Abstract
In accordance with the established relationships between the indicators of the development of the government borrowing market and market rates, which acquire certain features in the process of the implementation of the Bank of Russia's monetary policy and performing its functions of placing government debt obligations on the exchange market, a representative instrument of the debt market is determined. It is the most sensitive to changes in market rates and flexibly protects investments from inflation. At the same time, the authors take into account the growth trends in the volume of public debt in recent years, the extent of the use of state debt obligations by organizations of the corporate banking sector in portfolio investments. The period of the key rate increase, which is characterized by an atypical situation for the exchange market: a weak inverse relationship between the studied indicators was additionally studied on the basis of duration. As a result, it was found that bonds with a duration of 1–3 years were the most profitable, according to the evaluation results, since there was a close relationship between the return on investments in them and market rates: a decrease in market rates led to an increase in their yield. Moreover, the main directions for the expansion of the generalized analysis of market parameters of the circulation of government bonds were identified in order to determine more stable, characteristic trends in its development and factor relationships in them.
Keywords: Correlation rate, index bonds, key rate, state valuable paper, stock market, score
Introduction
Government bonds are a universal tool that allows the state to manage the volume of money supply, finance the budget deficit at different levels by attracting free financial resources of enterprises and the population (Demilkhanova, 2016). Today their demand are increased by the need for modernization, the introduction of large innovative projects based on digital technologies and therefore they are the cornerstone of the modern financial system (Feder-Sempach & Stawasz-Grabowska, 2019).
One of the areas of regulatory activity of the Bank of Russia is to provide conditions for the growth of capitalization of the exchange market of government bonds, the importance of which in the accumulation and redistribution of financial resources is increasing significantly in many countries, including the Russian Federation. The current stage of development of this segment of the Russian financial market is characterized by:
The creation of favourable conditions for private investors to enter the market;
The development of the exchange infrastructure responsible for the bond circulation market;
The development of the accounting infrastructure of the exchange, as well as institutions for external risk assessment.
The increase in the average duration to 3.3 years, which indicates a lengthening of the terms of borrowings;
The increase in the volume of attracting financial resources through the placement of state debt instruments for the implementation of socio-economic policy, effective monetary and debt policy.
Problem Statement
The modern market of sovereign debt obligations (state short-term bonds and federal loan bonds (SSTB-FLOB)) operates in the context of the development of world securities trading on exchange markets in the following areas:
The growth of trading in derivatives for international stock assets;
The consolidation of the securities market in space and time;
The concentration of the market in the leading financial centers of the world and in the ownership of legal entities;
The creation of new market instruments (Pryanishnikova, 2016).
In the context of blurring the boundaries between the markets of financial and derivative instruments, the growing role of non-residents in the Russian debt market, the emergence of new instruments intended for credit institutions, companies in the corporate sector of economy and individuals, the importance and significance of research conducted in the field of the functioning of the debt market is only increasing. It is also necessary to note the question of the results of the influence of the monetary policy pursued by the Bank of Russia on the peculiarities of the functioning of the government debt instruments market, the relationship between the operations of credit institutions in the stock market, their profitability and the conditions for their implementation.
Research Questions
Nowadays we more and more refer to debt financing of economic growth, which allows overcoming crisis phenomena and solving social and economic problems, achieving the competitiveness of the state in the international market (Stolyarov & Transition, 2019). In this regard, the use of government bonds and the potential inherent in this instrument require, first of all, a comprehensive study of the problems of the functioning of the Russian debt market, multifactorial dependencies that exist between the parameters of its development. Many Russian and foreign scientists follow this path, devoting their research to the development of assessment methods:
The degree of influence on the profitability of long-term financial instruments of such factors as inflation (Mikhailov, 2012, 2016), duration and frequency of coupon income payments, foreign exchange reserves (Tiunova, 2019), exchange rates (Megasari et al., 2019), stock market (Cheng, Yang, 2017) and others,
The effectiveness of the mechanism for using this tool in financing the deficit of the federal regional and local budgets (Levin & Polkin, 2018);
The effectiveness of debt instruments as highly liquid assets in the portfolio of companies, banking and non-banking credit institutions, etc. (Ushanov, 2016);
The relationship between bond indices (government, corporate) and broad market stocks, as well as between bond indices and duration (Demilkhanova, 2019).
