Abstract
This article deals with regional franchising, one of the most popular trends in the development of franchising in the world and in Russia. At present, regional franchising is expanding rapidly, gaining new potential for development with every new enterprise. The development of networks in the regions is supported by the constantly growing popularity of chain stores, which allows Russian brands to significantly enlarge their sphere of influence by opening franchise concepts in towns located far from capital cities. The article presents the results of the research of domestic franchise companies that prefer regional aspects of network expansion, as well as the main types of barriers hindering a more active expansion of franchise concepts in regions. In addition, the analysis and the results of the development of regional franchising in Russia are given which show a rapid growth of this type of business as one of the winning strategies in the time of recession. The statistical data are presented on how franchising has been developing for the past 10 years, as well as the ratings of leading companies which have chosen franchising as the key direction for their activity.
Keywords: Regional franchisingfranchise conceptfranchising in Russia
Introduction
Regional franchising, or master franchising as it is referred to in the western literature (Berdina & Berdin, 2019) is a special type of franchise relations which grants an entrepreneur exclusive rights to sell or open a certain number of franchise outlets in a large geographical zone. In other words, it means that a franchisee is entitled to develop a franchise system on a certain territory. “A territory” is any city, region, district, state, or several states or a whole country.
Master franchising usually covers regions with a significant amount of financially reliable population, primarily, million-plus cities. In such territories, an entrepreneur who receives master franchising, controls the locations of all franchise outlets as well as their number, however, a master franchise agreement might specify how many such outlets must be set up and at what time.
Investments in such type of franchise might be large but the outcome can far exceed the benefits of other franchise opportunities. As a rule, this is a business with low current expenses, which requires rather a small number of employees at the launch phase, if any. With the franchise adequately selected and high-quality work, the territory can be methodically turned into a business worth millions of dollars.
Problem Statement
One of the main advantages of a franchise model is ensuring maximum speed of expansion. Therefore, franchisers make package offers for any amount of initial investment, and the number of industries where such offers can be found is growing every day. Most often, franchisees are entrepreneurs who seek to minimize risks of starting their own business. However, before achieving such successful development, it is necessary to consider a number of subtleties and possible problems. In particular, such “stumbling blocks” are:
the peculiar features of Russian regions in general and regional business in particular which affect the specifics of regional franchising.
the existence of barriers for the development of a franchise network
lack of specific legal framework for franchising
the activity of “pseudo-franchises”
Regional franchising: terms and features
Working as a master franchisee, or sub-franchiser, an entrepreneur has much more ways to make a profit than concluding a single traditional franchise agreement.
In traditional franchising, a business owner usually offers goods or services directly to the end customer, for example, at a retail outlet. Choosing a master franchise, an entrepreneur has several important advantages:
When a master-franchisee sells a franchise to a buyer in the regions, they get a part of the franchise fee in return. Some agreements allow the master (sub-franchiser) to retain up to a half of the franchisee’s net fee.
The master-franchisee has an opportunity to open their own additional franchise outlets at a much lower franchise fee.
The master-franchisee receives permanent monthly royalty for the services or goods sold in the region. After having found their own franchisees in the regions, a master-franchisee receives revenue within the rest of the franchise term, usually from 2% to 4% of the franchisee’s revenue each month.
In case real property is included in the franchisee’s location description, often a master-franchisee can participate in the development and improvement of such territories (regions) and get other types of income related to real property. This type of income is not necessarily received by a master-franchisee.
The main responsibility of a master-franchisee is to act as a business consultant for their franchisees and help them succeed in their own business. The following key features are typical of a classical version of master-franchising (Ingram, 2016):
Very few clients: in this case the clients of a master-franchisee are ordinary franchisees. The master helps to support a small number of franchisees, each of whom can own several franchise outlets.
Very few employees. Usually, at the start, a master-franchisee works without staff and employs the personnel as the business continues to grow.
Very little office space: many master-franchises can start working from a home office and then (as the business grows) rent an external office later, if necessary.
