Abstract
The article is devoted to the analysis of the existing financial and economic mechanisms of state support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in times of crisis and current COVID-19 pandemic. Support of the SMEs sector is recognized to be one of Russia’s economic policy priorities. The main scientific question is what the main factors affecting the development of the SME sector, as well as the SME support system. The results of this study indicate the effectiveness of some instruments of the state support for SMEs and their influence on the development of entrepreneurship in Russia. The most effective direct federal support measures and tools have been identified. Russian Agency of small and medium business support pays serious attention to the stimulation of the economic potential of SMEs. It is one of the first business support organizations in providing information, analytical and marketing, consulting and training services. Now it with the assistance of the Agency for Strategic Initiatives is developing a range of services for businessmen, executive and legislative branches of the federal and regional levels, development institutions, infrastructure organizations as well as improvement measures and state support tools. There are some indicators characterizing the implementation of government measures aimed at the development of SMEs. In addition, the interrelation of the number of support tools and support infrastructure organizations presented in the article. The development of the entrepreneurial sphere is revealed. According to the research, some recommendations were made.
Keywords: Anti-crisis policy measuresentrepreneurshipgovernment supportsmall and medium-sized enterprises
Introduction
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is one of the sectors of the market economy that provides the most important needs of the national economy. Its development is viewed as one of the priority areas in Russian economic policy. The main goals and objectives of SME development are defined in the National project "Small and Medium Enterprise and Support for Individual Entrepreneurial Initiatives". However, despite the active discussion of its role in the economy and the need to support it, SMEs occupy limited positions in the Russian economy compared with Western countries. In 2020, the share of SMEs in Russia's GDP was 22.9%, the number of people employed in this segment was 19.6 million, and the part of SMEs in the total volume of non-resource exports of Russia reached 9.8%. At the same time, in developed economies, the SME sector occupies half or more of the economy: for example, in Germany, SMEs provide 55% of GDP, in the USA - 44%, in OECD countries - about 33% (Avdeeva et al., 2020).
During 2020, the situation worsened as a result of the aggravation of the crisis, the consequences of the COVID pandemic, restrictive measures and self-isolation. Most Russian entrepreneurs have lost a significant share of their revenue and are faced with the need to reform the business model as a result of falling demand, especially in the restaurant business, tourism and entertainment. Entrepreneurs needed new support mechanisms appropriate to the situation in the country, as evidenced by a decline in the business activity index of enterprises and a drop of revenue in almost a third of the surveyed SMEs. The state is forced to take adequate measures to support SMEs, since difficulties in its development can have a significant impact on the dynamics of growth of the national economy and aggravate socio-economic problems in society. In the context of the crisis and pandemic, the main direction of government policy is to stimulate the development of SMEs, facilitating the possibility of obtaining financial and non-financial assistance, including reducing interest rates on loans, stimulating demand in the domestic market, as well as providing tax incentives. In fact, if the state does not take measures to support SMEs, then it will have to admit that its efforts aimed at developing SMEs and improving the business climate in previous years were in vain.
Problem Statement
Small business is an important subject of the country's economic activity, and it is an active participant in the formation of a modern structure of the economy focused on innovative development. SMEs are formed by technology startups and disruptive innovations. SMEs participate in solving socio-economic problems that ensure the socio-economic stability of society. In periods of prolonged economic crisis, the development of SMEs should be considered as one of the priority tasks of the government, for the solution of which it is necessary to take various support measures for SMEs, which should help increase the stability of companies, stimulate their activities and improve the environment for expanding of their entrepreneurial activity. Long-term comprehensive measures are needed to support SMEs, which should be based on the goals of the country's economic policy and long-term development priorities. Changes in the economy and politics require the adaptation of the federal policy concerning the development of entrepreneurship, as well as using the opportunities of the regions, their specialization, economic and geographical conditions for more effective and long-term development of SMEs. The viability of small business and its future development will depend on the effectiveness of government support measures.
