Abstract
The paper outlines the role of the culture of leisure of the rural population in increasing the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex. The purpose of the study was to monitor the cultural and leisure activities of Russian youth in the countryside and to assess the effectiveness of cultural and leisure services provided in rural areas. The methodological basis of the study included the processing of statistical books, sociocultural design, analysis and synthesis, questionnaire. It is determined that the leisure culture of rural youth varies in nature and content. It was revealed that the greatest preference was given to the passive-consumer character and the entertaining content of cultural and leisure activities. There is a discrepancy between the demand of rural youth for leisure services and the real opportunities provided by rural cultural institutions. The results of the sociological survey made it possible to identify a number of conditions and factors that allow young people making cultural choices, which will contribute to increasing the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex. The development of the culture of leisure for rural youth is possible through the implementation of cultural and leisure activities that could relate, firstly, to the socio-cultural needs of rural youth, secondly, to the real capabilities of cultural institutions, thirdly, to the quality of services provided and the degree of their satisfaction by young people.
Keywords: Cultural and leisure activities, rural areas
Introduction
The culture of leisure of the rural population is one of the urgent strategic tasks to achieve and constantly improve the quality of the human life environment on the basis of innovative economic and social policies of the state. In turn, this leads to an intensification of the human factor, an increase in the productive potential in rural areas, an increase in economic and social efficiency, which is an integral part of the agrarian policy, the tasks of which are reflected in the Federal Law “On the development of agriculture” (Federal Law, 2006) and are presented in Figure 01.
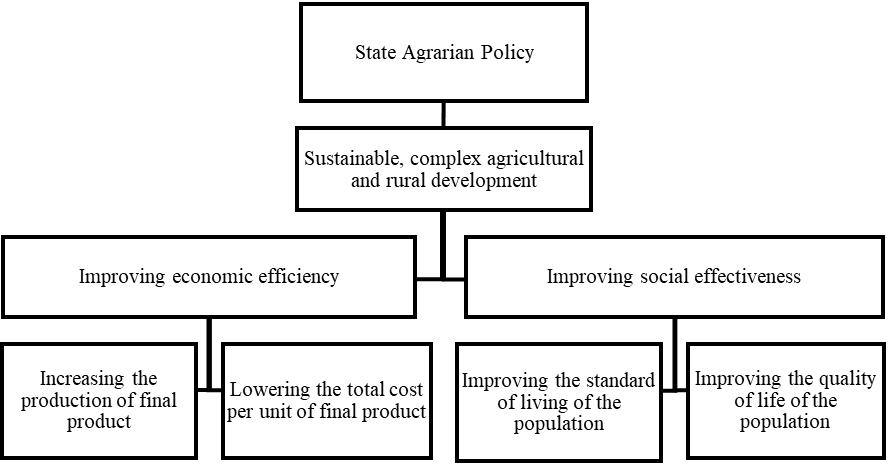
Many scientific works are devoted to the problems of cultural and leisure organization in the regions of Russia. The works of Astafieva, Lukova present the strategy for the sustainable development of Russian regions in relation to cultural policy, indicating the need to shift guidelines towards improving the quality of life, a strategy worthy of a modern person and strengthening cultural diversity (Astafieva, 2019); the concept of youth is put forward on the basis of the interpretation of orientation complexes (thesauruses) (Lukov, 2012).
The works of Gorushkina, Kokorina, Murzina, Surtaev are devoted to socio-cultural processes taking place among the youth subculture. Based on the material provided by the Center for Sociological Research of the Russian Presidential Academy of Public Administration, the authors analyze the trends in the formation of sociocultural preferences of the Russian population (Gorushkina, 2012); reveal the peculiarities of organizing leisure activities for young people taking into account their modern needs (Kokorina & Murzina, 2016); describe the socio-cultural space of modern youth, explore the features of the phased formation of the youth leisure culture (Surtaev, 2006).
The All-Russian informational works consider the formation of leisure culture of modern Russian society in general, Russian youth in particular; its socio-cultural needs and preferences are being taken into account (Culture of Russia, 2012; Study of the Russian ticket market, 2018).
As part of the implementation of the decree of the President of the Russian Federation since 2013, the Belgorod Region repeatedly undergoes the independent assessment of the effectiveness of cultural services provided to the population of the region in order to protect the interests, rights and freedoms of citizens. The specialists evaluated the official websites of organizations, the quality of conditions for the provision of services, conducted a survey of recipients of services and developed action plans to eliminate disadvantages in institutions and organizations (People’s expertise, 2019).
