Abstract
The active development of non-financial reporting is necessary according to recent trends in the global economy. Most standards, although they determine the order of non-financial indicators in reporting, are not mandatory. The lack of methodological issues development concerning this special type of reporting is caused by the novelty of the problem, the short period of the integrated system existence. The world experience in the disclosure of non-financial information with structural detailing was analyzed. The modern practice of non-financial reporting by foreign companies shows the gradual and sustainable development of the integrated reporting model. The structural and content analysis of integrated reporting in leading oil and gas companies has led to the following conclusion: there are significant shortcomings that create a gap between the users` informative expectations for reporting and the actual information disclosed by companies in their reporting. The set of measures developing the concept of the integrated reporting in the modern economy is offered in this study. Increasing transparency of reporting will lead to a decrease in corruption and will contribute to a better investment climate. Higher credit ratings, attraction of new investors, improved competitiveness of company as well as increased market capitalization by improving its business reputation will be an unconditional advantage of implementing the integrated reporting system in the view of companies.
Keywords: Integrated reportingnon-financial reportingenvironmental reportingstrategic reportingtransparencythe quality of reporting
Introduction
The requirements of the largest stock exchanges related to sustained development of companies and social responsibility in business have increased annually. In particular, the London Stock Exchange (LSE), the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE), the Malaysian Exchange (Bursa Malaysia), the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) have recommended the disclosure of information on risks in value changes of companies and their capital under the influence of ecological, social, scientific and technical, economic and other factors in order to increase business transparency. Non-financial disclosure is recommended by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. The requirement for organizations to disclose the information on environmental policy and GHG emissions of the company was established at the legislative level in many developed and developing countries. It is enshrined in the standard of the reporting of Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and ISO 26000:2010 "Guidance on social responsibility". This is due to the increasing problem of global climate change into a consequence of high concentration of GHG and a problem of deficiency of natural resources.
Problem Statement
The change of approach to the definition of the company`s goal, changes in inquiries of interested users concerning business transparency and the reporting led to the active development of an integrated reporting model that combines both financial and non-financial indicators of the company. The conceptual basis of this reporting system is laid down in International Standard for integrated reporting. The composition and content of each section in the integrated report shall comply with the requirements of relevant standards (GRI recommendations, standards of the ISO, АА 1000, Carbon Disclosure Project, CIMA, the Corporate Governance Code, etc).
The analysis of scientific publications showed that the foreign practice of formation and presentation of integrated reporting in the last few years has been actively investigated. This problem is revealed in the works of such foreign scientists as Bernardi and Stark (2018), Dumay, Bernardi, Guthrie, and Demartini (2016), Lee and Yeo (2016), Reimsbach, Hahn, and Gürtürk (2017), Serafeim (2015), Stacchezzini, Melloni, and Lai (2016), Stubbs and Higgins (2018), Zhou, Simnett, and Green (2017). However the lack of basic research in this field resulted from the short period of existence of the integrated reporting model.
Analysis of foreign practice indicates that the non-financial reporting model and, as a result, the model of integrated reporting has gradually developed. Nevertheless, many companies continue to use the term "annual report" concerning their reporting. It is connected to the fact that companies have listing on the London and New York Stock Exchanges where the concept of integrated reporting is not as well developed. There has been a tendency from 2014 to 2018 to increase the amount of information disclosed in integrated reporting. It should be noted that companies aim to improve their integrated reports. Increased analytical data on some sections of the reporting, more detailed description of a business model, the purposes and the development strategy of organizations is observed in the integrated reporting of almost all considered companies. Some organizations presented a number of indicators in the form of "the effectiveness panel" which makes the data more visible and simplifies the process of analyzing the organization's activities.
Research Questions
According to the revealed insufficiency in formation of a categorical position concerning system of integrated reporting methodology within this research the following questions were formulated:
What is the international practice of non-financial disclosure?
What factors will contribute to the development of integrated reporting methodology?
Purpose of the Study
The purposes of this study:
To analyze the international practice in disclosing of non-financial information.
To reveal the factors contributing to the development of integrated reporting methodology.
