Abstract
This article investigates the issues of social responsibility of small enterprises. The authors’ position is that the term “socially oriented activities” should be only used to refer to activities driven by the own initiative and will of the enterprise's owners, rather than activities driven by requirements of public authorities or the need to provide conditions for business operations. The authors have examined the external and internal areas of socially oriented activities of a small enterprise, presented their content and features. A layered structure is proposed for the internal area of socially oriented activities, making it possible to assess the quality of the policy of a small enterprise in relation to its personnel. When studying the problems of social responsibility of small enterprises, it is important to take into account the peculiar qualities of the latter: short life cycle, minor scope of activities, lack of publicity, limited resources to finance social programs. These entities are subject to government support themselves. Therefore, it is important for the government to make them more involved in social and public life. Small enterprises demonstrate some examples of social responsibility, but in general, these activities have not become systematic yet. The authors have considered possible measures to increase the level of social responsibility of small enterprises and have established that these measures have limited scope of application and low efficiency. The increase in social activities of small enterprises is inextricably linked to the creation and strengthening of appropriate enabling institutional changes.
Keywords: Social responsibilitysmall enterprisessocially oriented activities of small business enterprises
Introduction
The desire of the entrepreneur to conduct business activities by focusing only on profit has been losing its unconditional importance. We are witnessing the development and strengthening of a new progressive trend: the importance of the social component of business is growing, as well as the attention to the moral and ethical aspects of companies' activities. This trend is due to the following factors:
growing importance of intangible production factors, in particular human capital and the intellectual component, for the company's operations;
strengthening of the role of business in solving social problems of varying degrees of complexity and scale: within the company itself, the local community, municipal territories, regions, etc.
increasing importance of the status of a socially responsible company for its successful development.
Social responsibility of business is a special kind of innovation that contributes to the achievement of economic and social strategic performance at the level of regions and the country as a whole. As such, corporate social responsibility has become an important instrument of public policy, for example, in the EU countries (Antošová & Csikósová, 2015).
Examples of socially oriented entrepreneurship in the Russian Federation have been demonstrated by the largest Russian companies: Rosneft, Gazprom, Tatneft, Nornickel, AvtoVAZ and many others. At the same time, small economic entities are poorly involved in business socialization processes. With the growing importance of small business for the national economy, an increase in the level of social responsibility is expected. Accordingly, it is necessary to take measures aimed at the formation and sustainable development of this positive trend.
Problem Statement
The review of the scientific literature shows keen interest of researchers in the issues of social responsibility of companies. These studies are generally focused on large corporations. This can be explained by the large scale of activities of the latter, public availability of their reporting on sustainable development, and the visibility of the results of their work for society. Small enterprises (hereinafter referred to as SEs) are more difficult to study: the scope of their activities is insignificant, they are more closed to the public in terms of reporting and have limited resources to finance social programs (Korovina, 2015; Deviatlovsky & Pozdniakova, 2014). Moreover, every SE is characterized by a high degree of individuality.
Researchers have addressed a large number of aspects reflecting the ability of small enterprises to implement social responsibility policies. In particular, the following issues have been covered in scientific literature: differences in the social responsibility of small and large enterprises (Mousiolis, Zaridis, Karamanis, & Rontogianni, 2015; Ma, 2012); the positive impact of social responsibility policies on the activities of small enterprises (Lee, Herold, & Yu, 2016; Nigri & Del Baldo, 2018); determining the degree of dependence between the business success of small enterprises and the level of social responsibility of their managers (owners) (Pletnev & Barkhatov, 2016); responsibility of a SE employer in labor relations (Sizova & Chilipenok, 2017); features of manifestations of social responsibility by micro-enterprises and small family enterprises (Castejón & López, 2016). There is a growing number of terminological and conceptual aspects used in the scientific literature to characterize the social responsibility of small enterprises (Ortiz-Avram, Domnanovich, Kronenberg, & Scholz, 2018).
However, the results of the studies do not make it possible to state unequivocally that SEs are better or worse suited for implementation of social projects compared to large companies (Mousiolis, Zaridis, Karamanis, & Rontogianni, 2015).
There are multiple views of the meaning of the definition of “social responsibility of small business”. The study of socially oriented activities of SEs and individual areas of such activities involves the systematization of these individual areas. In Russia, the issue of encouraging small enterprises to engage in socially responsible behavior has becoming particularly relevant. All this confirms the need for further research in the field of social responsibility of small enterprises.
Research Questions
A number of questions correspond to the problems formulated above:
What are the boundaries of social responsibility of small enterprises? How does this area relate to the business interests of a small enterprise?
What are the areas of implementation of socially-oriented activities of small businesses? Is it possible to systematize them to reflect the nature of these areas?
