Abstract
As contemporary business is experiencing digital transformation, the role of a viable strategy is becoming crucial for any company. There are different essential aspects to be focused on when developing a digital business strategy: primarily, enhanced scope of business operations as well as application of latest IT solutions to make this strategy a “scaling-up” long-term plan intended for sustaining the company’s performance and contributing to the accomplishment of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Creating and implementing a digital business strategy that is based on the company’s specific objectives involves utilizing new approaches and designing novel business models based on the application of up-to-date IT solutions (i.e. increasing business digital capability). An efficient business strategy developed in the era of digital transformation is aimed at building a competitive advantage in the international market of products and services in the global agenda of achieving Sustainable Development Goals, the SDGs facilitating the alignment of the strategy with the needs of modern society. The purpose of the paper is to examine some original strategic initiatives defined and prioritized in the digital business strategy of a successful company. In the paper, the use of innovative (sustainability-related) strategic initiatives is demonstrated with a real-life example – Amazon’s business strategy. The research conducted in the paper is supposed to provide some insights on the development of an efficient business strategy of a multi-business company in the age of digital transformation.
Keywords: Digital capability, strategic priority, strategic initiative
Introduction
Modern global economy is under significant impact of digital technologies that are quickly transforming business practices, increasing companies’ performance and encouraging innovation in all business areas (OECD, 2019; OECD, 2021). In the manufacturing area, digital transformation is associated with the “Industry 4.0 concept”, which comprises such technological innovations as automation, the Internet of Things, Big Data, Cyber-Physical Systems, Cloud technology and Smart Factory technologies to be applied in manufacturing processes (Gilchrist, 2016; Khan, 2021; Machado & Davim, 2020). Following the fast development of highly sophisticated technologies, Society 5.0 has arisen leading to a “dramatic societal shift” (Khan, 2021; Salgues, 2018). Digital transformation of business makes entrepreneurs develop and use innovative technologies and business models for gaining a competitive advantage, at the same time reviewing incurred costs, associated benefits and threats (Chaffey, 2011; Chaffey et al., 2019). By digitalizing business processes in the online environment modern companies seek to boost value offered to customers in the context of increasing demand for improved products and services and internationalization of markets (Aagaard, 2018; Morabito, 2016; Presser et al., 2018).
Digital transformation can be defined as the use of digital technology in various aspects of modern society that goes far beyond digital literacy and competence (Baker, 2015); it is associated with the company’s ability to successfully apply new technologies and procedures for enhancing their business operations (Herbert, 2017). As companies are now going through digital transformation for achieving sustainability of their business operations, the role of an efficient strategy aligned with the needs of contemporary society – in the global agenda of achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as part of competitive advantage – is growing. Strategy is vital for any business; it represents a long-term plan integrating an enterprise’s major goals (related objectives) and a set of actions that support these goals into a “cohesive whole” (Lynch, 2018). The multifarious “pattern” of many contributing impacts governs the decisions modern managers take in terms of developing a variety of supporting strategic initiatives (Stukalina, 2013). A digital business strategy must be well-defined based on the company’s specific objectives; it should be aimed at avoiding the following risks: poor assessment of business prospects or inadequate resources allocation for different digital business initiatives; unsuitable digital business strategy direction owing to poorly formulated business objectives; inadequate technical support; waste of resources, etc. (Chaffey et al., 2019). Digital business strategies, as long-term development plans, are based on the company’s current performance in the market, outline the way the company will allocate resources necessary for meeting strategic goals and objectives and identify competitive advantage in the global business market (Chaffey, 2011). Developing a digital business strategy involves using new approaches and creating novel business models in terms of a marketing strategy, HR strategy, supply chain management strategy, IT strategy, etc. (Chaffey, 2011). The paper discusses some innovative (sustainability-related) strategic initiatives that are defined and prioritized in the digital business strategy of a prosperous multi-business enterprise based on the Amazon.com case study.
Literature Review: Business Digital Transformation
The rules that governed business in the “pre-digital era” have changed significantly; transforming for the new “digital era” makes businessmen to update their “strategic mind-set” and re-examine strategic planning principles, as the impact of digital transformation can be traced in every of the five domains of business strategy – customers, competition, data, innovation, value (Rogers, 2016). Staying competitive in the modern turbulent environment demands a wide-ranging digital transformation for boosting growth and innovation (Sacolick, 2017). This is especially important in the period of transition to greener and more inclusive economies in pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals – SDGs (The Sustainable Development Goals Report, 2021), which calls for a fundamental “change of mind” from businesses worldwide (Walker et al., 2019).