Research Methods
On forming the research hypothesis
Н1 The number of published non-financial reports is growing annually.
Н2 Today the main part of non-financial reporting consists of the reports in the field of sustainable development prepared with the GRI methodology.
H3 The UK is a leader in the field of non-financial reporting. The share of non-financial reports falling on the developing countries is insignificant.
Research methodology
General scientific methods, such as analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction, comparison, abstraction, specification and generalization, system approach were the methodological basis of the research. The research object is the corporate reporting system of oil and gas companies. The research subject is the problem of forming the integrated reporting.
Data collection for research
Scientific publications on the studied subject, reports of Corporate Register, the materials of the International council for the integrated reporting, the reporting of the foreign enterprises of the oil and gas industry published on their official sites formed information base of research.
The structure and content of integrated reporting in the largest foreign oil and gas companies has been analyzed within the research. Identification of shortcomings in foreign practice of non-financial reporting as well as advantages of this reporting was the purpose of the analysis. The following organizations were selected for studying: BP - Great Britain (British Petroleum, 2018); Exxon Mobil Corporation – USA (Exxon Mobil Corporation, 2018); PetroChina Company Limited – China (Petro China Company Limited, 2018); Equinor ASA – Norway (Equinor ASA, 2018); ADNOC – UAE (Abu Dhabi National Oil Company, 2019). The information in integrated reports of companies listed above is clearly structured, the main focused is on significant issues.
Findings
Today 17823 companies which published 106452 non-financial reporting are registered in the www.corporateregister.com project (Corporate Reporting Dialogue, 2019). Publications of non-financial reporting have been evenly increasing in recent times (Figure
According to the statistic, the registration of non-financial reporting was smooth and progressive, except for two hikes in 2012 and 2013, and it affected the world's economies. The hikes could be caused by preparations for the EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive 2014/95/EU.
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is another large non-financial reporting database, which collects reporting data using only GRI standards (Figure
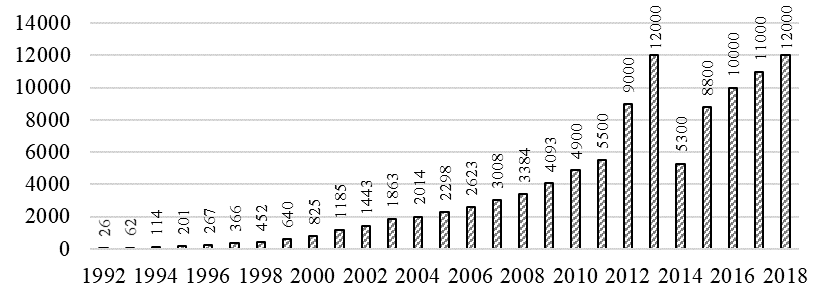
Source: authors based on The Sustainable Development Goals and the future of corporate reporting (Corporate Reporting Dialogue, 2019).
