Abstract
The research is based on the idea that selective regional policy is an independent thread of regional policy of the state. One of the main features of the present stage in implementation of selective regional policy of the Russian Federation is that the objects of its selective impact are the country’s geostrategic territories. Different tools of state stimulation of regional development are used in respect to these territories. It is established that the current practice of territorial development management in the Russian Federation is ahead of the development of state regional policy theory itself. Thus, geoselective regional policy, that is a new thread of selective regional policy, has been formed. The example of regions of the Far Eastern Federal District as geostrategic territories shows the mechanism for implementing geoselective regional policy in the Russian Federation. In the framework of implementation of state regional policy in the Russian Federation, geostrategic territories are the objects of selective stimulating influence. Evaluation of the mechanism for implementation of state regional policy for the development of Far East regions as geostrategic areas of the Russian Federation showed that FEFD uses a wide range of methods and tools to stimulate regional development such as state program, creation of special legal regimes in the form of PSEDA and the Free port of Vladivostok, state funding of social infrastructure, tax incentives. This confirms the conclusion that geoselective policy, a new model of selective regional policy, is being implemented in modern Russia.
Keywords: Selective regional policy, geostrategic regions
Introduction
One of the most difficult tasks of the state regional policy of Russia in modern conditions is to ensure a balanced socio-economic development of the regions and reduce the level of inter-regional differentiation.
The choice of objects, tools and methods of implementing the state regional policy of the Russian Federation is the subject to discuss for many scientists and politicians. At the present stage, the works of many scientists (Armstrong & Taylor, 1993; Kuznetsov & Kuznetsova, 2015; Leonov, 2020; Minakir & Prokapalo, 2018) etc. are devoted to the formation of new mechanisms in the implementation of regional economic policy.
This research is aimed to define the implementation features of the modern regional policy of the Russian Federation. This research is based on the scientific idea that selective regional policy is an independent thread of state regional policy (Sidorenko & Tishutina, 2019). The choice of objects of selective region-al policy depends on the goals of regional economic policy of the state. These potential goals form two models of regional policy and, depending on the targets, might selectively impact on either problem regions ("Equality" model), or on more developed regions called "growth poles" ("Efficiency" model).
Problem Statement
One of the main features of the present stage in implementation of selective regional policy of the Russian Federation is that the objects of its selective impact are the country’s geostrategic territories. Different tools of state stimulation of regional development are used in respect to these territories. This is represented in the Spatial Development Strategy of the Russian Federation until 2025. The geostrategic territory of the Russian Federation is "a territory within the borders of one or more constituent territories of the Russian Federation that is essential for ensuring sustainable socio-economic development, territorial integrity and security of the Russian Federation, characterized by specific living conditions and economic activity". The Spatial Development Strategy of the Russian Federation identifies two types of geostrategic territories: priority and border territories (Table 01).
According to Strategy of Spatial Development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2025
In this regard, the analysis of the features of the selective regional policy for the development of geostrategic regions of Russia is an important research task (Strategy of Spatial Development…, 2020).
Research Questions
The current practice of territorial development management in the Russian Federation is ahead of the development of state regional policy theory. Thus, theoretically there are two models of regional policy: "Equality" and "Efficiency". However, since priority and border geostrategic territories are the objects of selective impact, a special model of regional policy is being implemented in the Russian Federation at the present stage. This conclusion allows us to formulate a new thread of selective regional policy - geoselective regional policy. The paper will analyse the methods and tools of the geoselective regional policy of the Russian Federation, including state programs for regional development, state investments in the construction of infrastructure facilities, the creation of priority areas of socio-economic development etc.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this article is to study the mechanism of implementation of geoselective regional policy in the Russian Federation on the example of the territories of the Far Eastern Federal District (FEFD) and confirm the hypothesis about the formation of a new model of regional policy.
Research Methods
Theoretical and methodological basis of this research is a scientific paradigm, namely that the state regional policy includes the implementation of two directions of state influence on the regional development: region-wide and selective. The region-wide influence of the state on its regional development is related to the establishment of the rules and regulations for the distribution of financial resources, as well as to the federal-regional division of property for all regions in the country. The selective influence of the state on its regional development is related to the selective impact on the regional space, based on the public goals and priorities of the state policy, formulated in the Strategy of Spatial Development of the Country. This article considers the objects, tools and methods of implementing the selective policy in the Russian Federation. The research uses the methods of comparative analysis, grouping and statistical analysis.