Business digital transformation: in search of innovative and sustainable solutions
Digital transformation – as transformation of business relationships and interactions between organizations, consumers, suppliers and employees – is supposed to avoid the gap between customers’ expectations and what traditional business models can offer; it is also associated with customer behaviours, technological and societal change (Vaz, 2021). Digitalization of business is understood as the use of “digital opportunities” through combining various Internet-based technologies – as drivers of business digital transformation (Jabłoński & Jabłoński, 2020; Maheshwari, 2019; Strømmen-Bakhtiar, 2020):
- Internet of Things/IoT (linking a set of devices into a complex system).
- Artificial Intelligence (using systems that imitate human intelligence) and Cognitive computing (a combination of Artificial Intelligence and signal processing).
- Advanced robotics (using semi-autonomous robots).
- Cloud technology (renovating applications and platforms as a service).
- Blockchain (transforming data sharing among users).
- Big Data (transforming decision-making information).
However, digital transformation is a process that goes beyond technology; it is more associated with reacting in a timely manner to current challenges, building a competitive digital capability and adopting processes that will enable the company’s leadership in the industry (Herbert, 2017; Vaz, 2021). Digital transformation has a strong economic impact (OECD, 2019), initiating new paradigms and approaches to economic development. At the heart of the “new digital economy” is knowledge and knowledge-based solutions (Strømmen-Bakhtiar, 2020). Some popular approaches to the “new economy” (both greener and more inclusive) in the digital era are listed below (Jabłoński & Jabłoński, 2020):
- Creative economy (development of creative industries).
- Network economy (transforming seller-buyer into supplier-user relationships using networks).
- Social economy (based on the social business model).
- Platform economy (utilizing online platforms for providing cooperation of businesses).
- Reputational (trust) economy (building trust capital in the network).
- Sharing (access) economy (using collaboration platforms to create a publicly available market).
- Experience economy (based on building a positive customer experience).
The support of the above approaches in the frame of digital transformation of business, involves the following (Herbert, 2017): a) applying more cost-effective business models; b) developing more effective operating practices; c) getting better access to markets; d) enriching the choice of offerings to consumers. Today, there is an increasing demand for innovative and sustainable solutions, which can result in further development of business processes in terms of sustainability in the agenda of achieving SDGs (as drivers for investors and consumers) and improving the company’s reputation, so investing in science and technology, data and information infrastructure is crucial (The Sustainable Development Goals Report, 2021). New technologies should be used “strategically” on a continuing basis, the anticipated results being 1) boosted revenue; 2) enhanced competitive advantage; 3) increased efficiency and coordination of operations (Herbert, 2017). The above demands developing an appropriate digital business strategy aimed at gaining a competitive advantage in an uncertain international environment, which is aligned the SDGs. Below, a few essential issues related to the development of a digital business strategy are discussed.
Digital business strategy: Building a competitive digital capability
Strategy development is viewed as key issue in the context of achieving a competitive advantage (Koontz & Weihrich, 2010; Thompson & Strickland, 2010). There exist several approaches to designing a strategy, and not a standard paradigm is established; this is determined by the diversity of functional business sectors (Jeffs, 2008; Harrison & St. John, 2014). Digital business strategies are similar to corporate, business and marketing strategies; they include the following aspects Chaffey, 2011; Chaffey et al., 2019): 1) mobile commerce strategy; 2) customer relationship management (CRM) strategy; 3) E‑procurement strategy; 4) Supply chain strategy; 5) Social media strategy; 6) Multichannel strategy, etc.
Digital channel strategies are associated with different digital business strategy process models applied. These models are likely characterized by the following features (Chaffey, 2011):
- Performing regular external and internal environment scanning (analysis of external and internal factors influencing a particular business).
- Stating the company’s vision and its objectives (related to the company’s values) clearly.
- Putting emphasis on evaluating the “differential benefits” contributed by e-channels.
- Selecting most suitable channels for various business activities and business partners (“right-channelling”).
- Performing regular control for identifying problems and adapting the digital strategy to the changes in the market.
A digital business strategy contains a few basic components (Chaffey et al., 2019): 1) digital business priorities relevant to the current context; 2) business and revenue models used in the organization; 3) type of restructuring needed; sub-strategies utilized for market and product development and marketplace reorganization; 4) differentiation and positioning strategies applied in the company.
