Abstract
The article examines the processes of recession in the coordinates "performance - time" through indicators of business activity (level of business confidence; industrial production: index of consumer sentiment; index of industrial sentiment) in various countries during the period of economic stagnation. The COVID-19 pandemic has become an enormous shock for the world community and led to a sharp recession in the economy, a decrease in activity in the service sector, and a disruption in production chains in many countries around the world. The study attempts to improve existing financial, economic and management tools to mitigate the impact of the crises in Russia. The evidence is given to the fact that the effects of financial shocks are accumulating. Operational priorities, including the adaptation of processes, systems and approaches, and changes in the financial policies of companies should now be given particular attention. The authors have proposed new guidelines for solving the financial problems facing Russia’s small and medium-sized business. It is the financial policies of companies that should be affected in the first place. It is described Russian conceptual model for improving financial policy is described focusing on a combination of various scientific approaches, in which it is viewed from the perspective of the value chain in the context of pandemic.
Keywords: Crisisfinancial policysmall and medium-sized businesses
Introduction
The pandemic period in Russia is characterized by a prolonged recession in the real economy, a sharp decline in production efficiency, a crisis in finances, and a decline in the living standards of the majority of the population (Russian Government Analytical Centre, 2020). This data is confirmed by the consequences of the recessive period at coordinates "performance - time" which includes economic performance of various industries during the period of stagnation. This situation is also typical for other countries. Business activity indicators presented on the Trading Economics agency website confirm the slowdown all business processes in the countries with the largest economies (Trading Economics, 2020). Thus, data published for the Euro Area for the two-wave pandemic period reached its minimums for almost all performance:
1. Business confidence ranged from 1.64 to minus 3.1 at its lowest. The values for Russia are from 7 to minus 20 at their minimum.
2. Industrial production decreased from 9.7 points to minus 28.6 at its lowest. Values for Russia - from 17.7 to minus 16.9 at their minimum.
3. Sentiment Services or the Consumer Sentiment Index did not exceed minus values (11.8 - 11.2) for the most part in 2020 to a maximum of 35.40 points before the start of the pandemic, while their minimum value was minus 43.6 points . The values for Russia - from 51.1 to minus 31.3 at its minimum.
4. The Industry Sentiment Index ranged from 10.3 to minus 37.6 at its lowest. Values for Russia - from 41.9 to minus 27.0 at their minimum (Trading Economics, 2020).
Analysis of statistical data over time shows that the quarantine measures taken have caused the worst impact on the economies of all countries in the world (Trading Economics, 2020; Russian Government Analytical Centre, 2020). All minimum values for business indicators account for April - May 2020. Most international organizations estimate that Russia's economic growth will recover by 2022. The COVID-19 pandemic has become an enormous shock to the global community and has led to a sharp economic downturn. It also has reduced activity in the service sector and disrupted the production chains in countries in the world (Kolinets & Uniyat, 2020). According to the estimates of most international organizations the economy in the range 3.3 - 7.0% by the end of 2020 (Russian Government Analytical Centre, 2020). However, some organizations predict an even greater contraction of Russia`s economy by the end of this year. For example, according to the baseline scenario Russia's GDP may decrease by 8.0–8.2%, BCG predicts temporary growth of unemployment in Russia to 8.0-10.0% (Interfax, 2020). This economic downturn will be the deepest in recent years. The ongoing situation will persist for 2020. However, the duration of the crisis in business will primarily depend on the duration of the acute pandemic period. If this period extends, the adequacy of state support for companies and the population, the effectiveness of banking systems and other factors have an increasingly important role. Now countries have had to mobilize the most of their domestic resources to the maximum and the economy has become more balanced. Enterprises have to change their work format and undertake strategic development. This situation leads to deformation of financial and market-based instruments. On the one hand, financial flows are being liberalized through open economy strategies. On the other hand, the uneven distribution of financial resources and balance of payments disequilibria are stimulated and many countries experience an increasing shortage of their own resources. Outlined processes are also intensifying in Russia, but at a significantly slower pace which is due to the peculiarities of the financial policies development of enterprises in Russia and in other countries. We consider the most recent crises in Russia and, as a result, the need to develop and use effective crisis prevention efforts have had the most significant impact on the evolution of financial, economic and management tools as well as actively developing information technologies (Barashyan, 2020), which are the basis of any financial manager's tools.
