Abstract
The author explores the problem of enhancing the foreign economic activity of the region. Globalization gives opportunities to find new customers all over the world. But to enter the world market successfully each company needs to have competitive prices. That is why the level of exporting and importing costs is one of the most important problems for regional companies. The main factors affecting the success of regional enterprises in entering the world market are the level of logistics infrastructure development and the effectiveness of customs services. Together, these factors form the customs and logistics framework of the foreign economic activity. The main factors of this framework are customs authorities, logistics providers and participants of the foreign economic activities. Each of them has own interests and problems to solve. In this article, the author defines the goals of creating the customs and logistics framework, explores phases and stages of its design. The concept of developing a customs and logistics framework suggests two possible vectors for its formation: “top-down” and “bottom-up”. The author describes the role of main framework development initiators, the basic principles and construction methods. The proposed concept can be used as the basis for further studies of individual regions integration processes into the system of world economic relations.
Keywords: Foreign economic activitycustoms and logistics frameworkregional integrationdevelopment vectorconceptmodelling
Introduction
In the modern world, integration into the world economic relations system is a prerequisite for ensuring the sustainable development of individual regions and the country as a whole. Many modern scientists emphasize the importance of a region entering the world market. For example, Portuguese researchers analysed the impact of the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (T-TIP) between the EU and the USA on a small island regional economy (Fortuna, Silva, & Teixeira, 2019).
One of the main success factors for regional business entering the world market is provision of necessary customs services’ development level for export-import flows and an adequate state of logistics infrastructure. Providing these conditions enables the increase of foreign economic activity (FEA) volume of the region. This, in turn, will allow the region to occupy a more advantageous place in the system of world economic relations.
Logistic infrastructure as a factor in the foreign economic activity development
The problem of including a certain region in the international trade system through the logistics infrastructure development is very important. It was studied in different modern scientific articles. So, Andreev and Makarov (2019) analysed the possibility of enhancing Buryatia’s foreign economic activity by modernizing the regional logistics infrastructure and its inclusion in the Mongolian economic corridor. Developing countries pay serious attention to the impact of logistics infrastructure on the activation of foreign economic activity. China has been steadily promoting port integration over recent years by giving the country's main ports in charge of one province-level platform (Dorathy, 2019).
The current state of logistics infrastructure is the subject of a number of modern studies (Pokrovskaya, Fedorenko, & Khramtsova, 2018). The weakness and lack of import and export logistics functions in inland regions create a bottleneck that restricts the development of foreign economies and trade (Wei & Dong, 2019). The development of trade relations between Russian organizations within the country and with foreign partners mainly depends on the effectiveness of logistics and its management (Potekhina & Mironova, 2017). Effective functioning of the transport sector is a necessary condition for development of foreign economic activities (Bosov et al., 2018).
Customs services and their importance for enhancing foreign economic activity
No less important is the problem of effective customs support of export and import transactions. Against the background of global economic integration, the international foreign trade market has further expanded (Pan, 2019).
The problem of customs service for international commodity flows is among the priority areas of many modern scientists’ research (Gupanova, Nemirova, & Suglobov, 2019). Serious attention is paid to innovations in the legal regulation of customs services (Smolina & Seryomina, 2019).
Optimization of customs services allows not only to escalate export and import indicators, but also to increase the transit potential of the region (Fedorenko, 2019). Customs services are a tool of state influence on the foreign economic activity level of the country and certain regions. Improving customs services through the introduction of logistics management principles and appropriate tools in customs processes creates the conditions for enhancing export-import activities and accelerating the processes of economic integration.
Formation of the customs and logistics framework of the region’s foreign economic activity
The importance of building an integrated system of customs and logistics support for foreign trade processes is due to the high level of international differentiation of labour and large volumes of foreign trade operations. Globalization, increased international competition and information technologies development heighten requirements for building a united customs and logistics framework for foreign economic activity. Such a framework can become the basis for deepening integration processes both at the country level and at the level of certain regions.
The rapid development of cross-border e-commerce has brought enormous challenges to the logistics industry around the world (Guo, Rao, Wang, Wu, & Chen, 2020). The increase in e-commerce and the expansion of circle of sellers and buyers inevitably lead to the need of improving the interaction of customs services and near-customs logistics infrastructure.
