Abstract
Digital organization and the work of HR management are considered in the context of the stakeholder approach. The number of active subjects of social action, whose interests should be taken into account and with which the HR service should interact, in the process of achieving the company's sustainable development goals, increases significantly. HR specialists have new functions that are related to the implementation of corporate social responsibility and sustainable development policies by companies. The article systematizes new methods for evaluating the work of HR management in the context of digital transformation of companies, taking into account the increased requirements for socially responsible policy. Along with financial indicators, the role of non-financial indicators should be increased to assess the performance of HR departments in the context of the transition to intelligent platforms. The results of the original author's sociological survey showed the understanding of HR specialists of the increasing role of stakeholders in the development of companies; insufficient willingness of HR specialists to take into account the opinion of stakeholders when assessing the effectiveness of the work done by HR departments to automate their functionality and integration into the company's digital processes. The assessment of the HR service by all categories of stakeholders, calculated on the basis of surveys, can potentially become a promising non-financial indicator for evaluating the performance of the company's HR management
Keywords: Digitalizationdigital organizationhuman resources managementstakeholderssustainable development
Introduction
Digital transformation of companies has become a significant trend that changes the architecture of the modern economy. Digital transformation refers to the use of modern technologies to increase the productivity and value of enterprises (Capgemini Consulting, 2011). Digital transformation of a company is a long process, the result of which should be the creation of a "digital organization".
The scientific community has not yet formed a clear definition of the term "digital organization". Some authors understand a digital organization as an organization in which most of the processes are performed automatically, without human participation. In this article the greatest value in understanding digital organizations are not digital technologies used by companies in the process of digital transformation, but how they affect organizational processes lead to the emergence of new HR-functions, how it affects the assessment of the effectiveness of HR-units and interaction between stakeholders. Therefore, the following definitions of a digital organization are closer to us:
- this is a company that uses digital tools, technologies, and ecosystems to deliver greater value to employees, shareholders, customers, and other stakeholders, usually through new experiences, solutions, and business models;
- the key components of digital organization are digital tools, technologies and ecosystems that are used by employees, shareholders, customers and partners, and other stakeholders to interact with the organization (Maramygin et al., 2019).
New challenges have accelerated the transition to digital formats of work. According to various experts, by 2022 up to 50% of office employees of companies could work from home (Ivanova et al., 2020). However, with the rapid spread of the COVID-19 coronavirus infection and the announcement of a pandemic, many companies had to urgently rebuild and apply digital technologies to a much larger extent in order to ensure the effective work of employees in remote mode. Digitalization is not only about digital technologies, it involves the transition to new business models and organizational changes.
The modern search for organizational innovations, optimal forms of combining social and economic aspects of interaction in the process of creating new value is due not only to the transformation of traditional organizations into digital ones, but also to another significant trend - the orientation of the international business community towards the implementation of the sustainable development goals. At the world economic forum in Davos in January 2020, the need to move from shareholder capitalism to stakeholder capitalism was declared as the manifesto of the year (Schwab, 2020). At the corporation level, this means paying more attention to the interests and expectations of all stakeholders. According to the sustainable development goals developed by the UN member states, in modern conditions, the activities of companies should be evaluated according to the triple total method: economic, environmental and social. For companies, this means shifting the focus from the economic result to the social result and socially significant goals, which, of course, increases the influence of HR departments on the restructuring of all business processes in the context of the company's implementation of sustainable development goals (Bataeva, 2018).
In recent years, there has been a significant shift in understanding the role of the employee in the company. This is due to new management trends in the ХХI century, which is called the century of humanistic, social, reflexive, solidary management (Kleiner, 2018). The humanistic approach reflects the search for the most optimal combination of social and economic aspects of management. Changes in business rethinking have led to an awareness of the need to move from meeting the interests of stakeholders (management of stakeholders), and often manipulating them, to stakeholders management. In the context of digital transformation, the role of employees in business development is increasing. Previously, according to the Mitchell classification, stakeholders were classified as a "dependent" group (Karpus, 2009). In total, the Mitchell model presents 7 categories: categorical, dominant, dangerous, dependent, inactive, controlled and demanding (Mitchell et al., 1997). Currently, in our opinion, employees in organizations of economy 4.0 are moving to the "categorical" group, along with shareholders.