Problem Statement
Against the background of rising Covid-19 pandemic an increasing number of researchers are grappling with this problem. The works published recently in the "Economics in the Time of COVID-19" book are of particular interest (Baldwin & di Mauro, 2020). A review of numerous scenarios of the public and private sectors demonstrates that the global economy will experience significantly reduced growth rates in 2021 with the reintroduction of restrictive measures (Baldwin & di Mauro, 2020). It is already noticeable that the consequences of financial shocks are accumulating. This is evidenced by changes in financial flows for 2020 (Table
Thus, unless the government takes new pre-emptive measures to support consumers and enterprise incomes to stave off growing non-payments, the recession may pose the biggest threat to the economy. Viable enterprises become illiquid and go bankrupt. We suggest that it will not be possible to overcome the crisis relying only on support measures. All the companies, regardless of their size and scope, will have to independently adapt their operational and strategic priorities. According to the authors of the study, business leaders should pay particular attention to operational priorities, including the adaptation of processes, systems and approaches, to the financial policies changes of companies. We assume that the period of companies restructuring should continue and it should affect financial policy precisely. Here, the study of the practice of overcoming crisis phenomena by companies that have maintained their positions in the market can serve as a good guideline for constructing their own economic and financial policies.
In this regard, the study of organizational and methodological aspects of building financial policies in foreign and domestic practice plays a significant role. According to Bolshakov et al. (2018) Russia already has its own extensive experience in overcoming the crisis phenomena. In globalization of economic processes business practices have been enriched by foreign methods of financial management, while companies are implementing new development strategies that are focused on years, not on a month or a quarter.
Research Questions
A large number of studies dedicated to the rationalization of schemes, algorithms, description of elements and concepts for the formation and implementation of the financial policies of companies has emerged over the past decade. In accordance with the existing practical results, approaches and the principle of scientific validity we have raised a number of challenging issues that still need to be addressed:
1. The financial crisis and the subsequent pandemic stimulate uneven distribution of financial resources and balance of payments disequilibria.
2. In order to prevent the growth of non-payments and bankruptcy the elaboration of pre-emptive actions to support consumers and business incomes imposes itself forcefully on the economies of all countries.
3. The pandemic has exacerbated issues related to the functioning of companies when temporary disruptions can have permanent consequences. The methods and financial management tools improvement is required to way out of such situations.
4. Examination and analysis of the experience of companies implementing new successful strategies for overcoming the crisis remains more relevant now. Building on this experience may help the companies management to identify the starting points for stabilization and ensuring the continuity of work and business profitability in the future.
5. To solve the identified problems we propose to use the experience already accumulated in the implementation of anti-crisis business strategies. Based on this experience, it becomes possible to model the stages of a financial policy construction that reflect practice-oriented approaches, since it is obvious that ambiguity in the composition and understanding of its new guidelines currently exists.
Purpose of the Study
In terms of the research questions posed the main goals are here to be formulated:
1. Create the author's model of financial policy improvement close to Russian reality focusing on a combination of various scientific approaches which consider financial policy from the perspective of the priority of certain strategic goals.
2. Observe the actions of a small and medium-sized enterprises by analyzing the quality of work of the elements of the value chain in the context of functioning, planning, management, development, accounting and supply and control that form the financial strategy of companies.
3. Assess the change in cash flows generated by the five surveyed companies when introducing corrective measures that affect the reduction of financial dependence, increase the efficiency of productive and economic activities in terms of the pandemics.
