Abstract
The development of cruise traffic accelerates every year along the growth trajectory. The analysis of the scientific literature showed the need to attract more cruise liners to the Primorsky territory and meet the needs of the guests and factors that may affect cruise traffic must be considered. The studies carried out using statistical and analytical methods determined the great potential of tourist resources of the Primorsky Territory capable of satisfying the needs of cruise travelers. The result of assessing the satisfaction of guests with the services provided in the city of Vladivostok carried out using a three-stage model for evaluating the impressions of guests showed coincidences in the planning, stay and departure stages of determinants satisfying their needs. The SWOT analysis highlighted the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of determinants that satisfy the needs of guests and affect the development of cruise traffic in the Primorsky Territory. The hypothesis about the return of tourists if the region is attractive to them affirmed.
Keywords: Cruisestouristsserviceswaterside cities
Introduction
The cruise industry is rapidly developing and the number of tourists is growing every year has a positive impact on the world economy. The world leaders in the cruise market are Europe and North America, with 85 % of cruise liners, while the Pacific, Far East and Asian cruise market is underdeveloped, but growing rapidly (Cruise Lines International Association, 2014). The most popular destinations for consumers were cruises in the Caribbean (35 %), the Mediterranean sea (18 %), Europe (9 %), the Bahamas ( 7 %), Alaska (6 %), Mexico (5 %), Panama canal (3 %), transatlantic cruises (3 %), cruises to Hawaii (2 %), round the world cruise (2 %), South America (2 %), the Pacific region (2 %), cruises to Bermuda(1 %), cruises in Southeast Asia (1 %), cruises with a call to Canada (1 %), the Far East (1 %), other (3 %) –cruises to the shores of the Arctic and Antarctica (Sea cruises – in the modern world, 2018).
The offers of the "high style of rest" available for tourists from many countries of the world have significantly affected to the increase of 5 % – Compared to 2016, the number of passengers who prefer cruise ships in 2017 amounted to 25.8 million people, and in 2019, the growth of tourists continues for impressions by sea continues. At the end of 2018, all the world's cruise companies carried more than 26 million passengers, which is 3.3 % more than a year earlier. The total capacity of all Airliners in the world amounted to 537 thousand people, the number of ships – 314 (Analytics, 2019).
Problem Statement
Russia does not take a leading position in the development, of cruise tourism, most of the ports hosting cruise ships were in St. Petersburg and Sochi (Nezdoyminov, 2016). Currently, Vladivostok is able to receive tourists traveling by ship. However, the rapid growth of tourist flow cannot be analysed without the interest of consumers who want to visit (Caric & Mackelworth, 2014; Lam-González, 2019) the Vladivostokk port, and those factors that affect the cruises industry development. However, cruise traffic determinants, as an important factor in attracting foreign visitors and contributing to national economic growth, the attention of scientists has not been paid. Determinants are those conditions, reasons, factors on which the development of cruise traffic in the region depends.
Research Questions
The trend in the development of cruise traffic on the territory of the Primorsky territory is reflected in the statistics of 2018, which showed 13487 passengers against 12455 in 2017 due to an increase in the number of cruise ships and the number of passengers on Board entering Vladivostok (Report, 2018). Rresearch analysis of domestic and foreign authors showed that tourists who are going to relax on cruise ships often study the entertainment program, excursions in the stops ports (Baker & Fulford, 2016).
It is established that the ports choice takes the second place after the cost (Lekakou, 2009; Marti, 1992), and one of the determinants of attracting cruise tourists is visa-free destinations (Infogroup, 2018).
The transport infrastructure deserves special attention, tourism potential and hospitality can meet travelers expectations (Stefanou & Sarmaniotis, 2003).
Logunova (2015) was analyzed 84 factors affecting the efficiency of cruise tourism and the tourists choice of a cruise center, among which the most important for tourists are: cultural and historical attractions, the presence of an international airport, the cost of services, security, the sufficient number of tour buses and routes, the depth of the port, the quality of services, a sufficient number of guides-interpreter, a sufficient number of taxis, information signs for tourists, cultural and entertainment events (system of attractions), the disabilities passengers infrastructure.
