Abstract
The restaurant business has changed due to a new trend of customer preferences and demand. As an entrepreneur, being flexible and adaptability to the changes needed to ensure they can serve and fulfil customer demand. Maintaining the service quality is the main strategies to tackle the customer to remain satisfied and loyalty with the restaurant service. Fail to maintain good service, and the restaurant may lose the customer and struggle to survive in the market and industry. Hence, the purpose of this paper is to investigate the underlying key dimensions of service quality in selected local restaurants influence customer satisfaction. The fundamental of the SERVQUAL model of reliability, responsiveness, empathy, price, tangibility and assurance has applied to this study. A survey conducted among local restaurants located in Bukit Jelutong and there were 238 customers have participated. Data further analysed using Partial Least Square (PLS), and the finding revealed only responsiveness and tangibility were not supported while assurance, empathy, price and reliability were significant to this study. The finding implies to further into the service quality factors as perceived by the customer in having a local restaurant in Malaysia. Besides, this the finding implies to managers to consider the strategies to sustain and maintain customer satisfaction.
Keywords: Customer loyaltycustomer satisfactionservice quality
Introduction
The business trend nowadays struggles to survive in the competitive restaurant industry. Most of the business strategy aims to attract more customers with dedicated services and high quality of food that ultimately will create customer loyalty and increase customer satisfaction ( Gilbert et al., 2004) through improving the service quality. Service quality has widely discussed in the foodservice industry, and most of the owner of the restaurant agreed that the service quality is one of the competitive advantages for them to offer to the customers and compete with other competitors. Throughout the service quality, a restaurant capable of increasing their customer satisfaction, gain more profit, attract more numbers of customers, and create loyalty among the customer ( Ha & Jang, 2010). Recently, the local restaurant industries are competing with the high numbers of the international restaurant such as China, United Kingdom, Australia and Indonesia. All the competitors' have started up their business in Malaysia. Therefore, customer, either local or foreigner may have varieties choice of restaurants and the restaurant is competing with each other to gain the number of customers.
Problem Statement
The critical challenge for foodservice is a competitive market where all the restaurants in Malaysia struggle to maintain and sustain their services in the market ( Seth et al., 2005). The competitive market influenced by the changes in customer preferences which are inevitable. Customers have their right and choice to fulfil their demand and intent to have a new experience of the services provided in the restaurant. To this point, a customer looking forward to the high service quality that can make them feel satisfied and willing to be a loyal customer. According to Munhurrun ( 2012), the elements that used to study service quality and customer satisfaction. However, most of the relevance of the findings and related to the practice in other countries such as the United States and China compared to practice among local restaurants in Malaysia ( Chow et al., 2007; Kim et al., 2009; Kivela et al., 2000; Soriano, 2002).
Service quality (SERQUAL) theory
Fundamentally Theory of Service Quality (SERQUAL) has been introduced by Parasuraman, Zeithaml, and Berry in 1988. Most of the studied in service quality applied the theory to measure the service quality in various areas included foodservice. There are five elements of services quality consist of reliability, assurance, empathy, responsiveness, and tangible assets. Reliability refers to the dependably and accurately of delivering services to customers. In restaurant practices, the service must deliver accurate information that offers and order by customers. The service and information that share to customers consistent with what the restaurant offer and practice. The second element is responsiveness which refers to the volunteering values to offer assistance to customers. The restaurant commonly is responsible and responsive to the demand of the customer to maintain and sustain customer satisfaction and loyalty ( Chen & Myagmarsuren, 2013). On the other hand, assurance relates to the service and staffs they have high courtesy when they serve customers, competency of employees to influence customers trust and confidence to the service offered. Moreover, empathy is another element that most of the restaurant needed to add in their service quality. Staffs and restaurant well understand the customer needs and demand. Finally, it is tangible that physically appear to the customer when they visit the restaurant. The facilities, furniture, equipment, ambience and personnel of staffs ( Yarimoglu, 2014).
Service quality and restaurant
Empirical studied of service quality, and restaurant highlight discussion of reliability and empathy are the most common elements that highlight in restaurant services studies. Studies conducted by Lee et al. ( 2007) investigated the internal service quality of few restaurants in Jordan found reliability and empathy are significant to increase the restaurant performance and customer satisfaction. Another finding found that reliability and tangibles are also elements to promote more customers to the restaurant ( Chowdhary & Prakash, 2007). Furthermore, Chowdhary and Prakash ( 2007) claimed elements of assurance and empathy are needed to have good communication and interpersonal relationship between staffs and customers. With those elements mentioned strongly convinced the restaurant to deliver high service quality to customers. However, the restaurant service quality is difficult to evaluate as the different assessments made to different service, theme, and operation of the restaurant. Therefore, the elements of service quality might be useful to drive the restaurant owners or managers to upgrade and deliver high service quality to the customers.