Problem Statement
The problem of combining the multidirectional interests of FEA participants and service providers during the organization of customs services for export-import cargo was studied in the author’s earlier papers (Fedorenko, Persteneva, Konovalova, & Tokarev, 2016). However, to ensure successful international expansion of regional business structures, an increase in the number of integration process agents is required. In addition to FEA participants and customs service providers, the work of logistics providers is of great importance. In order to create a customs and logistics framework for foreign economic activity, it is necessary to determine the concept of building a model for the effective interaction of regulatory authorities, logistics providers, as well as professional intermediaries in the field of customs.
Research Questions
In the process of developing a customs and logistics framework concept for the foreign economic activity development in the region, the author addresses the following issues:
Defining goals of the customs and logistics framework of the region’s foreign economic activity;
Formulating phases and stages of the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity;
Developing a variable-logic scheme for the customs and logistics framework creation for foreign economic activity.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to develop the theoretical foundations of the organization and economy of customs and logistics services system for foreign economic activity and to articulate recommendations for its further improvement. The object of the study is the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity, which is a combination of foreign economic activity participants, logistics providers and professional customs authorities interacting in the process of customs service provision. The subject of the study is the organizational and economic mechanism of foreign trade activities customs and logistics framework buildup.
Research Methods
The author applies modern interdisciplinary methods and practices in conducting scientific research. The main distinguishing feature of the study is its consistency, which allows comprehensive analysis. The methodological basis for the article was compiled by general scientific methods and practices, such as system-structural, causal, analysis, synthesis and decomposition, and graphic methods. The application of these methods, united by a common methodology and research algorithm, provided the reliability and well-reasoned validity of the results.
Findings
The objectives of forming the customs and logistics framework of integration processes
The starting point to develop the concept of the customs and logistics framework of integration processes is to determine its goals and objectives. At the level of certain regions, the main tool for integration into the world economic relations system is foreign economic activity. The economic goals of forming the customs and logistics framework should include ensuring the foreign economic activity progressive development both at the regional and country level.
The progressive development of foreign economic activity is of great importance for the economy. Collection of customs payments forms a significant share of the country's budget revenue part. Increasing the volume of foreign economic activity enables the payments volume growth without customs duties, excises and fees increase.
The purpose of designing the customs and logistics framework is to promote the development of foreign economic activity by improving the customs and logistics services for foreign trade participants. The goals definition is a complex process that is of high importance for the design effectiveness. At this stage, a large number of various mistakes can be made, the most common of which can be attributed to the transformation of the goal into a goal in itself and substitution of goal by means.
The formation of the customs and logistics framework concept is aimed at strengthening the economic interconnectedness of customs authorities and foreign trade participants. With the help of professional customs brokers, it is possible to reduce costs to individual traders, which leads to increasing profitability of foreign economic activity and, as a consequence, to the foreign trade turnover growth.
The development of a modern customs and logistics services system contributes to both economic and political rapprochement of countries. The political goals of forming the integration processes customs and logistics framework include deepening of international integration, inclusion of certain regions in the world economic relations system and the support of a positive image of the country.
Phases and stages of designing the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity
In this study, design is considered in successive stages and stages of its implementation (Figure
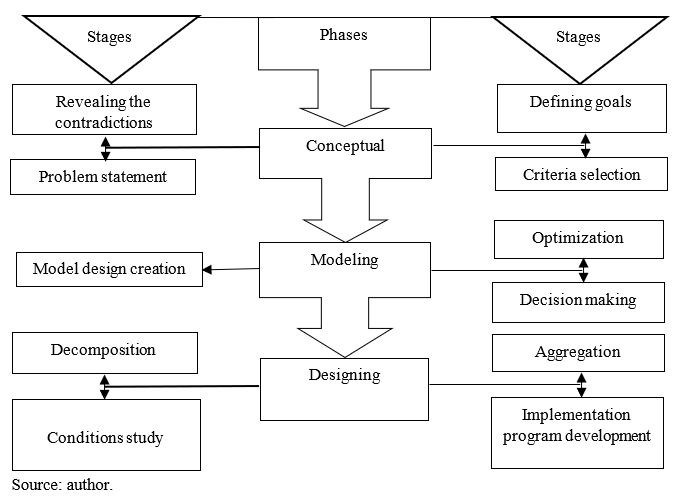
Designing at the conceptual phase starts with a detailed analysis of the situation in the customs sphere, which allows identification of a complex of contradictions, among which the main link should be pinpointed. One of the key problems is the contradiction between the interests of foreign economic activity participants and customs intermediaries, foreign economic activity participants and customs authorities, as well as customs intermediaries and customs authorities. Achievement of the stated goal of customs and logistics framework design for foreign economic activity can be assessed using volumetric, financial, time and quality criteria. The volumetric criterion will be the positive or negative dynamics of foreign trade turnover, which indirectly characterizes the profitability of foreign economic activity, the increase of which is ensured by the customs formalities simplification. Financial and time criteria reflect the costs incurred by foreign economic activity participants and related to the need to fulfill customs requirements and organize interaction with professional service providers in the customs sphere. Qualitative criteria include the size of fines and loss of time caused by violation or unfair execution of customs legislation.
