Abstract
In the article, the authors propose a methodological approach to determining the long-term need for personnel in economic specialties for the region's agriculture. The relevance of the research topic is due to the influence of the digital economy and the improvement of the distribution of control digits for reception between federal centers and regions of Russia. According to our calculations, the need for personnel is much higher than the number of vacant places. The educational process should include employees who, according to qualification requirements, must have higher education, but do not have it at the present time, and also take into account that some employees are in the pre-retirement or retirement age and can complete their work in the near future. The input parameters for the model are the number of vacancies, the staff of agricultural enterprises and organizations in accordance with the positions held, the age of employees, length of service and level of education. We used the websites of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Irkutsk Region and employment services, as well as departmental statistics as the initial data for testing the methodological approach we proposed. For a more detailed analysis of the staff of agricultural workers, the largest municipality of the Irkutsk region was chosen - the Usol district municipality, whose agricultural producers produce 1/5 of the gross agricultural output in the region. Then, the data from the sample survey were extended to the entire population.
Keywords: Personneleconomic specialtiesagricultureneed
Introduction
The country's food security and sustainable agricultural development are the most pressing problems of our time. They cannot be solved without the participation of highly qualified personnel. In turn, the problem of agricultural staffing is due to the retirement of a large number of agricultural enterprises from the competition, a decrease in the attractiveness of rural life due to poorly developed social infrastructure, a decrease in the prestige of labor on land, and low wages. In the context of the digitalization of the economy and in connection with the improvement of the mechanism for distributing control numbers of applicants between the federal center and the regions, educational organizations are faced with the question of not only training higher education personnel with key competencies in the digital economy, but also the issue of determining the region's need for these personnel.
Problem Statement
Predicting the need for personnel for the economy of the region was carried out by many domestic and foreign scientists ( Digilina, 2004; Huffman & Orazem, 2004; Ivanyo et al., 2019; Kalinina et al., 2020; Orlov et al., 2019; Petrusha et al., 2019; Rudoy et al., 2015; Shelkovnikov et al., 2018; Stadnik et al., 2015; Taylor & Martin, 2001; Trufanova, 2019; Vasilevska, 2015). In their proposed methods, a number of assumptions are taken into account, designed to mitigate the sign of uncertainty in modeling economic processes (various forecast scenarios are used). As a result of the implementation of such calculations, as a rule, a forecast of the structure of employment in the region’s economy is presented; a forecast of the average annual number of people employed in the region’s economy, including by type of economic activity and a forecast of additional staffing needs (excess) in the economy. At the same time, there are no methods for determining the need for personnel of individual sectors of the region’s economy in the context of specific specialties and areas of training, for example, economists, for agriculture.
According to the Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation dated 01.24.2020 No. 41 “On approval of calculation methods for the federal project “Personnel for the Digital Economy ”of the national program“ Digital Economy of the Russian Federation ”” as part of the training areas and specialties of higher education, education in which is associated with the formation of two or more key competencies of the digital economy, included 38.03.01 (38.04.01) Economics, 38.03.02 (38.04.02) Management, 38.03.05 Business Informatics. These areas of training are implemented at the Federal State Budget Educational Establishment of Higher Education Irkutsk State Agrarian University named after A.A. Ezhevsky at the Institute of Economics, Management and Applied Informatics.
Research Questions
To identify the prospective need for personnel of economic specialties for agriculture, we proposed a methodological approach. We proceeded from the fact that the need for personnel is much higher than the number of vacant places, and, therefore, analysis of indicators characterizing the labor market (vacancy rate, stress coefficient) will not be enough. We also took into account that some of the leading employees and specialists who, according to qualification requirements, must have higher education, but do not have it at present, should be included in the educational process. In addition, some employees are in the pre-retirement or retirement age and in the near future can complete their labor activities.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the work is to propose a methodological approach to determining the need for personnel in economic specialties for agriculture. Test this approach on the example of the Irkutsk State Agrarian University named after A.A. Ezhevsky. The object of the study is the staff of economic specialties for agriculture in the region. The subject of the study is the organizational and economic relations that arise in the process of providing personnel for the economic specialties of the region's agriculture.
