A., & Sinarasri, A. (2018). Analysis of the Factors Influencing E-Commerce Adoption and Their Influence on the Performance of MSMEs (Case Study of MSMEs in the City of Semarang). Maksimum, 8(1), 1. DOI:
Olowookere, J. K., Odetayo, T. A., Adeyemi, A. Z., & Oyedele, O. (2021). Impact of Covid-19 On Working Capital Management: A Theoretical Approach. Journal of Business And Entrepreneurship, 10(1), 38. DOI:
Puspitaningtyas, S. A., Dian, P., Kusuma, I., Pratiwi, U., Dian, P., & Kusuma, I. (2021). The Effect of the Use of E-Commerce and Accounting Information System on SMEs Revenues. International Sustainable Competitiveness Advantage, 315–323.
Putri Hidayati, E. (2016). The Influence of Working Capital and Marketing Strategy on the Success of the Glass Bead Craft Business in Plumbon Gambang Village, Gudo District, Jombang Regency. Jurnal Pendidikan Ekonomi (JUPE), 4(3).
Rakhmawati, F. F. (2018). The Influence of Financial Literacy, Use of Accounting Information and Human Resources on UKM Performance (Case Study of Batik Tulis UKM in Pekalongan Regency). Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, 1–16. http://eprints.ums.ac.id/id/eprint/68993
Romus, M., Anita, R., Abdillah, M. R., & Zakaria, N. B. (2020). Selected Firms Environmental Variables: Macroeconomic Variables, Performance and Dividend Policy Analysis. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 469(1), 012047. DOI:
Rudiatin, E., Patrianti, T., & Sugiatmi, S. (2021). Building Brand In Virtual Marketing: Maintaining Business Sustainability In The Era Of Covid-19. Prosiding Konferensi Nasional Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat dan Corporate Social Responsibility (PKM-CSR), 4, 1255-1261. DOI:
Selahudin, N. F., Zakaria, N. B., Sanusi, Z. M., & Budsaratragoon, P. (2014). Monitoring Financial Risk Ratios and Earnings Management: Evidence from Malaysia and Thailand. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 145, 51-60. DOI:
Siswanti, I., & Nawangsari, L. C. (2023). Various Sources Working Capital Financing For The Sustainability Micro, Small And Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) Business In Rancabungur-Bogor. Jurnal Abdimas Perbanas, 4(1), 28-32. DOI:
Suhendi, C., Ifada, L. M., Layla, S., & Istanti, W. (2022). The Role of Accounting Information Systems in Improving SMEs’s Successful. Jurnal Akuntansi Multiparadigma, 13(2). DOI:
Umami, L., Kaukab, M. E., & Romandhon, R. (2020). Use of Accounting Information in Batik Industry SMEs. Journal of Economic, Business and Engineering (JEBE), 2(1), 66–75.
Wadesango, N., Mutema, A., Mhaka, C., & Wadesango, V. (2018). Tax Compliance of Small and Medium Enterprises Through the Self-Assessment System: Issues and Challenges. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 22(3), 1528–2635. https://www.abacademies.org/articles/Tax-Compliance-of-Small-and-Medium-Enterprises-through-the-Self-Assessment-System-1528-2635-22-3-201.pdf
Wibowo, A., & Kurniawati, E. P. (2016). The Effect of Using Accounting Information on the Success of Small and Medium Enterprises [Studies at Convection Centers in Tingkir District, Salatiga City]. Jurnal Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, 18(2), 107. DOI:
Widayanti, R., Damayanti, R., & Marwanti, F. (2017). The Influence of Financial Literacy on Business Sustainability in MSMEs Jatisari Village. Jurnal Ilmiah Manajemen & Bisnis, 18(2), 153. DOI:
Yanti, V. A., Amanah, S., & Muldjono, P. (2018). Factors Affecting the Sustainability of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises in Bandung and Bogor. Jurnal Pengkajian Dan Pengembangan Teknologi Pertanian, 20(2), 137–148.
Ye, J., & Kulathunga, K. (2019). How Does Financial Literacy Promote Sustainability in SMEs? A Developing Country Perspective. Sustainability, 11(10), 2990. DOI: 10.3390/su11102990
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
15 November 2023
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-130-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
131
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1281
Subjects
Technology advancement, humanities, management, sustainability, business
Cite this article as:
Permatasari, D., Yulianto, A. R., Mohammed, N. F., & Shafie, N. A. (2023). Factors Influencing Business Sustainability of SMEs in Indonesia Post Covid-19 Pandemic. In J. Said, D. Daud, N. Erum, N. B. Zakaria, S. Zolkaflil, & N. Yahya (Eds.), Building a Sustainable Future: Fostering Synergy Between Technology, Business and Humanity, vol 131. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 167-178). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2023.11.14

