Abstract
At the present stage, it became necessary to develop and adopt new investment mechanisms in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises. State investment in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises is implemented within the framework of the State Program and the federal project titled “Export of agribusiness products”. Much attention is paid to the development of a logistics system for the export of agricultural products. Regional export support centers are established. Targets and measures of state support for the development of foreign trade activities at the federal and regional levels and their effectiveness are discussed. Due to imperfect investment mechanisms and insufficient volumes of state investment, the most agricultural enterprises did not use existing support measures, and a small part of enterprises benefited from the support in the field of exhibition and fair activities. Despite the government support for the development of foreign trade activities, the low efficiency of the existing investment mechanisms and the need to improve them are noted. The experience of investment policy of some countries showing a high rate of development is analyzed. New mechanisms for attracting investments, primarily from private investors, are proposed. It has also been proposed to differentiate a set of mechanisms for attracting investments in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises into groups of direct and indirect investments.
Keywords: Agribusiness, development, enterprises, foreign trade activities, investments, state support
Introduction
In recent years, the foreign policy situation around Russia has predetermined the need to develop and adopt new investment mechanisms for the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises. In his message to the Federal Assembly, the President of the Russian Federation set the task to exceed the world level of GDP growth by 2021, which implies a significant increase in investment in the creation and renewal of jobs, material and technical equipment, infrastructure, etc. Investment growth should be at least 5%, the investment share in the country's GDP should grow from 21% to 25% by 2024 (Message from the President of the Russian Federation to the Federal Assembly, 2021).
Given the insignificant growth in domestic consumption of agricultural products, it is necessary to stimulate the development of exports. Currently, the departmental project titled “Export of agribusiness products” as part of the State Program for the Development of Agriculture and Regulation of the Markets of Agricultural Products, Raw Materials and Food (hereinafter referred to as the State Program) is being implemented. The implementation of the project led to an increase in the volume of supplied products. The agricultural products and food were supplied abroad for almost 26 billion US dollars in 2018, which was almost 20% higher than that in 2017 (Government of the Russian Federation, 2020; Shagaida & Uzun, 2020).
Problem Statement
Leading scientists of the industry have noted that despite the presence of investment in foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises at the federal and regional levels there are no significant growth in agricultural exports.
It is known that the existing structure of sources of investment in the development of agricultural exports is subdivided into: i) main investment objectives: direct portfolio, real and non-financial investments; ii) form of ownership of investment resources (state, private, foreign, and mixed ones). The existing mechanisms for investing in foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises have not lead to a significant increase in the volume of agricultural exports.
Research Questions
State investment in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises is implemented, allocations in the amount of more than 746 million roubles are envisaged. However, the share of food products and agricultural raw materials in the commodity structure of Russian exports amounted to only 5.8% (Certificate). The analysis of the reasons for the imperfection of the existing mechanism of the investment in foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises is very relevant.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the study is to analyze the factors hindering the development of export activities of agricultural enterprises and the elaboration of new investment mechanisms in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises. To do this, the materials of the State Program and the priority project titled “Export of agribusiness products”, statistical information, data from the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Agriculture of Russia have been investigated.
Research Methods
In the course of the research, the methods of comprehensive and structural-dynamic analysis, mathematical modeling, expert assessments, extrapolation and others methods were used.
Findings
State investment in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises is implemented within the framework of the State Program and the federal project titled “Export of agribusiness products”, which provides for measures of non-financial investment support in three areas: formation of a system for promoting the export of Russian agricultural products in foreign markets; assistance to the activities of the Federal Service for Veterinary and Phytosanitary Supervision to expand access to foreign markets for products of the Russian agribusiness; creation of a center for analysis of exports of agricultural products and study of potential foreign sales markets (Stepanova, 2020). In order to implement these measures, allocations in the amount of more than 746 million rubles are envisaged. The planned volume of food exports should amount to USD 45.0 billion by 2024, which is 2.5 times more than that in 2016. Use of state support for 2020 ensured to increase the export of poultry meat by 42%, that of pork by 44.7%, that of frozen fish by 9.4 %, that of wheat by 30.4%, that of barley 1.6 times, etc., as compared with 2019. However, the share of food products and agricultural raw materials in the commodity structure of Russian exports amounted to only 5.8% (Certificate).
Much attention is paid to the development of a logistics system for the export of agricultural products through the implementation of 12 concepts for the promotion of products from the key agribusiness sectors (fat and oil, dairy, confectionery, meat and industries, etc.) to promising markets, as well as through the creation of 220 export guides for information support based on a practice-oriented approach (including a country description, a detailed analysis of market conditions and recommendations for doing business and a list of potential partners) of manufacturers and holding 77 events: workshops and trainings, business missions, exhibitions, forums and gastronomic festivals. Sevostyanov (2021) identified in his work the following main areas of an integrated sectoral system for promoting agricultural products to foreign markets (Table 01).