How to encourage socially responsible behavior of a small enterprise? What measures can be proposed in this field?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to increase scientific knowledge in the field of social responsibility of small enterprises. Within this purpose and in accordance with the questions posed, the following problems were stated:
Clarify the definition of “social responsibility of a small enterprise”;
Reflect the areas of socially responsible activities of a SE and the characteristic features of these areas;
Identify the main measures aimed at encouraging social responsibility of small enterprises.
Research Methods
The theoretical basis of the study is scientific works of foreign and Russian researchers in the field of corporate social responsibility. The research methodology is based on logical, systemic and structural approaches. Information support of the study is represented by secondary qualitative (results from scientific literature) and quantitative (official statistics) information.
Findings
The definition of “social responsibility of business” is complicated by the fact that its content and boundaries can be set in multiple varying ways. There is an opinion that the very functioning of a small business is a demonstration of its social responsibility, as business operations solve issues of employment and self-employment, provide the consumer market with goods and services, supplement national budgets with taxes, etc. (Zhikharev, 2008). However, this is also true for large companies. Therefore, this opinion should be considered neutral in the study of features of SEs. In addition, there are cases of creation of SEs in Russia solely for the purposes of money laundering, tax evasion, redistribution of profits through counterparty chains. Business activities of some SEs may qualify as fraudulent (for example, fake recruitment agencies). Having a formal legal cover, such enterprises pursue illegal activities, and in this case, we should consider their effect to be anti-social.
Some authors interpret social responsibility in a fairly broad way. For example, responsible relations with partners and responsibility to consumers are seen as its components (Deviatlovsky & Pozdniakova, 2014). We tend to consider these components to be elements of business responsibility: a) building effective long-term mutually beneficial relations with counterparties increases the effectiveness of activities of a SE; b) SE's responsibility, which implies observance of consumers' rights to quality products and reliable information about them, is determined by the requirements of the Russian legislation.
In our opinion, social responsibility of a SE is a product of voluntary and conscious activities aimed at solving social problems and not directly related to the company's business goals. The sphere of social responsibility of SEs should remain beyond the boundaries of their business activities. We suggest that socially-oriented activities demonstrated by a SE should be considered in two profiles: externally and internally oriented (Figure
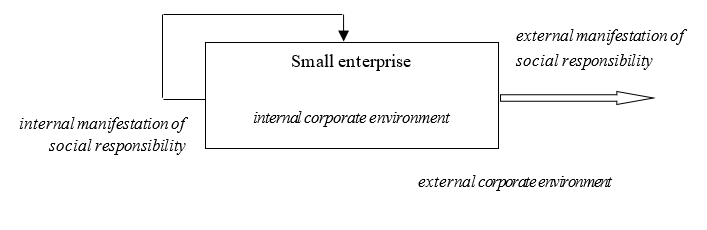
A) External socially oriented activities. A feature of this area is that it is determined not by the needs of the business, but by the position of the SE on social issues. The content of this area includes voluntary actions aimed at improving the life of society: charity, solving certain social problems, participating in the implementation of social programs and projects.
The scope of social support is determined by the SE independently and depends on its financial capabilities. Experience shows that such support, as a rule, is targeted and aimed at the nearest environment of the SP and its owner. For example, a charity payment is given to the school attended by the child of the entrepreneur; funds for landscaping are provided at the location of the enterprise's facilities, etc.
B) Internal socially oriented activities. Unlike external activities, it is conditioned not so much by the free will of the entrepreneur as by the conditions dictated by the business environment. Its main target is the staff personnel of a small enterprise as one of the main factors of production activities. There is an opinion that the interests of the workforce are strategic imperatives that should be taken into account by a small enterprise to improve its financial performance and establish a good reputation (Nejati, Quazi, Amran, & Ahmad, 2017). We believe that the economic concern becomes the enterprise's priority in this regard: employers receiving decent wages and care from the employer increase their performance.
It is possible to introduce a conditional scale of internal socially oriented activities of SEs in accordance with their level of security provision. This hierarchy includes:
the bare minimum level is determined by the requirements of minimum wages, benefits and social security of the organization’s personnel set by the legislation;
the standard level is determined by the current state of sectoral and territorial labor markets, in accordance with which the SE determines the level of wages, forms systems of benefits and increases the professional skills of its personnel;
the increased level includes socially-oriented activities taken at the initiative of the SE itself in excess of the standard level, and having a strategic nature. The personnel is provided with additional social benefits, creating an attractive job. SE directs efforts towards the formation of long-term human resources, intellectual capital and sustainable competencies of its employees.
We believe that activities of a small enterprise organized at standard and increased levels can be fully considered to be socially responsible.
