Abstract
High production costs, an increase in the share of indirect and fixed costs, a large number of business processes and other factors do not allow Russian industrial enterprises to compete on prices in the foreign market, flexibly respond to demand in the industry. This prevents them from integrating into global value chains. The question of calculating the cost of a unit of production remains unresolved, in terms of a competent and reasonable distribution of indirect costs. In this regard, there are difficulties with the implementation of the method of target calculation of production costs, which has been widespread in recent years at enterprises in China, Japan, Europe and other countries. That is why the author aims to develop an algorithm for target calculation of the cost of production based on a process approach to cost management. The process approach to cost management is currently the most comprehensive, covering all cost management functions, allowing you to link existing business processes with the production of specific types of products, reduce costs. The process approach to cost management correlates with the principles of lean manufacturing, greatly simplifies the procedures for their implementation and implementation due to the competent building of the value chain. This allows you to minimize the costs of the enterprise by eliminating unnecessary operations, reducing the need for resources, and, most importantly, maintaining the competitiveness and the pace of sustainable development of the enterprise, despite the constant challenges and crisis changes in the socio-economic component of the global environment.
Keywords: Cost factorscost managementprocess approach to cost managementtarget costing
Introduction
Russian industrial enterprises need modern and effective tools and methods of cost management, since their products are currently not competitive, especially in the global market segments. According to the results of the last five years, Russia is in the late 20s in the rating of the leading states of world trade, the share in world trade does not exceed 2% (Credinform, 2019). In this case, the export of raw materials is taken into account here. In modern conditions of high competition, a decrease in the purchasing power of the population, the selling price is becoming the most significant factor in the competitiveness of an enterprise. The buyer dictates at what price he is ready to purchase the goods. Against this background, targeted costing is becoming very popular. Target costing is a customer-oriented method for calculating target cost indicators. It is widely used by Japanese companies, but in recent years it has also become actively used in China, Europe and the United States (Stadtherr & Wouters, 2021).
Target calculating is actively used in the design of new products (Wouters et al., 2016; Wouters & Morales, 2014). Currently, research is actively underway to take into account R&D costs in the target costing of developed products (Stadtherr & Wouters, 2021). The calculation of cost targets is applied not only for the enterprise as a whole, but also for individual business processes and industries (Li et al., 2020).
The general algorithm for determining the target cost of production is as follows:
- determining the target price that consumers are willing to pay for the product; analysis of the cost of competitive products;
- calculating the size of the target profit, setting the target cost of production;
- the ratio of the value of the target cost to the actual;
- development of measures to reduce the cost of manufacturing products and achieve target indicators.
The first step requires a market analysis that determines the value of the product from the customer's point of view. This value is set on the basis of functions and attributes (functionality), i.e. in the form of its differential value compared to competitive products and the price of these products. The calculation of the target profit is based on information about the required investments, strategic plans of the company. This is then broken down into profit targets for each product, which are subtracted from the target prices to determine the target cost values.
Next, it is necessary to compare the values of the target and actual cost, in some cases - with the standard. If the actual cost exceeds the target cost, a detailed factor analysis is carried out by cost item and measures are developed to reduce the company's costs and achieve target indicators. The main characteristic of target costing is the use of a team approach to achieve the target cost. The new product team includes designers, engineers, purchasing, manufacturing, marketing, and management accounting. Their goal is to achieve the target price set for the product at a given level of functionality and quality (Ma2business, 2014).
The main advantage of target costing is its use already at the planning and product design stage. In theory, the target costing method sounds quite simple, in practice, enterprises, in particular Russian ones, are faced with the problem of calculating the cost of a unit or batch of products. The applied approaches to calculating the cost of production do not allow to correctly distribute indirect costs per unit of production. The growing number of business processes, fixed and overhead costs exacerbate the situation. The process approach to cost management allows to solve the problems of competent costing. The process approach to cost management and the implementation of its tools will significantly optimize the level of companies' expenses, build a company's assortment policy based on profitability indicators, make a significant contribution to the development of the Russian processing industry, and allow domestic enterprises to take a significant share in global value chains.
Problem Statement
Traditional approaches to managing costs and calculating the cost of a unit of production at Russian enterprises do not meet modern requirements. Accounting methods for recording and allocating indirect costs distort information about the real cost of a particular unit of a product. Widespread cost management methods such as direct costing, standard cost also does not allow solving existing problems. The number of business processes at enterprises is growing, the share of overhead costs is constantly increasing. Now it can exceed half the cost, whereas in the days of Henry Ford it was interest. The imperfection of management accounting does not allow enterprises to reduce production costs as efficiently as possible. For this reason, Russian industrial enterprises are most often not competitive on the world market.
Research Questions
Russian enterprises are in a situation where target costing is a necessary method that requires implementation. This is necessary for successful integration into global value chains and increasing its competitiveness in the global market. In this regard, the author has set the task to describe the structural and logical algorithm for calculating the cost of production. This algorithm is most effectively implemented with a process approach to cost management. For the implementation and implementation of a process approach to cost management and the implementation of targeted costing of products, it is necessary to use an accurate system for measuring costs and analyzing variances. According to the author, it is advisable to evaluate deviations of actual costs from target costs by cost factors, in the context of business processes within each cost element. Therefore, the task is also set to systematize the factors that determine the level of production costs.
Purpose of the Study
The ongoing research is to develop and describe an algorithm for target costing with a process approach to cost management, aimed at:
- practical implementation of target costing in industrial enterprises;
- optimization and justification of the value of manufactured products in order to integrate Russian industrial companies into global value chains.
This requires:
- to systematize the factors that determine the level of production costs;
- describe the cost accounting algorithm in the process approach to cost management;
- to develop an algorithm for target calculation of the cost of production with a process approach to cost management.
