Abstract
The development of the innovative economy is a powerful incentive for business in the context of increasing efficiency, productivity and digitalization of business processes. To conduct a full-fledged assessment of the company's activities, the work of the heads of key areas and divisions, it is advisable to introduce a KPI system that can allow focusing exclusively on significant areas and indicators. In this part, it is particularly important to include non-financial indicators in the KPI system that allow you to analyze the business within the framework of those aspects that are related to changes in the internal and external environment, but it is impossible to evaluate them using monetary units. The article describes the principles of collecting non-financial information in an innovative economy and digital modernization. A two-stage study of non-financial statements of 30 largest companies in the Russian Federation was conducted in order to identify non-financial KPI in them and establish their relationship with management decisions. In this part, we examined aspects of the company's activities related to the indicators of the "Vector of sustainable development" index and the key thematic areas of GRI for improving the company's non-financial reporting. The significance of digitalization is considered in the context of using electronic document management and collecting non-financial information with its help in order to further include it in the KPI report.
Keywords: Innovative economymanagement decisionsnon-financial KPInon-financial informationnon-financial reporting
Introduction
Innovation processes that take place in the economy of all countries of the world are of critical importance. This is primarily because innovations bring to a qualitatively new level the financial and economic activities of the enterprise from the standpoint of ensuring sustainable development and efficiency of management decisions. This fact is particularly relevant in the current situation, when uncertainty in the external environment is increasing, because of the COVID-19 pandemic consequences. The turbulence observed by experts and analysts indicates that the business's financial strength and development potential may face the threat of not being able to implement them due to the significant risks inherent in the internal and external environment (Chuyang et al., 2020).
The development of the innovation sphere is actively supported by the government and state bodies of all countries of the world, which helps to stimulate the digital modernization of economic, social, legal and other processes in society. The number of innovative enterprises is growing every year. Figure
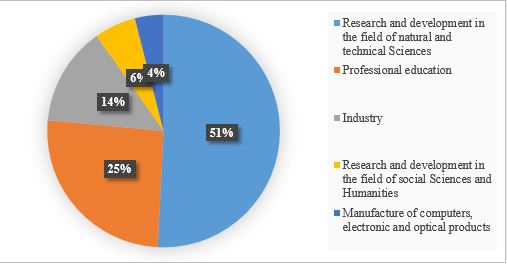
According to the presented analytical materials, it can be concluded that the specifics of the presented types of economic activity are correlated with the features of innovation processes. These types of activities have the goal of continuous improvement, increasing efficiency, which is impossible without the development and implementation of innovations. Non-financial indicators have a number of advantages that demonstrate the need to consider them when making management decisions, as well as the feasibility of integration with financial parameters as part of an integrated KPI system:
- non-financial indicators are correlated with the company's long-term strategy. As a rule, financial indicators are not designed to be used over a long period for making decisions based on them;
- non-financial indicators allow you to assess the degree of achievement of non-financial goals related, in particular, to customers, suppliers, competitors, the social sphere, the environment, and so on;
- a number of researchers note that due to non-financial indicators, it is possible to more reliably and objectively determine the value and value of intangible assets, intellectual (human capital), and innovative processes occurring in the company;
- non-financial indicators can reflect the long-term benefits of management decisions. This point is especially relevant in the conditions of an innovative economy, when economic entities are interested in investing research, development, and intellectual work. Forecasting future cash flows and financial results from the investment, in addition to determining non-financial parameters related to future benefits, will significantly increase the reliability of the estimated situation;
- non-financial indicators can be used by managers for self-assessment and self-monitoring in order to improve their activity performance.
Analysis of KPI and identification of factors that influence them are the stage before making management decisions. This raises the question how to collect the necessary information. Digital modernization of all processes taking place in the economy has "merged" into the corporate governance of modern business structures. Electronic collection and processing of information enable you to reduce time, labor and financial costs. Automation of information collection and processing processes allows you to configure algorithms so that the software product used by the company generates KPI set by managers in the context of financial and non-financial indicators.
