Abstract
The reengineering approach helps create a system of effective flexible company management in a changing innovative growth economy. The reengineering concept, formulated and introduced into management practice in the early 1990s, was positioned as a management business strategy, an alternative to the classical management paradigm of A. Smith. The desired method of effective enterprise management should take into account the economic, organizational and social constraints. Management proceeds from the need for optimal use of resources at the organization’s disposal. Value is created and realized by people who are able to identify new customer needs or open new paths for market development. This often requires innovative approaches and faces resistance from workers. In the face of change, they are worried about maintaining guarantees of labor remuneration and other types of social protection, and it is the team that creates a product which ensures competitive advantages of the business. The solution to the problem should satisfy all interested parties. The objective of improving the efficiency of enterprise management may be achieved through the use of the business reengineering method.
Keywords: Reengineeringcompany management; effectivenessbusiness processesinnovation
Introduction
An enterprise is a complexly organized system of relations that carries out its own development cycle as a result of complex interaction with other micro- and macro-level economic systems. Technological progress and globalization processes increase the strength of this mutual influence, the contradictions growth rate, and today, when the crisis has embraced the economic, political and social aspects of human activity on a planetary scale, and the risks of business insolvency are increasing, the need of managers for effective ways and methods of managing changes in the face of changes is especially relevant ( Kunde, 2000).
In addition, shareholders and investors are interested in effective management, which helps the company gain a leading position in the market, increase cash income and profit margins.
Problem Statement
Reengineering as a method of redesigning business processes was popular in the US business world and positioned as revolutionary: the practice of successful implementation showed an improvement in performance by tens and hundreds of times ( Hammer, 1990; Hammer & Champy, 1993). However, such results were rarely achieved, and over 50% of reengineering projects were completed due to a lack of results. Similar results were obtained in our country. Disruption of expectations was expressed in critical articles by foreign and domestic authors supporting less radical approaches and minimizing risks, especially in times of crisis. But while it may be enough to maintain efficiency with relatively stable operation of the reforms, the crisis conditions set special requirements for the methods and scale of the required transformations ( Gildingersh, 2016). It is important for us to clarify what made the method so effective that the reengineering theory is included in the training of economists in the world and in our country, and why it has become a source of frustration and criticism for others.
Typically, understanding of what to do comes from a general assessment of the situation. Today it is characterized by inconstancy and unpredictability of demand, competition and changes, as well as the impossibility of extensive development. Similar products and services compete in standards, price, choice, quality, service before, during and after the sale. This increases the risk of losing customers, each of whom knows what he wants, at what price and on what conditions. The dynamics of any changes is accelerating. Managers understand that business must be equally flexible and dynamic, offering new products, services and the highest quality service at a competitive price. But in practice, it is impossible to overcome a number of reasons for the total inefficiency: lack of attention to customers, bureaucratic delays, lagging behind the dynamics of changes in external conditions, immunity, disunity, concentration on personal work to the detriment of overall results, significant production costs and lack of innovation. The problem of inevitability of even obvious reasons is that the company does not change the behaviour model, therefore improvements do not occur ( Bandler & Grinder, 1979).
Research Questions
A halt in development and deterioration of indicators to varying degrees is evidence of a critical mismatch between the system and the environment and requires reengineering, which financially prosperous companies can resort to if they are focused on gaining leading positions in their market sector.
The essence of reengineering is innovation, i.e. abandoning customary ideas and rules and starting a fundamentally new type of thinking and behaviour ( Davenport, 1993; Davenport & Short, 1990):
Setting high goals, which require transition to critical rethinking of what exists and determination to rebuild structures and procedures if necessary (after reengineering the business process, it becomes clear what the structure and personnel should be like).
Focus on the process should identify and organize the key flows of the main activity around which business development will be going on, creating a valuable result for the client. In this case, the customer may be the buyer, contractor or unit of the company.
Violation of rules, traditions, structures and standards is encouraged if they conflict with the understanding of what and how should be done on the basis of today's situation.