The master-franchisee can generate capital much faster than a usual business. As soon as several franchise outlets are set up or open, the business value increases significantly. The master not only has an existing business with cashflow, but also additional franchise opportunities, which gives an entrepreneur a higher business rating. Instead of a classical revenue growth (by 2-3 times) for the majority of traditional businesses, regional franchising can increase revenue by 4-5 times on average (Bruce, 2012).
The master-franchisee do not need to have a prior working experience in a certain industry. An extensive industry training and support from the chief franchiser are included in initial investment.
Prior to opening a franchise outlet in the region, it is necessary to consider the following features of conducting business on the periphery:
Know the advantages of the region – as a rule, life expectancy of regional businesses is higher by 30% than of those in big cities, and big city residents spend twice as much time on commuting to work and back home – the time which could be spent on more important things.
Be like-minded. Regions mean a community spirit, that is why if you want to succeed, it is in your best interests to be as involved in local communities as possible. The more you are involved, the stronger your client base is (Chao, 2013).
Choose a perfect location. Due to high density population in all parts of a big city, less busy districts still have a tendency to intensive traffic. When you are in a provincial town, you have to be a little more experienced when it comes to selecting (or accepting) a location for your business as everyday people traffic is more limited (Bajwa & Siddiqi, 2011).
Do the networking. No one is a better source of information about the region than the owners of other local businesses, therefore, if possible, try to create a community of like-minded people who may give you valuable advice about this area.
Choose a supporting franchise. Some franchisers offer more support than others, so make sure you have chosen the one who makes franchisee support their priority. When you run into problems, you do not want to be made a fool of, so make sure that you have chosen a brand which will grant an access to other franchise owners and other support staff in the company.
Barriers for a franchise network
However, in addition to the goal of creating and successfully operating a network for both parties, the participants in this market identify a number of barriers and problems in understanding and developing regional franchising. According to experts and players in this market, franchising as a business model could become even more widespread if not for a number of serious barriers. Thus, Russian Franchise Association specialists conducted a survey of businesspeople who franchisers wanted to see as their potential franchisee candidates (figure
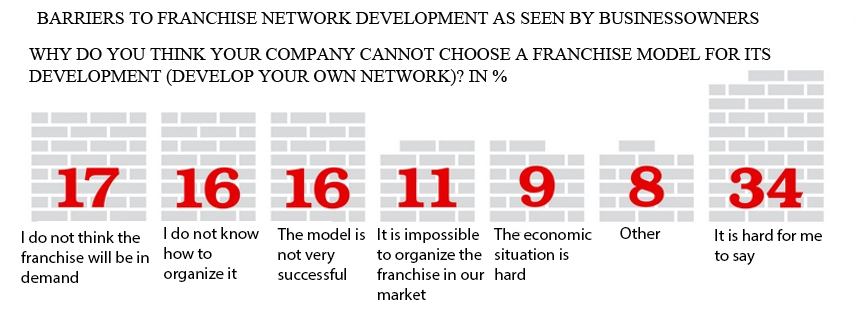
Another factor that hinders franchise development is an insufficient number of available project financing tools. For instance, in Western Europe, a business support system from various commercial organizations is well developed, for example, banks issuing loans at reasonable interest rates.
Lack of a specific legal framework for franchising
One of the serious problems which really exists in the Russian economy is a weak legal framework and unfair practices of the players. About 80% of franchisers behave unfairly: give false information to partners and fail to provide them with adequate support. That is why there is a need for the system of accreditation of those companies which sell franchises. At present, however, it is up to franchisees to conduct risk assessment. Excess negative experience can lead to buyers giving preference to popular brands and double-checking the franchisers.