Great importance is attached to research on the development of methods for assessing the impact of macroeconomic factors on indicators of the stock (exchange) market, on the basis of which cross-country comparisons can be made. The forecasts are developed on the state of the market, taking into account global trends in the development of the debt instruments market (Fedorova & Pankratov, 2010; Lakhno, 2017; Nikonorov, 2014; Vlasenko & Simanova, 2016) and others.
Purpose of the Study
Taking into account the growth trends in the volume of public debt in recent years, the extent of the use of state debt obligations by organizations of the corporate banking sector in portfolio investments, it is necessary to identify the most representative instrument of debt market, which is sensitive to changes in market rates and flexibly protects investments from inflation, based on the established relationships between indicators, the development of the government borrowing market and market rates, which acquire certain features in the process of the implementation of the Bank of Russia's monetary policy and performance of its functions of placing state debt obligations on the exchange market.
Research Methods
The total volume of government bonds in circulation in 2019 was 8894.3 billion rubles, in 2018 it was 7251.5 billion rubles. State short-term bonds and federal loan bonds occupies the largest share in the total amount of government borrowings. According to them, an index is calculated on the exchange market, which reflects the average market price of bonds included in the base of its calculation. In 2019, the turnover of these bonds was 6464.02 billion rubles, which was 73 % of the amount of government bonds in circulation in 2019. In 2018, they accounted for 67 %. State short-term bonds and federal loan bonds also occupy a significant share of the volume of securities in circulation: 35 and 20 % in 2018 and 2019, respectively. High shares for these types of bonds remain in the volume placed in 2019–2020 (Figure 01), but there is a decrease in the share of state short-term bonds and federal loan bonds from 67.0 % to 56.7 %. While the share of state short-term bonds and federal loan bonds increases from 18.4 % to 33.3 %.
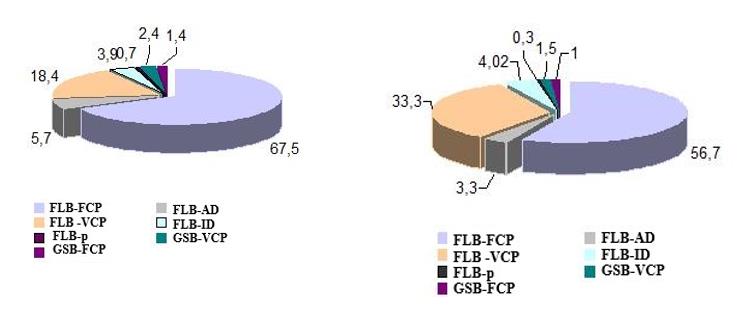
the author's calculations based on: Official website of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (https :// www.minfin.ru/ru)
The data in Table 1 show that during the entire analyzed period, the proceeds of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation from placed and additionally placed FLB-FCPs many times exceed their nominal volume. This means that government debt obligations were placed by the Bank of Russia at secondary auctions at prices exceeding their face value. The volume of issue of government bonds is increasing. In 2019 the nominal value of the placed bonds amounted to 659.6 billion rubles. Compared to the previous year, the growth amounted to 596.1 billion rubles, the growth rate for the studied period was 544.2 % (increase: more than 5 times).
The debt policy of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of recent years is characterized by the increase in the volume of federal domestic and external debt, the total state and municipal debt, as well as the state domestic debt. Government debt accounts for the bulk of federal debt. A sharp increase in public domestic debt, expressed in government bonds of the Russian Federation, has been observed since 2019, when its volume increased by 1.2 times compared to 2018. In 2020, compared to 2019, the public debt increased by 1.5 times and amounted to 14,057 billion rubles.
The debt of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation to the Bank of Russia, which invests in debt bonds of the Russian Federation Government and foreign states, has decreased in recent years on bonds of external bond loans from 150,985 million rubles to 70,966 million rubles. Federal loan bonds (FLB) debt increased from 60 million rubles in 2019 to 212,636 million rubles in 2020. At the same time, the share of bonds issued on behalf of the Russian Federation in 2019 decreased from 2.0 to 1.3 %. A significant share of investments was occupied by investments in debt obligations of European countries: 52.0 % in 2019 and 51.2 % in 2020 (Figure 2).