As a result, the analysis of scientific literature has shown that in order to increase the number of cruise liners and meet the needs of guests, it is worth remembering the factors that can affect this type of tourism (Castillo-Manzano, Fageda, & Gonzalez-Laxe, 2014; Weeden, Lester, & Thyne, 2011; Wild & Dearing, 2000).
Purpose of the Study
The purpose is to analyze the tourist potential and identify the determinants which satisfy the guests needs and affect the cruise traffic development in the Primorsky Krai.
Hypothesis. If we assume that the tourist potential of Primorsky Krai is able to meet the cruise travelers expectations, the number of guests will increase every year.
Research Methods
Methods of research were statistical, analytical, three-stage model for evaluating guests' impressions, SWOT analysis.
Findings
Based on the analysis of the water tourism development and cruise shipping, as a promising direction that can bring real income to the budgets of all levels, was determined the regulatory and legal support of the state. It considered the transport strategy of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030. It were considered the strategy for the development of inland water transport, which provides for measures to tourism business develop, a number of measures aimed at solving the updating the transport fleet problem, including passenger, tourist fleet, as well as stimulating transport enterprises. As state support for the construction of the fleet, the legislative measures provided for by the Federal law of 07.11.2011 No. 305-FZ "On amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation in connection with the measures implementation to support the Russian shipbuilding and shipping". In addition, the Federal law provides for a financial support mechanism for shipping companies in the construction of ships at domestic shipyards. By order of the Russian Federation of May 31, 2014 No. 941-R approved "Strategy of the tourism development in the Russian Federation for the period till 2020", which was tasked with the inbound tourism development, i.e., attracting foreign tourists.
In order to attract foreign tourist from Japan and the Republic of Korea to Primorsky Krai, systematic work was carried out to promote the Vladivostok city as a cruise distance and a transport hub to the Far East in terms of increasing the Charter number and regular international flights to the region
For first time ever the Vladivostok international airport served 1 million 151 thousand passengers on foreign routes (an increase of 47 %) last year, and only 2 million 634 thousand passengers, which is 21 % higher than in 2017. The main growth in passenger traffic on international routes was provided by flights from Vladivostok to the Republic of Korea – passenger traffic on South Korean routes increased by 73 % compared to last year. Flights to South-East Asia showed an increase of 40 %, while flights to China and Japan grew by 15 %. The greatest contribution to the increase in passenger traffic on international routes was provided by flights from Vladivostok to the South Korean cities of Seoul, Daegu and Pusan. The systematic work started in 2015 to attract cruise tourists to the region has led to an increase in the incoming flow in this segment. Border and customs services of Vladivostok have sufficiently worked out the procedures for simultaneous registration of a large number of passengers.
The Department, as a coordinator and travel agencies, established the organization for the tourist services excursion. In the 2019 season, it is scheduled the visit of 15 cruise ship. In addition, in December 2018, the dredging works at the first and second cargo and passenger berths of the Vladivostok seaport were completed, which made it possible to receive super-liners from the Royal Caribbean International cruise company, which confirmed the visits of two ships with a 5.000 people capacity to Vladivostok in September.
Every year, the quality of infrastructure and the number of cultural objects increases: the FEFU campus, the cable-stayed bridge connects the Russky Island and the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, cable-stayed bridge across the Zolotoy Rog (Golden Horn), Vladivostok International Airport, the Primorsky branch of the Mariinsky theater, the Aquarium, the Fetisov arena and sports complex, the Sedanka Patroclus low-water bridge.
The opening of the integrated entertainment (gambling) zone "Tigre de Crystal", which is a unique object for Southeast Asia and with further development will be an important accumulator of tourist and financial flows. On October 12, 2015, Vladivostok received the official status of "Free port of Vladivostok" – a port zone that enjoys special customs, tax, investment and related regulatory regimes.
