Abstract
The study's relevance determined a high socio-economic value of development of the recreational-tourism sphere in the Union territories to achieve the maximum multiplier effect for society and ensure a high level of competitiveness of the Russian Federation. The purpose of the research is to formulate and further classify the institutional factors of the development of the recreational and tourist sphere, which determine the essential basis of the spatial organization of the recreational and tourist sphere. The research's methodological basis is the theory of new institutionalism, supported by neoclassical realism, which is used for a comprehensive analysis of existing relationships at various levels of spatial orientation. The main methods used were analytical methods of complex and individual analysis of official statistics, comparative analysis of the development of tourist territories, multi-factor analysis of prospects for the development of the recreational and tourist sphere, and modeling and predictive methods. The study formulated the necessary factors of the functioning of the recreational-tourism sphere in the context of spatial development, the expedience and necessity of the mediation of financial, social, and legal institutions, as a way to reduce the overhead of maintaining the infrastructure.
Keywords:
Introduction
The modern development of the recreational and tourist sphere is inextricably connected with all sectors of society. According to the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), the share of tourism in world GDP in 2018 was 10.4%. According to studies, the tourism sector accounted for 6.5 per cent of total world exports and 30 percent of total world services exports (Kholodova, 2016). The recreational and tourism sector provides additional jobs by regulating the migration flow of the population to developing regions of tourism specialization, 10% of the total employment is directly in the tourism sector, that is, every 11 workers in the world are engaged in tourism, provides a powerful impetus for the development of regions with available recreational and tourist potential, thus stimulating the advancement of sparsely populated or underdeveloped areas, which are geographically remote, is the driving force of the world economy.
According to an analysis of data provided by UNWTO, the world has experienced a steady increase in international arrivals over the past decade, an average of 2-3% per year (figure
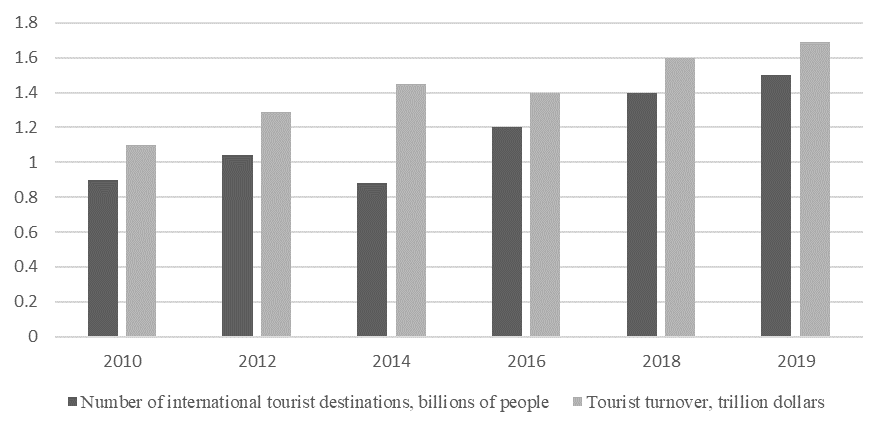
The development of the Russian Federation's recreational and tourism industry is accompanied by small jumps, caused by socio-economic and political problems of a national and global nature, which affects the share of tourism in the country's GDP (figure
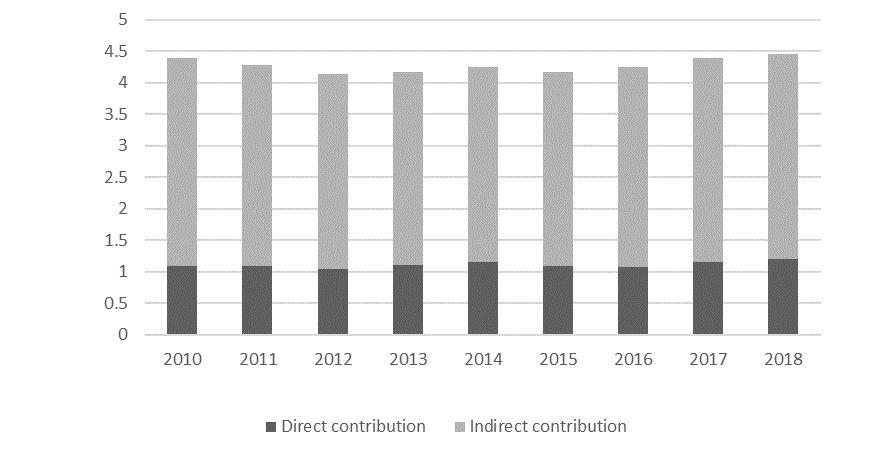
According to the Federal State Statistics Service, the number of entry tourist trips of foreign citizens to Russia for the 9 months of 2019 year amounted to 19 million 64 thousand trips, which practically reflects the indicator of 2018 year (19 million 245 thousand trips for 9 months of 2018 year), according to the Federal State Statistics Service of Russian Federation.
