Abstract
Russia is one of the largest producers of natural gas in the world. The article considers the prospects of the natural gas world market, taking into account the interests of Russia's economic development. The short-term prospects for shale gas production in the North American market are so that it will reach its limit in the next 10 years. Russia produces 17.2 % of the world's natural gas. In 2019, according to OPEC data, Russia produced 703.8 billion m3 of gas, the world's second largest gas producer. There is a fundamental restructuring of the general environment in which the gas industry operates, and the gas industries themselves are being restructured in accordance with the principles and practices of a market economy. The authors' argument is based on such methodological principles and methods as the principle of duality of the economic nature of economic entities, methods of system and institutional analysis. The authors consider the issues of economic security as a complex problem which determines the overall security of the state. On this basis, the article analyzes the current state of the world's natural gas resources and their macro-regional features in the context of maintaining and developing the Russia's economic security. The author's understanding of the perspective directions of the gas market development is offered. The authors see the Russia's prospects in the global natural gas market as stable and positive ones.
Keywords: Economic securityglobal natural gas resourcesmacro-regional features of the gas marketprospects of the natural gas market in the world
Introduction
Building the capacity in producing countries to effectively address a wide range of environmental issues related to the gas industry is important. Gas is determined as the most environmentally friendly fuel. Condensed natural gas (CNG) is gradually gaining an increasing share in global gas trade, especially in Asia. The share of CNG trade in total gas trade is projected to grow to almost 40% in 2023. By 2023, emerging Asian markets will account for about half of the world's CNG import (Zaitseva, 2016). The Asian gas market is expected to see the largest growth in export volumes. Meanwhile, even in the developed countries, such as Japan and Korea, the share of gas in the energy structure is only 15-20% and there are good prospects for replacing oil and coal with gas. In the most populous countries of the world (China and India), the share of gas in the energy balance is only 6-8%. It should be noted that these countries are quite rational about the use of natural gas to solve their environmental problems.
Problem Statement
There is a fundamental restructuring of the general environment in which the gas industry operates, and the gas industries themselves are being restructured in accordance with the principles and practices of a market economy. Gas relations between the EU (European Union) and Russia have become more predictable thanks to the resolution of long-standing commercial disputes. The main import partners of our country in Western Europe increase their energy purchases from Russia and seem to be interested in further economic cooperation in this field.
Considering the impact of Western sanctions on the Russian oil and gas sector, in our opinion, we need to take into account two points. Firstly, the effect of sanctions is zero, and even more, the sanctions have stimulated import substitution and the development of domestic technologies (Tele Trade, 2017). Secondly, sanctions lead to negative consequences, which can be manifested due to the high level of dependence of the sector on foreign finances and technologies (Dulaev, 2015). Gazprom controls 35% of the gas market in Europe, more than any other supplier, and aims to increase its share to 40% due to reduced European production and lower gas production costs in Russia. Russia may double its gas exports by 2030 to meet growing global demand (Reuters, 2018).
Research Questions
It is necessary to analyse the macro-regional features of the global natural gas resources. Consider promising areas of the gas market development. Develop recommendations for effective development of Russia's foreign economic cooperation in the gas sector. Active international cooperation is necessary. It is possible through the merger of international capital for the exploration and development of new fields, the construction of new transport infrastructure. Russia must find new target markets for its gas. A solution must also be found to transform Russia's export energy infrastructure. One possible solution is to convert natural gas into CNG and export it by tankers, potentially opening up the entire global market for Russia.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is related to the considered research questions. The authors aim to offer their understanding of the prospects for Russia's development on the global natural gas market. They are presented to the authors as stable and positive, meeting the interests of ensuring and developing Russia's economic security. Russia's international energy cooperation in the gas sector may have several positive effects. Energy cooperation will improve the fiscal and budgetary position of the Federal government and help the national economy recover faster. Some regions of Russia have not been centers of economic growth for a long time, for example Eastern Siberia and the Far East, and cooperation in the field of energy and pipeline construction in these regions increases the number of jobs and economic prosperity of the local population. It is possible that Japan and the Republic of Korea will participate in energy cooperation with our country. India is a major energy importer with ever-increasing demand. Russia is a key global producer and exporter of oil and natural gas. The needs of the two countries naturally complement each other. Currently, bilateral energy cooperation can significantly expand and switch to new sources (for example, CNG).
