Abstract
More and more researchers, representatives of different branches of scientific knowledge (economics, psychology, pedagogy) note the importance of soft skills to achieve competitiveness in the labor market of representatives of different professional fields. The article demonstrates the need for graduates of natural-scientific directions to develop not only hard skills, but also soft skills. In the process of research, it was possible to identify the most significant competencies for the performance of their professional duties, to identify the formation / non-formation of these competencies in studying process at the university. To achieve the goal of the research, in 2018, a survey of 68 graduates of the natural science profile of Surgut State University working in the specialty was conducted. The survey made it possible to confirm theoretical positions regarding the importance of soft skills in professional activity. The main research tool was a questionnaire survey. Questionnaires were distributed to respondents in printed copy. The questionnaire used questions that made it possible for employers to assess the importance of competencies and the level of representation of competencies among graduates by employers. By questioning and using methods of mathematical statistics, a statistically significant difference was determined between the level of development of competence formed at the university and the actual level necessary for fulfilling professional duties.
Keywords: Competitivenesssoft skillsemploymentcompetitive graduate
Introduction
The modern labor market dictates new requirements for candidates for employment in the organization. Analysts at the World Economic Forum made a forecast in which they identified ten key competencies that will be in demand in 2020. These included: integrated problem solving, critical thinking, creativity, people management, interaction with people, emotional intelligence, forming one’s own opinion and decision making, customer orientation, negotiation skills and flexibility of the mind. In the framework of the study “Russia 2025: From staff to talents”, carried out by the Boston Consulting Group with the support of Sberbank, WorldSkills Russia and Global Education Futures, the following range of demanded competencies was determined: communication, interpersonal skills, intercultural interaction, adaptability, solving non-standard tasks, achieving results, managerial skills, orderliness, self-development (Boutenko et al., 2017).
Nowadays, powerful business entities understand that innovative enterprise potentials and production efficiency are possible not so much thanks to equipment as to that human capital, to those employees who work at the enterprise. The company management has become more careful not only in the selection of ready-made specialists who have entered the labor market, but they are involved themselves in the process of training personnel in higher education (they train specialists “for themselves”) so that at the time of completion of training the graduate possesses precisely those competencies that the employer needs.
The quality of training of young personnel according to specified indicators of the state and the labor market has become the subject of research of many scientists. It is reflected in the scientific works of domestic and foreign researchers of various fields revealing various aspects of improving the quality of student learning, the development of young specialists.
The problems of recruiting organizations with well-trained personnel, obtaining and developing professional and managerial skills and competencies among employees were raised by scientists from many countries (Tsitskari, Goudas, Tsalouchou, & Michalopoulou, 2017). An applied research is that reveals the requirements of employers of industrial enterprises of several European countries for the formation and development of competencies among university graduates (Azevedo, Apfelthaler, & Hurst, 2012). The study of the formation of professional competencies of university graduates is of great interest (Zaitseva et al., 2017). The results of the study of our Ukrainian colleagues on the effectiveness of student services in the framework of an international project (Chernyak & Kharlamova, 2015) are also noteworthy. An empirical study is devoted to the issues of the impact of transformational and transactional leadership (Rawung, Wuryaningrat, & Elvinita, 2015).
In multi-aspect studies of both foreign and Russian scientists, the formation and development of soft skills has recently gained particular importance. Both foreign (Aeon & Aguinis, 2017) and Russian scientists (Vinichenko et al., 2018a) were engaged in the study of one of the most important components of soft skills. The vector of research attention is now significantly biased towards the formation of soft skills while studying at the university (Hajduk, 2016). The role of soft skills in the process of successful employment of university graduates has been convincingly proven (Bogdan & Chulanova, 2016; Demcheko, Karácsony, Ilina, Vinichenko, & Melnichuk, 2017; Vinichenko et al., 2018b).