In view of the above, it can be concluded that a digital strategy of a multi-business company can be discussed from different perspectives using a holistic approach. Section 4 provides an overview of Amazon’s digital business priorities relevant to the current industry context formulated with consideration to advanced digital technologies and platforms that may support sustainability-related strategic initiatives in the agenda of achieving SDGs.
Research Method
The aim of the paper is to explore some original (sustainability-related) strategic initiatives defined and prioritized in the digital business strategy of a successful multi-business company, which focus on accomplishing specific strategic objectives in the context of business digital transformation.
The goal of the literature review provided in the paper (relevant theoretical sources on digital business and strategic management, as well as previous studies on the research topic) is to introduce and describe the research problem and the rationale for investigating the issue. In the paper, various interrelated aspects of the observed phenomenon are investigated and highlighted.
Amazon.com – a multi-business company and acknowledged innovator – was chosen for analysis as one of the best digital transformation examples. The case study embraces the context, in which the company’s digital business strategy is designed and implemented, as well as different factors that contribute to achieving a competitive advantage in the international market of products and services. For this purpose, in order to support the author’s opinion with evidence, publicly available information from the company’s website was used and critically analysed.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 1 (Introduction) presents the research actuality and the purpose of the study. In Section 2 (Literature Review), the author discusses the main issues associated with business digital transformation and describes different approaches to designing a successful digital business strategy aimed at reaching a competitive advantage. In Section 3, the author describes the methodology of the study. In Section 4, the author examines main sustainability-related strategic initiatives based on the innovative IT solutions that are applied by Amazon.com in the framework of implementing their digital business strategy. In Section 5, the main finding and conclusions are presented.
Amazon’s Business Strategy in the Era of Digital Transformation: Shaping a More Sustainable World
Amazon.com: moving towards success
Amazon (Amazon.com) – a multinational technology company – is the world’s leading online retailing enterprise located in the U.S. It was founded in 1994. It belongs to the whole cluster of successful American online companies – GAFAM – Alphabet/Google (GOOG), Amazon (AMZN), Facebook (FB), Apple (AAPL), and Microsoft (MSFT). Since 1994, the company has experienced an extraordinary evolution. In 2020, the company demonstrated unprecedented growth in net revenues in different global markets – its net income almost doubled in that year (Statista, 2021). In the first quarter of 2021, Amazon.com witnessed a growth in global net revenue in all segments, the leading category being online stores with net revenue of approximately $52.9 billion, which marks a surge of about $15 billion compared to the same quarter of 2020; the online stores segment was followed by retail third-party seller services, with net revenues of $23.8 billion (Statista, 2021). In Figure 1, the annual net revenue of Amazon from 2004 to 2020 is shown.
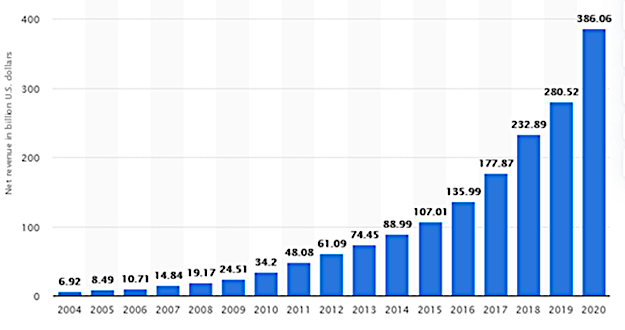
In Figure 2, the e-commerce net sales of Amazon from 2014 to 2021 are shown.
![E-Commerce net sales of amazon.com from 2014 to 2021 (in million $) (Statista: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1218313/amazon-revenue-development-ecommercedb)]](https://www.europeanproceedings.com/files/data/article/10092/15877/ISMC2021F07.fig.002.jpg)
As seen from the figures above, Amazon has been successful over the long-term. The following question arises: What makes Amazon’s business strategy succeed in the era of digital transformation? Below, the scope of Amazon’s digital strategy, its main strategic priorities, objectives and supporting strategic initiatives are discussed in detail.