At the modelling phase it is necessary to ensure models’ compliance with the requirements of simplicity, adequacy and environmental consistency.
The simplicity of the model involves the reflection of the designed frame basic elements and their relationships in it, which allows to use the model in different operating conditions. The adequacy of the model means that it is quite complete, accurate and true, which ensures the goal achievement. The third requirement for the model is its inherent nature, that is, a sufficient degree of created model consistency with the external environment. At the same time, not only the model should be embedded in the environment, but the environment itself should be ready to accept it.
The optimization stage involves searching among the many possible options (models of the designed framework) for the best in the given conditions and limitations, that is, for the optimal alternatives. The optimal solution obtained for a particular model is optimal in the sense that when it is applied, its behaviour complies with the requirements. The choice of model for further implementation is the final, most critical stage of the modelling phase, which implements the entire design process alignment with a specific goal.
The final phase of the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity design is the design, which consists of specific methods and means determination for implementing the selected model within the existing conditions.
The design process includes the stages of decomposition, aggregation, study of conditions and construction of the program. Decomposition involves the division of work on the selected model implementation into a set of separate operations, which allows to rationally implement the process organization and control. It should be noted that there is a certain conventionalism of services subsystem design process in the customs sphere into successive stages, since they can be performed in parallel.
The last stage of design is the program development for the model implementation, that is, the preparation of a specific action plan of model implementation in certain conditions. The design of the customs and logistics framework for foreign economic activity is an important element in the methodology of forming a model for the process of certain regions integration into the world economic relations system, which determines its focus on the interests of foreign economic activity participants.
Variable-logical scheme of formation of the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity
The customs and logistics framework is a flexible system to support export-import activities of a certain territorial entity. The principle of flexibility and adaptability implies the ability of the customs and logistics services system to fully take into account the prevailing features of the national and international market, the foreign trade development trends and the changing demands of consumers. Strictly regulated activities of customs authorities limit their ability to quickly respond to changing external conditions, while the subsystem of customs and logistics services, due to the market nature of customs intermediaries activities, provides the whole system with great adaptability and flexibility.
State authorities determine the general direction of development of foreign trade operations customs and logistics framework. Existing integration trends in the international trade development lead to an increase in the role of international conventions, charters and provisions of international organizations that influence the organization of customs and logistics services in the Russian Federation. Nevertheless, the main participants in the customs system formation are the customs authorities at all levels, professional customs intermediaries and enterprises participating in foreign economic activity.
Representing the interests of enterprises engaged in export-import activities, customs and logistics intermediaries at the same time contribute to the achievement of goals and objectives of the authorities. This determines the common interest in the near-customs area development based on a systematic approach.
The logical scheme of formation of the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity is presented in Figure
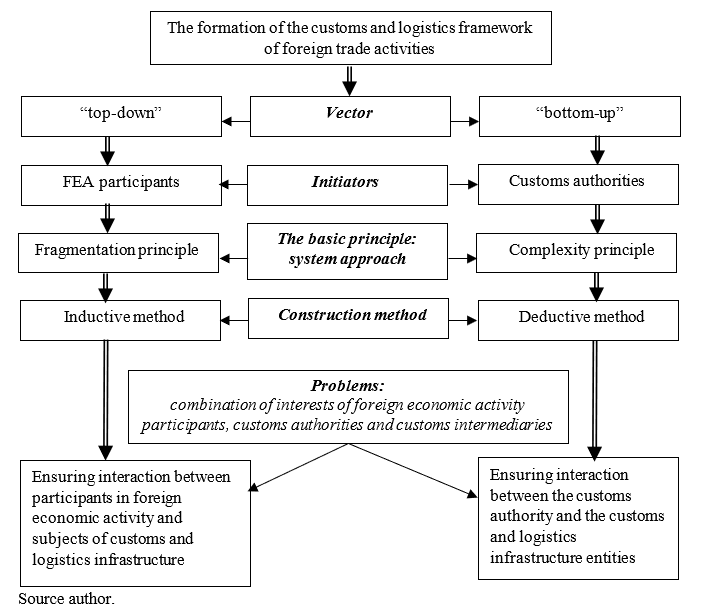
The variable-logic scheme of formation of the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity consists of two blocks. The first block reflects the main methodological characteristics of the process: vector, initiators, principles, methods. The second one reflects the general and specific problems that arise during the formation of the frame.