“Soft skills” is defined by us as a social and labor characteristic of set of knowledge, skills and motivational characteristics of an employee in the field of interaction between people, the ability to manage their time competently, having persuasion skills, negotiating ability, leadership, emotional intelligence, with the emergence necessary for successful performance of work and meeting the requirements of the position and the strategic goals of the organization, this is a characteristic of potential quality that allows you to describe almost all of the elements of personnel availability to work effectively in a given situation at the workplace in the labor team (Chulanova & Bogdan, 2018; Ivonina, Chulanova, & Davletshina, 2017; Vinichenko et al., 2018c).
Numerous surveys show that employers want to see purposeful employees who have innovative ideas and are able to take the initiative; flexible, oriented to development and effective result of activities; able to resolve conflict situations and having negotiation skills; having skills to solve problem situations; punctual, able to work in multitasking conditions, withstand deadlines, etc. (Chernyak & Kharlamova, 2015). Our studies are also devoted to the study of the formation of soft skills among engineering students in the process of integration into CDIO (Chulanova & Bogdan, 2018).
Problem Statement
The analysis of literary sources has demonstrated the importance of the development of certain personal and interpersonal graduates’ competencies to achieve competitiveness in the labor market. What methods and means can be used to develop these competencies among students in the process of studying at a university. Are graduates of a natural science profile really needed “soft skills” for successful self-realization in their professional activities?
The results of a survey of employers on satisfaction with the level of training of graduates, as well as surveys of graduates themselves, indicate that, in addition to the insufficient formation of some professional competencies, there is a lack of development of a number of graduates and soft skills which are noted as significant for professional activity. “Soft skills” for students of humanitarian areas of training are formed as a part of the development of certain academic disciplines and practices which is not so accessible to students of the natural sciences and technology, whose emphasis in training is mainly based on the development of hard skills.
Research Questions
Taking into account the relevance of the problem of developing personal and interpersonal competencies of university students in order to be competitiveness in the labor market, the authors of this paper considered the range of the questions. Is it really necessary for graduates of the natural science and technical training profile to develop “soft skills” to achieve competitiveness in the professional activities? How do graduates evaluate the development level of their “soft skills”?
Purpose of the Study
To answer the questions raised, the research aim was formulated. That is, to identify the role of soft skills in the professional activities of specialists in the natural sciences and the level of their formation in the process of studying at the university. To achieve this goal, we must solve the following problems: conduct a study and, using expert assessment, rank the list of soft skills according to their importance for work and career; to rank the list of soft skills by the criterion of the formation of these skills in the process of studying at a university; suggest corrective measures (introduction to the curriculum of the disciplines that form soft skills in the learning process of the natural sciences).
Research Methods
To achieve the goal of the research, in 2018, a survey of 68 graduates of the natural science profile of Surgut State University working in the specialty was conducted. The survey made it possible to confirm theoretical positions regarding the importance of soft skills in professional activity. The main research tool was a questionnaire survey. Questionnaires were distributed to respondents in printed copy. The questionnaire used questions that made it possible for employers to assess the importance of competencies and the level of representation of competencies among graduates by employers.
By questioning and using methods of mathematical statistics, a statistically significant difference was determined between the level of development of competence formed at the university and the actual level necessary for fulfilling professional duties. Despite the need of developed soft skills among the specialists for the modern economy, emphasized by the researchers, the term itself was unfamiliar for 93% of respondents. To the question “Are you familiar with the term soft skills, how do you understand it?” They could not explain the concept, or simply answered “no, I don’t know.”
In the next question, respondents had to rank the list of competencies proposed by the authors according to their importance for work and career; then, according to the criterion for the formation of these competencies, in the process of studying at a university. For ranking, a list of soft skills was proposed (compiled based on an analysis of the studies mentioned above): teamwork, persuasion skills, personal management, time management, emotional intelligence, critical thinking, flexibility, adaptability, business ethics, ability to work in situations of uncertainty.