Amazon’s digital business strategy: scope and priorities
In the context of digital transformation, a digital business strategy can be viewed as the “fusion” between IT s functional-level strategy and business strategy (Bharadwaj et al., 2013). The scope of the digital business strategy of a company embraces a range of its products and (or services). Knowing the scope of such kind of strategy enables better understanding of the relationships between a particular enterprise and its external environment, including IT infrastructures and, consequently, how the designed digital business strategy could be effective in various settings and situations (Bharadwaj et al., 2013). The scope of Amazon’s digital strategy is presented in Table 1.
As seen from Table 1, the scope of Amazon’s digital strategy is broad; it is closely related with the competitive scope of the company, as their strategy includes a certain number of value chains. Thus, an overall company’s strategy involves a number of e-channel strategies – Transportation, Marketing, Supply Chain, which utilize digital channels sustained by novel digital technologies and platforms. The scale of a digital business strategy in the agenda of enhancing a company’s profitability and sustainability based on its digital infrastructure is another important aspect of this strategy (Bharadwaj et al., 2013). So, a scale-up business strategy is based on the technological innovation.
Amazon’s digital business priorities identified in the context of a scale-up business strategy are supported by various strategic initiatives, which are used as profitability and sustainability drivers (Table 2).
Findings and Conclusions
The findings revealed from the case study can be summarized as follows. Amazon.com – one of the best examples of a business model innovator – goes beyond the traditional ways of implementing a digital strategy that is aligned with clearly formulated strategic priorities and associated strategic objectives. The above strategic initiatives are all aimed at reaching a competitive advantage in the uncertain business environment, a substantial contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) being significant part of their competitive advantage. At Amazon.com, they employ an innovative approach to implementing different sustainability-related strategic initiatives in the context of digital transformation; it integrates both technology and organizational processes for creating and delivering new services to a wide range of customers (Digital transformation checklist, 2017).
In the frame of the digital business strategy aligned with SDGs, a set of innovative scaling-up IT solutions have been developed by the company: Artificial Intelligence, digital streaming, cloud computing, etc. They are widely used for supporting their own trans-functional strategic initiatives and providing cutting-edge digital services to other companies as well – for enhancing and popularizing (and commercializing) their brand. For instance, Amazon.com is a distinguished provider of cloud services. Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched in 2006 and based on cloud computing offer an easily accessible, very reliable, and low-cost infrastructure platform for businesses in 190 countries worldwide as a response to the growing demand for digital services (https://aws.amazon.com): 1) Cloud-enabled secure backup and data-protection solutions; b) E-commerce cloud computing solutions for online sales and retailing; c) Blockchain on AWS; d) Machine Learning and fully managed databases; e) Analytics on AWS, and many others. In view of this, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- In the time of “new economy” and accompanying digital transformation, an innovative digital business strategy based on sophisticated IT solutions and aligned with SDGs is a great opportunity for a company to diverge from rivals and gain a competitive advantage.
- A digital business strategy contains a set of preferred strategic priorities and defines the activities aimed at meeting strategic objectives. Strategic priorities applicable to the current industry settings are formulated with consideration to advanced digital technologies and platforms used to support appropriate sustainability-related strategic initiatives.
- There are different essential aspects to be focused on when developing an efficient digital business strategy of a multi-business company: primarily, enhanced scope of business operations, and application of latest IT solutions for making this strategy a “scaling-up” long-term plan, which is vital for providing business sustainability.
- In the frame of business diversification, various e-channel strategies can be developed, with an emphasis on using novel digital solutions for sustaining a number of strategic initiatives. This would allow evaluating the differential benefits contributed by e-channels more effectively and choosing most suitable channels for various business activities and business partners (both in the internal and external contexts).
- The Amazon’s case proves that a successful digital strategy aligned with SDGs presupposes a broad trans-functional and trans-industrial scope; an integration of traditional and to a greater extent, non-traditional approaches to strategy development and implementation, focus on scaling up – with due account for advanced IT solutions applicable in various settings.
References
Aagaard, A. (2018). The concept and frameworks of digital business models. In A. Aagaard (Ed.), Digital business models: Driving transformation and innovation (pp. 1-26). Springer, Cham. DOI:
Amazon. (n.d.). Retrieved on July 10, 2021, from https://www.aboutamazon.com/facts
Amazon. (n.d.). Retrieved on July 11, 2021, from https://aws.amazon.com
Amazon. (n.d.). Retrieved on July 15, 2021, from https://developer.amazon.com/
Amazon. (n.d.). Retrieved on July 10, 2021, from https://www.amazon.com/
Baker, M. (2015). Digital transformation (4th ed.). Buckingham Business Monographs.