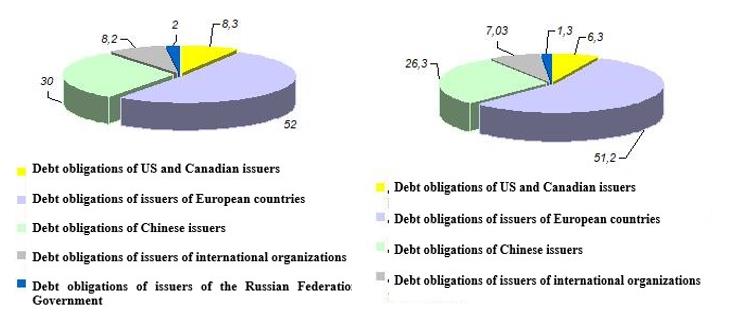
Legend: Author's calculations based on: Annual report of the Bank of Russia for 2020 [Electronic resource]. URL: https:// https://cbr.ru/Collection/Collection/File/32268/ar_2020.pdf. p. 310
The increase in government debt, expressed in government debt obligations, affected the volume of the Bank of Russia operations on the open market, carried out as a general agent for the placement of government bonds at auctions and secondary trading on the exchange market on behalf of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. In 2019, the volume of such transactions increased and amounted to 5 303 billion rubles, which was 3219 billion rubles more than the previous year, the growth rate was 254.5 %. (Table 2).
Findings
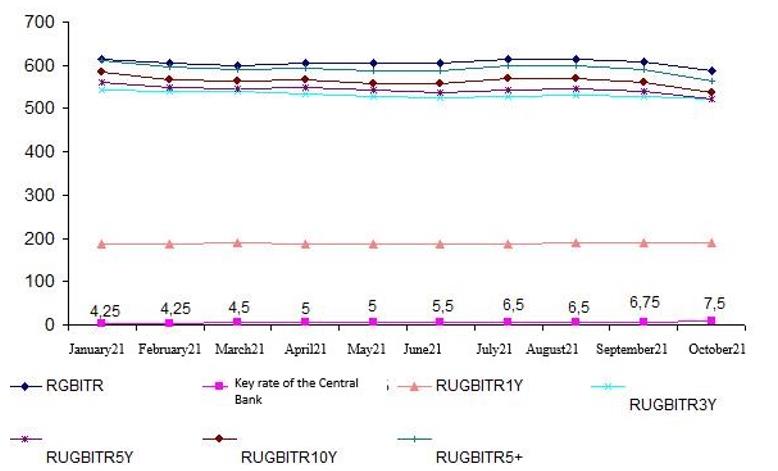
The study of the Relationships of Government Bond Indices of Total return (RGBITR) and the key rate of the Bank of Russia allows drawing the following conclusions:
The period 31.01.20–30.12.20 was characterized by a pronounced inverse relationship between the studied parameters (correlation coefficient: –0.88) (Table 03). A decrease in the key rate led to a decrease in the yield of FLB - an indicator of the market portfolio, which could be explained by the increase in demand for this financial instrument in the face of a decrease in the lending rate. However, at the same time, the effective yield of investments in bonds could not fall below the level of the market interest rate.
The period 31.01.21–30.10.21 was characterized by a weak inverse relationship between the change in the key rate of the Bank of Russia and FLB index (correlation coefficient: - 0.09). In order to identify the most representative instrument of the debt market, which was sensitive to changes in market rates and protected investments from inflation more flexibly, factor dependencies were estimated for other indices of government bonds that differed in duration (Table 4).
The most profitable, according to the results of the assessment of the relationship between the studied indicators, were bonds with a duration of 1–3 years. There was a close relationship between the profitability of investments in them and market rates: a decrease in market rates led to the increase in their profitability.
The bond index with a duration of less than 1 year demonstrated the opposite nature of the relationship with market rates compared to other indices: market prices increased along with an increase in the key rate of the Bank of Russia (correlation coefficient: 0.83) (Figure 03), which could be explained by the fact that these bonds were less dependent not only on changes in market rates, but also on other factors (sanctions, geopolitics, etc.).