Research Methods
The authors' argument is based on the methodological principles of duality of the economic nature of economic entities. Methods of comparative analysis, system and institutional analysis, economic and statistical method are used in this study. The economic security is not seen as an independent problem, but as a complex phenomenon. This is the basis for analysing the current state of the world's natural gas resources and their macro-regional features. The analysis is carried out in the context of maintaining and developing Russia's economic security. The article presents authors’ understanding of the perspective directions of the gas market. The article analyses the prospects for strengthening Russia's positions on the global natural gas market. Recommendations for developing cooperation in the energy sector are given.
Findings
Domestic production has not yet reached the goals set by the state, given the slow pace of development of the schistose industry. Gas prices also remain cumbersome, as they are carefully regulated in China. Unlike China, India's gas consumption has been declining since 2010. Despite the fact that by 2019 it has recovered to 58 billion м³ and consumption growth rates are still far from expected (Snam, IGU & BCG, 2019). The main barrier to growth was the regulated price structure, which limits the availability of domestic supply. Due to the reduced availability of cheap domestic gas, consumption in India has become dependent on more expensive CNG imports over this period. This led to a significant discrepancy in domestic prices depending on the source of supply.
This discrepancy was supported by a regulated pricing structure that provided preferential access to domestically produced gas to users of "urban gas distribution" (residential, commercial and transport sectors), while electricity generation and other sectors were exposed to CNG based on its high price. Until recently, the availability of gas on the North American market was supported by schistose production (Tirole, 2017).
The short-term prospects for shale gas production in the North American market show that it will reach its limit in the next 10 years. This may lead to a market fluctuation between the focus on providing gas resources for its own needs and the further possibility of exporting gas and coal.
Let us take a closer look at the European gas market, which remains the main gas export market for Russia in the long term. The problems of the European energy market are becoming even more complex due to the destructive influence of certain European norms (Motyashov, 2017).
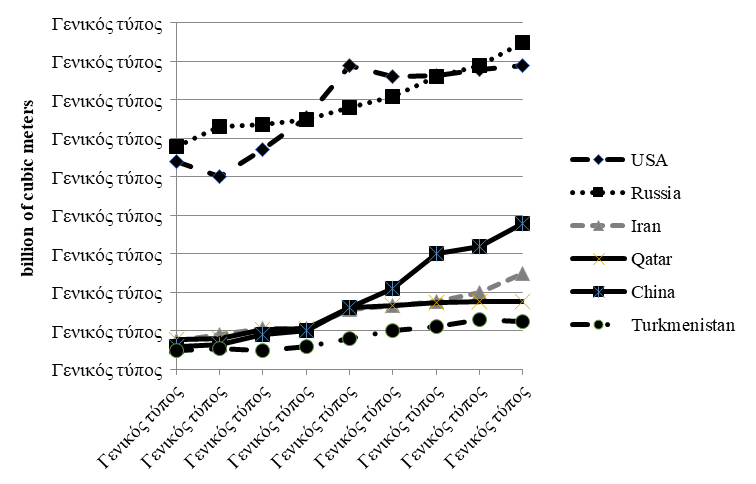
Source: authors based on (Makarov et al., 2016).
In the future, for the period up to 2040, according to experts, there will not be any significant changes in the group of major gas producers (Figure
The Yamal peninsula in Northern Siberia has the largest reserves of natural gas in the world – around Urengoy and Yamburg, to the East of the Gulf of Ob, and the world's largest gas field is located in Novy Urengoy. The estimated final production is 285 trillion м³. At the same time, gas production on the Yamal peninsula under the permafrost surface can be quite expensive (Murtazina, 2019). Buildings are built on stilts, and roads on several meters of gravel thickness. Gazprom currently dominates (almost three-quarters) in the Russian natural gas production sector. Despite the fact that oil producers such as OJSC NOVATEK and PJSC LUKOIL have become very important for Russia, production opportunities are still quite limited for independent producers. In addition, Gazprom's dominant position in oil production is enhanced.