Findings
The uniqueness of the FEFD is related to the fact that all the Far East constituent territories of the Russian Federation are designated as priority geostrategic territories (Table 1). The mechanism of implementation of selective regional policy for the development of FEFD territories is provided by a system of institutions (Table 02).
According to Official information portal of the Far East Development Fund (Official Information Portal…), Official Information Portal Agency for the Development of Human Capital in the Far East (Official Information Portal Agency…, n.d.).
The "Socio-economic Development of the Far Eastern Federal District" state program is the basic method of selective regional policy for the development of territories in the Far Eastern Federal District. One of its main objectives is "the development of economic growth centers on the constituent territories of the Russian Federation, members of the Far Eastern Federal District". The centers of economic growth of the Far Eastern Federal District regions are defined in conjunction with investment projects. These projects are the basis for economic growth and national employment. There are 56 centers of economic growth established in the FEFD regions. Diverse tools of state stimulation of regional development are used: state investment in building infrastructure, creation of priority social and economic development areas (PSEDA) and introduction of regime for the Free port of Vladivostok (FPV), etc.
A "Plan for Social Development of Economic Growth Centers in the Far Eastern Federal District for 2018 – 2021" was developed in the framework of the implementation of core measures of the "Socio-economic Development of the Far Eastern Federal District" state program for the development of FEFD economic growth centers. This plan includes 442 events for the development of industrial and social infrastructure [19] with the overall funding of 94253,259 million rubles (Table 03).
According to RF Government Decree of 30.07.2019 № 1681 «On the distribution of other inter-budget transfers provided in 2018 - 2021 from the federal budget to the regional budgets for the implementation of measures of social development for economic growth centers of the Far Eastern Federal District» (RF Government Decree…, 2020).
Implementing a selective approach in regional policy, the Federal center commits significant financial resources to the geostrategic territories of the Far Eastern Federal District. The largest amount of funds from the Federal budget for the development of economic growth centers was allocated to the constituent territories of the Far Eastern Federal District in 2019. The share of regions receiving funds is shown in Figure 1.
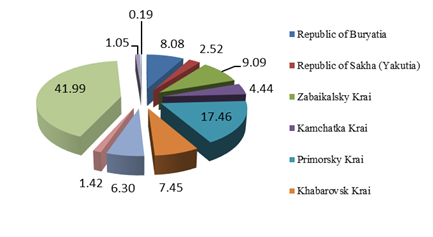
In 2019 the largest share of Federal budget funds was allocated between Sakhalin Oblast (41.99% of total funds), Primorsky Krai (17.46%), Zabaykalsky Krai (9.09%), the Republic of Buryatia (8.08%), Khabarovsk Krai (7.45%) and Amur Oblast (6.3%). In 2018, the Republic of Buryatia and Zabaykalsky Krai did not receive any funds from the Federal budget, since these constituent territories were included in the Far Eastern Federal District only in 2019.
In addition to the allocation of the Federal budget funds for the development of economic growth centers, a part of the financial resources for the construction and modernization of social infrastructure is received by the constituent territories of the Far Eastern Federal District from the Far Eastern sections of state programs. Thus, "Far Eastern Sections" are included in 29 state programs.
Since 2015, in order to stimulate investment activities in economic growth centers of the Far Eastern Federal District, priority social and economic development areas (PSEDA) have been created. 22 PSEDAs are functioning on the FEFD territory. Moreover, the Free port of Vladivostok regime has been created (Table 04).
Along with direct support for these territories from the Federal budget, regional budget co-financing is used as a tool for state stimulation of regional development of PSEDA on the Far Eastern Federal District. According to Table 05, the volume of Federal budget funds to support PSEDA on the Far Eastern Federal District has a multidirectional dynamics (with an increase by 178.17% in 2018 compared to 2017 and a decrease by 66.6% in 2019 compared to 2018).
According to Annual report on the implementation of the state program and the evaluation of the effectiveness of the state program of the Russian Federation “Socio-economic development of the Far Eastern Federal District for 2019” (Annual report…, 2019).