Research Methods
The study takes into account the technological and digital capabilities of Russian industrial enterprises in relation to the separation, construction and reengineering of business processes and the calculation of production costs. The most widespread in Russia are functional modeling methodologies IDEF0 (ITteach, 2020), ARIS (Frolov, 2019), graphic notations VAD, SIPOC, BPMN (Koptelov, 2020) and other, designed to highlight and describe business processes. On their basis, it is very effectively possible to link business processes with specific types of products, track the value chain, optimize the number of operations performed, and reduce the duration of the production cycle.
The calculation of the actual, standard and target costs can be carried out on the basis of standard accounting programs. In the process of designing new products or improving products, it is recommended to resort to layer-by-layer cost analysis and engineering. Layer-by-layer analysis (also known as reverse engineering) is the detailed study of a competitor's product in order to identify opportunities for improvement and / or cost reduction. The main goal is to get a rough guide to the cost of the product and compare it with your own costs of creating it. Cost engineering (also known as cost analysis) is a systematic complex analysis of factors affecting the costs of a product or service, which is carried out in order to develop a sequence for the release of this product with a given standard of quality and reliability and within the target costs. The goal of cost engineering is to achieve target costs by:
- identifying those characteristics of the product that can be improved by reducing costs without compromising the functional purpose of the product;
- removing unnecessary functions from the design that make it more expensive, but for which consumers do not want to pay.
Cost engineering requires the use of a cost functional analysis.
Findings
Target costing is impossible without an accurate cost measurement and variance analysis. For this, cost factors must be identified that largely determine costs by type of activity (product), broken down by business processes. To improve the efficiency of the analysis of deviations from the target costs, it is advisable to systematize them into their constituent elements (material costs, labor costs, insurance deductions, depreciation deductions, and other costs). The author proposes the following model of systematization of factors that determine the level of production costs (Table
The list of factors can be more deeply detailed, expanded and changed depending on the capabilities of cost accounting and the specifics of the enterprise. The general sequence of cost accounting in the process approach to cost management is shown in the figure (Figure
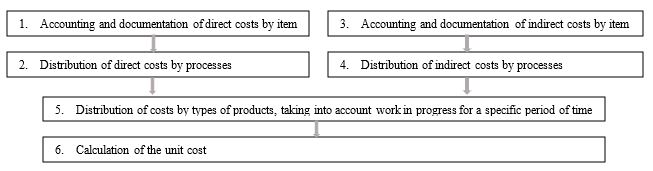
The algorithm for target costing when applying the process approach to cost management is as follows (Figure
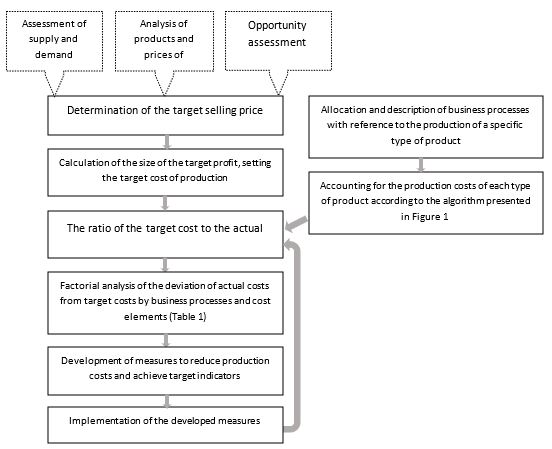
The systematization of the factors that determine the level of production costs allows not only to competently develop measures to reduce costs by elements, but also to compare business processes with the production of a specific type of product. Consequently, such a systematization of factors is a tool for distributing costs by processes, including indirect costs, and then by types of products. The target costing process is permanent. Achieving the target selling price is not the only goal, it is necessary to strive to increase the company's profits, therefore, constantly work towards optimizing cost items.
Conclusion
When introducing target costing in an industrial enterprise, an integrated approach is important. Each stage of the target calculation algorithm presented in the algorithm in Figure
References
- Credinform (2019). The leading nations in world trade. https://credinform.ru/ru-RU/Publications/Article/70c051c725f5
- Frolov, I. (2019). ARIS methodology. Business process modeling. https://fb-ru.turbopages.org/fb.ru/s/article/471175/metodologiya-aris-modelirovanie-biznes-protsessa.
- ITteach (2020). IDEF0 methodology. https://itteach.ru/bpwin/metodologiya-idef0.
- Koptelov, A.K. (2020). Business process modeling – Overview of notations. http://koptelov.info/publikatsii/modelirovanie-biznes-protsessov/
- Li, B., Ji, Q., & Arreola-Risa, A. (2020). Optimizing a production-inventory system under a cost target. Computers & Operations Research, 123, 105015.
- Ma2business (2014). Target cost calculation of products and services. http://ma2business.ru/celevaya-kalkulyaciya-sebestoimosti-produkcii-i-uslug/
- Naugolnova, I. A. (2020). The process approach to managing the cost of manufacturing innovative high-tech products. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, 82, 554-561.
- Stadtherr, F., & Wouters, M. (2021). Extending target costing to include targets for R&D costs and production investments for a modular product portfolio – A case study. International Journal of Production Economics, 231, 107871.
- Wouters, M., Morales, S., Grollmuss, S., & Scheer, M. (2016). Methods for cost management during product development: A review and comparison of different literatures. Advances in Management Accounting, 26, 139-274.
- Wouters, M., & Morales, S. (2014). The contemporary art of cost management methods during product development. Advances in Management Accounting, 24, 259-346.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Naugolnova, I. A. (2021). Target Calculation Of Production Costs In The Process Approach To Cost Management. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 135-141). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.17