Research Questions
Is there a significant relationship of reliability, assurance, empathy, responsiveness, and tangible assets towards customer satisfaction?
Purpose of the Study
Consequently, this study aims to investigate the five elements of service quality consists of reliability, assurance, empathy, responsiveness, and tangible assets on customer satisfaction within local restaurants in Selangor. This study expected to facilitate local restaurants in Selangor to boost customer satisfaction by strengthening their food service.
Research Methods
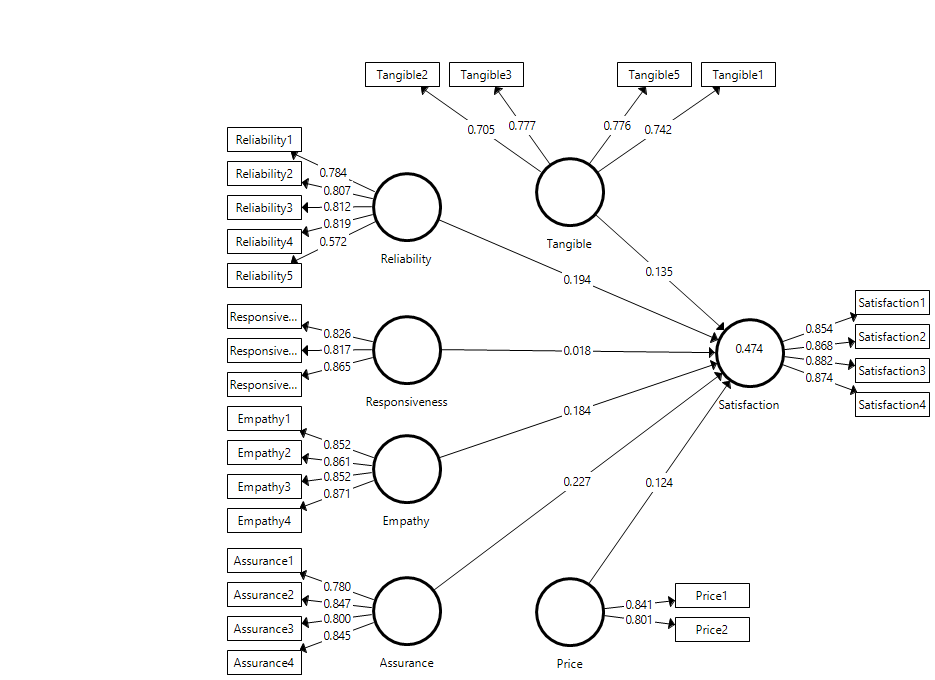
This study has surveyed 238 of customers who walked into the restaurant of One Serambi Cafe as located in Bukit Jelutong. There are 26 items of assurance, empathy, price, reliability, responsiveness and tangible and four items of customer satisfaction which adapted from Parasuraman et al. ( 1988). The selection of the customer used a convenient sampling technique that every customer entered the restaurant was selected as the sample of this studied. The data collected further analysis using statistical analysis of Partial Least Square (PLS) to investigate the significance of five dimensions of SERQUAL towards customer satisfaction. In PLS, there is a thorough analysis of the measurement model structural model.
Findings
Background of respondents
As shown in Table
Measurement model assessment
Table
Structural model
In a structural model, Table
The possibility of this happens to One Serambi Café highlight the most of the customer expects the employee knowledgeable of the food and attitude of the employees are presentable to the customer. The manager practically trains the employee to prioritise the customer. This possible create customer have appreciated and priority to the restaurant. More than that, this study highlights to understand the customer feeling and emotion are important due to minimising the feeling of dissonance or frustrated. For the price, this study explained that the affordable of the customer to pay the food and service with relevant price offer to them. Customer willing to pay more if the food and services meet their satisfaction. In the final finding, the reliability of the food and service delivery consistently significant to customer satisfaction as less error or mistake able to make the customer feel happy and satisfy. The dimension of responsiveness and tangible possible were not signed with customer satisfaction because the customer perceives and judge in a critical event such as peak hour of dining in, the employee lack of volunteering to assist the customers and provide excellent service. In the final discussion, the dimension of tangible was no significant due to the interior design, layout and physical of the restaurant need some improvement to fulfil the customer demand and satisfaction. The finding of this studied had similar finding with Lee et al. ( 2007) and Munhurrun ( 2012); however, all the dimensions of service quality measured were the strongest direct effects on user satisfaction. Hence, this study explained the different setting might influence the difference finding of this study.