A number of sociological surveys of rural youth on the attitudes to traditional values that contribute to the formation of the leisure culture in the countryside were conducted by (Belozerova, 2014; Belozerova & Krikun, 2020; Krikun, 2017; Krikun, 2019). A number of researchers analyse the worldview problems of modern youth, value preferences of students, The role of Orthodoxy in the spiritual life of Russia (Chernova & Davityan, 2020; Davityan, 2012; Elnikova, 2020; Korosteleva & Davityan, 2018; Maryenkova & Krikun, 2017; Pakhomova & Krikun, 2016; Prokopenko & Belozerova, 2018). Nikulina and Gordienko (2019) analyze the adaptation in the pedagogical practice of higher school in comparison with cultural values and landmarks (Nikulina, 2016).
These works analyze the interesting aspects of cultural and leisure activities of the Russian society, but little attention is paid to the process of creating a culture of leisure for the rural population as a factor that improves the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex.
Problem Statement
Within the framework of the programs for sustainable and complex rural development, the introduction of cultural institutions and the population growth provided by these institutions are among the key target indicators of modern transformations in the countryside, which contribute to a further increase in not only the quality of life of the rural population, but also the competitiveness of the domestic agro-industrial complex (Federal Target Program, 2013).
In modern conditions, the culture of leisure of the rural Russian population is complicated by a number of objective political, economic, social, and spiritual factors. This circumstance is associated with the instability of the development of these spheres of life of the Russian society, the conservatism of the authorities regarding innovative solutions, and the instability of the state’s price policy.
The problem field around this topic is formed due to the low activity and inclusion of the Russian youth in the cultural life of a village, which leads to an increase in the migration sentiment of rural youth towards the urban environment, and, as a result, to a decrease in the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex.
Research Questions
The object of the study is the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex, one of which target indicators is the sustainable social development of a village associated with improving the quality of cultural and leisure services to the rural population.
The subject of the study is the organization of cultural and leisure activities of the Russian youth in the countryside, which involves events held in their free time in order to realize their leisure needs and introduce them to diverse cultural values. The main types of leisure culture include recreation (restoration), rest, relaxation, holidays, entertainment, creativity, self-education. These activities have quantitative and qualitative characteristics of free time. Quantitative indicators are determined by objective socio-economic factors – sphere and level of human employment. Qualitative characteristics are caused by subjective factors – material security, individual choice, social status, physical condition.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to monitor the cultural and leisure activities of the Russian youth in the countryside and to assess the efficiency of cultural and leisure services provided in rural areas. The results of an empirical study make it possible to determine ways to optimize organizational measures in the field of leisure culture from the point of view of involving the Russian youth in the cultural and leisure life of a village.
Research Methods
The following were used as the methodological basis of the study: questionnaire, processing of statistical books, analysis and synthesis, socio-cultural design, methods of mathematical statistics. The study was conducted from two perspectives: cultural and leisure activities of cultural institutions, which were determined by agents, services and results of cultural institutions of the Belgorod Region of the country, and cultural and leisure practices of rural youth, which were determined by the results of a sociological survey of rural youth. The respondents were full-time and extramural students of Belgorod State Agricultural University named after Gorin, a significant part of which live in rural areas.
Findings
The development and optimization of the leisure culture of rural youth contributes to the activation of the human factor, the increase of labor potential in rural areas and, as a result, the improvement of the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex. Figure 2 presents this process.
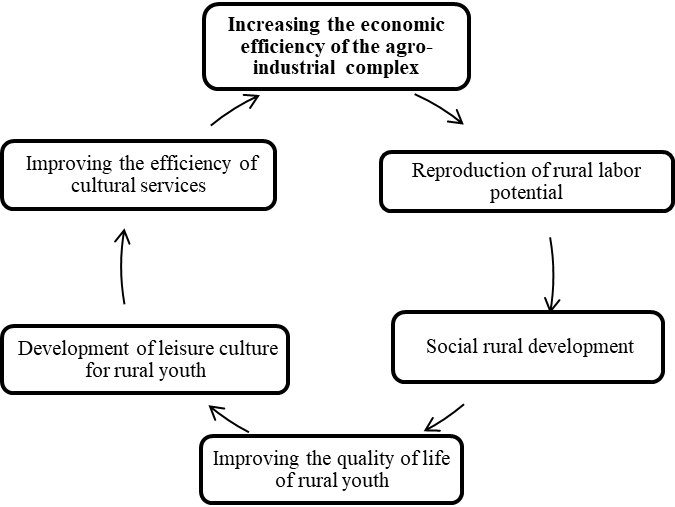
Let us consider this relationship in more detail. The improvement of the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex is determined by two groups of factors – external and internal. External factors include pricing, taxation, investments, subsidies, inflation processes, etc. Internal factors depend on the economic activity of an enterprise, material and natural resources, rural labor potential, the reproduction of which ensures a sustainable and long-term increase in the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex.