The stakeholder approach in terms of socially significant consequences for the company has been studied in recent years by Russian scientists (Tkachenko et al., 2020). The research raises, for example, such a socially significant question: how can automation help to make the remuneration of employees more objective, and therefore more socially fair (Ivanova et al., 2019).
In general, the transforming human resource management system can be represented as a relationship of processes aimed at sustainable development of companies, reaching agreement not only between the company's owners and employees, but also all stakeholders, including internal (staff) and external (consumers) customers. If the staff management subject of the organization remains unchanged – HR-experts, human resources management service, then the number of objects, acting in turn as active subjects of social action, whose interests should be taken into account and with which HR service should cooperate has increased considerably.
Ensuring that the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the personnel correspond to the strategic goals of the organization remains the defining direction of the HR service's work. Among the new areas of human resource management activities are the development of value promotion and promotion of the company's HR brand, communicating the company's values to all stakeholders, preparing employees for digitalization, automating the functions of the HR service itself, etc. All this complicates the process of evaluating the performance of the HR management service and forces to look for new criteria for this assessment. The development of the theory of stakeholders allowed not only to form more clearly the principles of interaction of the company with stakeholders, including employees, but also influenced the methods of evaluating the effectiveness of HR services, and was reflected in the adoption of programs and indices for assessing corporate social responsibility (CSR). At the same time, other criteria for evaluating the work carried out by HR services are emerging and actively developing.
It is very important to identify indicators that should be used to assess the performance of HR departments in automating their own functions, as well as to assess their contribution to the digital transformation of the company (Osipova, 2019). The share of scientific studies devoted to the study of the integrated assessment of the efficiency of the HR service is not significant. Studies in the field of human resource management shows that organizations are mainly focused on using financial performance indicators to assess the effectiveness of human resource management initiatives (Simarova et al., 2015). A number of foreign researchers are trying to expand the range of non-financial criteria for evaluating the work of HR departments, including in the context of the stakeholder approach. We consider it necessary to pay attention to the work of Ferrary, which not only emphasizes that the stakeholder approach to management in companies requires changing the ways of measuring the effectiveness of the HR service, but also presents the results of an original empirical study (Ferrary, 2008). A model for evaluating stakeholders in personnel training projects is proposed in (Erina et al., 2015) studies. Research on the possibility of using a stakeholder approach to improve the assessment of the effectiveness of the HR service for digital transformation of the company is currently absent in the Russian scientific literature.
Problem Statement
Employees are the primary stakeholders of the organization and its direct beneficiaries, as opposed to secondary stakeholders – local communities, customers, etc. Employees can join unions to justify the legitimacy of their expectations and actions, and to defend their interests in a particular organization. In the context of digital technologies and the speed of information dissemination via the Internet, the possibility of strikes, protests and damage to the company by disgruntled employees increases. Any transformation of the organization, including digital, can potentially cause rejection and resistance. Therefore, one of the central tasks in the work of HR services in recent years has become not only the automation of its own functionality, but also the training of personnel to work in the conditions of digital transformation. All stakeholders are interested in the effectiveness of this work. However, there are no studies that would study 1) the degree of understanding by Russian HR specialists of the increasing role of all stakeholders in improving the sustainable development of the company; 2) the readiness of HR managers to control the results of their work from the stakeholders.
Research Questions
All organizations are faced with the need to determine the quality of the functions performed by the personnel management service of the organization, the level of its effectiveness. How did the focus of business on the sustainable development of companies through strengthening the interaction of all stakeholders affect the system for evaluating the work of HR management? One of the most urgent tasks of the HR service at present is to prepare employees for digitalization and automate their own HR processes. What place in the system of evaluating the performance of HR departments on digitalization, in the opinion of HR specialists themselves, can the opinion of stakeholders take; what is the readiness of HR specialists to take their opinion into account when evaluating the performance of their work? Should the competence model of HR specialists include a new competence – the ability to work with stakeholders and organize their interaction?