Problem Statement
Management decision-making in an innovative economy should be based on a set of indicators that describe the financial and economic activities of the company from all its sides in the context of financial and non-financial indicators. To this end, it is necessary to create a KPI system, which, in particular, will include non-financial indicators and ensure their collection in the context of digitalization of economic processes. Doing business in an innovative economy involves many risks that can only be managed based on an analysis of the company's internal and external environment. It should be noted that the complexity and versatility of the internal and external environment of the company determine the relevance of research not only quantitative aspects of the business (expressed in financial indicators), but also qualitative (expressed in non-financial indicators). This is because it is often impossible to describe the observed economic processes unambiguously in the form of a financial indicator. Many factors that affect business performance are not measurable in monetary terms, but their impact on the business is significant. In addition, recent research shows that financial-oriented performance assessment systems are not effective enough.
At the same time, from the point of view of managerial decision-making in the context of managers’ efforts to take into account all aspects that affect the business, a situation of obtaining an excessive amount of information may arise (Myojung et al., 2019). This will inevitably lead to a decrease in its value and utility. It follows that choosing key performance indicators (KPI) and focusing on them when making management decisions will allow managers to focus on significant indicators that characterize the observed changes in the internal and external environment (Givoly et al., 2019). Non-financial KPI show how effectively the company conducts financial and economic activities, achieves its goals and adheres to the chosen strategy. Of course, the analysis of non-financial KPIs is appropriate only in conjunction with financial parameters to form a complete picture of the business.
Research Questions
From the point of view of this work, research questions were:
1.What are the factors of the innovation sphere development as an incentive to use non-financial information?
2.What are the principles of collecting non-financial information included in KPI in the context of digital modernization of economic processes for management decision-making?
3.What is the value of collecting non-financial information and disclosing it on the example of largest Russian companies?
Despite still existing concerns about the fact that "a machine will replace a person" and, as a result, the quality and effectiveness of management decisions will decrease, we note that experts hold a different position (Appleton, 2017). Automated processes are managed by a person, and the generated algorithms are continuously monitored, reviewed, and adjusted. Many large companies have already faced the problem of processing large amounts of data, and in the context of a permanent increase in the information field, the growth of information flows due to digitalization, it is possible to create favorable conditions for the effective operation of information and its preparation in order to present it to managers.
Purpose of the Study
During the research, the authors set the goal to identify the importance of collecting non-financial information for business structures from the point of view of making management decisions in an innovative economy in which digitalization is actively developing. Due to the redundancy of information flows and the continuous increase in data volumes for selecting non-financial indicators that will be relevant to the company when making decisions, it is proposed to create a KPI system so that it serves as a starting point for managers to form a professional judgment regarding the observed changes in the internal and external environment. Non-financial KPIs have unlimited potential and can be used in the long term, as well as to control the actions of managers. According to the National register of corporate non-financial reports, the number of companies publishing non-financial reports increases every year. Companies representing key sectors of the economy, which form a significant share of GDP, are most active in this issue. These include companies in the oil and gas, metallurgical, chemical, nuclear, and electric power industries. According to the analysis, these companies pay special attention to introducing innovations and stimulating the digitalization of all processes within the business.
Research Methods
The global reporting initiative (GRI) identified key thematic areas for improving the company's non-financial reporting. Based on the results of their analysis, was concluded that from the point of view of choosing non-financial KPI, the following list is relevant:
the "efficiency problems" direction, which includes the following aspects: efficiency of production and distribution of goods and services, new production models and technologies;
direction "problems of management and economic models": development of a new generation of economic growth and development models;
global challenges: the digital age.
These areas determine the scope of the research. Of particular relevance is their relationship with the conceptual positions of the United Nations. This study analyzes non-financial information published in open sources by the largest companies in the Russian Federation. Non-financial reports of 30 companies were examined. The research was conducted in the following stages:
Stage 1-Research of aspects of the company's activities related to the indicators of the "Vector of sustainable development index";
Stage 2-Research of aspects of the company's activities related to the key thematic areas of GRI for improving the company's non-financial reporting.
During the first stage of the study, the questions presented in Table
The answers on the questions presented in Table
The proposed research structure allows us to study business in the context of a number of aspects: non-financial aspects of activity; the level of innovation; the degree of digitalization of all internal processes; compliance with modern economic conditions and the current market situation.
Findings
There is no doubt that the development of an innovative economy is influenced by many factors. Among the factors that arise from the internal environment, it is possible to distinguish:
mission, business strategy;
material and technical base of the enterprise;
financial resources of the enterprise;
human resources (level of qualification and availability of necessary competencies for employees);
the degree of development of the technologies used;
the state of the internal environment: the climate in the team, culture, ethics.
