Abstract
The paper considers the theoretical basis for assessing the financial sustainability of a commercial bank: the essence and content of the category “financial sustainability” are defined, factors affecting the financial sustainability of a bank are classified, criteria of financial sustainability are defined. The current state of the Russian economy, which is based on various small and medium-sized business organizations, strongly depends on reliability and sustainability of the banking system. The sustainability of the banking system is inextricably linked to the ability of a system to withstand the negative processes taking place at the level of individual elements. Commercial banks, in turn, are the main link of the banking system. With temporarily surplus funds in the credit resource market, they satisfy the need of the economy for working capital, contribute to the transformation of money into capital, and meet the needs of the population for consumer credits. All economic actors – the population, the state, shareholders, investors and, mainly, the banks themselves – are interested in assessing the sustainability of commercial banks. Commercial banks are already looking for sustainability: they monitor the quality of their resource base and assets, replenish the reserve fund, manage risks and diversify their products and services. In Russian scientific and practical communities there is a constant search for assessment methods. However, to date, theoretical issues of assessing the financial sustainability of banks remain insufficiently developed, so the chosen topic is relevant from the point of view of its practical application.
Keywords: Sustainabilityassessmentmethodologymarketbanking system
Introduction
First of all, the subject of the analysis contains two concepts. Among them is the concept of “sustainability” and the concept of “bank”. Therefore, in order to understand the essence of the basic concept, it is necessary to study both elements.
In the modern edition of
The following conclusions can thus be drawn with regard to sustainability:
Sustainability is the quality of the state and process of movement of a system.
Sustainability gives a characteristic of the process, which is interpreted both in terms of its condition and its development. Development from a sustainability perspective always leads to a positive outcome. It can accelerate or slow down, but it expresses improvement, progress.
Sustainability is a complex characteristic of the movement towards progress reflecting the interaction of its elements with each other and with the external environment.
All these conclusions, while important, will prove to be a complete abstraction if we do not link sustainability to the bank’s activities. According to Federal Law No. 395-I
Bank sustainability can be divided into several types:
Economic sustainability of a bank – the bank, being an economic institution, specializes in economic relations, their sustainability is naturally economic.
Political sustainability of a bank – the bank’s activities strongly depend on political relations and events. As an economic structure, the banking system remains the hostage of political relations that exist in a given society.
Moral sustainability of a bank – sustainability characterized by whether the values of the bank and the ways of their achievement correspond to moral principles, norms and standards accepted in the society. Moral sustainability of the bank requires it to counteract the breach of legislation, exclude currency fraud, observe transparency of bank reporting.
Operational sustainability – sustainability arising from individual operations and transactions in the market. Banks seeking sustainable development should strive to expand their activities, develop banking technologies and improve the quality of banking products and services.
Personnel sustainability – a sustainable bank with qualified staff.
In addition to the types considered, the economic literature also highlights balanced sustainability and sustainability with unsustainable equilibrium, constant and changing, rapidly developing, evenly developing and unevenly developing sustainability, constantly and often changing sustainability, socially useful and selfish sustainability, and other types. The reference to them, while debatable, generally expands our knowledge of the content of sustainability underlying its model.
In summary, it is possible to define the financial sustainability of a commercial bank as the bank’s ability to function stably, meet its obligations, provide the full range of permitted services and generate profits under the influence of changing external and internal factors.
Problem Statement
The problem of sustainability of the banking system has recently become particularly relevant due to the increase in the number of licenses being revoked from banks. The number of banks in Russia is rapidly decreasing: since 2001 the number of banks has decreased by 698 or 55 % (Fig. 1).
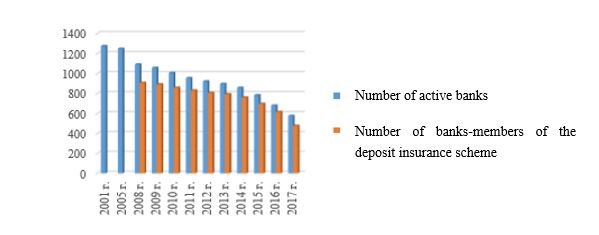
As of 1 September 2017, there are 576 banks, and as of 1 September 2016 – 610, i.e. during the year the number of banks decreased by 6 %. In turn, an important indicator of the reliability of a commercial bank in Russia is its participation in the deposit insurance scheme (DES). The number of banks participating in DES is decreasing as quickly as the number of banks operating in Russia: by 2017 their number has decreased by one third (Fig. 1).