Research Methods
The algorithm for determining the need for personnel for the region's agriculture in the context of specific specialties and areas of training is presented in Figure
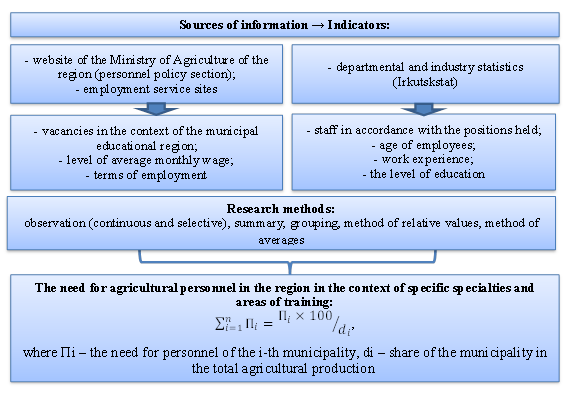
The websites of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Irkutsk Region (personnel policy section) and employment services, as well as departmental statistics, were used as initial data for testing the methodological approach we proposed. For a more detailed analysis of the staff of agricultural workers, the largest municipality of the Irkutsk region was chosen – the Usolsky district municipality, whose agricultural producers occupy 1/5 of the gross agricultural production in the region. Then, the data from the sample survey were extended to the entire population. The error of representativeness of the sample does not exceed 5%.
Findings
We propose to begin calculating the need for personnel in economic specialties for the region’s agriculture by studying vacancies for the position of accountant, economist, deputy head in the region’s municipalities in the labor market in the Irkutsk region. Vacancies for these positions in the municipalities of the Irkutsk region as of 01.01.2020 are presented in Table
As of 01.01.2020, in the municipalities of the Irkutsk region there are 22 vacant jobs for specialists requiring economic training for agriculture. It is worth paying attention to the fact that the level of proposed wages on average does not significantly exceed the minimum wage in the Irkutsk region established from 01.01.2020. Since the Irkutsk region is equated to the Far North (group 3-4), where 50,0% the second and 30,0% bonus, taking into account this, the size of wages in the Irkutsk region from January 1, 2020 should be at least 15769 rubles (12 130 x 1.3) in the southern regions, and 18195 rubles (12 130 x 1.5) - in the north. So, for example, in the Zhigalovsky district, which belongs to the northern territories, the proposed level of wages is lower than the minimum for these territories by 28.6% (Table
Further, a more in-depth analysis of the personnel composition of agriculture was continued on the materials of the largest municipal formation in the region – the Usolsky district municipal formation of the Irkutsk region (Tables
In the Usolsky district municipality, 34 people work as farm managers, including 52.9% of them at the age close to the retirement age and (or) at the retirement age (Table
The grouping of farm managers by experience in the Usolsky district municipality in 2019 is presented in Table
The grouping of farm managers by the level of education in the Usolsky district municipality in 2019 is presented in Table
So, the heads of farms with higher education – 55.6% of the total number, the chairmen of the cooperative – 100%, the directors of agricultural enterprises – 72.7%, managers and specialists of the agricultural department – 100%, respectively.
According to qualification requirements, employees holding the positions of managers and specialists must have higher education. An analysis of the number and composition of employees replacing the positions of managers and specialists of farms in the Usolsky district municipality in 2019 indicates that as of 01.01.2019, the proportion of employees holding the positions of managers and specialists requiring higher economic education is 61.8 % of the total number of managers and specialists, of which 51.2% have higher education, 22.2% have secondary vocational education and 26.6% have neither higher nor secondary vocational education I. Also, it is worth noting that persons over 55 years of age among women and 60 years of age among men work in these positions – their share is 16.7% (104 people).
According to the draft Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation “On the approval of the professional standard “Economist ”( prepared by the Ministry of Labor of Russia on November 10, 2017), employees in the following positions must meet the qualification levels:
positions of specialists (for example, economist) – 6th level – higher education in the undergraduate program;
posts of managers of financial, economic and administrative activities, heads of planning, economic, financial, economic and administrative departments; 7th level; higher education in specialty or master's programs. This level corresponds to the qualifications of the senior management responsible for the work of large organizations or departments, therefore, the employee must possess management skills and strategic planning.
Further, it is possible to calculate the need for personnel in economic specialties for agriculture in the Irkutsk region (Table
The need for personnel with higher education in the direction 38.03.01 Economics (undergraduate level) for the next five years may reach 1626 people, i.e. on average, 325 people should be accepted for training per year. In the direction 38.04.01 Economics (master's level) – 479 people (average for the year - 96 people). Form of study can be both full-time and part-time.
Conclusion
In the context of the digital economy, it is necessary to change the training strategy, therefore, the methodological approach we have proposed to determine the prospective need for personnel for agriculture will be in demand in other regions and sectors of the economy. According to our calculations, the need for personnel is much higher than the number of vacant places. Therefore, in the educational process should be included employees who, according to qualification requirements, must have higher education, but do not have it at present, and also take into account that some employees are in pre-retirement or retirement age and can complete their work in the near future.