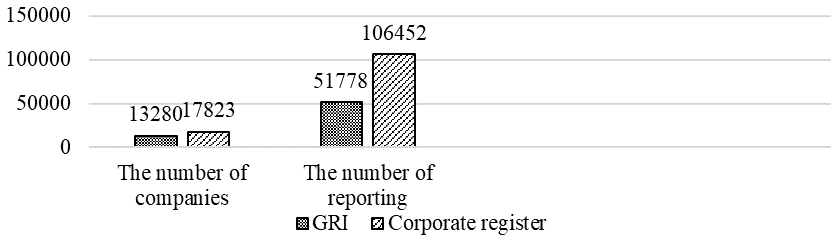
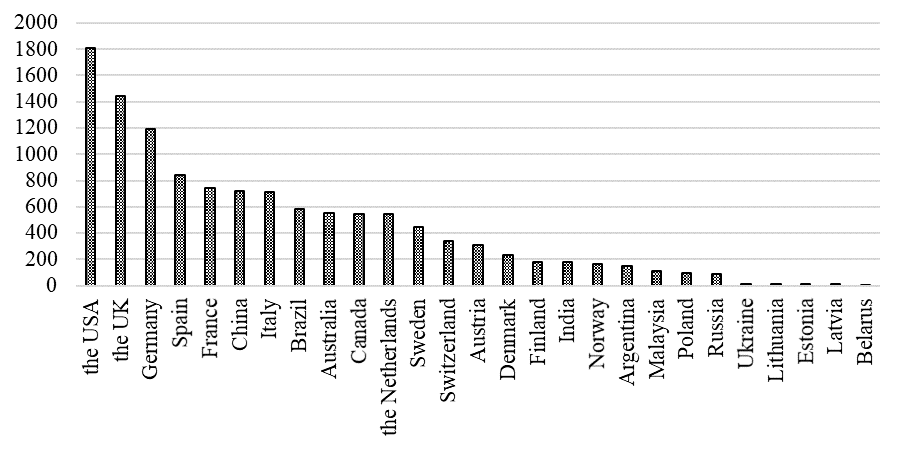
The leaders have been changing in recent years. The UK was the absolute leader in non-financial reporting 5 years ago, but in 2019. The largest number of reports were released by American companies (Figure
Source: authors based on Corporate Register (Corporate Reporting Dialogue, 2019)
There are 16 countries with the most active development of non-financial reporting in the world. Today they can be named leaders of this area (Figure
BRICS countries have recently followed global trends in non-financial reporting. The leader is still Brazil (Brazilian companies have begun to produce non-financial reporting before others), and significant progress has been made in India and China. Russia is comparable to Malaysia and Poland in terms of the scale of the non-financial reporting model, which means that transparency of Russian companies for potential investors and counterparties is not comparable to companies from other countries
The leading industries in the development of the non-financial reporting model are oil and gas, energy, metallurgical, financial, and telecommunication industries. It is discovered that corporations often publish integrated reports on their official websites in two formats: XBRL and PDF. At the same time, organizations increasingly prefer the XBRL format in the formation of integrated reporting and its publication. It is explained by the rules of exchange of business information between reporting companies and supervisory bodies in international practice.
The amount of information disclosed in the report is gradually increasing. The results of the integrated reports analysis of the above companies show the volume increasing of annual reports and reports in the field of sustainable development. The average integrated report was 222 pages in 2018, but in 2017 it was 205 pages and 189 pages in 2016 (Corporate Reporting Dialogue, 2019). This was mainly because of the idea of more detailed information on the development strategy, the main risks of organizations. Besides, some organizations started to write additional environmental and sustainable development reports.
According to the analysis of the structure and content of the integrated reporting of leading international oil and gas companies, the main disadvantages in reports of almost all organizations considered to be:
a lot of descriptive information;
insufficient description of internal control and audit system;
insufficient description of the risk management system;
little analytical data;
incomplete description (lack of description) of the results of environmental and social policies;
lack of a unified reporting structure.
It is necessary to standardize the structures of integrated reporting, to develop a system of non-financial indicators disclosed in the reporting, to use XBRL-format in the generation and presentation of integrated reporting. This will help to develop the concept of integrated reporting, improve the quality of audit procedures for integrated reporting, and improve the reliability of integrated reporting financial and non-financial information presented in reporting.
The standards system will identify the essential topics that need to be included in the report, identify the system of non-financial indicators that sufficiently disclose information about key aspects of the company's activities, risks and opportunities, business models, strategies and prospects, etc.
Conclusion
Globalization, the increasing role of corporate social responsibility, the increasing influence of environmental factors lead to the importance of providing non-financial information in reporting of organizations. The results of the analysis show an even increase of non-financial reports publishing and an increase in the number of companies providing reports. The most progressive form of public non-financial reporting is integrated reporting, where conceptual approach is based on integrated, system thinking.
It is advisable to use the XBRL-format in the integrated report of Russian companies. This requires the development of an XBRL-taxonomy that takes into account both financial and non-financial indicators. World practice shows that using the XBRL format will reduce the time for reporting by almost 90%; reduce IT cost of ownership by 40%; will make it possible to reduce costs and speed up the process of business information exchange. Reporting in a standardized format for all interested users makes reporting more transparent and comparable. In addition, reporting in the XBRL format will contribute to the integration of national business into the international information space.