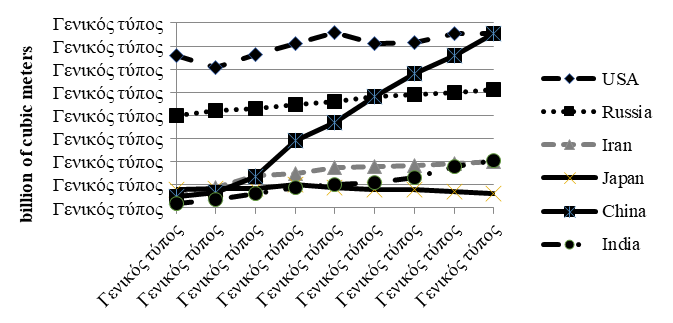
Source: authors based on (Makarov et al., 2016).
A number of initiatives and policies of the Russian government set goals to reduce the routine burning of associated gas. Little progress has been made in reducing conventional gas flaring in Russia. Russia produces 17.2 % of the world's natural gas. In 2019, according to OPEC data, Russia produced 703.8 billion м³ of gas, after the United States (Figure
Cooperation in new areas (natural gas mobility, CNG, financial energy markets, renewable energy sources) can significantly contribute to the Russia-India partnership. Indian oil companies have several investments in Russian oil fields -investments exceed $ 10 billion. For India, CNG is the only viable way to import natural gas. India has four operational CNG import terminals and more than nine in the development. These terminals can be a place for gas export from Russia. For Russian companies, the alliance with partners from India will open new markets in South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Africa.
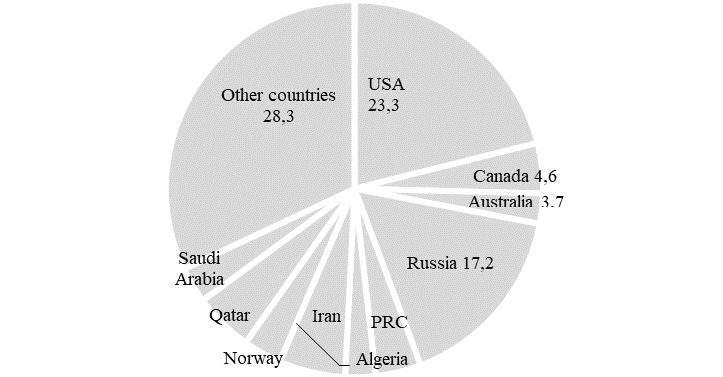
Source: authors based on (OPEC, 2020).
The growing share of gas reserves is difficult to restore (Aleshkova et al., 2021; Gordeeva & Antipina, 2021). The Russian Federation may keep such a production level through deeper development of existing oil wells using some intensification techniques (such as hydraulic fracturing) and development of unconventional oil reserves onshore (Western Siberia) or offshore (including the Arctic) (Mitrova, 2018).
The situation with gas export may also be more difficult. Russia hardly will be able to increase the gas transit to Europe in the near future because of the lack in the increased demand, but the country is oriented to China as a partner in this context and it still has the post-Soviet market for export. Russia can replace unavailable technologies with its own means. The development comes despite repeated calls from the US to Europe to diversify its gas import from the pipeline monopoly "Gazprom", which, according to Washington, uses energy as a tool of intimidation.