Research Questions
In 2016 the Strategy for the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030 (approved by the order of the Government of the Russian Federation of 06/02/2016 N 1083-r (as amended on 03/30/2018) was developed and adopted with the purpose to support SMEs. The main indicators characterizing the development of SMEs include the role of SMEs in the country's GDP, the part of the employed population in the SME sector, the turnover of SMEs, and labor productivity. This Strategy formulates the main targets and goals for the growth of the SMEs. From 2016 to 2019 the functioning of development institutions in the field of SMEs has improved and new development institutions were created (SME Corporation, Regional guarantee organizations). The SME Corporation provides financial, guarantee, information, legal and property support to SMEs and the access to the purchasing system. During 2015–2019 the administrative burden on SMEs was reduced by using a risk-based approach in control and supervisory activities (Goldina & Fateeva, 2016).
Financial resources have become more available for SMEs as a result of the adoption of such special programs as the SME Lending Incentive Program, the Investment Lift Program, as well as the implementation of credit and guarantee support. The access of SMEs to public procurement has expanded. In 2019, the National Project " Small and Medium Enterprises and Support for Individual Entrepreneurial Initiatives" (National Project) was adopted, which defines the goals, objectives and timing of their achievement. So, by 2024, according to the National Project the number of people employed in SMEs will increase to 25 million; the share of SMEs in the country's GDP to 32.5%; the exports of SMEs and individual entrepreneurs in the total volume of non-resource exports to 10%. The budget of the National project was provided at the level of 481.5 billion rubles, of which 416.2 billion rubles accounted for the Federal budget, 11.4 billion rubles - regional budgets; 53.9 billion rubles - extra-budgetary sources..
In October 2020, the National project was adapted to the existing situation and is already focused on achieving specific significant results. The number of federal projects included in it has decreased from the initial version of 2019 to four, but support measures have expanded. The updated version includes the following federal projects:
1.Creation of a digital platform with a mechanism for targeted selection, remote support measures and special services by SMEs and self-employed citizens.
2.Acceleration of SMEs.
3.Creation of conditions for an easy start and comfortable business.
4.Creation of favorable conditions for the activities of self-employed citizens.
The updated National project will pay more attention to digital tools that will make it easier for entrepreneurs to create and run business. All services for SMEs will enter a new ecosystem based on a digital platform "one window", which will allow for targeted selection of support tools. An entrepreneur can list taxes, get information about all available support measures (access to guarantees, sureties, grants, subsidies and leasing programs), make an application, undergo scoring and obtain a bank loan, as well as consider possible options for selling products, get consulting services and access to educational programs. The volume of financing for the national SME project in 2021 will remain at the level of 2019 - 56.3 billion rubles, in 2023 it will grow to 78.7 billion rubles.
The federal projects "Acceleration of small and medium-sized businesses " and "Creation of conditions for an easy start and comfortable doing business" investigate the problems of commercialization and accelerated development (acceleration) of SMEs. Gradually, various tax regimes will be introduced to change the tax burden on growing SMEs as well as registers of recipients of support. By 2021 rates on concessional lending will be reduced, a transition to a system of quick payments will be made, and comprehensive export support will be created on the basis of regional centers. A new aspect in the project is the support of social business. These entrepreneurs will be provided with comprehensive services and financial support in the form of grants. Social entrepreneurship appeared in Russian legislation in 2019. In 2020, all information about social enterprises is entered into the unified register of SMEs. The federal SME acceleration project includes financial and tax instruments to support business, as well as the development of infrastructure for the effective work of entrepreneurs and ensuring their access to the procurement system of the largest customers. According to this project, the volume of purchases of the largest Russian customers from SMEs will increase from 3.7 trillion rubles in 2019 up to 5 trillion rubles in 2024, it is planned to use special tools to support R&D. From 2021, it is planned to introduce a system of concessional lending for small businesses with a reduced interest rate to less of 7%.
