Abstract
The article discusses the philosophy of Total Quality Management (TQM) from a position where the consumer and his interests are the determinant; its adaptation to the realities of modern Russian business. The modern application of quality management for Russian companies is not limited to the use of mathematics and statistics; it requires professional knowledge in the field of economics and management. The company's management system should be focused not so much on the quality of a specific product as on the quality of the entire production system as a whole. Research methodology involves the use of process and system approaches, the use of empirical and theoretical methods. The approaches to improving the organization's management system and increasing its competitiveness are based on the principles of TQM, focused on the interests of consumers, a process approach, and involve continuous improvement. TQM resists authoritarian management style, and creative, innovative solutions will ensure the achievement of the company's strategic goals. The implementation in the Russian economy, formulated on the Western example, of the principles of quality management, will make it possible to formulate development priorities based on the existing approach, focused on the use of standards and continuous improvement, systematization of work aimed at achieving a high level of product quality. The lack of a basic TQM culture prevents the implementation of modern approaches and tools in quality management as applied to Russian business.
Keywords: overall quality management: approaches, tools, indicators
Introduction
Total Quality Management is a well-known quality-focused approach to company management, widely used in Western economic practice. Total quality management (TQM) is a crucial parameter that determines the quality of products and services, focused on the maximum possible satisfaction of customer needs. Thus, paramount importance is attached to quality in the organization of all production processes and the management system of the company as a whole.
The business climate that has been formed in the modern Russian economy makes it possible to orient internal processes towards creating sustainable competitive advantages for manufacturers who use TQM in order to maximize the satisfaction of consumers '(clients') demands in quality products (services).
Problem Statement
The problem of the study is the use of universal approaches to Total Quality Management, which have been approved at the level of the world community.
Research Questions
The subject of research for this article was the modern methods of general quality management, which ensure the state of competitiveness of the manufacturer concerning the conditions of doing business in the Russian economy. Questions that were identified for research:
1. Adaptation of the basic principles of TQM to the realities of conducting business processes in the Russian economy;
2. Application of modern tools to improve quality management;
3. Formation of a system of evaluation criteria in an accessible form allows determining how the current quality system corresponds to the philosophy of General Quality Management.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to determine the possibilities of active adaptation of Total Quality Management to the real conditions of conducting business processes in the Russian economy.
Research Methods
The research methodology involves the use of empirical and theoretical methods, which include: abstraction, analogy, deduction and induction, analysis and synthesis.
Findings
The goal of improving the quality level is to achieve the maximum possible degree of satisfaction of consumer demand and benefit from the actors involved in this process: owners and employees, suppliers and subcontractors, and other interested parties. The company's management must understand that it is necessary to work on the quality not only of a specific product but also of the entire production system as a whole. TQM opposes an authoritarian management style. The required level of quality is achieved in the process of improving economic activities with the involvement of all company personnel in the management process. Total quality management presupposes well-coordinated work of a team, which is united by a leader to achieve a quality result. The emphasis is on creativity, implementation of innovations, and delegation of authority to performers, optimization of resources throughout the company, decisions that are strategic in nature.
Figure 1 demonstrates the structural components of TQM (TQM – Total Quality Management – philosophy of total quality management, 2019).
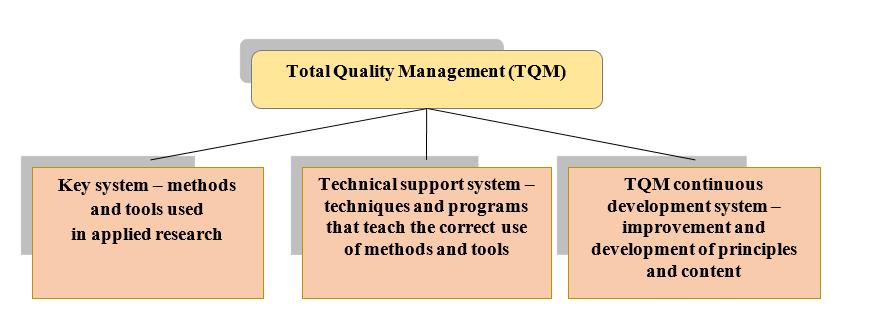
TQM contains a quality management mechanism that works in two directions. The first area is presented as quality control. It is possible to maintain the required level of quality by providing guarantees from the manufacturing company. The result is customer confidence in the quality of the product. The second direction involves maintaining the required, already established level of quality, and the prospects for its improvement. Accordingly, the level of warranty support for manufactured products is growing.
The consistent implementation of TQM in world practice has shown the need to form a system of assessment criteria, which is an accessible form makes it possible to determine how the current quality system complies with the philosophy of Total Quality Management (TQM – Total Quality Management, 2019). Table 1 presents a systematization of the criteria for assessing the quality of the company.