Creative use of computer technology in the creation of new models of information flows and the business process itself ( Alexankov et al., 2017).
As a result, reengineering allows for less resources to achieve radical improvements. Consider why and how this happens.
Purpose of the Study
Reengineering turns disparate interaction into a process that unites the entire company into a single whole, which leads to the birth of a competitive product, increased demand and spasmodic improvement in performance indicators. Obviously, the synergy effect is manifested in reengineering when every company employee is involved in creating value for internal or external client (Figure
Scheme A shows formation of a competitive product as a result of reengineering of a company's business processes. Scheme B shows the formation of the company's key competence as a result of interaction with customers on the reengineering principles.
A company implementing a reengineering project (Figure
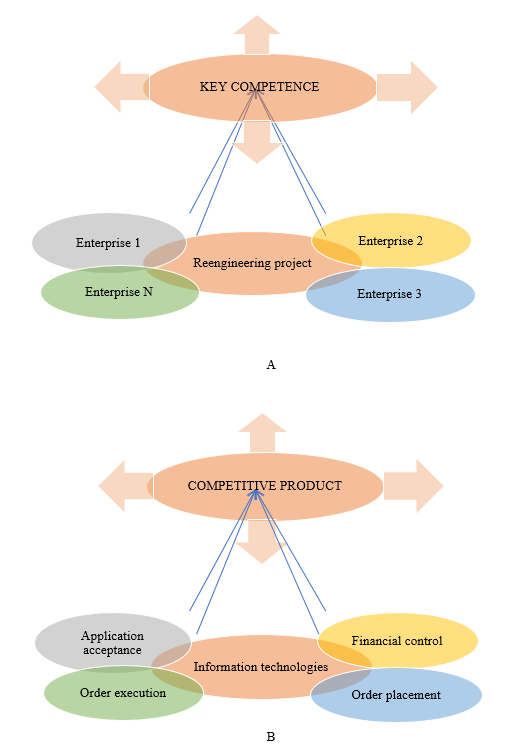
Thus, reengineering simplifies the processes that can improve the quality and level of service, reduce unproductive costs and ensure business dynamics. Business processes get new features:
a combination of positions or specialists (focus and project groups);
the appearance of a responsible manager for contacts with the client on all issues;
reduction in the share of control and approvals;
delegation of responsibility;
change of sequence of work;
the rejection of standardization, flexibility, variability;
work outside the types of work, organizational structures and companies.
Reengineering excludes those costs that do not add value (reconciliation, tracking, etc.), thereby freeing up time for productive work ( Wei & Pokrovskaia, 2017).
Research Methods
Since the main goal of reengineering is to ensure stability and prosperity of the entire company, it is important to convey this idea to employees in order to reduce resistance to change ( Csikszentmihalyi, 1990). It may be useful to change the organizational structure and the system of relations between departments, and also implement changes in the personnel sphere. In the transition from traditional methods of work, the most difficult thing is to create new value for the client inside and outside the company using modern technologies. To make the unthinkable a reality, you need to destroy the usual ideas and create a new process structure where multifunctional groups can fully satisfy the needs within the organization and the needs of customers (price, service, speed, assortment, reliability, etc.). The system of remuneration and career advancement of employees should be brought into line with the goals of reengineering. And the leader must become the leader of change.
Thus, reengineering is relevant for those who are in a crisis of efficiency and/or are actively seeking leadership. Also, it changes the idea of the role of each person in economic relations ( Ababkova et al., 2018).
Findings
The old model of economics considers a person only as lab or force. But human behaviour is determined by the presence of one's own will, the ability to interpret phenomena through the prism of one’s own consciousness, and not only be a participant in events but also actively shape them. When creating plans to meet his needs, a person takes into account external conditions (favourable or limiting ones), and also what other people plan and desire. The resulting difference between the desired (“I want to do”) and necessary (“I have to do”) behaviour creates another external condition in addition to environmental circumstances.