Research Methods
Today, the only way to understand how your business works in order to shape the financial-policy processes is to know and analyze what processes are going on inside your business and who is responsible for them. That means responsibility centres are to be allocated. In this case the value chain is the best tool for solving this task since the company's position can only be improved using subject to availability of competitive products focused on the needs of the consumer, not of the maximization of profits. According to Kuznetsova and Alekseeva, the value chain is a practical tool to assess competitiveness. Its main advantage is the generalization of the tasks facing the enterprise by the main types of activities. Thus, using this tool makes possible the impact assessment of financial, investment and operational flows on the array of financing strategies. The value chain provides the opportunity to focus on those types of activities which provide the maximum potential of the enterprise's competitiveness (Kuznetsova & Alekseeva, 2016).
In this regard improving financial policy within the elements of the value chain will lead to positive results due to the fact that:
1. The product flow becomes the basis for building a financial policy algorithm. This fact enables to focus the goals and objectives of financial analysis on the results (products, services) of processes.
2. Clarity and logic in defining financial management processes will emerge and decomposition of processes will become achievable. It is always possible to enlarge the presentation of cash flows and processes by creating a top-level diagram or, conversely, to detail the chains.
The company's finances will be considered not only to describe the work of financial services managers but also to describe cash flows that affect the execution of business processes and transform the material flow into cash. For example, the decomposition of the financial management process begins with a description of the "Planning" block, the "information on the market structure" block, the "product line creation" block. Then a more detailed division of the “Planning” block is carried out where the decomposition of the distribution of funds is provided (money is distributed among items of expenditure) in the amount necessary for full payment. Also a description of business processes for each of the blocks is conducted, up to data flows called "Registration of documentation and contracts", data storages called "Services", "Agreement", "Client" can be shown, as well as an external link "Information about the agreement. In this case the estimated indicators of financial policy can be the rate of production, the volume of procurement of supplies, planned production; the rate of products sales by each outlet; the volume of salaries of administrative and management staff, production departments and services; the amount of delay in transferring money to the account; delayed issuance of salary, the actual amount of required funds in the company's account, etc.
According to research companies, after automating processes related to the creation of the value chain, which comes to the fore in the conditions of remote forms of work, they receive such competitive advantages as (Bolshakov et al., 2018): a 20 – 40% reduction in the cost and time of order processing; a 5 – 15% reduction in purchasing costs; a 15 – 30% reduction in time of market entry; a 20 – 40% reduction in warehouse inventory; a 5 – 15% reduction in production costs; the total income of the company increases by 5-15%. The values of each economic entity are unique and are related to the definitions of key processes in the business (Figure
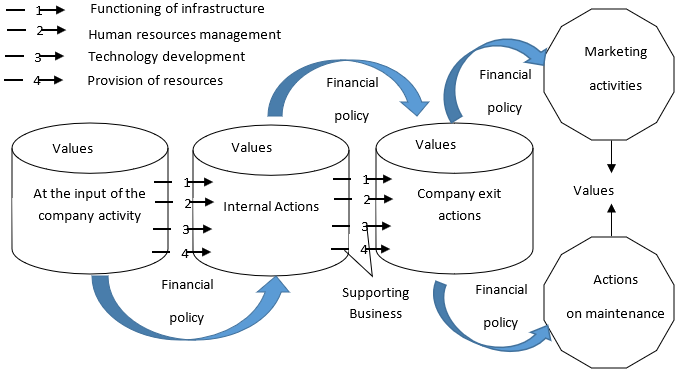
The core activities of any company include: actions at the entrance (necessary when receiving, storing and distributing raw materials); actions inside (necessary when producing finished products and services, i.e. transforming of raw materials, supplies, components, services); actions at the exit (necessary when organizing the sale of products, services, storage); marketing actions (necessary to stimulate customers, form sales channels and inform consumers about the company's product); maintenance actions (characterize after-sales service of the product, services to maintain its working condition). Financial policy refers to ancillary types as it describes the financial actions required to meet general requests; actions necessary for development, remuneration, disciplinary measures application and dismissal; actions in the forms of updating, selling, purchasing equipment, software and processes; actions required to purchase raw materials needed for all core activities. It is important to note that the decision should be made basing on two components. The first component is to satisfy the financial status and the second one is to draw up a business plan for each decision with a justification of its economic efficiency for the company. Namely the business plan includes the synthesis of all the elements: marketing, production, logistics. It also prescribes institutional and management aspects, all the components are justified and confirmed by the results of the analysis carried out for a specific managerial decision. As a result, a business plan makes it possible to economically justify decisions and create the necessary set of financial strategy scenarios.