At the regional level, the investment of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises repeats the federal one taking into account the specifics of agricultural production in the regions. The production of competitive crop and livestock products is invested in almost all the regions. Investment (subsidizing) of interest rates on loans and lease payments for crop insurance is performed (Olgarenko et al., 2020; Shabanov et al., 2021). Many regions of the Russian Federation where investments from regional budgets are used have established export support centers, which provide information, analytical, consulting and organizational support for export activities to agricultural enterprises and assist in the organization of joint ventures with foreign partners in the Russian Federation and abroad (Gusakova et al., 2021; Maslova et al., 2019).
At the same time, leading scientists of the industry have noted that despite the presence of investment in foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises at the federal and regional levels there are no significant growth in agricultural exports, which indicates the low efficiency of investment mechanisms and the need to improve them. Due to imperfect investment mechanisms and insufficient volumes of state investment, 74% of agricultural enterprises did not use existing support measures, and only 7.5% of enterprises benefited from the support in the field of exhibition and fair activities. The imperfection of the existing investment mechanism for the foreign trade activity of agricultural enterprises is due to the fact that domestic scientists are actively studying the possibilities, patterns and practice of public investment and public-private partnerships, while losing sight of the practice of attracting private investment and creating mechanisms for attracting them. It should be noted that there are only 1.7% of private investors (of the population) in Russia, i.e. about 2.5 million people. For comparison, this figure is 11% of private investors in China and on average 39% in Japan, and there are more than 52% in the USA of private investors of the total population.
According to some estimates, the potential for private investment in Russia is comparable to that of China (i.e. about 10% to 12% of Russia's population can invest directly or indirectly through funds or stock exchanges in the development of the agribusiness). The main reason for the low potential of private investment is the high likelihood of a private investor losing his resources, while there is no guarantee of receiving passive investment income. This is due to the fact that currently the investment institution cannot guarantee high investment returns and quick investment returns, which, in conditions of high political and economic uncertainty, should be considered as a limitation and a direct threat to the well-being of a private investor.
In China, where the state policy of guaranteeing investments is still in force, the following basic strategies are used to ensure the diversified development of exporting enterprises and to increase their innovative activity:
- A special refinancing rate for the development of exports and special guarantees for commercial banks (including those of foreign origin) investing or attracting investments in foreign trade activities,
- Permission for state insurance companies and state off-budget funds (for example, pension and social insurance funds) to invest directly in the development of foreign trade activities,
- Stimulation of small forms of public-private partnerships to enhance the activities of private investors and small investment funds,
- Encouraging the intensification of cooperation between small and large businesses (including private investors and corporations) on projects related to the development of foreign trade (Antonova & Bardal, 2020; Orden et al., 2007).
The experience of India is important in this regard, which has shown that the development of the investment sector and the admission of a wide range of private, corporate or institutional investors to it contribute to the activation of the investment process of the development of foreign trade activities of enterprises, including the agricultural industry, and the implementation of corporate development projects in this area of activity (Orden et al., 2007). Obviously, in the context of the export-oriented development of the agricultural sector, exporting enterprises need to use new mechanisms for attracting investments (primarily from private investors: individuals and individual entrepreneurs) in for the development of foreign trade activities (Voytyuk et al., 2021). To do this, it is necessary to strengthen the investment activity of private investors based on ensuring legal certainty and the subjective usefulness of investments for private investors. In addition, the protection of investors’ interests in the medium and long term is guaranteed (Voityuk & Marinchenko, 2021).
Considering the above, it is advisable to differentiate the set of investment mechanisms for attracting investments in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises into two basic groups: direct and indirect ones (or direct and spin-off models), which are based on the principles of investment transparency and investment responsibility of economic entities (Fig. 01).
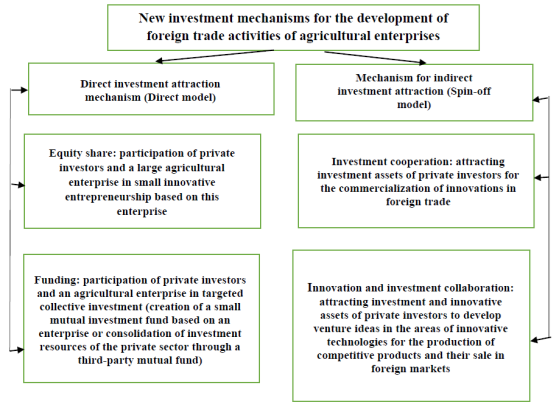
The group of mechanisms for direct attraction of investments from the private sector should include capital participation and funding. Capital participation is expected through the creation of exporting enterprises based on large agricultural enterprises (cluster-network associations), the capital of which will be formed through direct deposits of individuals and deposits passing through targeted development funds (including venture capital and mutual investment funds) using the direct model, which involves the participation of individuals (as investors, managers, performers) in specific development programs initiated by agricultural enterprises to implement their chosen strategy for the development of foreign trade activities.
The investment profitability of private investors is determined by the effectiveness of the implementation of development programs. In the case of participation of private investors in the capital of an enterprise, the investment yield is formed based on the results of the completion of the development program (start-up). In this case, the private investor receives additional guarantees, including investment risk insurance.