The factors that arise from the external environment should include:
state of the market, features of entering and exiting it;
legal regulation of companies activities;
the nature of the competitive struggle;
access to credit resources;
degree of development of science and technology, scientific and technological progress;
information environment.
These factors not only influence the development of innovation, but also encourage the use of non-financial information to improve business efficiency through the introduction of innovations and new technologies. An important point is the need to digitalize processes in order to speed up the processing time of large data sets and select the most useful information in them. Non-financial indicators are defined as indicators that use natural measures (for absolute indicators), shares, and percentages (for relative indicators) rather than monetary units. Non-financial KPI, along with financial KPI, allow to assess the degree of achievement of the goals set by the company's management, the effectiveness of business processes, and control significant areas of the business. A number of scientists hold the position that the methodology for calculating many financial indicators is based on non-financial indicators (for example, the number of finished products sold multiplied by the sales price will form a revenue indicator) (Bradshaw et al., 2016). The growing interest in using non-financial KPIs in decision-making is observed all over the world: companies decide to disclose non-financial information in addition to mandatory financial statements, thereby attracting the interest of a wider range of stakeholders, since non-financial indicators are quite difficult to collect and evaluate, however, they are easier to interpret than financial ones. Analysis of the latter requires some training in the form of special education, regular training and advanced training, and understanding the differences between existing calculation methods (Rezaee, 2016). A two-stage study of 30 major Russian companies showed a significant interest of domestic business in collecting and disclosing non-financial information, which proves the validity of its inclusion in the KPI and its significance in decision-making. The implementation of the first stage of the study allowed us to formulate the following conclusions:
The integral score can range from 0 to 15. It allows forming a judgment about the quality of non-financial reporting.
The average integral indicator is 10 points. 26 of the 30 companies analyzed disclosed non-financial information to the extent that allowed them to answer all the questions listed in table
01 . 4 companies did not provide information on social investment, water and energy use, which led to a decrease in the sample average.The results obtained allow us to express a judgment that Russian companies conduct their activities in accordance with the concepts of non-financial reporting accepted in international practice, and therefore understand the significance and prospects of using non-financial information.
The implementation of the second stage was complicated by the fact that there was not enough information disclosed by companies to get answers to the key questions raised. A number of parameters (defects, equipment wear, sales channels, and so on) can be classified by the company as a "trade secret", and, as a result, not disclosed in open sources. However, the study of the company's web sites allowed us to form a conclusion about the significant digitalization of many of the company's processes. In particular, preparation of reports (financial and non-financial), its presentation to stakeholders, explanatory notes for interested parties. The development model and approach to risk management and decision-making can be judged from media reports about the company's management. In this case, such an assessment will be subjective, since the researcher in this case does not directly communicate with the management, but forms his judgment on the assessments provided by journalists. In the context of digital modernization of economic processes, the principles of collecting non-financial information included in the KPI can be represented as a tree of principles, establishing a subordination between strategic and operational principles (Figure
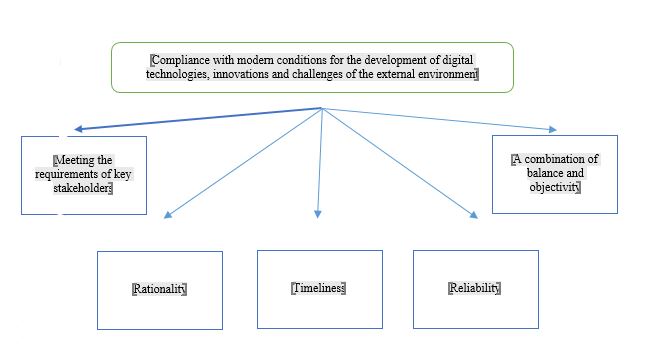
Based on the proposed principles of collecting non-financial information included in the KPI, it is advisable to pay attention to the features of generating data in the electronic document management system. For example, the indicator "Time spent per unit of production" can be specified in the statement of output of finished products. This indicator can be determined in two ways: either calculate the time of release of each unit of production, or determine the start and end time of production, and divide the result by the number of products produced according to the statement. Entering the specified time indicator in the automated accounting system allows you to further summarize information about the time spent on production and include this indicator in the KPI report. The indicator "Number of distribution channels for goods and services of the company" can be included in an electronic document generated during the shipment of products. For example, in invoice, adding the "distribution channel code" column. When processing electronic documents, the automated accounting program will provide information within the KPI report about which sales channels were used during the analyzed period and with what intensity, which will allow to make a decision about the effectiveness of distribution channels for goods and services.