It is important to pay attention to the amount of analytical information in integrated reporting. The use of comparative industry and regional analysis data as reporting information, the use of coefficients, graphs, schemes, tables in the disclosure of financial and non-financial data, as well as the use of quantitative industry indicators, increase comparability of reporting, make it more understandable and allow users to reduce the cost of searching for the necessary information.
References
- Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (2019). ADNOC: Review report and unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial information for the six month period ended 30 June 2019. Retrieved from: https://adxservices.adx.ae/WebServices/DataServices/contentDownload.aspx?doc=1709584 Accessed: 01.09.19.
- Bernardi, C., & Stark, A. W. (2018). Environmental, social and governance disclosure, integrated reporting, and the accuracy of analyst forecasts. The British Accounting Review, 50(1), 16-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2016.10.001
- British Petroleum (2018). Growing the business and advancing the energy transition. BP, Annual Report and Form 20-F 2018. Retrieved from: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/investors/bp-annual-report-and-form-20f-2018.pdf Accessed: 23.08.2019.
- Corporate Reporting Dialogue (2019). The Sustainable Development Goals and the future of corporate reporting. Retrieved from: https://corporatereportingdialogue.com/publication/sdgs-and-the-future-of-corporate-reporting/ Accessed: 15.10.2019.
- Dumay, J., Bernardi, C., Guthrie, J., & Demartini, P. (2016). Integrated reporting: A structured literature review. Accounting Forum, 40(3), 166-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accfor.2016.06.001
- Equinor ASA (2018). Equinor Annual Report 2018. Retrieved from: https://www.equinor.com/content/dam/statoil/documents/annual-reports/2018/equinor-2018-annual-report.pdf Accessed: 22.08.19.
- Exxon Mobil Corporation (2018). Exxon Mobil 2018 Summary Annual Report. Retrieved from: http://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReports/PDF/NYSE_XOM_2018.pdf Accessed: 25.08.2019.
- KPMG (2017). The KPMG Survey of Corporate Responsibility Reporting 2017. Retrieved from: https://home.kpmg/xx/en/home/insights/2017/10/the-kpmg-survey-of-corporate-responsibility-reporting-2017.html Accessed: 23.08.2019.
- Lee, K. -W., & Yeo, G. H. -H. (2016). The association between integrated reporting and firm valuation. Review of Quantitative Finance and Accounting, 47(4), 1221-1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11156-015-0536-y
- PetroChina Company Limited (2018). 2018 Annual Report PetroChina Company Limited. Retrieved from: http://www.petrochina.com.cn/ptr/ndbg/201904/d9b6e14b8e0145d2bd3d075e0136dfee/files/39f6f62593624c6bbda8ecf626d2e282.pdf Accessed: 23.08.2019.
- Reimsbach, D., Hahn, R., & Gürtürk, A. (2017). Integrated reporting and assurance of sustainability information: An experimental study on professional investors’ information processing. European Accounting Revie, 27(3), 559-581 https://doi.org/10.1080/09638180.2016.1273787
- Serafeim, G. (2015). Integrated reporting and investor clientele. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 27(2). Retrieved from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2378899 Accessed: 15.10.2019.
- Stacchezzini, R., Melloni, G., & Lai, A. (2016). Sustainability management and reporting: The role of integrated reporting for communicating corporate sustainability management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 136(A), 102-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.109
- Stubbs, W., & Higgins, C. (2018). Stakeholders’ perspectives on the role of regulatory reform in integrated reporting. Journal of Business Ethics, 147(3), 489-508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-015-2954-0
- Zhou, S., Simnett, R., & Green, W. (2017). Does integrated reporting matter to the capital market? Abacus, 53(1), 94-132. https://doi.org/10.1111/abac.12104
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
09 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-078-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
79
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1576
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Korneeva*, T., Kozhuhova, V., & Potasheva, O. (2020). The Forming Of Non-Financial Reporting: Challenges And Opportunities. In S. I. Ashmarina, & V. V. Mantulenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 79. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 423-429). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.61