The creation of favorable conditions to increase activities of self-employed citizens is becoming a special area, which contains a lot of new support measures. It is a preferential tax regime, as well as the provision of microloans up to 1 million rubles for three years at a preferential rate not exceeding 1.5 times the key rate of the Central Bank. Self-employed have the right to rent equipped workplaces in the office, including business incubators and coworking spaces, where the necessary equipment is available. For the self-employed, a tax deduction is introduced in the amount of the minimum wage for persons aged 16-18 who have registered as self-employed for the first time. They also get access to other alternative financing instruments, for example, preferential access to crowdinvesting platforms. In 2020 in Russia, there were over 1.143 million self-employed and over 5.6 million SMEs. Self-employed citizens who provide paid services to individuals without hiring employees must pay 4% of their income to the budget and 6% when working with companies. SMEs are seen as the main actors of both national and regional development in Russia and all over the world (Wang et al., 2020). SMEs play an important role in the economy. Many programs have been implemented to improve their position. In this context it is very important to evaluate the results achieved in the implementation of programs aimed at developing and strengthening the position of SMEs in the economy, as well as their sustainability and the expansion of activities in different areas.
Purpose of the Study
The main purpose is to learn the main financial and economic mechanisms for supporting SMEs in the implementation of the National Project. The availability of finance is one of the most significant problems for SMEs functioning. There are some main areas of financial support for SMEs: stimulating lending to SMEs, guarantee support for SMEs as well as the Investment Lift Program and leasing support. We also investigate how the recent financial crisis affected SMEs. SMEs significantly decreased their leverage, particularly their short-term debt obligations. As a result, the short-term debt receipts are more sensitive to credit conditions for SMEs than the long-term debt receipts (D'Amato, 2020). Economic efficiency is largely determined by the business activities of SMEs. There is a direct positive relationship between the level of people’s well-being, the rate of national economic development and the efficiency of the SMEs. In accordance with the National project for the development of SMEs, there is an aim to increase this sector through concessional financing, simplified taxation, etc. This article is aimed at determining the effectiveness and nature of the impact of the government support system for SMEs.
Research Methods
We use the synthesis of methods of logical, statistical, qualitative and quantitative analysis to study financial and economic mechanisms of government support for SMEs in Russia. The methodology contains qualitative and quantitative measures that can quantify the opportunities and benefits of SMEs for the economy of Russia. The methodology includes collecting and analyzing data and establish new facts about the development of financial and economic mechanisms of government support for SMEs. Through a detailed data we analysis certain aspects of SMEs and identify prospects for the improvement of SMEs development. The study provides indicators characterizing the implementation of government measures aimed at the development of SMEs which will simulate the impact of the government measures on the development of SMEs. We illustrate the potential of innovation to determine the trajectories of SMEs development and provide some ideas about future. We identify existing methodological problems at the macro- and microeconomic levels and reveal possibilities for expanding analysis methods for solving problems in the field of the SMEs in times of crisis.
Findings
In 2014 the National Guarantee System (NGS) was developed. It is a three-tier system of guarantee organizations, including SME Corporation, SME Bank and 86 regional guarantee organizations (RGO) to support SMEs. This system makes available credit resources for small and medium-sized enterprises and includes different types of support for SMEs: access to procurement of companies with state participation; financial and guarantee support; marketing support; consulting support and training programs (Mordvinkin, 2019). The NGS is aimed at increasing the volume of guarantee support for SMEs and improving the efficiency of the use of guarantee capital. Regional guarantee organizations (RGS) provide guarantees to 25 million rubles, the SME Corporation and SME Bank provide guarantees to more than 25 million rubles (Table
Corporation SME is focused on providing guarantees to SMEs for the implementation of medium and large projects. The activities of SME Bank and the RGSs are aimed at the use of "flow" technologies and the provision of guarantees and sureties in the mass market segment. The total amount of guarantee support for NGS participants during the period from 2015 to 2020 increased to 720.7 billion rubles, which is very important for SMEs that don't have enough own funds. Table
The Special program of concessional lending to small and medium-sized businesses was launched at the end of 2015 and was developed by the Corporation together with the Bank of Russia. It stimulates the development of SMEs in priority sectors of the economy. Since 2019 the Concessional Lending Program has been implemented as part of the National project and will be implemented until 2024. Agriculture, production of essential products; health care, ecotourism; utilities, social entrepreneurship, IT are the priority spheres of economic activity. The special program of concessional lending to small and medium-sized businesses was approved by the Government of Russia. The purpose of the program is to expand opportunities for entrepreneurs to obtain a loan at a preferential rate. An authorized bank can provide a concessional loan for replenishment of working capital in the amount from 500 thousand rubles to 500 million rubles for 3 years, from 500 thousand rubles to 2 billion rubles for 10 years but only for investment purposes (Chistyakova & Babkin, 2019).