The reproduction of rural labor potential is a continuous and renewable process of rural labor production. Reproduction ensures the preparation of new generations for the performance of labor functions. Effective reproduction requires the improvement of the quantitative labor-intensive potential (reduction of emigration sentiment of the rural population, especially rural youth; the influx of young professionals into the countryside, etc.) and the qualitative characteristics (health status, skill level of rural workers, etc.), which requires an increase in the level of development and arrangement of rural areas. We called this process the “social development of a village”.
The social development of the village involves a steady set of measures aimed at creating comfortable living and working conditions for the rural population commensurate with modern standards for the development of society. The most important targets of these activities include addressing the housing problem; increased level of health, education and culture. Government documents on sustainable and integrated rural development pay particular attention to improving the quality of life of young people in rural settlements (Federal Target Program, 2013).
The improvement of the quality of life of rural youth ensures a decrease in the emigration mood of rural youth and the influx of young specialists into the countryside, creating conditions for improving the demographic situation in the countryside and, as a result, achieving a combined economic effect. One of the target indicators for improving the quality of life of young people in rural areas is the introduction and development of cultural and leisure institutions, the development of the leisure culture for rural youth.
The development of the leisure culture for rural youth is possible through cultural and leisure activities that could relate, firstly, to the socio-cultural needs of rural youth, secondly, to the real capabilities of cultural institutions, thirdly, to the quality of services provided and the degree of their satisfaction by young people.
Thus, the effective organization of leisure culture for rural youth contributes to the activation of the human factor, the increase of labor potential in the countryside and, as a result, the improvement of the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex.
For rural youth, leisure is now commensurate with the overall level of satisfaction with their lives. However, the nature of the leisure culture of young people consists of different types of activity and orientation (Table 1).
The content of the leisure culture of rural youth also has several varieties (Table 2).
The sociological survey showed that the leisure choice of a young man is significantly influenced by the company of people with whom he plans to spend his free time. Young people prefer to visit cultural institutions together with friends, acquaintances (first place according to the ranking of preferences), husband/wife, boyfriend/girlfriend (second place), children (third place), about 9% of residents go alone, mainly the female half of the rural population and, mainly, to museums and gyms (Table 3). The table shows that the most popular cultural institutions are theaters and cinemas.
Referring to the indicator of “livability” of a rural settlement in economic, social and cultural terms, let us conduct a detailed analysis of the efficiency of cultural and leisure services provided in rural areas.
Characteristics of respondents: 1) gender: men – 33%; women – 67%; 2) place of residence: residents of the district center – 15.3%; residents of the area outside the district center – 85.5%; other regions – 0.8%.
The monitoring analysis was carried out according to the following indicators: 1) importance: important/not very important / absolutely unimportant; 2) satisfaction: fully satisfied / not fully satisfied / absolutely not satisfied.
According to the monitoring study, all questions are important for the respondents (86%), but the satisfaction rate with the quality of leisure services remains relatively low. At the same time, the respondents indicated poor technical equipment (35%), unsatisfactory services (34%), low openness and accessibility of information (31%). Besides, the respondents want to visit cultural institutions more often. This was indicated by 75% of respondents.
The results of the sociological survey made it possible to outline a number of conditions and factors that allow a young person making cultural choices. They include popularity, accessibility, comfort, openness, technical equipment, optimal cost, quality, safety, awareness, starting conditions, territory and premises, location, multidisciplinarity, cooperation.
Conclusion
For the effective functioning of the agro-industrial production it is necessary to provide rural areas with a sustainable set of measures aimed at creating comfortable living and working conditions for the rural population commensurate with modern standards for the development of society. One of such factors is the optimal organization of the leisure culture of the rural population, especially rural youth.
The study allows determining ways to optimize organizational measures in the field of leisure culture from the point of view of involving the Russian youth in the cultural and leisure life of a village: information, popularity, comfort, openness, technical equipment, optimal cost, quality, safety for life and health, accessibility, multidisciplinarity, cooperation. This will help to increase the economic efficiency of the agro-industrial complex.