Purpose of the Study
This study is based on the consideration of the essence of the digital organization, its features. In addition, the conceptual framework of the study is the concept of stakeholders. The authors consider and substantiate the hypothesis that in the conditions of a digital organization, the role of stakeholders-employees increases. According to the authors, employees in a digital organization are the same "categorical" group of stakeholders, as shareholders in a corporation (whereas previously they were more often referred to as a "dependent" group of stakeholders). Increasing the importance of employees determines changes in the working methods of HR services of digital organizations.
The purpose of the study is to substantiate the feasibility of using the integrated opinion of stakeholders as one of the criteria for evaluating the work of the HR service.
Task 1. To summarize the new methods of personnel management and evaluation used by HR services in the context of digital transformation, taking into account the increasing attention of companies to the role of employees as "categorical" stakeholders.
Task 2. To determine the readiness of HR specialists to take into account the opinion of stakeholders when evaluating the performance of HR management.
Research Methods
As part of the implementation of the RFBR (The Russian Foundation for Basic Research) project "Conceptual foundations for the functioning of the organization's human resource management system in the digital economy", a survey of employees of HR services of Russian companies was conducted in June 2019. The questionnaire consisted of 5 blocks. This article analyzes the results of one of the questionnaire blocks. Research questions were related to the effectiveness of integrating digital technologies into HR processes, as well as identifying the methods used to assess the effectiveness of the HR service. The survey was conducted in a remote format using the GoogleDocs form editor. The obtained data were processed using the Excel program. 152 experts from 20 regions of Russia took part in the survey. A quarter of the surveyed companies represented the sector, including such highly digitalized industries as banking and finance; media and e-commerce, IT and telecommunications; every third - transport, logistics and distribution. Almost a third (29%) of the respondents represented organizations with more than 10,000 employees, and every fourth – from 1 thousand to 10 thousand employees. Such large organizations are expected to be the most automated. Description of respondents: 64.05% of respondents work in departments called "Personnel management (department, directorate)", 11.76% – "Personnel department", 8.5% – "Human resources management". In accordance with the official affiliation, 68.42% of the respondents were HR managers, heads of HR departments, 24.34% were HR partners, HR directors-7.24%. By gender, the respondents were distributed as follows: women-74.34%, men-25.66%.
The average age of the respondents was 35 years, which generally corresponds to the all-Russian indicators of the age of HR specialists. The vast majority of respondents have higher education 92.76%, secondary special and academic degrees of 1.97% and 3.95%, respectively. 36.18% of respondents had a total work experience in the service providing personnel management processes of 3 to 10 years, 26.32% of respondents had more than 10 years of experience, 23.03% - from 1 to 3 years. The group of HR employees with experience up to 1 year was 14.47%. This article uses only some of the results of a survey of HR managers of Russian organizations.
Findings
Task 1. To summarize the new methods of personnel management and evaluation used by HR services in the context of digital transformation, taking into account the increased attention to the role of employees as "categorical" stakeholders. HR services become agents and providers of the company's goals in the field of corporate social responsibility and the perception of the company as a socially responsible employer on the part of society depends on their work. The HR service functionality associated with the organization of projects and programs aimed at employees not only allows to attract talented personnel, reduces staff turnover, increases staff productivity, but also indirectly affects the value of the company, increasing its reputation as a responsible company in the eyes of shareholders, investors and society as a whole. Currently, along with the main methods of evaluating the work of HR services, such as expert evaluation; evaluation of the return on investment in personnel (ROI methodology), methods based on key performance indicators (KPI); satisfaction Index (loyalty) analysis of the functioning of human resources (Human Resources Accounting); social audit of personnel, labor relations, etc. are actively developing. New methods of assessment are due to the popularity of the concepts of corporate social responsibility and sustainable development, the spread of the practice of publishing non-financial reports by large companies in the world and in Russia. As a result, much attention from external stakeholders and investors is paid to employee engagement, the index of social investments and programs in relation to personnel, which shows the amount of the company's expenditures on social projects and programs per employee (Table
Automation of the main business processes potentially allows to fully apply the listed methods of assessment, both already classic and new, since operational data collection, often in real time, makes the assessment process more operational, objective and accurate. Therefore, in their work, HR departments pay considerable attention to the integration of digital technologies into HR processes, automation of their managerial functions (Osipova, 2019). This is confirmed not only by the results of our survey, but also by the data of a survey of HR specialists conducted by Coleman Services Russia in 2019, according to which 63% of respondents said that automation of the work of HR specialists is a priority one (Coleman Services, 2019).