The region has 184 units of state and public museums, art galleries, more than 2000 units of historical and cultural monuments (urban planning, architecture, monumental art, archeology); 9 theaters, 20 cinemas, 2 circuses, 1 Aquarium; more than 60 orchestras, concert organizations, cultural centers; more than 300 units of leisure facilities, about 30 units of large sports complexes, 10 stadiums, 7 specialized exhibition centers.
Collective accommodation facilities (CAF) of Primorsky Krai include more than 450 enterprises, including 224 recreation centers, camp sites and boarding houses. The hotel industry of Primorsky Krai has 191 enterprises with the hotel room capacity more than 5.5 thousand units. Thus, the analysis identified a large potential of tourist resources of Primorsky Krai can meet the cruise travelers needs (Report on the implementation of the state program of Primorsky Krai, 2018).
Discussing the results, the assessments of the guest services satisfaction provided in Vladivostok conducted with the help of a three-step model for assessment the guest experience, it is possible to see the similarities in the stages of planning, stay and departure of the determinants that meet their needs. Twenty people was attended by the assessment, guests from other Russia cities, the age of the survey participants 35-45 years, have higher education, average income, couples. The results of the impressions are presented in the scheme of guest satisfaction assessment at all stages (Table
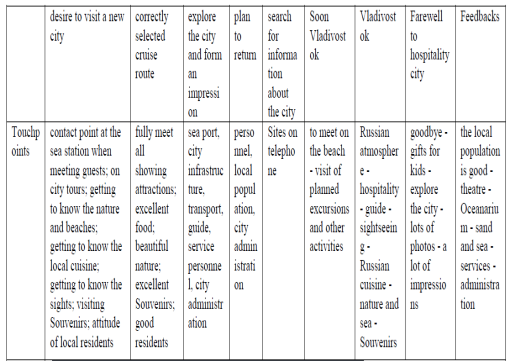
The three-step model for assessment the guest experience allowed to determine the factors of strengths and weaknesses. Table
Scores: Z – score, P – importance for us, V – significance (calculated as Z*P). Each factor is evaluated on the basis of its significance V – assessment of its importance for business, taking into account the certainty of this assessment (i.e. the probability that it is wrong). For each of the fields of the SWOT matrix, an average arithmetic estimate of U (Figure
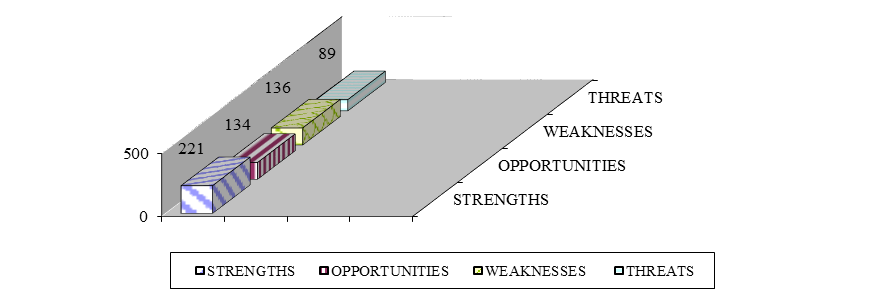
Based study, strong determinants were identified: seaport in the city center, international airport and railway station, excellent national cuisine, excellent hospitality, beach and nature, objects of display and entertainment, the weaknesses were the weather, fog, few percent of English speakers, not perfect waterside ecology, little information in English, not all objects have the accessible environment.
Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to analyze the tourist potential and identify the determinants which satisfy the guests needs and affect the cruise traffic development in the Primorsky Krai. Previous research has focused on the history of sea tourism in the Primorsky region of the Russian Federation, its status and future development (Derkacheva, Kosolapov, Galenko, & Makartseva, 2016).
This study continues the previous one, which identified the determinants which satisfy the guests needs and affect the cruise traffic development in the Primorsky Krai. It was proved that Vladivostok, as the capital of Primorsky Krai, is able to welcome guests and offer a program that can exceed the expectations of tourists, which shows an increase in the number of tourists over the past two years by 8 %. The interest of guests and strong complementarity is also observed between cruise traffic and traffic at the airports of the region.