References
Astafieva, O. N. (2019). Strategy for sustainable development of the cultural policy of the Russian regions. World of Russian-speaking countries, 1(1), 43-51.
Belozerova, I. A. (2014). Attitude of rural youth to festive and ritual folk traditions. Innovations in the agro-industrial complex: problems and prospects, 3(3), 49-54.
Belozerova, I. A., & Krikun, E. V. (2020). Monitoring of cultural and leisure activities student youth. Azimuth of Scientific Research: Pedagogy and Psychology, 9(3), 30-34.
Chernova, Yu. A., & Davityan, M. G. (2020). Measuring the cultural life of the population. Gorin readings. Innovative solutions for agribusiness. Vol. 4. Maysky village, Belgorod State Agricultural University named after V.Ya. Gorin. 331.
Culture of Russia (2012). Information and analytical collection: Topical tasks of spiritual revival of Russia. Moscow, Main Data-Computing Center of the Ministry of Culture of Russia. 283 p.
Davityan, M. G. (2012). Spiritual and moral values of the student youth of BelSAA. Bulletin of scientific works of the Belgorod State Agricultural Academy named after V.Ya. Gorin. 31. Maysky village, Belgorod State Agricultural University named after V.Ya. Gorin. 147-154.
Elnikova, G. A. (2020). Manifestation of the subjectivity of student youth in public and private life. Kazan Social and Humanitarian Bulletin, 4(45). Kazan, Russian Science.
Federal Law (2006). On the development of agriculture. Retrieved on 15 November 2020 from: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_64930/
Federal Target Program (2013). Sustainable Rural Development 2014-2017 and 2020. Retrieved from: https://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/70319016/
Gorushkina, S. N. (2012). On some aspects of the cultural needs of the Russian population. Journal of the New Economic Association, 2(14), 147-49.
Kokorina, K. A., & Murzina, E. I. (2016). Formation of youth leisure culture. World of Science, Culture, Education, 1(56), 71-73.
Korosteleva, M. V., & Davityan, M. G. (2018). Value preferences of students. Youth agrarian forum, Vol. 3. Maysky, Belgorod State Agricultural University named After V. Ya. Gorin. 217.
Krikun, E. V. (2017). Worldview problems of modern youth (on the example of Belgorod Region). Azimuth of Scientific Research: Pedagogy and Psychology, 6(4), 403-405.
Krikun, E. V. (2019). Perception of the world in Orthodoxy: traditions and modernity. Maysky village, Belgorod State Agricultural University named after V. Ya. Gorin.
Lukov, V. A. (2012). Theories of youth. Moscow, Canon.
Maryenkova, A. A., & Krikun, E. V. (2017). Attitude to freedom in the student environment. Materials of the international student scientific conference. Maysky village, Belgorod State Agricultural University named after V.Ya. Gorin. 207.
Nikulina, N. N. (2016). Spiritual and moral values of modern education. Belgorod, Constanta.
Nikulina, N. N., & Gordienko, I. V. (2019). Problems of Social Adaptation of Bachelor’s Degree Students of Pedagogical Field Under the Conditions of Study in Agrarian University. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT): vol 9, issue 2, Electronic Materials (pp 2036-2042). Retrieved from: https://www.ijeat.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v9i2/B3650129219.pdf
Pakhomova, A. S., & Krikun, E. V. (2016). The role of Orthodoxy in the spiritual life of Russia. Materials of the international student scientific conference. Maysky village, Belgorod State Agricultural University named after V.Ya. Gorin.
People’s expertise (2019). Retrieved on 17 November from https://www.bus.gov.ru/
Prokopenko, V. A., & Belozerova, I. A. (2018). Search for the meaning of life among student youth. Youth Agrarian Forum, Vol. 3. Maysky village, Belgorod State Agricultural University named after V.Ya. Gorin. 83.
State Development Program (2019). Complex Development of Rural Territories. Retrieved on 12 October, 2020, from https://base.garant.ru/72260516/
Study of the Russian ticket market (2018). Retrieved on 12 October, 2020, from https://clck.ru/RnW7o.
Surtaev, V. Ya. (2006). Sociocultural space of youth: methodology, theory, practice. St. Petersburg, St. Petersburg State University of Culture and Arts. p. 271.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 July 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-112-6
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
113
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-944
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Belozerova, I. A., Krikun, E. V., & Davityan, M. G. (2021). Leisure Culture In Rural Areas And Effıciency Of The Agro-Industrial Complex. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & V. V. Kuznetsova (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 113. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 425-432). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.07.50