The examination of the organizational and methodological aspects of the entire range of financial policy models demonstrates that the most common one is a model based on a description of the processes related to the management of property (assets) and capital (liabilities). The central in the structure is the balance sheet of the company and the tasks of its improvement are to eliminate shortcomings in the existing system of its financial management. In terms of the pandemics we considered it possible to use the obtained operational data on the situation in companies to increase the degree of validity. The survey used data gained from five enterprises related to the category of small business. To evaluate the effect obtained from the implementation of business ideas aimed at adjusting the existing financial policy in the context of the ongoing pandemic, we applied the methodology for calculating the indicator that characterizes the profitability of the enterprise, the result of its work (EBITDA). This indicator appears in the calculations of a large number of qualitative indicators and has long been used in foreign and Russian methods for calculating efficiency. The projected income values were calculated using the revenue planning method based on the calculation of the profitability threshold. When forming expenses, it was taken into account that the change in variable costs occurred proportionally depending on the ratio of changes in costs and volume of production.
Findings
Monitoring the external environment and system analysis of signals indicating possible changes in the state of the organization demonstrated the existence of threats to the company`s activities but it is possible to avoid bankruptcy and stay afloat under the condition of taking right management decisions. A list of business ideas implemented by companies during the period from January to October 2020 is provided in Table
Studying and analyzing the experience of the companies presented in the table, implementing new strategies for overcoming the crisis, which helped the management to stay afloat without considerable losses, made it possible to identify the starting points for stabilizing and ensuring business continuity. Almost all of the listed companies switched to work with remote trading platforms, in particular «Accept» and «SLT AQUA» undertook work to update the existing websites. Thus, according to the director of «Bergner», the implementation of a flexible discount system and lending policy for customers became the main link in the developed crisis preventing financial strategy.
All company executives believe that despite the measures taken, their business suffered significant losses, most of which accounted for the "quarantine vacations". As a result of the emerged diagnostics it is proposed to adjust the financial policy in the framework of two main directions: the first business idea is to reduce financial dependence on borrowed capital (increase the level of financial security of the enterprise); the second business idea is to increase the efficiency of production activities and business operations through the formation of additional competitive advantages. In this case, we suggest a business idea as a set of measures aimed at implementing a strategy to limit the growth. Issues related to the methodological side of assessing the parameters of the limited growth strategy are planned to be covered in greater detail during the next research. Among the targets the most noteworthy are the following: maintaining the required level of financial security of the enterprise; ensuring the specified totals of income and profit; ensuring the stability of cash flows; efficient use of financial resources.
Significant deviations in profit (EBITDA) values were revealed while comparing the data collected in the areas of company diagnostics (Table
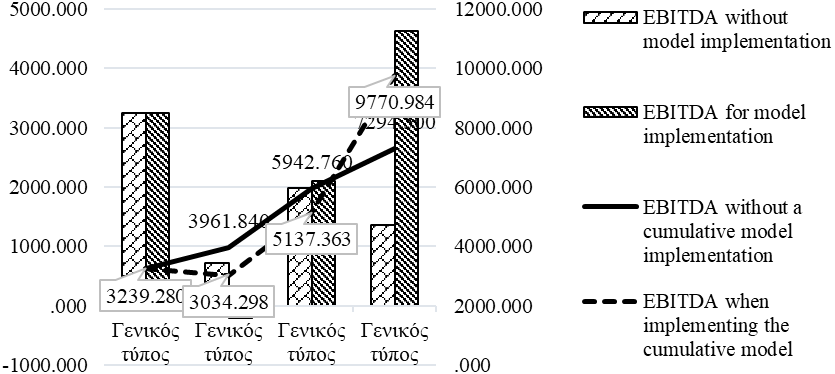
The chart demonstrates that with the same initial result of 3239, 28 thousand rubles’ profit when implementing improving financial policies within the value chain leads to positive outcomes. On an accrual basis EBITDA increased to 9,770.98 thousand rubles and without the implementation of corrective measures it accounts for only 4055, 22 thousand rubles and amounts to 7294.5 thousand rubles. Thus, we believe modeling the financial policy of an organization allows to achieve an optimal ratio of the capital structure and the potential for maneuvering a company in an aggressive business environment.