Opposite to the most significant competency the respondent had to put a number one, opposite to a little less significant - two and so on. Also, respondents were offered the right to supplement the list of competencies with their option if they considered the list incomplete.
In addition, in the framework of another study, the authors conducted a survey of 204 graduates of the natural science profile from 2000-2018. They were asked two questions: 1- what skills from the proposed list (a list of skills from the study “Russia 2025: from personnel to talents”) are most important for professional activities; 2 - what skills were formed during the training at the university. Respondents had to tick (V) opposite the chosen skills. The results are shown in Figure
Findings
We conducted an analysis of the questionnaires completed by the respondents and the following results were obtained: Figure
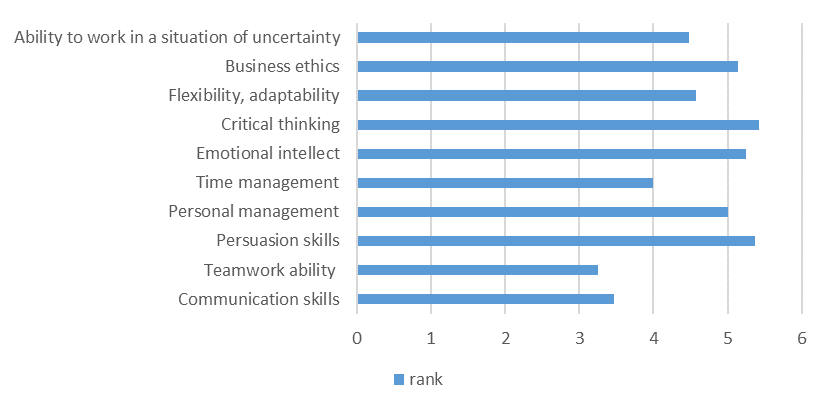
Respondents' answers regarding how the university contributed to the formation of the competencies indicated in the questionnaire indicate that more developed competencies are business ethics (3.6), critical thinking (3.8) and time management (4). Communicative skills leading in the previous question (rank 3.47), teamwork ability (3.25) in the second question are 4.5 and 4.55, respectively (figure
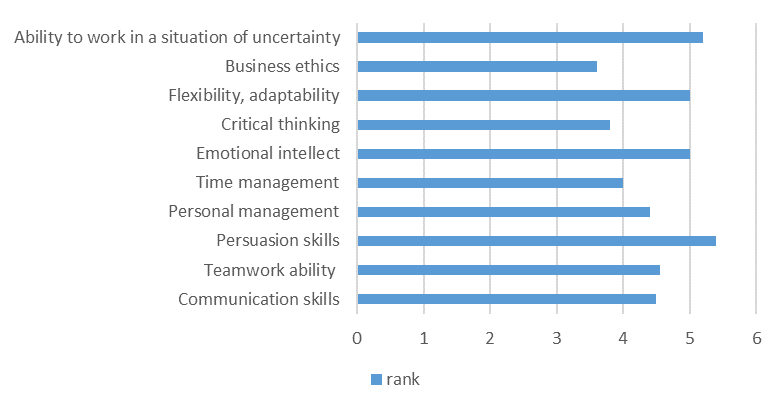
To the question “What disciplines in the educational process could help develop your abilities?” the respondents gave a wide range of answers, ranging from purely specialized ones (engineering graphics and descriptive geometry, industrial safety, occupational safety and health management at the enterprise, reliability of technical systems and technological risks, higher mathematics, genetics, life safety, the study of rules, laws, regulations on labor protection and industrial safety, etc.). It allows us to formulate the hypothesis about the fact that the respondents did not fully understand the problem and began to list the disciplines that allow them to form professional skills, ending with the following: practice, management basics, psychology, management, physical education, business ethics. Also, respondents indicated not only disciplines, but also other types of educational and extracurricular activities: “course paper defence, participation in scientific conferences, and it is difficult to name the subject”; “Rather not discipline, but the grafted teamwork skills, skills of independent work, etc.”; extracurricular activities.