The presented scheme reflects two possible options for constructing a customs and logistics framework for foreign economic activity, characterized by different vector orientations. The process of forming the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity can be an element of the state’s general strategy in terms of enhancing foreign economic activity and improving the customs system. In this case, the development vector is “top-down”, which implies amendments to the legislation and regulations of customs intermediaries. The focus of the “bottom-up” process is based on the requests of end consumers, periodically changing under the influence of external factors.
The “top-down” system formation is the result of the initiative efforts of the customs authorities based on a comprehensive analysis of foreign trade statistics. A comprehensive information base enables the problem areas identification in the process of foreign trade activities customs support and definition of the most requested activity areas of customs intermediaries. At the same time, the customs authorities and the state as a whole, possessing powerful leverage, are able to provide significant support in the customs and logistics infrastructure formation, focusing on key areas of its development.
On the other hand, in market conditions, specific requests are formed based on territorial differences, the export-import operations product structure, the level of the transport and logistics infrastructure development. This requests are initiated by foreign economic activity participants. As a result, customs and logistics infrastructures form new companies whose activities are focused on meeting the needs of companies engaged in foreign trade.
For any option of the customs and logistics framework for foreign economic activity buildup, the application of a systematic approach, which involves both determining the structural elements of the subsystem and the relationships between them, and embedding the resulting organizational model in a common customs service system, is fundamental. The process of forming a framework from top to bottom is based on the principle of complexity, the essence of which is the construction of a common model of customs and logistics infrastructure that determines the content of its individual elements activities. The bottom-up approach is characterized by the application of the principle of fragmentation, in which the issues of creating and developing individual enterprises of customs and logistics infrastructure are solved in stages, as the need arises for each of them.
In accordance with the outlined principles, , the deduction method is applied in the first version of the frame formation, according to which the customs authorities establish general rules, norms and requirements for the organization of customs services; the establishes rules serve as basis for activities regulation in each particular case. The second option for building the framework is based on the induction method, in which individual subjects of the customs and logistics infrastructure, adapting to the current needs of foreign economic activity participants, develop a flexible and efficient subsystem of customs and logistics services.
The combination of interests of foreign trade participants, customs authorities and customs intermediaries is a key problem, which in the first version focuses on the need for close interaction between customs authorities and customs and logistics infrastructure, and in the second case - between professional customs intermediaries and foreign trade participants.
Conclusion
To formulate the concept of customs and logistics framework for the development of foreign economic activity in the region, it is necessary to present the structure and content of activities of customs and logistics services provision through the models. At the same time, the customs and logistics framework itself is an object consisting of a number of parts interacting with each other in such a way, that each part’s behaviour understanding does not yet allow to draw an obvious conclusion about the behaviour of the entire system as a whole. A large number of modern studies have been devoted to the study of individual elements of the customs and logistics framework, however, the problems of interaction between the customs and logistics services subjects are still relevant for study.
The vector of the customs and logistics framework formation can equally be directed both from top to bottom and from bottom to top. The top-down vector implies the active participation of the state, which can have both direct and indirect effects on this process. The state initiates the creation of a customs and logistics services nationwide system, establishing new structures that provide comprehensive services in the customs sphere, or providing additional functions to enterprises already operating in the customs sphere. Thus, the paper studied (Al Anshori & Ahamat, 2019) the experience of customs and logistics services system modernization in Indonesia on the top-down vector. The “bottom up” vector can be expressed by both intensive and integration development of customs and logistics infrastructure entities. In general, the proposed concept of the customs and logistics framework of foreign economic activity enables the scientific approach to the issue of facilitation of regional business foreign economic activity. It is especially relevant in the current conditions of economy globalization and the need to integrate the region into the world economic relations system.