Task 2. To determine the readiness of HR specialists to take into account the opinion of stakeholders when evaluating the performance of HR management. Since the importance of automation processes for the successful transformation of organizations from classical to digital is especially great, it was necessary to find out whether HR specialists are ready to take into account the opinion of stakeholders when assessing the effectiveness of their work in the field of HR-digital, and how such a criterion is important for evaluating their work for them.
We put forward a hypothesis: for HR specialists, the opinion of stakeholders is as important as the opinion of experts in assessing the effectiveness of their work.
To test the hypothesis, respondents were offered a choice of possible methods for evaluating their work on integrating digital technologies into HR processes (the choice was limited to no more than 6 indicators). The answers to the question of what should be the key indicators for evaluating the effectiveness of integrating digital technologies into HR processes are presented in Figure
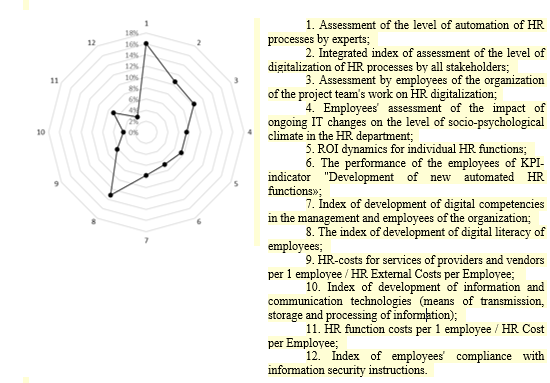
Source: authors.
As follows from the data in Figure
The survey showed insufficient attention of HR specialists to the issues of interaction with stakeholders. To the question "How will the transition from a traditional to a digital organization affect the work of HR managers?" only 12.5% of respondents said that the range of interaction between HR managers and stakeholders will expand. In other words, while a small proportion of HR employees are aware of the increasing importance of different categories of stakeholders and their right to participate in the assessment of the quality of their tasks performed by the HR service.
Conclusion
As part of the company's CSR activities, employee programs and projects are an important indicator of the company's social responsibility. Among the new methods of personnel management and evaluation used by HR services, the social investment index, which shows the size of the company's expenditures on social projects and programs per employee, the OKR (objects and Key Results) management methodology, methods for evaluating the effectiveness of remote work of employees, etc., is increasingly taking place. Automation of key business processes will allow organizations to fully apply these assessment methods as they grow in digital maturity, as rapid data collection, often in real time, makes the assessment process more efficient, objective and accurate.
Digitalization of the company today implies not only the digitalization of the labor activity of a particular employee, but also the integration of each stakeholder into the modern digital ecosystem. Therefore, it is extremely important to maintain the competitiveness of companies not only the presence of digital platforms themselves, but also the work of HR departments in preparing a number of categories of stakeholders to work on these platforms, the organization of their interaction on a fundamentally new technological basis. So far, only one of the five HR specialists believes that the opinion of stakeholders is a significant indicator of evaluating the integration of digital technologies into HR processes. The willingness of HR specialists to take into account the opinion of stakeholders when assessing the effectiveness of the work done by HR departments to automate their functionality and integratedness into the company's digital processes indicates an increase in their understanding of the importance of the stakeholder approach in implementing the company's sustainable development goal. It is necessary to put a new competence in the model of competencies of HR specialists – the ability to work with stakeholders, organize their interaction, including on the basis of high-tech platforms. Integrated assessment of the work of the HR service by all categories of stakeholders can potentially become a promising non-financial criterion for evaluating the effectiveness of the company's HR management.