The leaders in the growth of inbound tourism to the Russian Federation in 2019 are China (1,594 thousand trips for 9 months of 2019, which reflects an increase of 13% compared to 9 months of 2018) and South Korea (356 thousand trips, which is 22% more than in 2018). The growth of inbound tourism from Japan in 2019 amounted to 7% (93 thousand trips), India - 3% (73 thousand trips), Thailand - 18% (46 thousand trips), Vietnam - 5% (45 thousand trips).
The total number of foreign citizens' entry tourist trips to Russia in 2018 amounted to 24,551 thousand people (figure
According to the results of 2019, there is a significant increase in domestic tourist flows in many regions of Russian Federation, due to a shift in the vector of tourist interests and an increase in the tourist attractiveness of Russian regions.
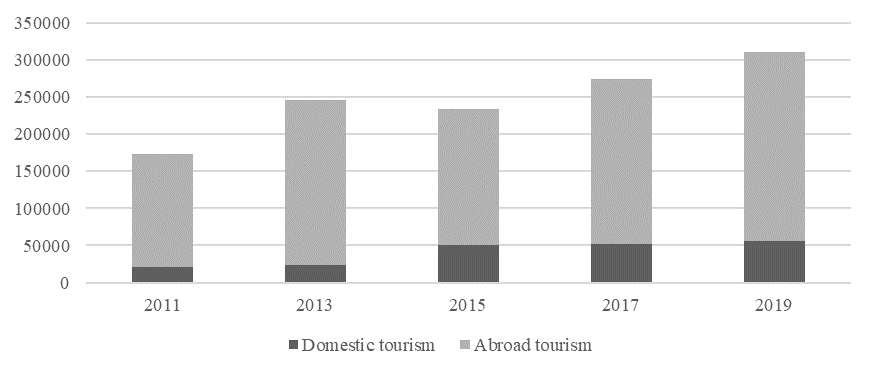
The number of tourists in the Stavropol Territory increased in 2019 by 6.7% compared to 2018 and amounted to 1.6 million people. Including the resorts of the Caucasian Mineral Waters were visited by 1.2 million people, which is 9.1% higher than in 2018 (Margieva, 2020). A significant increase in tourists (12%) according to the Agency for Tourism and External Relations of the Kamchatka Territory was recorded in Kamchatka - 240 thousand people. The number of tourists who visited Crimea in 2019 amounted to 7.5 million people, which is 10% more than in 2018. In the Krasnodar Territory, the total number of tourists amounted to 17.3 million people, which reflects a total dynamic growth of about 6-8% per year. The resort city of Sochi is located on the 3rd place in Russia in the number of tourists (6.5 million people) received after Moscow (25 million people) and St. Petersburg (10.4 million people). Only in the winter season 2019-2020. the mountain resort "Rosa Khutor" was visited by 800,778 people, despite the premature completion of the tourist season, largely due to the fact that a wide variety of options attractive to tourists for high-quality and diverse recreation were introduced in the new season (Kuchumov et al., 2018).