Bharadwaj, A., Sawy, O., Pavlou, P., & Venkatraman, N. (2013). Digital business strategy: Toward a next generation of insights. MIS Quarterly: Management Information Systems, 37(2), 471-482. https://
Chaffey, D. (2011). Digital business and e-commerce management. Strategy, implementation and practice (6th ed.). Pearson.
Chaffey, D., Hemphill, T., & Edmundson-Bird, D. (2019). Digital business and e-commerce management (7th ed.). Pearson.
Digital transformation checklist. (2017). Using technology to break down innovation barriers in government. Amazon Web Services, Inc. Retrieved on July 22, 2021, from https://d1.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/digital-transformation-checklist.pdf
Gilchrist, A. (2016). Industry 4.0: The Industrial Internet of Things. Apress. DOI:
Harrison, J. S., & St. John, C. H. (2014). Foundations in strategic management (4th ed.). South-Western/Cengage Learning.
Herbert, L. (2017). Digital transformation: Build your organization’s future for the innovation age. Bloomsbury Publishing.
Jabłoński, A., & Jabłoński, M. (2020). Digital business models: Perspectives on monetisation. Routledge. DOI:
Jeffs, C. (2008). Strategic management. SAGE Publications.
Khan, S. (Ed.). (2021). A Step towards Society 5.0: Research, innovations, and developments in Cloud-based computing technologies. CRC Press. DOI:
Koontz, H., & Weihrich, H. (2010). Essentials of management: An international perspective (8th ed.). Tata McGraw Hill.
Lynch, R. (2018). Strategic management (8th ed.). Pearson.
Machado, C., & Davim, J. P. (Eds.). (2020). Industry 4.0: Challenges, trends, and solutions in management and engineering manufacturing design and technology series. CRC Press. DOI:
Maheshwari, A. (2019). Digital transformation: Building intelligent enterprises. John Wiley & Sons.
Morabito, V. (2016). The future of digital business innovation. Trends and practices. Springer. DOI:
OECD. (2019). Measuring the digital transformation: A Roadmap for the future. OECD Publishing. Retrieved August 10, 2021, from DOI:
OECD. (2021). Going digital in Latvia, OECD Reviews of digital transformation. OECD Publishing. Retrieved on August 10, 2021, from DOI:
Presser, M., Zhang, Q., Bechmann, A., & Belliatis, M. J. (2018). The Internet of Things as driver for digital business model innovation. In A. Aagaard (Ed.), Digital business models: Driving transformation and innovation (pp. 27-56). Springer, Cham. DOI:
Rogers, D. (2016). The Digital transformation playbook: Rethink your business for the digital age. Columbia University Press. DOI:
Sacolick, I. (2017). Driving digital: The leader’s guide to business transformation through technology. American management Association.
Salgues, B. (2018). Society 5.0: Industry of the future, technologies, methods and tools. USA: John Wiley & Sons. DOI:
Statista 2021. (n.d.). Retrieved on 30 June, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/999686/ amazons-net-revenue-by-product-group-quarter/
Strømmen-Bakhtiar, A. (2020). Introduction to digital transformation and its impact on society. Informing Science.
Stukalina, Y. (2013). Management of the educational environment: the context in which strategic decisions are made. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 99, 1054-1062, https://
The Sustainable Development Goals Report. (2021). United Nations. Retrieved on 17 September, 2021, fromhttps://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2021/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2021.pdf
Thompson, A. A., & Strickland, A. J. (2010). Crafting and executing strategy: The quest for competitive advantage. Concepts and cases. McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Vaz, N. (2021). Digital business transformation: How established companies sustain competitive advantage from now to next. John Wiley & Sons.
Walker, J., Pekmezovic, A., & Walker, G. (2019). Sustainable Development Goals: Harnessing business to achieve the SDGs through finance, technology and law reform. John Wiley & Sons. DOI: 10.1002/9781119541851
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 December 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-120-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
121
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Ed.
Pages
1-286
Subjects
Strategic management, Leadership, Technology, Sustainability, Society 5.0, New strategic challenges
Cite this article as:
Stukalina, Y. (2021). Developing An Efficient Business Strategy In The Era Of Digital Transformation. In M. Ozsahin (Ed.), New Strategic, Social and Economic Challenges in the Age of Society 5.0 Implications for Sustainability, vol 121. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 54-63). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.12.04.7