Conclusion
The results of a comparative analysis of changes in the parameters of the bond market and market rates provide a generalized picture of the factor relationships between them. During the analysis of the dynamics of the government bond index, correlating the dynamic series of government bond indices with market rates, each of the stages of the generalized analysis must be expanded with more detailed analytical procedures that would give a more complete picture of the dynamics of indicators of a certain segment of the financial market, in particular, the government bond market and relationships between them (Table 5).
Thus, according to the established relationships between indicators of the development of the government borrowing market and market rates, which acquire certain features in the process of the implementation of the Bank of Russia’s monetary policy and performing its functions of placing government debt obligations on the exchange market, the most representative instrument of the debt market, sensitive to changes in market rates and flexibly protects investments from inflation. Moreover, the main directions for the expansion of the generalized analysis of market parameters of government bonds circulation were identified in order to determine more stable, characteristic trends in its development and factor relationships in them.
The research conducted in the field of the functioning of the debt market is important and significant, which is explained by its role in the achievement of the goals of the budget process and the debt policy of the state, the participation of the market not only in the achievement of high rates of development of the banking and financial sector of the economy, but the economy as a whole.
References
Cheng, K., & Yang, X. (2017). Interdependence between the stock market and the bond market in one country: evidence from the subprime crisis and the European debt crisis. Financial Innovation, 3(1), 1–22.
Demilkhanova, B. A. (2016). Formation of profitability in the market of government borrowings. Economics and management: problems, solutions, 1(12), 85–91.
Demilkhanova, B. A. (2019). Comparative assessment of the relationship between stock and bond indices. National economic systems in the context of the formation of the global economic space. In 2 volumes. (pp. 492–496). Limited Liability Company Publishing House Typography Arial.
Feder-Sempach, E., & Stawasz-Grabowska, E. (2019). Reserve Currency Status as a Safe Asset Determinant. Empirical Evidence from Main Public Issuers in the Period 2005–2017. Comparative Economic Research, 22(3), 65–81.
Fedorova, E. A., & Pankratov, K. A. (2010). Influence of macroeconomic factors on the Russian stock market. Forecasting problems, 2, 78–83.
Lakhno, Yu. V. (2017). Analysis of the adaptive development of the Russian securities market. Finance and credit, 23, 2243–2256.
Levin, V. S., & Polkin, E. N. (2018). Bonded loans of the Orenburg region in the system of public debt management in the region. Finance, 9, 21–28.
Megasari, D., Siregar, H., & Syarifuddin, F. (2019). Asymmetric volatility and macroeconomic factors on Indonesian government bond returns. Jurnal Keuangan dan Perbankan, 23(3), 430–442.
Mikhailov, A. Yu. (2012). Evaluation of the effectiveness of the functioning of investment funds. Economy and entrepreneurship, 4, 43–53.
Mikhailov, A. Yu. (2016). The relationship between macroeconomic parameters and the yield of Russian government bonds. Finance and credit, 22(48), 18–27. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vzaimosvyaz-makroekonomicheskih-parametrov-i-dohodnosti-rossiyskih-gosudarstvennyh-obligatsiy
Nikonorov, A. E. (2014). Efficiency of using the MICEX and RTS index in correlation analysis with foreign indices using the Pearson method. Finance and credit, 37, 60–65. https://www.fin-izdat.com/journal/fc/detail.php?ID=63520
Pryanishnikova, M. V. (2016). The main directions of development of world trade in securities on organized stock markets. Finance, 2, 56–61.
Stolyarov, A. I., & Transition, S. A. (2019). The potential of debt financing of public investment spending and Russia's economic growth. Finance, 3, 31–36.
Tiunova, M. G. (2019). Influence of monetary policy on the dynamics of the Russian financial market. Finance and credit, 25(3), 618–635.
Ushanov, A. E. (2016). Short-term banking liquidity: new requirements and management tools. Finance and credit, 22(34), 2–14. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/kratkosrochnaya-bankovskaya-likvidnost-novye-trebovaniya-i-instrumenty-upravleniya
Vlasenko, R. D., & Simanova, I. A. (2016). Analysis of the dynamics of stock indices in Russia. Young scientist, 101, 645–648. https://moluch.ru/archive/114/30247/
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 November 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-127-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
128
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-742
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Demilkhanova, B. A., & Dzobelova, V. B. (2022). Government Bond Indices And Market Rates: Evaluating Relationships. In D. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism (SCTCMG 2022), vol 128. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 177-185). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.11.25