Conclusion
In accordance with the existing practical experience, approaches and the principle of scientific validity, the author of the work has compiled the own Russian conceptual model of the financial policy of the enterprise. In our opinion, it will be correct to indicate that the financial strategy is formed within the framework of the general financial policy of the enterprise, since enterprise practice very often does not include a financial strategy in general and any strategy is absent as such in particular. At the same time the existence of a financial policy is approved at the legislative level of the Russian Federation. The determination of the features and the development issues of the Russian model of financial policy was carried out by examining of the chronology and causes of crises in Russia from 2018 to the present day. The place of financial policy in the company's value chain is revealed. Financial policy refers to ancillary activities as it describes the financial actions necessary to meet general requests; actions necessary to develop, remunerate, initiate disciplinary proceedings and dismissal; responses to initiate renewal, sale, purchase of equipment, software and processes. The priorities and development goals are revealed in two directions: the goals of financial policy within the elements of the value chain; the relationship between the goals of financial policy and priorities in the financial strategy of the enterprise. The assessment of the effectiveness of changes in the financial functional ties of companies was undertaken on the basis of the indicator (EBITDA) and the obtained forecast values prove the effectiveness of the business provided that the financial policy model is implemented within the elements of the value chain. Therefore, with the purpose for the company's management of adequately and actively responding to changes in external and internal factors, it seems appropriate to implement the developed model of the company's financial policy within the elements of the value chain as a method of strategic planning and development of its own financial strategy, which may reduce the consequences of the general decline in production when not bringing the company to bankruptcy.
References
- Baldwin, R., & di Mauro, B.W. (Eds.) (2020). Economics in the time of COVID-19. https://cepr.org/sites/default/files/news/COVID-19.pdf
- Bank of Russia (2020). Monitoring of industry financial flows. https://cbr.ru/Collection/Collection/File/29417/finflows_20201105.pdf
- Barashyan, V. Yu. (2020). Anti-crisis financial strategy as an effective tool for anti-crisis financial management of entrepreneurial structures in conditions of instability of the business environment. Financial Economy, 8, 260-263.
- Bolshakov, S. V., Bulava, I. V., Germogentova, M. N., Lakhmetkina, N. I., Mingaliyev, K. N., Setchenkova, L. A., Slepneva, T. A., Shokhin, E. I., & Talimova, L.A. (2018). Corporate finance and business management: Monograph. KnoRus.
- Interfax (2020). BCG experts predict a temporary increase in unemployment in the Russian Federation to 10%. https://www.interfax.ru/business/710800
- Kolinets, L., & Uniyat, A. (2020) Crisis measures to ensure the stability of the country financial system. Sciences of Europe, 48-3(48), 59-63.
- Kuznetsova, N. V., & Alekseeva, E. A. (2016). M. Porter value chain as part of an assessment of the competitiveness of metallurgical enterprises. Young Scientist, 27(131), 418-423.
- Russian Government Analytical Centre (2020). Bulletins on the current trends in the Russian economy. Ecology and economics: The trend towards decarbonisation. https://ac.gov.ru/uploads/2-Publications/BRE/_%D0%BE%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%8F%D0%B1%D1%80%D1%8C_web.pdf
- Trading Economics (2020). Euro area-Business confidence. https://ru.tradingeconomics.com/euro-area/business-confidence.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Savoskina, E. V., Kosyakova, I. V., & Solopova, N. A. (2021). New Guidelines For Solving Problems Facing Russian Business. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 411-420). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.50