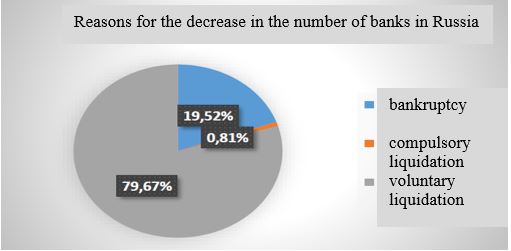
Thus, the question arises as to what exactly causes such a decrease in the number of banks and non-bank credit institutions. According to statistical data of the report of the Bank of Russia, as of 01.01.2017 the absolute majority of credit institutions stopped the activity as a result of voluntary liquidation, i.e. they failed to meet the requirements of creditors (Fig. 2).
Voluntary liquidation of the bank is carried out by the decision of its participants with notification of the Bank of Russia.
The grounds for voluntary liquidation may include the following ( Dobrynina et al., 2014; Kuznetsova & Vasilieva, 2016):
insufficient performance of a bank;
disagreements within the founders of a bank, etc.
Compulsory liquidation is the liquidation of banks which license was revoked by the decision of the Bank of Russia. The license is revoked in extreme situations where there is a real threat to the interests of creditors and the founders themselves.
The sustainability of the banking system in today’s world is not a problem of just one particular country, but rather a global problem. The development of the economy is impossible without taking into account the state of the monetary system. Instability and disequilibrium are becoming increasingly evident. Increasingly, the world is experiencing crisis periods, downturns in economic growth, and hence the society that seeks sustainability needs to take preventive measures, develop a model of a sustainable banking system.
Commercial banks are already looking for sustainability: they monitor the quality of their resource base and assets, replenish the reserve fund, manage risks and diversify their products and services. Some banks are increasing their sustainability by combining banking and insurance business, expanding investment banking. Credit institutions introduce new financial instruments, and their activities continue to be universalized. It shall be noted that recently the share of non-interest income from investment transactions of banks has been rapidly growing.
Research Questions
The subject of the study is the assessment of financial sustainability of a commercial bank adopted in Russian and foreign practice. The current state of the Russian economy largely depends on reliability and sustainability of the banking system. Commercial banks, in turn, are the main link of the banking system. The population of the country shall feel confidence in financial sustainability of banks, while the owners and investors – in quality and reliability of any commercial bank. The sustainability of a single credit institution forms the basis of the sustainability of the entire banking system, and is therefore an important strategic and current task of its development.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to analyze the theoretical foundations of the financial sustainability of a commercial bank, the existing factors of its assessment and their improvement.
In order to achieve the above purpose, the following tasks were solved:
to study the nature and factors of financial sustainability;
to analyze modern methods of assessing financial sustainability;
to develop the methodology for assessing the financial sustainability of a commercial bank.
Research Methods
The study uses common methods of scientific knowledge: observation, comparison, analysis, modeling. The system method is the main way of generalizing the information obtained in this study.
Findings
There are the following main methods for assessing the bank’s financial sustainability:
methodology of the Bank of Russia, which includes such groups of indicators as: group of capital estimates; group of asset estimates; group of indicators for assessing the management quality of a bank, its operations and risks; group of profitability estimates; group of liquidity estimates ( Gerasimova, 2015);
methodology by Vitaly Kromonov, which is a system of coefficients, on the basis of which the integral indicator characterizing the degree of reliability of a bank is calculated ( Gadzhiagaev, 2015);
CAMEL methodology formed from five integral indicators: Capital Adequacy, Asset Quality, Management factors, Earnings, Liquidity ( Dubovik, 2014).
The methodology for assessing the financial sustainability of a commercial bank proposed by the Bank of Russia is set out in the Bank of Russia Directive No. 1379-U
Therefore, based on the methodology of the Bank of Russia, we will develop our own methodology. In our opinion, the assessment of business activity ( Magomedkadiev, 2014; Yankina & Dolgova, 2016), which is not present in the Bank of Russia methodology but is used in the CAMEL methodology, is a significant indicator.
In order to improve the methodology of the Bank of Russia taking into account the indicator of business activity assessment, we will introduce the indicators specified in Table
In our opinion, the developed methodology, which takes into account the above factors, is more efficient and practical since it utilizes the data of public bank reporting. The proposed methodology is characterized by its rapid and easy exercising by public users.