The mechanism for attracting investments from private investors in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises of the second group using the spin-off involves the indirect participation of individuals in the innovative development of this area of activity of agricultural enterprises. As part of the innovation and investment collaboration, innovative technologies for the production of competitive agricultural products are accumulated, commercialized and promoted to foreign markets to generate income. The income received and distributed between agricultural enterprises and a private investor forms an investment return for the latter, while the investment return is formed only at the end of the commercialization and sale of export products in the foreign market. The risks of private investors in the spin-off mechanism are always higher than the risks of agricultural enterprises; therefore, it is necessary to form additional preferences (organizational and / or economic) for private investors. However, it should be emphasized that the sum of the results obtained in direct and spin-off models is a special form of development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises, the result of which can be a form of income through start-up projects and franchising projects for their subsequent sale in the respective markets.
Conclusion
To achieve the goals set to increase the level of GDP growth, it is necessary to significantly increase investments by 5% or more; at the same time, the agribusiness faces the task of increasing exports to USD 45.0 billion by 2024, which leads to the need to develop and adopt new mechanisms investing in the development of foreign trade activities of agribusiness enterprises. Since the existing measures of state support for the development of foreign trade activities do not provide the required level, it is necessary to analyze the reasons for the imperfection of the existing mechanism.
At the same time, the potential for private investment in Russia is assessed as high. From 10% to 12% of the Russian population can invest in the agribusiness development. The main reasons for the low level of private investment are the risk of a private investor losing their resources and the lack of guarantees of receiving passive investment income.
New mechanisms for attracting investments, primarily from private investors, have been proposed. A classification of mechanisms for attracting investments in the development of foreign trade activities of agricultural enterprises has been developed according to the characteristics of direct and indirect investments. It should be borne in mind that they include direct and indirect (derivatives or spin-off) mechanisms. The summation of the results obtained under these mechanisms will provide agricultural enterprises with additional income by converting the results obtained into start-up and franchising projects intended for sale.
References
Antonova, N. E., & Bardal, A. B. (2020). Institutional and transport conditions for the development of agricultural exports from the Far East region. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 547, 012001.
Certificate of the Export of Agricultural Products federal project. Retrieved from http://mcx.ru/upload/iblock/013/013f266cee8d39bce5ca867381ff0da1.pdf
Government of the Russian Federation (2020). On the Progress And Results of the Implementation in 2019 of the State Program for the Development of Agriculture and Regulation of Markets for Agricultural Products, Raw Materials and Food. National report.
Gusakova, E. P., Tsirulev, D. E., & Prokopenko, I. S. (2021). From import substitution to export orientation in the regional agribusiness, Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 160, 76-83.
Message from the President of the Russian Federation to the Federal Assembly (2021). Retrieved from http://kremlin.ru/events/president/news/65418
Maslova, V. V., Chekalin, V. S., & Avdeev, M. V. (2019). Agricultural development in Russia in conditions of import substitution. Herald of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 89(5), 478-485.
Olgarenko, G. V., Ugryumova, A. A., & Pautova, L. E. (2020). The export potential of the agricultural sector is ensuring the food security of Russia. 20th Int. Multidisciplinary Scientific Geo Conference Ecology, Economics, Education and Legislation: issue 5.2 (pp. 563-570). SGEM.
Orden, D., Cheng, F., Nguyen, H., Grote, U., Thomas, M., Mullen, K., & Sun, D. (2007). Agricultural producer support estimates for developing countries: measurement issues and evidence from India, Indonesia, China, and Vietnam. Research Report of the International Food Policy Research Institute, 152, 1-140.
Sevostyanov, A. L. (2021). Logistics concept of export and international trade of agricultural products, Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2(89), 160-166.
Shabanov, V. L., Vasilchenko, M. Ya., Derunova, E. A., & Potapov, A. P. (2021). Formation of an Export-Oriented Agricultural Economy and Regional Open Innovations. Journal of Open Innovation Technology Market and Complexity, 7, 32.
Shagaida, N. I., & Uzun, V. Ya. (2020). Development Trends and Main Challenges of the Agrarian Sector of Russia. Analytical Report.
Stepanova, E. (2020). Innovative development of the export oriented regional agro-industrial cluster. In 2nd Int. Scientific Conference on Innovations in Digital Economy (pp. 563-570). ACM DL.
Voityuk, V. A., & Marinchenko, T. E. (2021). Modeling of export development of agricultural enterprises of the Kaluga region. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 659(1), 012126.
Voytyuk, M., Voytyuk, V., & Marinchenko T. (2021). Increasing the competitiveness of agricultural enterprises based on a cluster strategy. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 677(2), 022083.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 February 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-123-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
124
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-886
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Voytyuk, V., Voytyuk, M., & Marinchenko, T. (2022). New Mechanisms For Investing In The Agricultural Enterprise Foreign Trade Activity Development. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & E. V. Demchuk (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 124. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 862-869). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.02.107