References
- Digilina, O. (2004). Chelovecheskij kapital v sisteme trudovyh otnoshenij [Human capital in the system of labor relations]. RGB.
- Huffman, W., & Orazem, P. (2004). The Role of Agriculture and Human Capital in Economic Growth: Farmers, Schooling, and Health [Adobe Digital Editions version]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5132487_The_Role_of_Agriculture_and_Human_Capital_in_Economic_Growth_Farmers_Schooling_and_Health
- Ivanyo, Y., Dmitriev, N., & Adushinov, D. (2019). Cistema vedeniya sel'skogo hozyajstva Irkutskoj oblasti [System of agriculture of the Irkutsk region, Volume Part 1]. Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation, Ministry of Agriculture of the Irkutsk Region Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Irkutsk State Agrarian University named after A.A. Ezhevsky." Irkutsk State Agrarian University.
- Kalinina, L., & Zelenskaya, I. (2017). Tendencii formirovaniya i ispol'zovaniya trudovyh resursov v sel'skoj mestnosti Rossii [Trends in the formation and use of labor resources in rural areas of Russia]. Mongolian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 21(2), 101-108. https://www.mongoliajol.info/index.php/MJAS/issue/view/94
- Kalinina, L., & Zelenskaya, I. (2017). Sglazhivanie prostranstvennoj neravnomernosti raspredelenij trudovyh resursov [Smoothing out spatial disparities in the distribution of labor resources]. Economics and Entrepreneurship, 1-2(66), 346-349. http://195.206.39.221/fulltext/i_004100.pdf
- Kalinina, L., Zelenskaya, I., & Trufanova, S. (2020). Algoritm opredeleniya celevyh rynkov sbyta sel'skohozyajstvennoj produkcii, proizvodimoj v regione [Algorithm for Determining Target Markets for the Sale of Agricultural Products Produced in the Region]. Proceedings of the First International Volga Region Conference on Economics, Humanities and Sports (FICEHS 2019), 114, 133-136. https://doi.org/10.2991/aebmr.k.200114.030
- Orlov, V., Ivanova, T., Brenchagova, S., & Rumbayeva, N. (2019). Mathematical modeling of economic factors impact: Reproduction of personnel potential in agriculture sector of Russia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 433(1), 012012, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/433/1/012012
- Petrusha, P., Kozlova, D., & Ivanova, K. (2019). The human capital: Education and the green economy. E3S Web of Conferences, 110, 02074, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201911002074
- Rudoy, E., Shelkovnikov, S., Matveev, D., Sycheva, I., & Glotko, A. (2015). "Green Box" and innovative of agriculture in the Altai territory of Russia. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 6(3), 632-639. https://doi.org/10.14505/jarle.v6.3(13).17
- Shelkovnikov, S., Kuznetsova, I., Denisov, D., Peshkova, O., & Malyshev, Y. (2018). Enhancing the instruments of state support for the process of building human capital. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 9(8), 1633-1641. https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=36048977
- Stadnik, A., Shelkovnikov, S., Rudoy, E., Matveev, D., & Petukhova, M. (2015) Improving the methodology of disposition of state support funds for agriculture under the WTO rules. Asian Social Science, 11(14), 133-140. https://doi.org/10.5539/ass.v11n14p133
- Taylor, J., & Martin, P. (2001). Chapter 9 Human capital: Migration and rural population change Handbook of Agricultural Economics, 1, 457-511. [Kindle DX version]. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B7P5B-4FPWV0B-1F/2/616be8314f71a936ac13cf0105c761b8
- Trufanova, S. (2019). Trudovye resursy sel'skoj mestnosti v sisteme vedeniya sel'skogo hozyajstva [Rural labor in the agricultural system]. In the collection: Agrarian science – to agriculture. Collection of materials of the XIV International Scientific and Practical Conference, 126-128. https://www.elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_38199555_27749459.pdf
- Vasilevska, D. (2015). Education as a factor in the development of human capital: Case of Latvia Universal Journal of Management, 3, 79. [Kindle DX version]. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujm.2015.030205
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
21 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-089-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
90
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1677
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Kalinina, L. A., Trufanova, S. V., & Zelenskaya, I. A. (2020). Methodological Approaches To Specific Needs In Agriculture. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, G. Herwig, U. Umbetov, A. S. Budagov, & Y. Y. Bocharova (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST 2020), vol 90. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 831-839). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.03.98