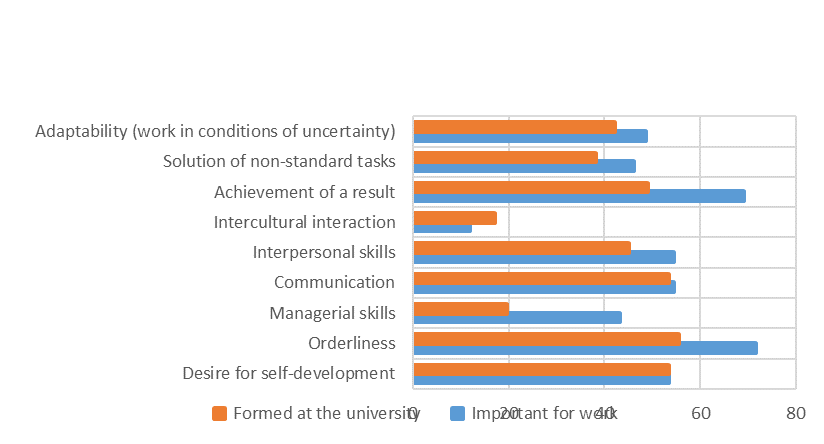
The answers of 204 graduates to the questions which skills from the proposed list are most important for professional activities and which skills were formed during the training at the university allow us to judge that orderliness, managerial skills and achievement of the result were the least formed in this sample (Figure
Conclusion
Surgut State University is introducing modern approaches to the organization of student studying. In 2017, representatives of the Administration of SurGU in Canada (Calgary) signed an agreement to join the CDIO international initiative which suggests that educational programs should provide not only the development of theoretical knowledge, but also the formation of personal and interpersonal competencies, the ability to come up with a new product or new technical idea, to carry out all design work on its implementation (or to give the necessary instructions to those who will do this), to introduce what has turned out into production.
Successful experience in introducing engineering and technical directions in the preparation of disciplines that form soft skills into the educational process has already been gained at SurGU. The curriculum for the preparation of bachelors in engineering areas included the disciplines of “Team Building”, “Effective Interaction in Project Teams”, and “Fundamentals of Image Communication” (developing public speaking skills, emotional competence, an effective negotiation process, etc.). The competencies formed in the process of studying these disciplines contribute to the implementation of complex engineering, interdisciplinary research and design activities in the field of creating new competitive automation, control and control systems; contribute to collective (team) activities in the professional field, the development of students' motivation for self-education and improvement in the professional field (Chulanova, 2018).
In further studies, possible changes in the workplans of the natural sciences are planned to consider (taking into account the positive experience in the engineering fields), the inclusion of disciplines that will allow to form the missing soft skills in the training process.
References
- Aeon, B., & Aguinis, H. (2017). It`s about time: New perspectives and insights on time management. Academy of Management Perspectives, 31(4), 309-330. https://doi.org/10.5465/amp.2016.0166
- Azevedo, A., Apfelthaler, G., & Hurst, D. (2012). Competence development in business graduates: An industry-driven approach for examining the alignment of undergraduate business education with industry requirements. The International Journal of Management Education, 10(1), 12-28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2012.02.002
- Bogdan, E. S., & Chulanova, O. L. (2016). Research competencies competitive high school graduate in the labor market in the region: Challenges, trends and challenges. Internet Journal "Naukovedenie", 8(6(37)), 31. [in Rus.].
- Boutenko, V., Polunin, K., Kotov, I., Sycheva, E., Stepanenko, A., Zanina, E., … & Topolskaya, E., (2017). Russia 2025: From personnel to talents. Retrieved from: http://image-src.bcg.com/Images/russia-2015-eng_tcm26-187991_tcm9-192725.pdf Accessed: 18.09.2019. [in Rus.].
