Abstract
The widespread and global development of information technologies have a significant impact on all spheres of public life, including the processes of interaction between citizens of the country and the state. A key trend in the development of public administration is the creation of e-government. In order to ensure a high degree of integration of the Russian Federation into the world information society, the Government of the Russian Federation has formed the national program "Digital economy of the Russian Federation". One of the areas implemented under this national program is the Federal project "Digital public administration". The main goals of the project are to provide citizens and organizations with access to priority public and digital services, create a national data management system, develop e-government, and implement integrated platform solutions. The project provides for the creation of users ' access to information created by state authorities and local self-government bodies, including using a single standard of visual and graphic design and common means of information and content, in a "one-stop-shop" model through a Single portal of state and municipal services. It informs the public about available electronic public services and the advantages of receiving state and municipal services in electronic form. Considering the popularization of e-government services as one of the key elements of increasing the degree of loyalty of citizens to the authorities, we identified the population groups that need support in obtaining public services, and proposed the concept of using effective methods to promote e-government.
Keywords: Digital literacyelectronic servicespublic servicespublic awarenesspopularization
Introduction
Modern development of the public administration system and improvement of its efficiency is based on the large-scale use of information and communication technologies that offer a variety of tools to improve the quality of public administration, ensure transparency of decisions and facilitate access of the population and civil society institutions to electronic services based on the principles of open government. The development of e-government, which makes it possible to expand the volume and variety of public services, increase the speed of their provision and improve the quality, is a key feature of the modern model of public administration (Wichmann et al., 2021). Implementation of measures to form e-government in the Russian Federation has become a priority.
However, e-government services are not separate types of public services and cannot be considered in isolation from the state and its main functions. The transition to an electronic format for providing services is only a modern way of providing them and contributes to improving the quality of life of the population, improving the efficiency of state and municipal management, developing civil initiatives and business activities through the use of modern information technologies (Pavlova & Ashmarina, 2021).
The state program of the Russian Federation "Information society (2011-2020)" (The Ministry of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media of the Russian Federation, 2019a) was developed to improve the system of public administration based on the use of information and telecommunications technologies. Among the key indicators of the program is the achievement by 2024 of preferential interaction between the authorities and the population of the country based on the use of information and telecommunications technologies, as well as ensuring a high degree of integration of the Russian Federation into the world information society. At the same time, one of the priorities for the development of the information society in the Russian Federation is to increase public awareness of electronic services and increase the level of digital literacy of the country's population.
Problem Statement
The Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated 21.07.2020 "On the national development goals of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030" sets a target for implementing the national goal "Digital transformation": increasing the share of mass socially significant services available in electronic form to 95% by 2030.
Understanding the "availability of services" includes a simultaneous combination of two factors: the possibility of their provision by the contractor, as well as the willingness to receive them and the customer's interest in receiving them. Thus, the achievement of the established indicator, provided that the state is fully ready to switch to electronic services, is possible only if the population is ready to receive such services. Considering the popularization of electronic services as one of the key elements of increasing the degree of loyalty to the authorities, the author of the study was tasked to analyze the degree of awareness, involvement and satisfaction of citizens of the Russian Federation with electronic public services, to identify target groups that need support in obtaining electronic public services in order to further develop effective, accessible and understandable methods for popularizing e-government services.
Research Questions
The key question of the study is how ready is the population of the Russian Federation to receive public services in electronic form? To answer this question, it is necessary to determine the level of awareness of citizens. Assess the level of satisfaction with e-services and their availability to the population. First of all, it is necessary to answer the question of which groups of the population are marginalized from the process of receiving electronic services? What are the reasons why services are not provided? How to increase the coverage of e-services? What measures have already been taken?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to identify target groups of the Russian Federation population who need to be informed about available electronic services. Identify the need for training and support at all stages of receiving public services. Assess the population's satisfaction with the services provided. Determine the level of digital literacy in various target groups of the population. Find the possibility of using a system of universal, accessible and effective methods aimed at popularizing electronic public services. Determine the direction of optimization of Internet sites of public authorities.