Activity of pseudo-franchises
If a positive trend of franchise development is its active growth, then the reverse side of the coin is the growth of the so-called “pseudo-franchises” (Goryakina, 2019), i.e. such companies which either have no own outlets or have one or two, but still offer to buy a “network” franchise from them. In this case, it is important for the franchisee to carefully select a partner. In order not to be deceived by an unfair franchiser, it is better to verify everything that the franchiser claims – to pay a visit to the head-office of the company, have a talk with the employees who accompany the franchisee’s business, talk to franchisees who are already in business.
Research Questions
The following questions are raised in the research:
What is the scale of a successfully developing franchise business in Russia?
What are the opportunities and directions for the successful development of regional franchising?
What financial and legal opportunities are there for the existing franchisers and franchisees to attract more regional partners?
Purpose of the Study
The authors believe that the issues outlined in the study will help to achieve goals and will contribute to the development of recommendations for the further development of franchising in the regions, not only within one country, but also as a model of regional franchise concept development abroad.
Research Methods
At present, franchising is the most effective instrument for business development in the regions, especially in such a big country as Russia, which consists of small towns with good prospects for the expansion of franchising networks. All popular brands which have been enjoying customer loyalty for some years now, are expanding their regional franchising networks gaining profit for themselves and giving earning opportunities to franchisees. However, this process requires a right approach under which all risks will be taken into account and the opening of a franchise business will become perspective and profitable (Ponosov, 2015).
The Analysis of Regions Chosen for Franchise Network Expansion
Initially, the research was based on the effective selection of those regions which are the most suitable for a successful franchise concept development in the regions. Obviously, business expansion in depressive regions is not considered by successful franchisers due to several reasons: no suitable franchisee candidates with adequate investment potential, no expected demand from financially reliable customers, etc. So, for the development of their business, franchisers opt for the regions which are leading the market according to a number of social and economic factors (Table
Franchise Business Growth Estimations
The study of statistical information, including the data on the franchise market structure in Russia and in RF regions, as well as the rating analysis of Russian leading regions in terms of the level of social and economic development, allow to suggest and highlight certain directions of the most active sectoral and regional franchise development in Russia (Figure
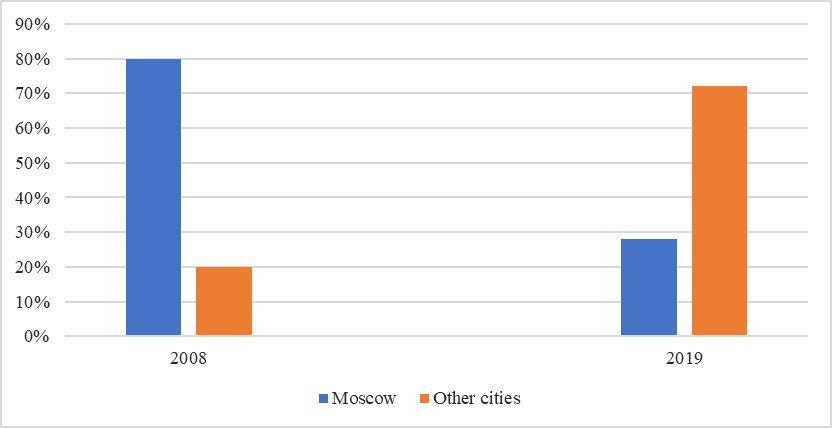
At present, franchise market in Russia is enjoying a stable growth. According to statistics, in 2016 the country had about 1,400 operating networks, in 2017 – 1,500, by the end of 2018 there were about 1,900 networks, and at the beginning of 2019 – already 2,250. It is worth mentioning though, that only 1,000 companies actively sell their franchises. Besides, the demand for franchising has also grown: the number of franchise applications grew to 300% in January 2019 as compared to January 2018.