This double conditionality significantly increases the unpredictability of human behaviour and the development of business systems, and change management is impossible without understanding the individual psychological characteristics and laws of personality formation. For example, the classical model of the economy has signs of anal-narcissistic narcissism ( Freud, 1990) whose destructive features are possible but difficult to fix: The power of the “ego”. Focus on "special rights". Demonstration of grandeur. Overvaluation of money. Expansion. Control. High level of aggression. Ignoring ethics and morals: “nothing personal, only business”, “thanks do not fill a purse,” “money does not stink!”
Reengineering destroys artificial limitations and, creating unity and integrity of business processes, returns meaning to the person’s activity, increases his satisfaction from joint achievements and personal growth. The bar for workers and candidates rises, and only qualified positions remain in the company's organizational structure. The delegation of authority and responsibility requires the ability to make independent decisions in the context of continuous changes and organize activities within their obligations to the company, and a person will need ongoing education for this. Thus, the complexity and energy intensity of work on the principles of reengineering increases and creates favourable conditions for the development of each person.
Payment of remuneration to the employee is brought into line with his effectiveness, and since it is not constant, the salary is made up of a constant part adjusted for inflation and a bonus for special achievements. Career advancement is associated only with abilities: a good professional is not necessarily a good leader. But such a distinction of concepts sets the potential for growth and stimulates the development of even professionals.
Reengineering will reorient the company's activities from manager to client: remuneration is paid by a satisfied customer. This value forms the general interest of employees in the outstanding result. Quantitative and qualitative criteria for evaluating the effectiveness, abilities and principles of payment for a personal contribution to creating value for a client are being formed naturally.
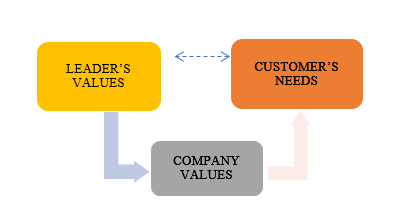
The customer-responsive environment is reinforced by the management system and the real actions of the leader. If the leader cultivates his power, experience and devalues the importance of cooperation, the creation of competitive value will not take place. Phrases like “these are your problems” (addressed to the employee and/or client) will show not the declared but actual characteristics of the personality and philosophy of the leader, which will guide the employees (Figure
Reengineering turns a supervising head into a coach: he does not participate in business processes, but he is close by in order to help an employee or team to complete their work in case of difficulties ( Gildingersh & Gornykh, 2016).
Tasks are distributed among team members and controlled without the participation of a coach. And the head solves problems that affect the efficiency of the overall process:
providing conditions for development and formation of skills of independence among employees;
counselling;
formation of a long-term career development program for staff.
Coach is a new leadership profession related to the art of management. Only mature people with creative and analytical thinking, good interpersonal skills, able to be proud of another person's achievements, can be such leaders.
After reengineering, the organizational structure becomes flat and, as such, is no longer important because people are doing the same job together. Horizontal ties are developing between employees interested in the best overall result. Each of the employees is responsible for the full production cycle of value for customers within the company, including managers who are responsible for the full cycle of communication with external customers. The ratio of managers to employees in the hierarchical structure is 1: 7, and in the horizontal one, where the manager acts as a mentor, 1:30.
Thus, the innovation of reengineering covers all elements of the business system (Figure
Goals that determine the scale of changes
Technologies used to achieve new goals
Rules updated following changes in external conditions
Processes creating value for the customer
Employees contributing to customer value
Mentoring management
Quality of work evaluated by the client
Capacity building education
Scope of decisions made independently
Performance fee remuneration
Career-matching ability
Culture that reinforces the value of cooperation
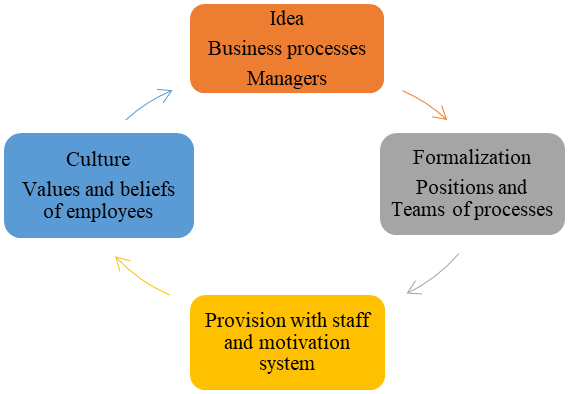
Radical reengineering transformations are expressed by a spasmodic improvement in performance indicators due to such a redesign of business processes in which unproductive labour costs are reduced and competitive value is created for the client, providing the enterprise with increasing demand and income. By the nature and characteristics, reengineering is in strict accordance with the requirements that the crisis sets to the business and contributes to the enterprise transition to a new level of development. Therefore, reengineering can be recommended as an effective strategy for enterprises in times of crisis or for enterprises claiming to gain key competencies and a leading position in their area of specialization.