Problem Statement
In 2020, in the context of the difficult epidemiological and economic situation in the country in the world, there is an excess of the growth rate of domestic tourism in the Russian Federation, as well as recreational and tourist trips to neighboring or nearest countries, over the growth rate of the number of travelers to distant countries, the acquisition by tourists of cheaper tourist packages.
The recreational and tourist sphere is a kind of multiplier of the socio-economic development of society, which determines the growth of the domestic economy. The expansion of the geography of the recreational and tourist industry in the Russian Federation ensures the development of cities of narrow tourist specialization and remote areas, while forming additional demand for local and regional goods and services, contributing to the development of additional domestic industries that benefit the region and increasing the standard of living of the local population. The development of the recreational and tourist sphere contributes to the general development of production, ensuring the integrated interaction of regional industries, improving infrastructure, implementing the concept of municipal, regional and national development, and forming a positive image of the territory on the regional, national and world tourism market. Thus, the recreational and tourism sector is considered as one of the key factors determining the functioning of the leading sectors of the economy: the production and sale of goods and services, construction, agriculture, transport, communications (Zigern-Korn, 2019). In addition, the tourism sector itself is a mobilizer of investment attractiveness, an activator of entrepreneurial activity, and a common engine for tolerance of the public environment.
Research Questions
According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 20, 2019 No. 2129-r On the Strategy for the Development of Tourism in the Russian Federation for the Period up to 2035, within the framework of the Tourism Development Strategy in the Russian Federation for the period up to 2035, Federal executive bodies, executive bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as local authorities, it is necessary to ensure the implementation of measures to form and implement a plan for the spatial development of tourist territory at the regional and municipal levels, which determines the localization of projects for the development of tourist territory (Aleksandrova, 2018). Spatial development in this context involves an augmented positive transition from one spatial orientation to another, provided that the possible costs of maintaining infrastructure for all economic actors are minimized and the unity of the Territory is maintained through social, legal and financial institutions.
Thus, it is of paramount importance to mediate the institutional environment of the functioning of the recreational and tourism sphere in the context of ensuring sustainable spatial development.
The main issue of the study is the concretization of institutional factors that form positive conditions for ensuring a constructive transformation of the recreational and tourist sphere in a spatial context.
Purpose of the Study
Given the trends in the development of domestic tourism in the Russian Federation and the modern global statistics of world tourism, in the context of the difficult epidemiological situation and the closure of the state borders of Russia and most countries of the world, the conceptual basis will be the mediation of stable socio-economic relations governing the development of the recreational tourism sector of the Russian Federation in the aspect of spatial interregional development, taking into account modern trends and tourist preferences (Leukhin, 2018). The pandemic was a kind of trigger that determined the trends in the formation of the domestic tourist market. The Russian economy, including the recreational and tourism sector, due to its actual monopolization, is more interested in global spatial development than ever.
Research Methods
In addition to the widespread globalization associated with the expansion of the market, horizontal and vertical integration, consolidation and wide spread of network business between the interacting sectors, the development of the recreational and tourism sphere is due to the era of informatization, communication and knowledge. Actual trends reflecting the current institutional environment of the development of the recreational and tourist sphere in the Russian Federation in the context of spatial development can be distinguished:
Globalization of recreation and tourism institutions - formation of a single tourist space, operating in direct interaction between the political, economic and social institutions of tourism, Based on collective and concerted activities aimed at the spatial transition from one territorial orientation to another, which is determined, first of all, by the increased interest of tour operators in mass tourism, striving to realize the maximum number of formed tours, lower prices for air travel, increasing number of charter flights, offering new directions and types of tourism, unique and interesting programs for group tours.
Glocalization is a global regionalization that forms a unique tourism product identified in the context of national and regional development, mediating the emergence of a wide variety of types and forms of tourism activities based on the individual preferences of tourists, as well as forming a sustainable environment for the spatial development of tourism (Azernikova, 2017).