Conclusion
As a conclusion, this study aimed to predict the reliability, the validity of determinant service quality and predict the relationship of the model in this study. The finding found that only responsiveness and tangibility were not statistically supported. In contrast to assurance, empathy, price and reliability supported by this study. The finding implies to perspective as manager. As a manager, the finding facilitates to learn about the demand of the customer towards their services and product. The entrepreneur has to improve the platform for the customer to give feedback while the staff will get feedback from the customer. Consistently, employees need well trained to response ethically and professional ways to customer‘s feedback and complaint. Training should concentrate not only to the business product and services but need included emotional intelligence as managing their own emotion and customer’s emotion.
Further, improve and bring a new and creative idea to tackle the demand and changes in customer preferences. The change of customer preference is unpredictable; therefore, as an entrepreneur, they should be agile to the changes of the customer. The services and product that will increase the values of assurance, empathy, price and reliability. In a future study, this study recommends reviewing the SERQUAL dimension to purchase a mediating effect on customer loyalty and satisfaction among local restaurant.
Acknowledgments
The research project conducted under the provision of a grant, the Internal Grant (DUCS 038/2018), awarded by the Universiti Teknologi MARA, Cawangan Selangor, Puncak Alam Campus for the support and other assistance.
References
- Chen, C. F., & Myagmarsuren, O. (2013). Exploring the moderating effects of value offerings between market orientation and performance in the tourism industry. International Journal of Tourism Research, 15(6), 595-610.
- Chow, I. H., Lau, V. P., Lo, T. W., Sha, Z., & Yun, H. (2007). Service quality in restaurant operations in China: Decision and experiential-oriented perspectives. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 26(3), 698–710.
- Chowdhary, N., & Prakash, M. (2007). Prioritising service quality dimensions. Managing Service Quality, 17(5), 493-509.
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences (2nd ed.). Lawrence Earlbaum Associates.
- Compeau, D. R., Higgins, C. A., & Huff, S. (1999). Social cognitive theory and individual reactions to computing technology: A longitudinal study. Management Information System Quarterly, 23(2), 145–158.
- Gilbert, G. R., Veloutsou, C., Goode, M. M. H., & Moutinho, L. (2004). Measuring customer satisfaction in the fast-food industry: A cross-national approach. Journal of Services Marketing, 18(5), 371-383.
- Ha, J., & Jang, S. C. (2010). Effects of service quality and food quality: The moderating role of atmospherics in an ethnic restaurant segment. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 29(3), 520-529.
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis. Prentice-Hall.
- Kim, W. G., Ng, C. Y. N., & Kim, Y. S. (2009). Influence of institutional DINESERV on customer satisfaction, return intention, and word-of-mouth. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 28(1), 10-17.
- Kivela, J., Inbakaran, R., & Reece, J. (2000). Consumer research in the restaurant environment, Part 3: Analysis, findings and conclusions. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 12(1), 13-30.
- Lee, H., Kim J., & Kim, J. (2007). Determinants of success for the application service provider: An empirical test in small businesses. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 65, 796–815.
- Munhurrun, P. R. (2012). Perceived service quality in restaurant services: Evidence from Mauritius. International Journal of Management and Marketing Research, 5(3), 1-14.
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1988). SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scales for measuring consumer perception of service quality. Journal of Retailing, 64(1), 12-37.
- Seth, N., Deshmukh, S., & Vrat, P. (2005), Service quality models: A review. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 22(9), 913-949.
- Soriano, D. R. (2002). Customers’ expectations factors in restaurants: The situation in Spain. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 19(8/9), 1055-1067.
- Yarimoglu, E. K. (2014). A review of dimensions of service quality models. Journal of Marketing Management, 2(2), 79-93.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-087-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
88
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1099
Subjects
Finance, business, innovation, entrepreneurship, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues
Cite this article as:
Razak, N. A., Aminuddin, Z. M., & Ghazali, A. R. (2020). Service Quality And Customer Satisfaction In Restaurant Industry Using Partial Least Square. In Z. Ahmad (Ed.), Progressing Beyond and Better: Leading Businesses for a Sustainable Future, vol 88. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 218-225). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.20