Conclusion
The main driving force of reengineering is a business strategy that regulates the changes in the organization (hierarchy levels, units and work flows between them), technological (information technology as a catalyst for new forms of association, interaction and other forms of communication), human (education, training, motivation and incentive system) aspects of management ( Gildingersh et al., 2018).
References
- Ababkova, M. Yu., Pokrovskaia, N. N., & Trostinskaya, I. R. (2018). Neuro-Technologies For Knowledge Transfer And Experience Communication. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences (EpSBS), XXXV, 10-18.
- Alexankov, A. M., d’Ascenzo, F., & Pokrovskaia, N. N. (2017). The management for cyber-physical systems in the context of Industry 4.0 and regulatory mechanisms. In XXI Int. conf. “Systems analysis in engineering and control” (SAEC-2017). St.-Petersburg Polytechnic University.
- Bandler, R., & Grinder, J. (1979). Frog into princes: Neuro Linguistic Programming. Real People Press.
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. Harper and Row.
- Davenport, T., & Short, J. (1990). The New Industrial Engineering: Information Technology and Business Process Redesign. Sloan Management Review, Summer 1990, 11–27.
- Davenport, T. (1993). Process Innovation: Reengineering Work Through Information Technology. Harvard Business School Press.
- Freud, S. (1990). Psychology of the Unconscious. AST Publishing House.
- Gildingersh, M. G., Gornykh, E. V., & Pokrovskaia, N. N. (2018). Reengineering of corporate management in the innovative economy and reengineer’ professional competencies. In III International Conference “ERGO 2018: The Human Factor in Complex Technical Systems and Environments” July 4 - 7, 2018 Russia, St. Petersburg. Publishing House "LETI".
- Gildingersh, M. G., & Gornykh, E. V. (2016). Personnel as an object of reengineering Journal of Legal and Economic Research. State Institute of Economics, Finance, Law and Technology, 2, 128-132.
- Gildingersh, M. G. (2016). Reengineering as a method of managing change in organizations. In Problems and ways of socio-economic development: city, region, country, world: VI international scientific-practical conference: collection of articles. Leningrad State University named after A.S. Pushkin.
- Hammer, M., & Champy, D. (1993). Reengineering the corporation: a manifesto for business revolution. Harper Collins.
- Hammer, M. (1990). Reengineering Work: Don’t Automate, Obliterate. Hardvard Business Review, July – August, 104-112.
- Kunde, J. (2000). Corporate Religion: Building a Strong Company Through Personality and Corporate Soul. Financial Times Prentice Hall.
- Wei, F., & Pokrovskaia, N. N. (2017). Digitizing of regulative mechanisms on the masterchain platform for the individualized competence portfolio. IEEE VI Forum Strategic Partnership of Universities and Enterprises of Hi-Tech Branches (Science. Education. Innovations) (SPUE). IEEE Explore, 73-76.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
21 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-089-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
90
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1677
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Gildingersh, M. G., Martynova, J. A., & Sirotkin, V. B. (2020). The Essence Of Business Process Reengineering As An Effective Management Method. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, G. Herwig, U. Umbetov, A. S. Budagov, & Y. Y. Bocharova (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST 2020), vol 90. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 647-654). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.03.75