The main task of the survey was to study the degree of maturity of the digital transformation of HR departments, to understand the readiness of HR specialists to work in a digital format and to find out what competencies will be required in the future. There were few questions directly related to working with stakeholders. At the same time, the necessary data were obtained to solve the research tasks set out in this article. In the future, it is advisable to conduct a special study on:
- the work of HR services to improve work with stakeholders;
- assessment of the weight of each group of stakeholders in the integrated indicator for evaluating the work of HR services.
The analysis of the development of the concept of stakeholders and the original sociological survey allowed us to take a fresh look at the possibility of including stakeholder surveys in the methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of HR services. International experience shows that establishing communication between stakeholders and, above all, with internal and external clients, will be one of the defining trends in modern conditions. Therefore, Russian companies and scientists need to activate their work on this direction.
Acknowledgments
The reported study was funded by RFBR, project number 19-010-01042.
References
- Bataeva, B. S. (2018). Stakeholder engagement: The case of the Russian largest oil and gas companies. The Manager, 4(9), 20-27.
- Capgemini Consulting (2011). Digital transformation: A road-map for billion-dollar organizations. https://www.capgemini.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Digital_Transformation__A_Road-Map_for_Billion-Dollar_Organizations.pdf
- Coleman Services (2019). HR functions: Today's tasks, priorities and challenges. https://www.coleman.ru/getattachment/e6d4f0ae-927a-4e5b-ae28-dddc56135caa/HR-%D1%84%D1%83%D0%BD%D0%BA%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8_2019.pdf
- Erina, I., Ozolina-Ozola, I., & Gaile-Sarkane, E. (2015). The importance of stakeholders in human resource training projects. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 213, 794-800.
- Ferrary, M. (2008). A stakeholder’s perspective on human resource management. Journal of Business Ethics, 87(1), 31-43.
- Ivanova, I., Osipova, О., & Pulyaeva, V. (2020). Еvolution of process of automation of HR-departments of Russian organizations. The European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, 79, 998-1005.
- Karpus, P. A. (2009). Meeting the interests of stakeholders as a basis for developing the strategy of an oil and gas company. Oil, Gas and Business, 7(8), 30-35.
- Kleiner, G. B. (2018). Humanistic management, social management and system management — The way to the management of the 21st century. Russian Management Journal, 16(2), 231-252.
- Maramygin, M. S., Chernova, G. V., & Reshetnikova, L. G. (2019). Digital transformation of the Russian financial services market: Trends and features. The Manager, 3(10), 70-82.
- Mitchell, R. K., Agle, B. R., & Wood, D. J. (1997). Toward a theory of stakeholder identification and salience: Defining the principle of who and what really counts. Academy of Management Review, 22(4), 853-886.
- Osipova, O. (2019). Digital transformation of personnel management services. In I. V. Ilin (Ed.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Transformation in Logistics and Infrastructure (ICDTLI 2019). Atlantis Highlights in Computer Sciences, 1 (pp. 327-329). Atlantis Press.
- Schwab, K. (2020). Davos manifesto 2020: The universal purpose of a company in the fourth industrial revolution. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/12/davos-manifesto-2020-the-universal-purpose-of-a-company-in-the-fourth-industrial-revolution/
- Simarova, I. S., Ilina, D. A., & Rudneva, L. N. (2015). Methodological approach to the comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of HR processes of companies. The Manager, 3(55), 34-40.
- Tkachenko, I. N., Pervukhina, I. V., & Zlygostev, A. A. (2020). Modeling the contribution and benefits of the company's stakeholders. The Manager, 2(11), 2-15.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Osipova, O. S., & Bataeva, B. S. (2021). Evaluation Of HR-Management Work Of Digital Organization In Context Of Stakeholders Concept. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1545-1554). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.185