Figure
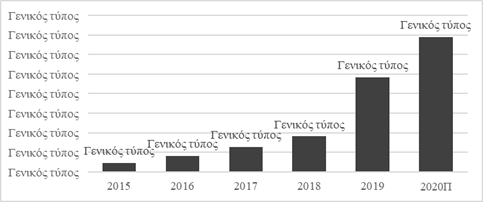
In 2020, the SME Corporation's lending promotion program was updated in response to the crisis and pandemic. At present, in accordance with the Program, it is envisaged to establish an interest rate on loans at 8.5%. 123 partner banks and authorized banks of the SME Corporation and 84 regional guarantee organizations participate in the program. The Program states that loans should be used to finance investment activities only. A new type of loan has appeared in the program, under which an entrepreneur can receive a loan to 10 million rubles for 5 years at a preferential rate not exceeding 9.95%. Under this Program from 2020 borrowers can be individual entrepreneurs (self-employed) who apply a special tax regime for professional income tax. In accordance with the changes in the program, now it is possible to apply the securitization mechanism for portfolios of commercial banks loans issued to SMEs. In 2021, preferential lending to small and medium-sized enterprises is expected to be carried out with a reduced interest rate, but no more than 7%.
In July 2020, SMEs and socially oriented non-profit organizations (NPOs) concluded an agreement with banks to receive loans at a rate of 2% in the amount of 420 billion rubles. The volume of loans increased to 1.04 trillion rubles. The concessional lending program made it possible to support more than 5 million jobs. The funds received under the program were used to maintain jobs and pay salaries to employees. Small and medium-sized enterprises were able to apply for subsidies for April and May - 12,130 rubles per month if they retain at least 90% of employees.
In November 2020, the government has extended the deferral of taxes and insurance premiums for SMEs until the end of 2020. Deferrals for rent and tax payments, as well as a moratorium on company bankruptcy, have been introduced. A 0% loan program to finance employee salaries was launched. Еhe restructuring of debt obligations of SMEs is very important measure to improve the position of SMEs. Major banks restructured SME debts. Loans have a big impact on the development of companies and are socially responsible (employee salaries) in different countries (Xu et al., 2020).
The system of the Investment lift consolidates different measures to support SMEs in their high-tech investment projects, and in non-resource exports and import substitution. The Investment Lift system is implemented according to the Agreement between the SME Corporation, the Industrial Development Fund (IDF), the Russian Export Center (REC) and the Russian Direct Investment Fund (RDIF). In 2016–2020, funding for 41 projects with a total amount of 31,677 million rubles was approved under this program, of which 34 projects for 28,759 million rubles have already received financial support. At the same time, the share of high-tech export-oriented and import-substituting projects in the amount of financial support provided by development institutions amounted to 15,414 million rubles, which is almost half of the total. Similar systems exist in other countries. They provide a particularly important competitive advantage for SMEs that face various constraints related to their size and resource base (Knight et al., 2020).
The SME Corporation provides credit and guarantee support to SMEs. The IDF provides loans for the implementation of industrial investment projects. The financial support of the RDIF is aimed at participation in equity capital. The REC provides legal, consulting and credit and insurance support for the export of goods and services of Russian production. The National project "Small and Medium Enterprises and Support for Individual Entrepreneurial Initiatives" initiated the creation of regional leasing companies which provide assistance to SMEs in crisis. These companies provide new industrial high-tech innovative equipment for leasing. Equipment is provided to individual entrepreneurs and SMEs at a rate of 6% (for domestic equipment) and 8% (for foreign equipment). Some trends in the development of financing with leasing support are presented in Table
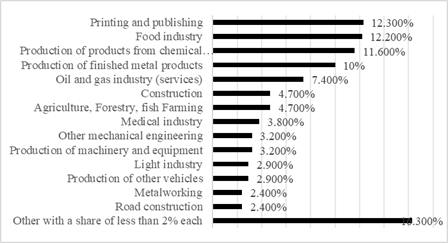
Figure
Large state-owned companies and natural monopolies are required to purchase goods, works, services from SMEs in the amount of at least 18% (20% from 01/01/2020) of the total volume of their purchases. In order to participate in public procurement, an organization or an individual entrepreneur must be included in the Unified Register of SMEs (Federal Law of 18.06.2011 N 223-FZ).