Research Methods
The analysis of the readiness of the population of the Russian Federation to switch to the use of electronic public services is based on the results of applied sociological research using statistical and integral evaluation algorithms, followed by comparison and approximation of the obtained information (Pleger et al., 2020).
Research conducted in the fields of public administration is well known in Russia. In the course of the work, the author studied and summarized the results of:
- analysis of the distribution of the population of the Russian Federation by gender and age;
- analysis of the number of registered users on the Unified portal of public services and the number of services;
- applied sociological research on assessing the population's satisfaction with the activities of local self-government bodies of urban districts and municipal districts of the Samara region and the quality of public and municipal services in the Samara region (stage III), commissioned by the Department of administration of the Governor Of the Samara region and the government of the Samara region in 2018;
- applied sociological research of digital literacy of Russians conducted by the NAFI analytical center in 2020;
- assessment of the Russian Federation's involvement in the processes of digital transformation of society using the integrated index of digitalization of the economy and society DESI (Digital economy and society index), used to assess the degree of digitalization of society and individual countries.
The author studied information from open sources and official Internet sites of the Russian Federation, analyzed and compared the information received. The information obtained was summarized, which allowed us to conclude that it is necessary to popularize electronic public services.
Findings
Currently, key infrastructure systems that are the technological basis of electronic public services have been implemented and are effectively operating: a unified identification and authentication system, channels for electronic access to state and municipal services (a single portal of state and municipal services; regional portals of public services; official websites and portals of state and local government bodies; various mobile applications; infomats), the state information system on state and municipal payments, the register of state and municipal services, a network of multifunctional centers. In 2019, more than 790 state services and functions were available to users of the Federal register of state and municipal services. Among them: 70 services from Federal agencies, 170 services of control and Supervisory authorities, more than 500 services of various state authorities.
According to the report on the results of the research work on "Evaluation of satisfaction with the activities of local governments of city districts and municipal districts of Samara region and the quality of rendering state and municipal services of the Samara region in 2018" (stage III) (Samara Region Government, 2020) level of public awareness about the Unified portal of public and municipal services (further – a Uniform portal) it was 85.1% of respondents (compared to the results of the study conducted in 2016-2017, this indicator increased by 8.3%). 93.8% of users of the Unified portal created a personal account, 91.5% of users of the portal were satisfied with the quality of its work and the quality of e-services provided. At the same time, the level of awareness of the population of the Samara region about the Regional portal of state and municipal services was only 58.0%, and the share of users of the Regional portal was 8.9%, of which 93.8% gave a good assessment of the resource. It should be noted that the total sample of the study was 17.8 thousand. The research method is an individual interview using a questionnaire recommended by the Ministry of economic development of the Russian Federation. The object of the study is citizens of the Russian Federation living in the Samara region from different demographic groups aged 18 years and older who applied to state authorities and (or) local self-government for state and (or) municipal services and at the time of the survey received the final result. The margin of error is no more than 2% with a confidence probability of 95% (Samara Region Government, 2020).
Taking into account the annual increase in the informed population of 8.3% and assuming that the growth rate will remain within the specified limits due to an advertising campaign conducted in public media (television, radio, Internet), by the beginning of 2020, the total number of informed citizens about the Single portal should approach 93.4% (85.1% + 8.3% increase in 2019) of the total population 18 years and older of age with a confidence probability of 95%. Thus, approximating the information obtained, it is highly likely that the absolute majority of citizens who have ever applied for public services in any form (up to 94% of users) should have been informed about the Unified portal of public services by the beginning of 2020. The permanent population of the Russian Federation as of January 1, 2020 was 146.7 million people, of which 114.6 million people are the population aged 18 years and older (Statdata, 2020). Thus, the number of people informed about the Single portal at the age of 18 and older in 2020 should be 107.7 million. According to information published on the Unified portal of state and municipal services, in 2019, 103.2 million users were registered on the portal, and the total number of operations and services provided through the Unified portal and mobile application was 1.8 billion services. At the same time, not only citizens of the Russian Federation are registered on the portal, but also legal entities, as well as citizens of foreign countries. The portal administration did not provide information on the author's request to the hotline of the Unified portal about the number of Russian citizens registered on the portal. Taking into account that the total number of active legal entities and individual entrepreneurs registered in the Russian Federation according to the Federal Information Service as of November 22, 2020 was 7.4 million organizations (The Federal Information Service, 2020), assuming that 50% of organizations have a personal account on a portal, we can assume that the number of citizens permanently residing in the territory of the Russian Federation registered on a Unified portal at the beginning of 2020 was 95.8 million people.