Quality and efficiency are not mutually exclusive notions. Efficiency in the implementation of TQM processes is achieved by observing the following basic conditions:
- the institutional level of company management not only does not hinder but actively fights to improve the quality of the product;
- investment investments are aimed not only at creating a material and technical base but also at forming the company's human resources capable of carrying out the planned cardinal changes;
- organizational restructuring is carried out purposefully and is focused on TQM.
- minimization of production costs and delivery on time.
The basic principles of quality management were laid down in the period of the socialist economy. Undoubtedly, the dramatic changes that have taken place (the transition from the "seller's market" to the "buyer's market") have determined that the main advantage in the competition is the level of quality. This tendency is reflected in the first principle. Figure 2 shows the current perception of TQM principles.

The principle of the functional distribution of responsibility directs line managers to control previous technological operations. Product quality assurance must be carried out at every stage of the product life cycle, from research development to after-sales service. For example, control by direct executors is more effective and increases the efficiency of its implementation several times. The opinion is expressed that its effectiveness exceeds the effect of material incentives (TQM, 2020). The use of this principle in the company determines the responsibility redistribution for ensuring the quality of the manufactured product.
The process approach allows representing the process model of the company as a set of business processes, where the main participants are management and structural units. The introduction of control over the implementation of a separate business process implies optimisation in the use of each type of resource and the development of measures aimed at reducing the cost of manufacturing a product. Management of a company at the level of institutional leadership is considered as the management of a group of business processes.
The principle of the unity of the system is implemented according to the following scheme: internal processes within each structural unit of the company are integrated through horizontal and vertical links into processes common to the entire organisation. The barriers between the divisions (services) of the company must be removed that prevent their interaction. The quality of the final product is achieved by observing the quality parameters in each structural unit and at each stage of the technological process.
The strategic approach assumes that quality improvement acts as a strategic goal and is a component of the company's strategic plan. A consistent relationship should be established between the company's objectives and quality management plans.
The systematic approach focuses on carrying out continuous, systematic work in the field of quality, presenting it as a system of interrelated processes. The company should focus its activities on combining the processes of creating a product with processes that monitor the conformity of the product to the needs of the consumer. A systematic approach assumes the presence of feedback between the manufacturer and the consumer, allows developing a company strategy focused on improving the quality of the product being created.
TQM is focused on the continuity of the process of improving the quality of production. It does not imply a quick result in the short term. The manager should analyse emerging problems; after the manager should develop proactive measures to prevent their occurrence in the future. From a strategic perspective, it is necessary to achieve continuous improvement of the quality system in the company. The principle of continuous improvement creates the image of the company, determines the style of its activities, which presupposes the cyclical nature of improvements and the prevention of subsequent problems (Lapidus, 2002).
The availability of facts, accurate information, knowledge of the current characteristics of the product allows managers at all levels of management to make decisions based on facts rather than intuitive ones. Of course, intuition plays a unique role, but only when it is supported by accumulated knowledge and experience, verified by facts (corresponding measurements) in practice. When making management decisions aimed at improving the quality of production, it is advisable to conduct analytical research, actively realising the creative potential of employees in developing measures aimed at increasing the company's competitiveness by improving the quality of production.
Communication processes, both in the internal and external environment of the organisation, should become commonplace for the company. The effectiveness of communications is manifested in several ways:
- explanation of the goals and objectives set for the company in the field of quality for a strategic perspective;
- the motivation of personnel and management at all levels of management;
- building relationships with suppliers of raw materials, materials, semi-finished products. It is crucial to ensure the quality control of raw materials before they enter the production process, preferably at the enterprises of the leading suppliers, since the quality of components or raw materials from suppliers determines the quality of the finished product.
For Russian business, an advantage in the current environment is the integration of TQM and business process reengineering, which makes it possible to achieve superiority over competitors. On the one hand, TQM is aimed at continuous improvement of the quality of the manufactured product, on the other hand, at increasing labour productivity, which involves organisational changes in business processes based on information (computer) technology (Hammer, Champy, 2001). General for the areas under consideration:
- initiated at the institutional level of management;
- focused on increasing labour productivity and the level of product quality;
- involves teamwork and enhancing the creative potential of each of its members;
- they erase previously formed boundaries between structural divisions.
The differences are expressed in the following:
- the process of restructuring with TQM strives for endless improvement (improvement), dynamic development, while reengineering presupposes the completion of the process;
- TQM is more focused on qualitative parameters, and reengineering – on commensurate quantitative ones.
Possible options for restructuring business processes, organisational modelling involves the development of alternative operating strategies, forecasting sales, the sensitivity of all employees of the company to the necessary changes, and increasing the return on investment in TQM processes.
Expanding the range of impacts of TQM have a substantial impact on business process restructuring (Williams, Davidson, Waterworth, Partingto, 2003). An emphasis on sales growth, customer retention focuses business processes on reducing the time spent on the production of a unit of production, control at all stages of the production process, streamline control over the storage of stocks.