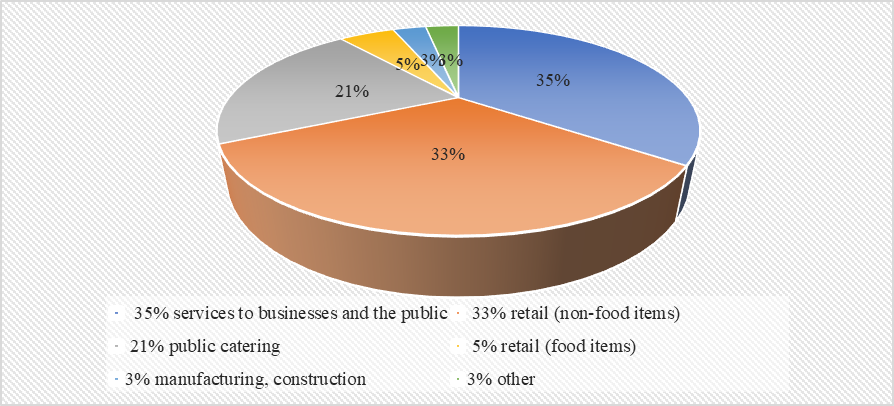
According to the statistics (Nikonorova & Krasilnikova, 2020), the biggest part of the structure of Russian franchising is retail sector (37%), almost the same amount is accounted for by the service sector for legal entities and individual citizens (33%), 16% is public catering, and the rest of it is divided between food trade, manufacturing and construction sectors (figure
Primary Research Results
The results of the survey among franchisers with franchises located in regions allow to make a rating of networks (Berdina & Berdin, 2020).
The position that the network takes in the rating is determined by the number of contracts concluded in 2018. If two different brands have the same number of contracts, then the one that leads in the total number of contracts takes a higher place. The overall growth of the number of franchise applications was 300% in January 2019 as compared to January 2018.
1C, the software provider for business process automation has been in the top position for four years in a row in the general rating and in IT rating. 1C consistently concludes 650-750 contracts with franchisees per year, while cancelling about 90. The company’s total number of contracts at the end of 2018 was 8,906. 1C explains its leading position by the availability of their franchise and by the interest of end customers in business process automation. The current top ten most popular franchises included one of 1C’s partners – “First Bit” (№10) (Melnikova & Lindell, 2019).
Franchising is actively developing in the segment of car maintenance service and car spare parts stores (“EuroAuto”, Auto3N). The favorite company in 2018 rating was Fit Service car maintenance station (№3 against the 17th place in 2017). According to Rospatent, in 2018, it concluded twice as many franchise agreements (121) as during the whole prior period of active franchise sales. The boom in a number of franchisees was triggered by Fit Service federal marketing campaign launched in the middle of 2018.
Franchise concepts in the sector of food items are in stable demand. They are offered mainly by producers of meat, milk, cheese, ice cream, confectionery, etc. Among them are “Chebarkulskaya Ptitsa” (or “Chebarkul Bird”) which has opened a total of 192 franchise outlets within three years in Chelyabinsk and neighbouring regions, “33 Penguins”, which has launched 250 café – stores around Russia since 2006, “Zorka and Milka”. The rating also shows newcomers to this segment: “Dobryninsky” (it has opened 49 outlets in Moscow within a year of franchise sales), and “Remit”, which has opened 27 stores in Moscow and the Moscow region. A good result in this segment has been shown by “Fasol”, which has doubled the dynamics of opening new stores, and has risen from the 19th place in the rating to the 9th (Berdina & Berdin, 2020).
Findings
The development of franchising business is associated with several factors (Franchising in the regions…, 2016):
Firstly, regional businesses have realized the advantages of franchising over other types of business. Almost all developed countries have followed this path – initially there was a boom in franchise networks in capital city regions, then – in other regions.
Secondly, an increased interest in franchising is a phenomenon which is typical for the economy in the recession period. Now, there is a demand for those concepts which have already proven to be stress-resistant business models and which, even in a crisis, are capable of retaining savings and bringing a stable income, if not gaining excess profits.
Thirdly, competition in such segments as public catering, services and, partially, retail has reached its maximum value in big cities, so the focus of large franchise networks is beginning to shift to the regions.