Given the above, it is highly likely to determine the number of people who should be targeted for the promotion of e-government services, including, but not limited to, information and support at all stages of obtaining e-services:
- 11.9 million people-informed population, but not having a personal account on a Unified portal;
- 8.14 million people-an informed population that has a personal account on a Unified portal, but is dissatisfied with the quality of services provided.
However, 48.13 million people should be informed about the availability and Regional portals of state and municipal services, established in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and 0,63 million people, dissatisfied with the quality of electronic services provided by regional administrations, the need for training to improve digital literacy, as well as support in obtaining electronic services.
The Federal project "Personnel for the digital economy" (The Ministry of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media of the Russian Federation, 2019b) sets target values for the share of Russians with digital literacy and key competencies of the digital economy. This is 26% of the population in 2018, 27% in 2019, 30% in 2020 and 32% in 2021. According to a study conducted by the NAFI analytical center "Digital literacy of Russians: research 2020", it was found that in 2018, 26% of Russians had a high level of digital literacy (NAFI, 2020). As of January 2020, this share was 27% - 3 percentage points behind the Federal project's target values. At the same time, the digital literacy index of Russians in the 1st quarter of 2020 was 58 points on a scale from 0 to 100 (increased by 6 percentage points compared to the same indicator in 2019). At the same time, the proportion of the population with high digital literacy increased by 1% to 27%. The index was calculated using the Digcomp methodology for five main parameters, such as information literacy, communication literacy, digital content creation, digital security, and problem-solving skills in the digital environment (Tikhomirova, 2020). The study found that the level of digital literacy depends more on a person's age, professional activity, and status (Table
As can be seen from Table
According To the international integrated index I-DESI (International Digital Economy and Society Index), an assessment of the degree of digitalization of society and individual countries outside the EU, in accordance with the methodology of the European digital economy and society index 2018, Russia ranked 12th among 17 countries whose indicators were analyzed in the study, ahead of China, Turkey, Mexico, Brazil and Chile. In the overall I-DESI world ranking, the Russian index was higher than the minimum average European index-at the level of Greece, Cyprus and Bulgaria. At the same time, in the overall rating, Russia entered the second group of countries with a low degree of digitalization (Ivanichkin et al., 2021).
As a result of the research, the author identified groups of citizens who need information, training and support at all stages of receiving electronic public services:
- 11.9 million people-informed population, but not having a personal account on a Unified portal;
- 8.14 million people-an informed population that has a personal account on a Unified portal, but is dissatisfied with the quality of services provided;
- 48.13 million people - not informed about the work of Regional portals of state and municipal services;
- 0.63 million people-informed population about the work of Regional portals of state and municipal services, but dissatisfied with the quality of electronic services;
- 41.6 million people are citizens of the Russian Federation aged 55 years or more who need to improve the level of digital literacy in order to use e-government services.