Conclusion
The methodological basis of quality-oriented business processes is mainly based on foreign sources. International experience shows that TQM cannot be regarded as a standard; on the contrary, it is a set of provisions in management based on the General Quality Management of the company's activities and subject to positive dynamic changes. There are not enough practical results from the adaptation of TQM to the conditions of the Russian economy. There is a need, using the accumulated empirical base, to form a scientific base for the adaptation of TQM for Russian business. Russian business uses modern tools to improve quality management, for example, ISO 9000, quality awards, benchmarking, and self-assessment. The positive and negative experience of building and developing quality management systems makes it possible to identify trends and formulate the foundations of a scientific approach to solving this problem for the Russian economy.
A general improvement in the quality of domestic products and services should become Russia's national idea. The emphasis is on promoting ideas and stimulating the quality of products and services. The state formulates the main directions in the implementation of the policy in managing the quality of manufactured goods:
- quotas for goods in areas that are identified as strategically important for the country;
- targeted investment of federal projects and programs promoting the implementation of breakthrough areas in the creation of the latest technology and technology;
- attracting foreign capital in the field of scientific research and the creation of innovative products;
- government guarantees that encourage private investors to invest in innovative areas of economic development;
- the provision of benefits in the field of lending to enterprises that implement actions aimed at improving the quality of their products and services;
- introduction of a preferential taxation scheme for enterprises that have the capabilities and implement them in a short time to ensure the quality of products, which makes it possible to increase the company's competitiveness.
At the company level (taking into account the specifics of the behaviour of Russian managers seeking to impose their product on the consumer), it is crucial to improve the quality management system (Maslov, Watson, Belokorovin, 2011):
- to develop a logic of relations with the consumer, which is based on the conscious satisfaction of the consumer and is expressed in loyalty to the company (increase in the share of regular customers).
- to consider the activities of the company as a set of processes focused on the internal consumer (Watson, 1993). This process dependence assumes that each subsequent process is presented as a consumer of the current one; therefore, the quality of an individual process creates the overall quality of the entire business process and the quality of the product being created.
- rejection of the authoritarian style of government in favour of a democratic one. Successful implementation of TQM presupposes that an institutional-level manager has the following skills:
- professional is a piece of specialised knowledge and skills, realised in the performance of specific functions, the ability to apply tools competently and other means to resolve a specific work task;
- conceptual (the ability to think strategically, the breadth of consideration of the problem, the determination of the significance of the impact of individual factors on the decisions made, the ability to rank and analyse the incoming information);
- human, first of all, these are personal qualities that manifest themselves ineffective interaction, motivation and coordination of the activities of subordinates (team members), enthusiasm, disclosure of the employee's creative potential and the ability to resolve conflicts that arise;
- the formation of a culture of quality under the influence of the consumer. On the one hand, the quality of the product, and not its price, should be a factor that determines consumer demand; on the other hand, quality ensures the state of the company's competitiveness, its survival in the market.
Companies focused on the implementation of quality management improvement processes gain competitive advantages and are more resistant to unpredictable market fluctuations. The evolution of TQM in Russia is based on respecting consumer interests, ensuring the company's competitiveness, creating a culture of quality and defining the innovative direction of development of our state.
References
Deming, W.E. (2019). New time management. Simple mechanisms leading to growth, innovation and market dominance. Moscow: Alpina Publ.
Hammer, M., Champy, J. (2001). Reengineering the Corporation: A Manifesto for Business Revolution. New York: Harper Collins Publ.
Lapidus, V.A. (2002). Total quality (TQM) in Russian companies. Moscow: Novosti Print. House
Maslov, D., Watson, P., Belokorovin, E. (2004). Total quality management in Russia is a difficult path to perfection. Quality. Innovat. Education, 4, 47–51.
TQM (2020). Business Portal “Production Management”, TQM. Retrieved from: www.up-pro.ru
TQM (2019). TQM – Total Quality Management – philosophy of total quality management. Retrieved from: http://progressive-management.com.ua/glossary-management/57-tqm-total-quality-management.
Watson, G.H. (1993). Strategic benchmarking: how to rate your company's performance against the world best. Michigan: John Wiley & Sons.
Williams, A., Davidson, J., Waterworth, S., Partingto, R. (2003). Total quality management versus business processre-engineering: a question of degree. Design and Innovation Research Group, University of Salford, Manchester, KU. Proc. Instn Mech. Engrs Vol. 217, Part. J. Engineering Manufacture. Retrieved from: B14201#IMechE http://www.reengine.ru/index.asp?Menu= 3&Sub=4
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 May 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-106-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
107
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2896
Subjects
Science, philosophy, academic community, scientific progress, education, methodology of science, academic communication
Cite this article as:
Andreevich Surzhikov, M., Alekseyevna Saltanova, T., Alexandrovna Chlysheva, E., & Alexandrovna Mitina, I. (2021). TQM - Adaptation For Russian Business. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Knowledge, Man and Civilization - ISCKMC 2020, vol 107. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 2451-2458). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.05.328