Uneven distribution of tourist flows in different regions of the Russian Federation on the basis of intra-regional concentration, due to the surging development of tourist territories, localization of the efforts of the state and society on the development of certain tourist regions, which in modern realities tends to fade and the issue of functional expansion of the geography of recreational tourism sphere in the aspect of spatial development is updated.
Shifting tourist interests towards recreation: at the end of the 20th century, business tourism dominated the structure of tourist flows, while, currently, most tourists (60%) travel for recreation and recovery, and only 40% - for business purposes (Gataulina & Topchiy, 2018).
The increase in the number of short-term tourist trips due to the increase in the number of short holidays and the spread of youth tourism with a period of 2-3 days, due to the reluctance to allow long work breaks and the desire to relax "on the weekend."
Informatization of tourism is a high growth of e-commerce associated with the modern trends of information openness and freedom of choice, as well as the desire of the consumer to be fully informed regarding the entire package of tourist services (accommodation and catering facilities, transport, infrastructure, additional services, etc.).
Mobilization of tourism, due to the hobby of population mobility, growth of tourist expenses, shifting the interests of tourists to individually built trips along their own route, increased congestion of non-traditional accommodation means - mountain chalets, hunting lodges, beach bungalows, etc. (Bunakov et al., 2018).
Individualization of tourism - the transformation of mass tourism in favor of individual tours based on personal preferences, due to the constantly increasing education of tourists, acquisition of tourist experience, the desire to get a new unique tourist product. According to Rosstat, the distribution of tourist flows is uneven: mass and group tours make up only 20-30% of the total number of trips, while individual trips make up about 70-80% (Ivanova, 2016).
Dynamic packaging - the technology of tourism, the emergence of global and national systems for the sale of tourism services, allowing in real time to form an individual tour in accordance with their own preferences, without the help of travel agents and third parties, contacting the service provider directly, book and pay for it.
Virtual consolidation - a combination of tourism companies providing various services in the field of recreation and tourism, and information technology companies in order to create Internet platforms that provide services for choosing a tourist product, booking, prepayment, cancellation, etc., using virtual travel, allowing online, without interrupting daily activities, to visit the Internet - The site of a hotel, restaurant, travel company and any organization providing tourist services, which ultimately leads to the formation of a more conscious profile of tourists, with established preferences and interests. This trend determines the appearance of "virtual tourists" (Shvets, 2018), which in a limited territorial framework directly mediate the spatial development of the tourist sector, narrowly oriented niche types of tourism (photographic, film tourism, autotourism, retroturism, gastronomic, archaeological, identic tourism related to the search for its cultural, ethnic or national affiliation, intercultural tourism, hereditary - aimed at studying cultural, historical and natural heritage, communicative - the purpose of which is communication with representatives of different cultures, etc.).
The need to liberalize legislative institutions - simplification of entry and exit tourist formalities, and, as a result, the integration of international and domestic tourism (a single tourist space of the European Union with open borders for citizens of the Schengen zone, uniting 26 states (Ivanova, 2014), ensuring the free movement of tourists within the tourist zones designated by law.
A retrospective analysis of trends in the development of the recreational and tourist sector shows that being one of the significant areas of the economy that provides additional jobs, the development of infrastructure that creates the investment attractiveness of tourist territories supporting the economic growth of the country as a whole, it needs to form a favorable institutional environment, which is formed under the influence of constructive factors that ensure sustainable spatial development and growth. It is generally accepted by the term "factors" to mean the causes, conditions, driving forces that determine the positive or negative result of a process (Frolova, 2017). Institutional factors that determine the spatial development of the recreational and tourist sphere, due to the endogenous nature of the term itself, should be understood as the causes, conditions and drivers that have a relevant impact on the behavior of economic actors, which form a positive institutional environment for the functioning of tourist actors and facilities.