Acknowledgments
The reported study was funded by RFBR and FRLC according to the research project № 19-510-23001.
References
- Al Anshori, M. R., & Ahamat, H. (2019). The use of customs law and regulation to support the development of small and medium enterprises: Evidence from Indonesia. World Customs Journal, 13(1), 129-140.
- Andreev, A. B., & Makarov, A. V. (2019). The routes of the Mongolian economic corridor: Development prospects, transport and logistics constraints. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 320(1), 012014. DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/320/1/012014
- Bosov, A., Khalipova, N., Prohoniuk, I., Kuzmenko, V., Duhanets, V., & Shevchenko, I. (2018). Development of method of multifactor classification of transport and logistic processes. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2(3-92), 60-78. DOI: 10.15587/1729-4061.2018.128679
- Dorathy, M. B. C. (2019). Port integration for enhancing competitive advantage. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(9S2), 278-280. DOI: 10.35940/ijitee.I1056.0789S219
- Fedorenko, R. V. (2019). Modern issues of development of the customs and logistics infrastructure of the international north-south transport corridor. In S. Ashmarina, M. Vochozka (Eds.), Sustainable Growth and Development of Economic Systems. Contributions to Economics (pp. 63-75). Cham: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-11754-2_5
- Fedorenko, R. V., Persteneva, N. P., Konovalova, M. E., & Tokarev, Y. A. (2016). Research of the regional service market in terms of international economic activity’s customs registration. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 6(5S), 136-144.
- Fortuna, M. J. A., Silva, F. J. F., & Teixeira, J. C. A. (2019). International transatlantic trade liberalization: Zooming in on regional impacts. Applied Economics, 51(41), 4527-4538. DOI: 10.1080/00036846.2019.1593937
- Guo, H., Rao, W., Wang, J., Wu, P., & Chen, Z. (2020). Logistics mode analysis under the background of cross-border ecommerce era. In J. Abawajy, K. K. Choo, R. Islam, Z. Xu, M. Atiquzzaman (Eds.), International Conference on Applications and Techniques in Cyber Intelligence. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 1017 (pp. 801-810). Cham: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-25128-4_98
- Gupanova, Y. E., Nemirova, G. I., & Suglobov, A. E. (2019). The analysis of customs services practice in the conditions of the Eurasian economic union: Problems and directions of improvement. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 9(4), 1259-1266. DOI: 10.14505/jarle.v9.4(34).11
- Pan, H. L. (2019). Research on international logistics supply chain management mode from the perspective of cross-border e-commerce. In Z. Xu, K.K. Choo., A. Dehghantanha, R. Parizi, M. Hammoudeh (Eds.), International Conference on Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 928 (pp. 737-744). Cham: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-15235-2_101
- Pokrovskaya, O. D., Fedorenko, R. V., & Khramtsova, E. R. (2018). Study of the typology of logistic entities using functional and logistic approach. In V. Mantulenko (Ed.), International Scientific Conference "Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development". The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 57 (pp. 91-101). London: Future Academy. DOI: 10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.10
- Potekhina, E., & Mironova, O. (2017). Logistics supply control in conditions of customs relations development. In K.S. Soliman, (Ed.), Proceedings of the 30th International Business Information Management Association Conference. Sustainable Economic development, Innovation Management, and Global Growth, 1-9 (pp. 4824-4834). Norristown, P.A.: INT Business Information Management ASSOC-IBIMA.
- Smolina, E. S., & Seryomina, R. N. (2019). Prospects for the functioning of the new customs code of the Eurasian Economic Union. In S. Ashmarina, M. Vochozka (Eds.), Sustainable Growth and Development of Economic Systems. Contributions to Economics (pp.77-85). Cham: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-11754-2_6
- Wei, H., & Dong, M. (2019). Import-export freight organization and optimization in the dry-port-based cross-border logistics network under the Belt and Road Initiative. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 130, 472-484. DOI: 10.1016/j.cie.2019.03.007
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 April 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-081-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
82
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1004
Subjects
Business, innovation, management, management techniques, development studies
Cite this article as:
Fedorenko, R. V. (2020). Customs And Logistics Framework Of Foreign Economic Activity: Conceptual Basis. In V. V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Problems of Enterprise Development: Theory and Practice, vol 82. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 225-234). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.04.29