Conclusion
Natural gas pipelines are currently in high demand. The first place in the world for pipeline gas transportation is occupied by Russia, which has the world's largest gas pipeline system. Its length is 160.4 thousand km. The largest gas pipelines in Russia: "Urengoy-Pomary-Uzhgorod". Their length is 4451 km, "Soyuz" is 2750 km, "Yamal-Europe" is 2000 km, and «Nord stream" is 1224 km. СNG has great prospects due to its convenient storage and transportation, non-toxicity, and the possibility of Intercontinental transportation by special gas tankers. Main СNG exporters: Qatar is 106.4 billion m3, Australia is 39.8 billion m3, Malaysia is 34.2 billion m3, Nigeria is 27.5 billion m3, and Indonesia is 21.9 billion m3. The main CNG importers are Japan (118 billion m3), Korea (43.7 billion m3), China (26.2 billion m3), India (21.7 billion m3), and Taiwan (18.7 billion m3). Russia's CNG market has only just begun to develop. Projects such as Yamal CNG, Pechora CNG, a joint project of Rosneft and Exxon Mobile on Sakhalin, Vladivostok CNG, and Baltic CNG should be implemented.
In 2019, gas production and export broke record levels. The Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug stands out from all regions in gas production. In 2019, 502.3 billion cubic meters of gas were produced there. The leader in the production of gas is a public joint-stock company "Gazprom". In 2019, they produced 471 billion cubic meters of gas, 12.4% more than in 2018. The main part of export falls on European countries, such as the "Powers of Siberia", "Turkish stream", and "Nord stream 2", shows that Russia can and is ready to export gas to any place of the world. Gazprom plans to increase gas production to 483 billion m3. Gas production and export will increase. «Novatek» company, which launched the "Yamal SG" project, can successfully compete with the global СNG producer due to the low operating costs. New CNG plants will be opened in Russia in the near future.
References
- Aleshkova, D. V., Shepelev, A. V., & Salikhov, K. M. (2021). Innovative methods of managing the company’s financial results. In S. Ashmarina, V. Mantulenko, & M. Vochozka (Eds.), Engineering Economics: Decisions and Solutions from Eurasian Perspective. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 139 (pp. 649-658). Springer.
- Dulaev, M. H. (2015). Export of gas and oil to the Russian Federation under sanctions. Young Scientist, 24(104), 428-430.
- Gordeeva, E. S., & Antipina, Z. P. (2021). Business group contradictions as a factor of integration into the global economy. In S. Ashmarina, V. Mantulenko, & M. Vochozka (Eds.), Engineering Economics: Decisions and Solutions from Eurasian Perspective. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 139 (pp. 253-261). Springer.
- Makarov, A. A., Mitrova, T. A., Kulagin, V. A., Melnikova, S. I., & Galkina, A. A. (2016). Global gas horizons until 2040. Gas Business, 3, 21-28.
- Mitrova, T. (2018). Western sanctions on Russia’s oil and gas sector: A damage assessment. https://carnegie.ru/commentary/76909
- Motyashov, V. P. (2017). Gas and geopolitics: The chance for Russia. Lenand.
- Murtazina, S. (2019). By the road of development and partnership. Yamal Meridian, 5, 18-19.
- OPEC (2020). OPEC annual statistical bulletin 2020. https://asb.opec.org/
- Reuters (2018). In terms of sanctions, Russia sets the records on the gas export. https://www.golos-ameriki.ru/a/russia-sets-records-in-gas-pipeline-exports/4599288.html
- Snam, IGU, & BCG (2019). Global gas report 2019. http://www.snam.it/export/sites/snam-rp/repository/file/gas_naturale/global-gas-report/global_gas_report_2019.pdf
- TeleTrade (2017). European gas market: Sanctions and confrontation between Russia and the United States. http://investfuture.ru/articles/id/evropeyskiy-rynok-gaza-sankcii-i-protivostoyanie-rossii-i-ssha
- Tirole, J. (2019). Economics for the common good. Princeton University Press.
- Zaitseva, E. V. (2016). Sanction on sanction: Bans imposed by Russia and the West, the impact on the further development of the Russian Federation. Young Scientist, 2(106), 493-49
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Noskov, V. A., & Nesterov, O. V. (2021). Global Natural Gas Market And Economic Security Of Russia. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1642-1648). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.196