- Buijsen, F., Jewell, D., McDonald, A., Michalik, B., Poltal, W., Stahl, E.,…, & Waltmann, K. (2018). Performance and capacity implications for a smarter planet. Retrieved from: http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/redpapers/pdfs/redp4762.pdf Accessed :10.10.2019.
- Chernyak, O., & Kharlamova, G. (2015). Problems of the effectiveness of student services in Ukraine: The experience of the international project. Vìsnik. Kiïvsʹkogo Nacìonalʹnogo Unìversitetu ìmenì Tarasa Ševčenka. Ekonomìka, 11(176), 55-58. https://doi.org/10.17721/1728-2667.2015/176-11/9
- Chulanova, O. L. (2018). Challenges and trends in the labor market: The synergy of digitalization and soft skills. Human Resources and Intellectual Resources Management in Russia, 7(3), 66-72. [in Rus.].
- Chulanova, O. L., & Bogdan, E. S. (2018). Formation of competitive graduates’ competencies in extracurricular activities. In V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Proceedings of GCPMED 2018 – International Scientific Conference "Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development". The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences EpSBS, 57. (pp. 177-184). London: Future Academy. https://doi.org/ 10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.18
- Demcheko, T. S., Karácsony, P., Ilina, I. Y., Vinichenko, M. V., & Melnichuk, A. V. (2017). Self-marketing of graduates of high schools and young specialists in the system of personnel policy of the organization. Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods, 7(9), 58-65.
- Hajduk, S. (2016). The concept of a smart city in urban management. Business, Management & Education, 14(1), 34-49. https://doi.org/10.3846/bme.2016.319
- Ivonina, A. I., Chulanova, O. L., & Davletshina, Yu. M. (2017). Modern directions of theoretical and methodological developments in the field of management: The role of soft-skills and hard skills in the professional and career development of employees. Internet Journal "Naukovodenie", 9(1), 90. [in Rus.].
- Rawung, F. H., Wuryaningrat, N. F., & Elvinita, L. E. (2015). The influence of transformational and transactional leadership on knowledge sharing: an empirical study on small and medium businesses in Indonesia. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 20(1), 123-145.
- Tsitskari, E., Goudas, M., Tsalouchou, E., & Michalopoulou, M. (2017). Employers’ expectations of the employability skills needed in the sport and recreation environment. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport and Tourism Education, 20, 1-9. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jhlste.2016.11.002
- Vinichenko, M. V., Chulanova, O. L., Karacsony, P., Bogdan, E. S., Melnichuk, A. V., & Makushkin, S. A. (2018a). Model of competences of graduates of high schools of engineering directions: Research of stakeholders. Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods, 8(3), 369-380.
- Vinichenko, M. V., Chulanova, O. L., Oseev, A. A., Bogdan, E. S., Makushkin, S. A., Grishan, M. A. (2018b). Interaction of the higher education and key employer for the formation of the actual profile of the competences of graduates of engineering. Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods, 8(5), 333-342.
- Vinichenko, M. V., Karacsony, P., Kirillov, A. V., Oseev, A. A., Chulanova, O. L., Makushkin, S. A., …, & Shalashnikova, V. Ju. (2018c). Influence of time management on the state of health of students and the quality of their life. Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods, 8(5), 141-156.
- Zaitseva, N. A., Larionova, A. A., Fadeev, A. S., Zhenzhebir, V. N., Filatov, V. V., & Pshava, T. S. (2017). Development of a strategic model for the formation of professional competencies of university students. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 12(7b), 1541-1548. https://doi.org/10.12973/ejac.2017.00283a
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
09 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-078-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
79
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1576
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Сhulanova*, O. L., & Bogdan, E. S. (2020). Formation Of Students’ Soft Skills In The Process Of Integration In Cdio. In S. I. Ashmarina, & V. V. Mantulenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 79. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 526-533). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.76