At the same time, the share of the Federal budget in the total volume of resources for PSEDA on the Far Eastern Federal District decreased to 1.1%. Considering the allocation of funds from the regional budgets of the constituent territories of the Far Eastern Federal District, there is an annual financial support for PSEDA with amount of 2.3 to 3.1 billion rubles. The major volume of resource support for PSEDA on the Far Eastern Federal District is invested by legal entities.
In order to stimulate attraction of investments in the FEFD PSEDA, there are instruments of tax regulation in the framework of geoselective regional policy (Table 06).
According to Annual report on the implementation of the state program and the evaluation of the effectiveness of the state program of the Russian Federation “Socio-economic development of the Far Eastern Federal District” for 2019.
Table 6 shows that in 2019, FEFD PSEDA’s investors were granted 9 billion rubles tax exemptions. This sum exceeds the amount of funds (8 billion rubles) allocated from the Federal budget and regional budgets of the Far Eastern Federal District in 2019 (Table 05).
Conclusion
To summarize that, in the framework of implementation of state regional policy in the Russian Federation, geostrategic territories are the objects of selective stimulating influence. Evaluation of the mechanism for implementation of state regional policy for the development of Far East regions as geostrategic areas of the Russian Federation showed that FEFD uses a wide range of methods and tools to stimulate regional development such as state program, creation of special legal regimes in the form of PSEDA and the Free port of Vladivostok, state funding of social infrastructure, tax incentives. This confirms the conclusion that geoselective policy, a new model of selective regional policy, is being implemented in modern Russia. It represents the selective influence of government bodies by stimulating economic activity and improving the quality of life in the country's geostrategic territories in order to ensure its national security and territorial integrity.
References
Annual report on the implementation of the state program and the evaluation of the effectiveness of the state program of the Russian Federation “Socio-economic development of the Far Eastern Federal District” for 2019. Retrieved on 15 October 2020 from https://minvr.ru/upload/iblock/3ca/soprovod-_-otchet-2019-god.pdf
Armstrong, H., & Taylor, J. (1993). Regional Economics and Policy. Harvester Wheatsheaf.
Decree of 30.07.2019 № 1681 «On the distribution of other interbudget transfers provided in 2018 - 2021 from the federal budget to the regional budgets for the implementation of measures of social development for economic growth centers of the Far Eastern Federal District» (2019). Retrieved on 15 October 2020 from https://minvr.ru/about/struktura
Kuznetsov, A. V., & Kuznetsova , O. V. (2015). Regional'naya Politika: Zarubezhnyy Opyt i Rossiyskiye Realii [Regional policy: Foreign Experience and Russian Realities]. IMEMO.
Leonov, S. N. (2020). Preferential Regimes of Established Local Growth Points and ist Impact on the Economy oft he Far East. Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, No. 3(13), 28-45.
Minakir, P. A., & Prokapalo, O. M. (2018). Dal'nevostochnyy prioritet: investitsionno-institutsional'nyye kombinatsii [Far East-Priority: Combinations of Investment and Institutes]. New Economic Association, 2(38), 146-155. [in Russ.].
Official information portal of the Far East Development Fund. Retrieved on 15 October 2020 from http://www.fondvostok.ru
Official Information Portal Agency for the Development of Human Capital in the Far East. Retrieved on 15 October 2020 from http: // www.hcfe.ruRF Government
Sidorenko, O. V., & Tishutina, O. I. (2019). Problems and Mechanisms of Regional Policy of Russia. Proceeding of the International Science and Technology Conference «FarEastCon 2019» Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, 172, 243-249.
Strategy of Spatial Development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2025. (2020). Retrieved on 15 October 2020 from http://static.government.EN/media/files/UVAlqUtT08o60RktoOXl22JjAe7irNxc.pdf
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
21 June 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-110-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
111
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1168
Subjects
Social sciences, education and psychology, technology and education, economics and law, interdisciplinary sciences
Cite this article as:
Sidorenko, O., & Tishutina, O. (2021). Selective Regional Policy For The Development Of Geostrategic Regions Of Russia. In N. G. Bogachenko (Ed.), Amurcon 2020: International Scientific Conference, vol 111. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 988-996). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.06.03.130