In the course of the study, the author formulated a problem and identified a contradiction that needs to be eliminated: the insufficient level of digital literacy among citizens of the Russian Federation and the insufficient level of public awareness about electronic public services do not allow citizens to receive public services in electronic form (Figure
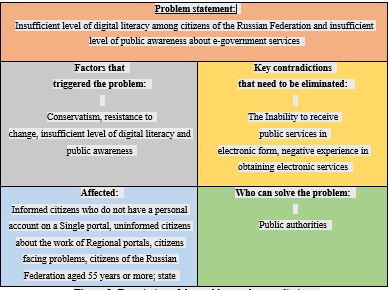
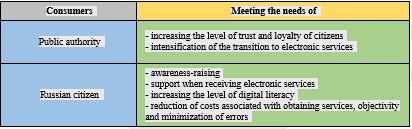
To solve this problem, the author proposes to Supplement the existing system of informing the population about electronic public services with universal, accessible and effective methods of popularization. The proposed measures should be implemented within the framework of the Federal project “Digital public administration” of the national program “Digital economy of the Russian Federation”. The expected result of the implementation of the proposed measures is to increase the level of awareness of Russian citizens about available e-government services, advantages and methods of obtaining them to 100%, increase the level of digital literacy of Russian citizens aged 55 years and older to 60%, and support the population in obtaining e-government services at any stage of their receipt to the expected result (Figure
Key steps in implementing measures aimed at promoting e-government services:
1. Organization of subsystems for informing and supporting citizens of the Russian Federation about the methods, opportunities, type and list of public services in electronic form, by means of:
- engage the transmission channel related information (Teletext) in one of regionalized TV channels – the TV channel "Public television of Russia", included in the list of mandatory nationwide public TV channels and radio channels approved by the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 24.06.2009 №715 "On mandatory nationwide public TV channels and radio channels" in order to embed in its structure of an information subsystem of informing and supporting citizens in obtaining public electronic services at any stage;
- optimization of public authorities websites on the principle of a single window, avoiding multiple sites, integration with the application installed on mobile devices;
- creating a user-friendly interface of a Unified portal that is easy to use and understandable for all categories of citizens, simplifying the mechanisms of interaction when receiving public services, creating a voice assistant system (on-line operator);
- conducting explanatory work with the population on the basis of the Multi-Function Centers and mobile teams of informing citizens formed on the basis of state social protection services;
- use of alternative, including innovative channels of communication with the population (through electronic Bulletin boards in transport, installation of a network of info-mats and training stands in places where people gather and live, printing on utility bills and cash receipts, notification through mailboxes).
2. Content creation and content subsystems of the information content
3. Development and implementation of adaptive training programs for all groups of the population, including students of secondary and higher educational institutions, as well as the population of age groups 55 years and more, regular training on the basis of educational institutions and multifunctional centers in order to increase the level of digital literacy of citizens.
Conclusion
Summing up the results of the study, it can be noted that in 2020 the population of the Russian Federation was not fully ready to receive public services in electronic form (Alruwaie et al., 2020). The main factors that ensure the readiness of the population of citizens to switch to digital public services are:
- the necessary and sufficient level of awareness and awareness about electronic public services, the method of their provision, the place of provision and the result;
- formed demand among citizens for e-government services;
- the necessary and sufficient level of digital literacy among all groups of the population, including among the age categories of citizens (55 years and older), to receive public services in electronic form;
- a sufficient level of provision of the population with the necessary technical means and opportunities for obtaining state electronic services (electronic computing equipment, mobile devices, communication channels, high-speed Internet access);
- high quality indicators of public services, transparency of their provision, convenience of receiving, compliance of the result with the user's expectations (Alhawawsha & Panchenko, 2021);
- the absolute majority of public services transferred to the electronic format of service provision;
- a high degree of satisfaction of citizens with public services received (Jarke, 2021).
At the same time, the author notes a fairly high level of awareness of the Russian population about the possibility of receiving public services in electronic form (95% among all citizens aged 18 years or more) and citizens satisfaction with the work of e-government services (93.8% among those who have ever used the service). The digital literacy rate of the population is 58%, but this indicator is not uniform among all population groups. Despite the fact that the maximum level of digital literacy of the population aged 18-24 years (working student), determined based on the analysis of five key digital competencies of the population, reached 64%, the level of digital literacy of retired people is only 51%, and only 27% of citizens of the Russian Federation have a really high level of digital literacy that allows them to freely receive any electronic services. However, this indicator is still 3% behind the target values set by the Federal project "Personnel for the digital economy".