Conclusion
Any bank operates under many factors that directly or indirectly affect it. In a situation where any of the factors are neglected, the assessment of the impact of other factors may not be correct. Most scientists divide the bank’s sustainability factors into external and internal factors ( Kim, 2016), but pay attention to the conditionality of such division because many factors are dual in nature.
The following external factors can be identified from the study: state banking targets; potential of the real economy; GDP; confidence in banks; cash flow position; macroeconomic factors; legal factors; political factors; state of the banking system and the economy of partner banks; market environment factors.
The considered factors often have a different influence on the bank’s financial sustainability: some may have a positive impact, others may have a negative impact, and either factor may have a stronger impact. Often all these factors function together, acting simultaneously to determine the economy and finances of a credit institution; individually show their action in the bank’s economy.
The financial sustainability of banks is dependent on the competitive environment ( Magomadova et al., 2019). Sufficiently developed competition forces banks to monitor the work of rival banks more closely, to act more actively, to implement measures to expand their operations, to improve the quality of service provision, to offer new products, to improve banking technologies.
Among other factors that have a strong impact on the financial sustainability of banks, we have highlighted the state of the banking system as a whole and its components. Its development potential represents an environment in which commercial banks function.
Internal factors affecting sustainability are more likely to play a key role. Their division into groups is traditionally based on the impact of certain reasons on commercial banks.
Thus, it seems appropriate to identify the following internal factors that influence banks’ sustainability: choice of mission, strategy, development goals, financial resource forecasting; risk resistance; ability to mobilize financial resources; increasing the quantity and quality of banking activities on an expanded basis; cost savings; marketing and management quality; organizational structure; orientation towards the development of modern banking technologies.
Marketing and management quality have an important impact on achieving financial sustainability. Poor marketing and poor management are grounds for poor bank performance. In our view, the quality of management is a decisive organizational factor affecting the financial sustainability of the bank. In order to increase sustainability, the bank’s management shall identify the needs of its clients and provide the opportunities that their competitors cannot offer, seeking leading positions in the banking market. In today’s world, banks face obstacles that can only be overcome using the latest information technologies. Their application allows to significantly increasing the speed and quality of banking services.
In summary, factors can contribute to both increasing the bank’s financial sustainability and decrease it. The influence of certain factors shows to what extent the bank is ready for any deviations in order to continue its stable functioning. Consequently, banks seeking sustainability need to consider and analyze the impact of each of the above factors.
References
- Dobrynina, E. S., Serdyuk, A. E., & Yakovleva, K. A. (2014). Banking system of the Russian Federation and problems of its development. Achievements of univer. Sci., 10, 214.
- Dubovik, M. V. (2014). Financial sustainability of commercial banks – guarantee of economic sustainability. In Scientific works of teachers of the Moscow Academy of Economics and Law (pp. 185–193). Moscow Acad. of Econ. and Law.
- Fetisov, G. G. (2005). The Great Russian Encyclopedia Dictionary. RAS.
- Gadzhiagaev, M. A. (2015). Quantitative and qualitative indicators of stress resistance and reliability of a commercial bank. Fundam. Res., 7-4, 811.
- Gerasimova, E. B. (2015). Phenomenology of financial sustainability of a commercial bank. J. of Financial Acad., 2(34), 81.
- Kim, A. D. (2016). Main factors and criteria influencing financial sustainability of a commercial bank. Scientific discussion: issues of economy and management, 2(46), 176.
- Kuznetsova, N. V., & Vasilieva, A. G. (2016). To the issue of evaluation of the level of reliability of a commercial bank. Econ. and Polit., 1(7), 62.
- Magomadova, M. M., Edrenov, G. D., & Izotov, A. B. (2019). Russian banking system in economic and social development of the country. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, SCTCGM 2018, 1000–1006.
- Magomedkadiev, A. A. (2014). Current problems of development of the banking system in the Russian Federation at the present stage. Econ. and society, 2-3(11), 161.
- Yankina, I. A., & Dolgova, E. E. (2016). Analysis of operational risk exposure of commercial banks in Russia. Finance and Credit, 3(675), 17.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-091-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
92
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3929
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Hominich, I., Chelukhina, N., Savvina, O., Asyaeva, E., & Bisultanova, A. (2020). Methodology For Assessing The Financial Sustainability Of A Commercial Bank. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism» Dedicated to the 80th Anniversary of Turkayev Hassan Vakhitovich, vol 92. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1886-1892). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.05.249