Thus, cruise tourism has a huge potential for the regional economy development and contributes to the consolidation of the Vladivostok brand in the international information space of the cruise market as a "Sea gate to Russia".
The hypothesis about the return of tourists if the region is attractive to them affirmed.
Large waterside cities that can provide services and attractions to guests, effectively manage thousands of tourists – these are the areas that are designed to play a leading role in the cruise traffic development in the region. The identified determinants are able not only to meet the guests needs, but also with their subsequent improvement to make tourists once again return to the Vladivostok with friends. In addition to the size and population of the city, it is important that it is attractive for tourists and, in particular, the capital of the region, which has a certain mystery for this type of tourism.
The analysis of the obtained data allowed us to focus on strategies for the development of marine tourism for further research.
Acknowledgments
We thank the administration for providing data on the development of the cruise industry in the region and the respondents for their useful comments.
References
- Baker, D. Mc. A., & Fulford, M. D. (2016). Cruise passengers’ perceived value and willingness to recommend. Tourism & Managemnt Studies, 12(1), 74–85.
- Carić, H., & Mackelworth, P. (2014). Cruise tourism environmental impacts–The perspective from the Adriatic Sea. Ocean & coastal management, 102, 350-363.
- Castillo-Manzano, J. I., Fageda, X., & Gonzalez-Laxe, F. (2014). An analysis of the determinants of cruise traffic: An empirical application to the Spanish port system. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 66, 115-125.
- Cruise Lines International Association. (2014). North American cruise market profile. Retrieved from: http://www.cruising.org/docs/defaultsource/research/clia-naconsumerprofile
- Derkacheva, L. N., Kosolapov, A. B., Galenko, E. V., & Makartseva, E. V. (2016). Sea tourism in the southeast of Russia: status and trends of development. International review of managemnt and marketing, 6(4), 673–676.
- Infogroup. (2018). “TURPROM.ru”. Retrieved from: https://www.tourprom.ru/news/40645/
- Lam-González, Y. (2019). Maritime Tourism: Modelling consumer behaviour and itsmanagerial implications. Doctoral Dissertation Summary. European Journal of Tourism Res., 23, 208–211.
- Lekakou, M. B. (2009). Which Homeport in Europe: The Cruise Industry’s Selection Criteria. An International Multidisciplinary Journal of Tourism (TOURISMOS), 4(4), 215–240.
- Logunova, N. A. (2015). Ensuring the conditions for the effective development of cruise tourism in Crimea. Modern problem of service and tourism, 1(9), 86–96.
- Marti, B. E. (1992). Passenger perceptions of cruise itineraries: A Royal Viking Line case study. Marine Policy, 16(5), 360–370. Retrieved from: DOI:
- Nezdoyminov, S. G. (2016). The modern potential of regional markets for sea cruises. Economy, business and law, 6(2), 135–146.
- Sea cruises – in the modern world. (2018). Retrieved from: http://www.atlantisline.ru/Sea–cruises.aspx
- Stefanou, C. J., & Sarmaniotis, C. (2003). CRM and customer-centric knowledge management: an empirical research. Business Process Management Journal, 9(5), 617–634.
- Weeden, C., Lester, J.A., & Thyne, M. (2011). Cruise tourism: emerging issues and implications for a maturing industry. Journal Hospital, Tourism Manage, 18, 26–29.
- Wild, P., & Dearing, J. (2000). Development of and prospects for cruising in Europe. Marit. Policy Manage, 27(4), 315–333.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
07 December 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-095-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
96
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-833
Subjects
Management, human resources, resource efficiency, investment, infrastructure, research and development
Cite this article as:
Galenko, E. V., Ovcharenko, N. P., & Orlovskaia, I. V. (2020). Analysis Of The Cruise Industry In Primorsky Krai. In A. S. Nechaev, V. I. Bunkovsky, G. M. Beregova, P. A. Lontsikh, & A. S. Bovkun (Eds.), Trends and Innovations in Economic Studies, Science on Baikal Session, vol 96. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 243-250). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.12.32