To achieve the necessary indicators, it is necessary to develop and implement a system of criteria for assessing the degree of satisfaction with public services (Menshchikova et al., 2021), ensure the popularization of electronic services, and therefore inform the population about the types and methods of obtaining public services, provide support to citizens at all stages of their receipt, and contribute to improving the level of well-being and digital literacy of citizens. The author suggests the concept of applying universal methods for popularizing e-government services. Taking into account that the popularization of electronic services is one of the key elements of increasing the level of loyalty of the population and strengthening the dialogue with the authorities, the implementation of these initiatives should be carried out on an ongoing basis, provided that resources are effectively used.
References
- Alkhavavsha, M., & Panchenko, T. (2021). OPEN data platform architecture and its advantages for open e-government. In Z. Hu, S. Petukhov, I. Dychka, & M. On (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and Education Applications. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 1247 (pp. 631-639). Springer.
- Alruwaie, M., El-Haddadeh, R., & Weerakkody, V. (2020). Citizens' continuous use of eGovernment services: The role of self-efficacy, outcome expectations and satisfaction. Government Information Quarterly, 37(3), 101485.
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated 21.07.2020 "On the national development goals of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030". http://www.kremlin.ru/events/president/news/63728
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 24.06.2009 №715 "On mandatory nationwide public TV channels and radio channels". http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_88782/
- Ivanichkin, R., Kashirin, P., Sysoev, S., Shabunevich, O., & James, W.O. (2021). Features of the process of digital transformation of the Russian economy. In V. Murgul & V. Puhkal (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference on Energy Management of Municipal Facilities and Sustainable Energy Technologies. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 1259 (pp. 187-197). Springer.
- Jarke, J. (2021). Co-creating digital public services (1st edition). Springer.
- Menshchikova, V. I., Merkulova, E. Y., Molotkova, N. V., & Pecherskaya, E. P. (2021). Shaping the model of digital economy in Russia and its regions. In S. Ashmarina & V. Mantulenko (Eds.), Current Achievements, Challenges and Digital Chances of Knowledge Based Economy. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 133 (pp. 725-733). Springer.
- NAFI (2020). The digital literacy of Russians: A 2020 study. https://nafi.ru/analytics/tsifrovaya-gramotnost-rossiyan-issledovanie-2020/
- Pavlova, A. V., & Ashmarina, S. I. (2021) Transformation of public administration in the interests of digital economy development. In S. Ashmarina & V. Mantulenko (Eds.), Current Achievements, Challenges and Digital Chances of Knowledge Based Economy. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 133 (pp. 159-165). Springer.
- Pleger, L. E., Mertes, A., Rey, A., & Brüesch, C. (2020). Allowing users to pick and choose: A conjoint analysis of end-user preferences of public e-services. Government Information Quarterly, 37(4), 101473.
- Samara Region Government (2020). The final report on the results of the analysis and assessment of the quality and accessibility of the provision of state and municipal services in the Samara region in 2017-2018. https://www.samregion.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/ITOGOVYJ-OTCHET.docx
- Statdata (2020). The population of Russia: Number, dynamics, statistics. Operational information as of January 1, 2020. http://www.statdata.ru/russia
- The Federal Information Service (2020). The Distribution of acting legal entities and individual entrepreneurs as of November 22. https://xn--h1ari.xn--p1ai/Main/StatisticalInformation
- The Ministry of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media of the Russian Federation (2019a). State program information society. Retrieved from: https://digital.gov.ru/ru/activity/programs/1/
- The Ministry of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media of the Russian Federation (2019b). Personnel for the digital economy. https://digital.gov.ru/ru/activity/directions/866
- Tikhomirova, O. (2020). E-governance and social inclusion of entrepreneurship and businesses: Toward the social inclusive digital society. International Journal of E-Entrepreneurship and Innovation, 10(2), 1-25.
- Wichmann, J., Wißotzki, M., & Sandkuhl, K. (2021). Toward a smart town: Digital innovation and transformation process in a public sector environment. In A. Zimmermann, R. Howlett & L. Jain (Eds.), Human Centred Intelligent Systems. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, 189 (pp. 89-99). Springer.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Kurganova, M. (2021). Popularization Of Electronic Government Services In Russian Federation. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 946-955). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.113