A two-stage study of 30 major Russian companies allows to conduct an in-depth study of non-financial indicators disclosed in the financial statements, from the point of view of their feasibility as KPI. For example, the annual report of PJSC Gazprom for 2019 discloses the following indicators:
number of plants for processing, production and preparation of hydrocarbon and gas products (in units);
volume of natural gas reserves (in billion m3);
volume of natural gas production and sales (in billion m3);
replenishment ratio (in %);
labor productivity (in man-hours);
entering priority production facilities (in units);
integral key indicator of innovation performance (in%) and others.
Each of these non-financial KPI allows not only to evaluate the performance of the heads of the relevant departments and business processes in general, but also to make a management decision. For example, the indicator "Number of plants for processing, production and preparation of hydrocarbon and gas products" will affect the distribution of resources between production centers. The indicator "Volume of natural gas reserves" will be used for planning production and production. The "labor productivity" indicator allows you to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of employees work and, consequently, make the necessary personnel decisions. Thus, non-financial KPI can be used as well as financial KPI when making management decisions in corporations. The use of digital technologies will increase the speed of information processing and save time, labor and financial resources.
Conclusion
The key findings of the research:
- the development of an innovative economy is influenced by both external and internal factors. In particular, human resources in the form of intellectual capital are particularly important for such companies;
- the importance of collecting and using non-financial information is proved by a two-stage study of 30 largest companies in the Russian Federation, according to the results of which all the analyzed companies present non-financial reports in the public domain and pay special attention to the analysis of non-financial indicators and their inclusion in the list of key ones that influence decisions;
- developed a tree of principles for collecting non-financial information included in the KPI in the context of digital modernization of the innovative economy, including strategic and operational principles;
-the importance of digitalization development in business structures is proved, and on the example of electronic document flow, options for generalizing non-financial information are revealed, by establishing the relationship between the primary document and the KPI report;
- using the example of the annual report of PJSC Gazprom (Gazprom, 2020), examples of disclosed non-financial KPIs are given and the directions of decisions made by the business management are suggested.
Our research was based on a limited number of companies within a single country – the Russian Federation. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the fact that a whole range of non-financial information is a commerce secret, so the possibility of studying non-financial indicators of business structures was limited to the reports they disclose. Future research should be conducted on a larger number of large companies. Of particular interest is the study of non-financial indicators of small and medium-sized enterprises, as well as the adjustment of the tree of principles of their collection in an innovative economy. A separate area of research may be the development of a universal list of non-financial KPIs for a number of economic activities.
References
- Appleton, L. (2017). Chapter ten - How can KPIs be used in performance measurement? Libraries and key performance indicators. Chandos Publishing.
- Bradshaw, M. T, Lee, L. F., & Peterson, K. (2016). The interactive role of difficulty and incentives in explaining the annual earnings forecast walkdown. The Accounting Review, 91(4), 995-1021.
- Chuyang, L., Yiwei, H., Yibing, T., Xiaocun, L., Yujie, Z., Yifei, L., Wescott, P., & Stoikov, S. (2020). Using alternative date to predict key performance indicators. DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.3533358
- Federal State Statistic Service (2020). Science and innovation. https://rosstat.gov.ru/folder/14477
- Gazprom (2020). Annual report of PJSC Gazprom. https://www.gazprom.ru/f/posts/77/885487/gazprom-annual-report-2019-ru.pdf
- Givoly, D., Li, Y., Lourie, B., & Nekrasov, A. (2019). Key performance indicators as supplements to earnings: Incremental in formativeness, demand factors, measurement issues, and properties of their forecasts. Review of Accounting Studies, Forthcoming, 24, 1147-1183.
- Myojung, C., Salma, I., & Yan, Y. (2019). The use of nonfinancial performance measures in CEO bonus compensation. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 27(4), 301-316.
- Rezaee, Z. (2016). Business sustainability research: A theoretical and integrated perspective. Journal of Accounting Literature, 36, 48-64.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Burkina, T. A., Grabozdin, Y. P., & Tatarovskaya, T. E. (2021). Non-Financial KPI In The Context Of Business Management Decision-Making In Innovative Economy. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 769-779). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.92