Findings
Determining spatial development in the context of territorial expansion, the fundamental factors in the formation of recreational and tourist attractiveness of territories (economic, geographical, socio-cultural) are the basis for the development of tourism, the leading element of which is institutions that limit or determine development opportunities (figure
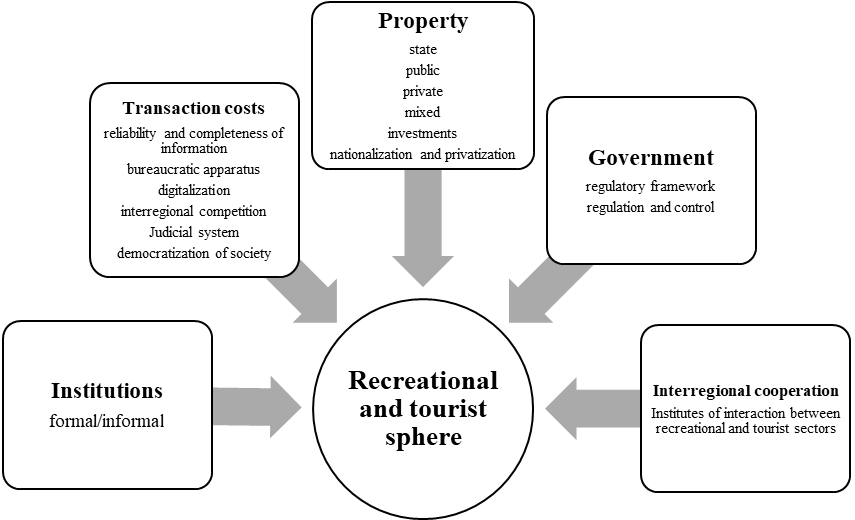
1. Economic institutions that ensure the sustainable functioning of the economic environment, healthy competition between types of tourism and tourist regions, the growth of the economy of the industry, the region and the country as a whole:
indirect demand for tourist products determined by the availability of material and temporary resources
offering a high-quality material and technical component of the tourist product: facilities of modern infrastructure, transport and service support, high quality of service that meets international standards, information technologies that operate continuously throughout the year
property relations determined in accordance with the structure of the distribution of property rights in the recreational and tourism sphere
investment sustainability
2. The political factors of institutional change affecting the development of recreational tourism through the control of economic institutions are actually represented in the form of state regulatory policies in the field of tourism, legislative acts, orders and decrees, as well as the legislative consolidation of state measures to support entrepreneurship and organizations operating in the field of tourism, that is, in the form of a formal framework, and informal expectations regarding the degree of compliance with these borders:
formal factors defining or limiting the boundaries of activity of recreational and tourist actors (bureaucratic apparatus)
informal factors (boundaries set by society)
factor of mutual influence of collective actions and institutions determining the degree of responsibility for carrying out economic activities
The creation of a system of support for entrepreneurship - small and medium-sized businesses - requires special financial and administrative state efforts to ensure the sustainable functioning and maintenance of demand for the national tourism product (Simonyan & Saryan, 2016).
3. Transactional factors related to information openness of recreational and tourist sphere, expressed in formation of full and open access to any information of interest related to tourist products (Valeeva, 2017)
expectation factor associated with incomplete information, which affects the reduction of motivation of the tourist activity
Information openness factor, which mediates the availability of full-fledged data on sold tourism products, is associated with widespread digitalization and encourages the spread of tourist flows in time, space and technology
the democracy factor that determines the equality of rights and obligations of consumers and producers of the tourist product to receive equivalent and reliable information
The presence of a judicial system that forms the dispute resolution system
factor of corruption spread and quality of bureaucratic apparatus
4. Interregional cooperation - a system of institutions that ensure the interaction of business entities and territorial management bodies, ensuring the spatial development of the recreational and tourist sphere, based on the generally accepted solution of the development of the market for recreational and tourist services within the framework of the multilevel system of the regional, federal and national administration, to ensure the extension of cooperation to the economy of the surrounding territories, including on a national scale, using the most effective institutional elements of market regulation, Having a direct impact on the stimulation and acceleration of the processes of formation and development of the recreational and tourism industry, both in the spatial context and in the context of the country's economic development.