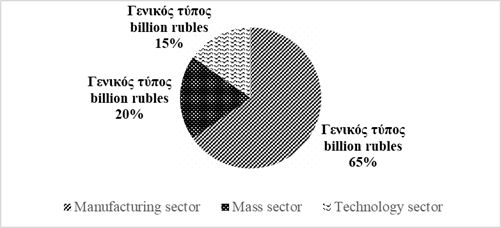
As can be seen in Tables
The government is considering financing measures to ensure preferential access for SMEs to the infrastructure of industrial parks and technology parks from 2022. Financial constraints affect firm sales, growth and employment (Ullah, 2020). Currently, SMEs and innovative companies can enter the technoparks and industrial parks, in which there are conditions for them that allow them to immediately start production or organize research activities without wasting time looking for the necessary equipment and there firms face lower levels of financial constraints. This will form the most favorable conditions for entrepreneurial initiative and increase the contribution of SMEs to the economy. The results show that SMEs have received great attention in recent years due to the important role they play in national economy. But since the coronavirus outbreak began, SMEs activity has been severely slowed. Affected by problems of logistics blocks, labor shortages, and drops in demand, a lot of SMEs closed. SMEs find themselves disadvantaged because they are disproportionately affected by inequalities of conditions for competition. The main goal of the Government is to provide SMEs with several types of support in accordance with existing programs and new ones introduced. SMEs are provided with financial assistance in the form of concessional lending, subsidies, stable tax conditions, leasing relations, public procurement, regulation of the activities of regulatory authorities and the introduction of a flexible legal regulation regime. The main factors constraining the activities of SMEs is the uncertainty of the economic situation and lack of own financial resources. So, the influence of government support is very important for the business activities. But government support measures for SMEs should be based on the goals of the country's economic policy and take into account long-term development priorities, as well as take comprehensive organizational measures to support development of SMEs.
Conclusion
1.Small and medium-sized businesses are very important for the economy and economic growth of Russia. But SMEs are vulnerable to negative changes in the economic environment. The business activity of SMEs has fallen.
2.Small and medium-sized businesses faced serious economic problems in such industries as wholesale and retail trade, construction, air transportation, hotel business, public catering, and real estate.
3.Companies are faced with many problems, such as a break in trade chains, a decrease in revenue and an increase in unforeseen expenses, interruptions in the activities of counterparties, their default on obligations, the inability to service the main debt or payment of taxes, insurance premiums, wages.
4.It is difficult for SMEs to withstand the consequences of the crisis without government support. So SMEs are in the focus of the government's attention
5.The effectiveness of state support measures for SMEs was assessed in the context of an unstable economic situation.
6.Comprehensive measures (tax, administrative, banking and financial support) should be implemented to support SMEs for reducing the negative effects of the economic crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic.
7.State funding is effective and capable measure to restore business activities of SMEs, but the volume of state funding should increase.
8.Existing assistance mechanisms are inadequate for SMEs to cope with the pandemic without additional targeted government support. There are a lot of serious problems in the development of SMEs. The state of the SMEs is unsatisfactory and requires constant attention from the government.
Our conclusions have certain limiting aspects and do not include government measures to support the innovation activity of enterprises in order to increase their innovation potential. Currently, the SME sector needs to develop innovation, because the innovation model should be used by SMEs to find new technologies in the market to solve their internal problems. The results obtained indicate that SMEs need to restructure and reorganize their work. It is necessary because the risks associated with economic uncertainty are quite high. The measures to support SMEs developed by the state should be based on the goals of the country's economic policy and considering long-term development priorities, as well as take measures to ensure that SME support is comprehensive. The results of the study can serve as a basis for further research on the problems of increasing the effectiveness of anti-crisis measures to support small and medium-sized businesses. In this regard, preferential lending and the provision of government guarantees, the introduction of measures to support the self-employed in the form of loans at low interest rates on working capital, the delay in repayment of loans with low interest rates, the introduction of tax holidays for affected enterprises should be studied more carefully. According to the research SMEs receive several types of government support in accordance with the existing concessional lending programs, since limited financial resources and borrowing opportunities are the most vulnerable factor for SMEs. In this connection, preferential lending and the provision of state guarantees, the introduction of measures to support the self-employed in the form of loans at low interest rates on working capital, a delay in the repayment of loans with low interest rates, the introduction of tax holidays for affected enterprises must be left.