Generally, regions show a high demand for the concepts with small investments (up to 5 million) and small royalties. However, large networks require large investments but “price-conscious” franchisers are trying to adapt their formats to the regions (fewer seats, smaller area) to reduce initial investment.
In fact, many segments in the regions have no other ways to develop business so franchising will develop fast. After having experienced more than one wave of crisis, it has become obvious for many companies that rapid business expansion is possible only through franchising.
However, the overall situation on the Russian market is still unclear for certain segments of franchise networks. This has led to a strict selection process of potential franchisees and increased requirements to them. Due to the fact that rent payment rates have fallen significantly in the regions, new interesting opportunities have appeared, though the economic situation remains difficult. Since prices are fluctuating and the consumption is not growing, regional players continue to go bankrupt, which leads to “uncivilized” methods of gaining revenue in the retail sector: 60% to 70% discounts, or even bigger discounts, which affects the margins this or that way. Now, it is very important to occupy good places in trading centres, but at the same time, it is impossible to make quick profit: it is the perspective which is in the focus. A couple of years ago, franchisers believed it was better not to start any business because then the owners of the trading centres did not feel the situation was serious and did not make any concessions, but now things have changed radically, and franchisers are actively moving to the regions, mainly to those cities which are the top ten leading regions in terms of their social and economic development (see Table
Conclusion
Opening a franchise outlet can be a great opportunity for the financial success of an entrepreneur. Today, those who are interested in buying a franchise have many opportunities which an entrepreneur may not always see, but which he can implement being outside capital city regions. Regional franchises are a great way to develop and expand a franchise network. Even though an entrepreneur is used to working in an urban environment, they can be surprised at how different the work can be in the region (Ingram, 2016).
Thus, taking into account the advantages of franchising as such and its perspectives for the development in the regions, the following conclusions can be made. Franchising in the regions is
legal protection of small businesses;
higher level of business culture;
local population secured with employment and additional working places created;
development of a real training system for representatives of small businesses;
no need in the creation of separate training centres and programmes;
higher quality of goods, services and business sphere systems;
increased activity of economically employed population.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank anonymous interviewers for providing information for this article.
References
- Bajwa, S., & Siddiqi, M. W. (2011). Regional Economic Integration. Academic Publishing.
- Berdina, M., & Berdin, A. (2019) International franchising: ways to transfer intangible business assets. Monograph. IScience.
- Berdina, M., & Berdin, A. (2020) Regional franchising: modern trend in business. Scientific research and developments. Economics, 1. https://doi.org/10.12737/issn.2308-2844
- Bruce, W. (2012). What Is a Master or Regional Franchise? https://williambruce.org
- Chao, Y. S. (2013). Global Value Chains and Regional Economic Integration Development. Academic Publishing.
- Franchising in Russia. Map of the new time. (2018). https://status-media.com
- Franchising in the regions: forecasts, trends, opinions. (2016). https://www.buybrand.ru/articles/11094
- Goryakina, D. (2019). 10 trends of franchising over the past 10 years. Encyclopedia of Russian business. https://www.openbusiness.ru
- Ingram, K. (2016). 5 Tips For Opening A Franchise In A Regional Town. https://www.kwikkopy.com.au
- Melnikova, K., & Lindell, D. (2019). TOP 50 most demanded franchises in 2018. www.rbk.ru
- Nikonorova, A., & Krasilnikova, E. (2020). Perspectives of franchising development in Russian regions. Innovative science, 1.
- Ponosov, I. (2015). Regional'nyy franchayzing vykhodit na mezhdunarodnyy uroven' [Regional franchising goes on international level]. Russian newspaper. [in Rus]
- RIA News (2020). The rating of the socio-economic development – 2019. https://riarating.ru
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-089-1
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
90
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1677
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Berdina, M., & Berdin, A. (2020). Franchise Concept Development In Russian Regions: Barriers And Features. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, G. Herwig, U. Umbetov, A. S. Budagov, & Y. Y. Bocharova (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST 2020), vol 90. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 83-92). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.03.11