Conclusion
The current state of the recreational and tourist sphere is influenced by many factors, including economic, political and social, which imposes certain restrictions on its development. In addition, the global epidemiological situation over the past year and a number of restrictive measures make it possible to annotate the tendency of tourist trips to shift towards domestic tourism. The concretization of institutional factors makes it possible to carry out analytical studies of predicted trends in the spatial development of the recreational and tourism sector within the framework of the national tourism development program.
References
- Aleksandrova, A. U. (2018). Modern features of spatial development of tourism. Geography and tourism, 2, 12-16.
- Azernikova, I. P. (2017). Human rights and tourism: cooperation in the era of glocalism. Westn. RGGU. It is gray. Political science. History. Mezhdunar. relations. Foreign regional studies. Oriental studies, 1(7), 146-151.
- Bunakov, O. A., Zaitceva, N. A., Larionova, A. A., Zigern-Korn, N. V., Zhukova, M. A., Zhukov, V. A., & Chudnovskiy, A. D. (2018). Development perspectives of “Last chance tourism” as one of the directions of ecological tourism. Ecology, 106, 441-447.
- Frolova, E. V. (2017). Factors of development of tourist attractiveness of municipalities of Russia. Question of state and municipality control, 3, 112-128.
- Gataulina, S. U., & Topchiy, A. V. (2018). On the state of methodological support for assessing the effectiveness of tourist activity in the region. Internet journal "Science Science", 4(23), 17-29.
- Ivanova, E. A. (2016). Spatial tourism development. Collection of works of the international scientific and practical conference, 410-416.
- Ivanova, I. S. (2014). Features and problem areas of visiting tourism (on the example of an analysis of empirical data from sociological studies of youth student groups in the Kuban). Scientific, 104 (10), 3-10.
- Kholodova, T. A. (2016). Modern trends in the study of tourism and recreational and animation activities in the context of the sociology of leisure. Humanist of the South of Russia, 4, 273-279.
- Kuchumov, A. V., Zigern-Korn, N., Zigern-Korn, N., Testina, Ya. S., & Boykova, Yu. M. (2018). Development trends of the tourism clusters in the Russian Federation. IOP Conference series: Earth and environmental science, 204(1), 165-168. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/204/1/012021
- Leukhin, A. N. (2018). The capabilities of spatial visionics in revealing the semiotic potential of territories. Bulletin of the Moscow State Regional University. Series: Philosophy, 4, 106-117.
- Margieva, N. T. (2020). Sphere of Tourism in Russia: State and Development Prospects. Economics and Entrepreneurship, 10-1(63-1), 141-145.
- Simonyan, G. A., & Saryan, A. A. (2016). Development of regional tourist and recreational complexes of Russia in modern conditions. Modern scientific thought, 16, 67-73.
- Shvets, I. Yu. (2018). Regional management of competitiveness of tourist services: methodology and practice. Emergency Enterprise Phoenix, 145-161.
- Valeeva, E. O. (2017). Tourism as a strategic priority of the territory. Modern problems of travel industry science Scientific-practical annual teaching conference, 9-16.
- Zigern-Korn, N. (2019). Theoretical substantiation of the state policy for spatial development of tourism. Bulletin of the Moscow State Regional University. Series: Natural Sciences, 2, 30-39.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
16 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-104-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
105
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1250
Subjects
Sustainable Development, Socio-Economic Systems, Competitiveness, Economy of Region, Human Development
Cite this article as:
Bodzhgua, A. (2021). Institutional Factors Of The Recreational And Tourism Sphere Spatial Development. In E. Popov, V. Barkhatov, V. D. Pham, & D. Pletnev (Eds.), Competitiveness and the Development of Socio-Economic Systems, vol 105. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 438-447). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.48