References
- Agreement between the SME Corporation, IDF, REC and RDIF on the interaction of federal support organizations and regional development institutions of 05.12.2019, No. С-141. https://gisp.gov.ru/support-measures/list/11631572/
- Avdeeva, D. A., Akindinova, N. V., Blinkin, M. Ya., Bryzgalova, S. M., Vitkov, G. V., Gershman, M. A., Golovin, A. V., Gokhberg, L. M., …, & Shishkin, S. V. (2020). Russia in a new era: The choice of priorities and goals of national development expert. https://www.hse.ru/mirror/pubs/share/401421877.pdf
- Chistyakova, O. V., & Babkin, A. V. (2019). Business development institutes as tool of state support of small and medium-sized innovative entrepreneurship. St. Petersburg State Polytechnical University Journal. Economics, 12(6), 128-138.
- D'Amato, A. (2020). Capital structure, debt maturity, and financial crisis: Empirical evidence from SMEs. Small Business Economics, 55(4), 919-941.
- Federal Law of 05.04.2013 No. 44-FZ “On the contract system of the federal and municipal procurement of goods, works and services". http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_144624/
- Federal Law of 18.06.2011 N 223-FZ "On Purchasing Goods, Work, and Services by Certain Types of Legal Entities". http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_116964/
- Federal project "Acceleration of small and medium-sized businesses" and Creation of conditions for an easy start and comfortable doing business. (approved by the Order of the Government of the Russian Federation on March 28th, 2020, N 774-r). http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_111344/b9c695cccc7ef205d1e06c7c65e7fc25890b724f
- SME Corporation (2020). Financial support for SMEs. https://corpmsp.ru/upload/iblock/62e/10.2020-Prezentatsiya-o-merakh-finansovoy-podderzhki-MSP.pdf
- Goldina, A. A., & Fateeva, E. A. (2016). Financing the priority development of small and medium-sized businesses. Models, Systems, Networks in Economics, Engineering, Nature and Society, 3(19), 32-42.
- Knight, G., Moen, O., & Madsen, T. K. (2020). Antecedents to differentiation strategy in the exporting SME. International Business Review, 29(6), 101740.
- Mordvinkin, A. N. (2019). Small business lending. INFRA M.
- National project "Small and Medium Enterprises and Support for Individual Entrepreneurial Initiatives" (approved by the Presidium of the Council under the President of the Russian Federation for Strategic Development and National Projects, on December 24th, 2018, N 16). http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_144624/
- Special program of concessional lending to small and medium-sized businesses (approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation on December 30th, 2018 No. 1764). https://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/72041688/
- Strategy for the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030 (approved by the order of the Government of the Russian Federation of 06/02/2016 N 1083-r (as amended on 03/30/2018). http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_199462/
- Ullah, B. (2020). Financial constraints, corruption, and SME growth in transition economies. The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 75, 120-132.
- Wang, M., Mühlbacher, H., Wittmann, X., & Perrett, P. (2020). Dynamic collaboration between small- and medium-sized enterprises from highly dissimilar markets. European Management Journal, 38(3), 357-366.
- Xu, B., Costa, R., Wang, Y., & Xiao, Y. (2020). Financial support for micro and small enterprises: Economic benefit or social responsibility? Journal of Business Research, 115, 266-281.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 April 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-105-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
106
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1875
Subjects
Socio-economic development, digital economy, management, public administration
Cite this article as:
Kapranova, L. D. (2021). Financial And Economic Mechanisms Of State Support For Smes In Russia. In S. I. Ashmarina, V. V. Mantulenko, M. I. Inozemtsev, & E. L. Sidorenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of The Modern Economic Development, vol 106. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 854-866). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.04.02.102