Every SE demonstrates limited socially oriented activities. There are several reasons for this: short life cycle, unsustainable development, limited resources, and weak impact of socially-oriented activities on the business process. The impact of an individual SE on the overall social situation is insubstantial. At the same time, large numbers of small enterprises (as of today, according to official statistics, 2.6 million small enterprises and micro-enterprises are registered in the Russian Federation make the total scope of their socially-oriented activities considerable at the scale of the national economy. Therefore, their great involvement in social and public life is important for the government. Government support is provided to small enterprises. Accordingly, there are appropriate expectations on the side of the government and society.
Studies show that some Russian SEs demonstrate examples of socially responsible behavior and initiatives. This is mostly determined by personal relationships, values, choices and beliefs of the owners. But in general, most managers of small business organizations lack a comprehensive understanding of the term “social responsibility of business” (Bataeva, Cheglakova, & Melitonyan, 2018). Researchers recommend encouraging of socially responsible behavior of participants in business relations in the entrepreneurial environment in a more active way. However, the real state of affairs indicates that at the moment, the state and society are unable to influence the intensity of external socially oriented activities of SEs in any significant way. Insignificant tax preferences cannot be an effective tool of encouraging socially-oriented activities of a small enterprise. The media fail to pay due attention to the achievements of individual SEs due to the lack of any significant response. Entrepreneurial unions and associations are focused on the regulation and harmonization of relations between business entities and government authorities, and often do not adequately promote social and public activities of enterprises. Thus, there is a problem of creating encouraging prerequisites that can interest a SE in engaging in socially responsible behavior.
Socially-oriented activities of a small enterprise are carried out solely on a voluntary basis. Because of this, the scope and areas of its implementation are expected to grow in an evolutionary way in accordance with a change in the mentality of civil society, and therefore citizens involved in small enterprises. The positive trend is the transformation of the perception of entrepreneurship in Russian society. According to the results of an all-Russian representative survey conducted by the Analytical Center of the National Agency for Financial Research, 74% of Russians have positive attitude to entrepreneurship. This should be seen as a reaction to the socially responsible behavior of business entities.
Conclusion
The provisions of the article enable us to refine the boundaries of social responsibility of small enterprises. Social responsibility of SE should be considered as an innovative product of voluntary and informed activities, not directly related to the business goals of the company, not attributed to the purpose of profit-making and aimed exclusively at solving social problems. By distinguishing external and internal components of social responsibility of a small enterprise, we are able to refine the content of these fields, their similar and distinctive characteristics. The external area, as well as the standard and increased levels of the internal one, can be fully considered to be socially oriented activities of a SE. Small Russian enterprises have potential readiness for socially oriented activities. At the same time in the modern period, neither the government nor the society are able influence the intensity of such activities in any significant way. This adds to the relevance of the problem of establishing the prerequisites that would encourage small enterprises to engage in socially responsible behavior.
References
- Antošová, M., & Csikósová, A. (2015). Influence of European Union policy to corporate social responsibility. In A.I. Iacob (Ed.), Proceedings of the 2nd Global Conference on Business, Economics and Management and Tourism. Procedia Economics and Finance, 23, 733-737. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Science BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2212-5671(15)00456-6
- Bataeva, B., Cheglakova, L., & Melitonyan, O. (2018). Social responsibility in Russian business: A researchof attitudes of owners and managers in a small and medium enterprises. Organizational Psychology, 8 (1), 13-52. [in Rus.].
- Castejón, P. J. M., & López, B. A. (2016). Corporate social responsibility in family SMEs: A comparative study. European Journal of Family Business, 6(1), 21-31. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ejfb.2016.05.002
- Deviatlovsky, D. N., & Pozdniakova, M. O. (2014). Corporate social responsibility in Russia: Problems of small enterprises. Problems of the Modern Economy, 2(50), 173-175. [in Rus.].
- Korovina, L. N. (2015). Tendencies of social responsibility of Russian business: State and problems (Part 1). Socio-Economic Phenomena and Processes, 10 (8), 48-55. [in Rus.].
- Lee, K. H., Herold, D. M., & Yu, A. L. (2016). Small and medium enterprises and corporate social responsibility practice: A Swedish perspective. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 23(2), 88-99. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1366
- Ma, J. (2012). A study on the models for corporate social responsibility of small and medium enterprises. Physics Procedia, 25, 435-442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.03.108
- Mousiolis, D. T., Zaridis, A. D., Karamanis, K., & Rontogianni, A. (2015). Corporate social responsibility in SMEs and MNEs. The different strategic decision making. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 175, 579-583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.1240
- Nejati, M., Quazi, A., Amran, A., & Ahmad, N. H. (2017). Social responsibility and performance: Does strategic orientation matter for small businesses? Journal of Small Business Management, 55(S1), 43-59. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsbm.12305
- Nigri, G., & Del Baldo, M. (2018). Sustainability reporting and performance measurement systems: How do small- and medium-sized benefit corporations manage integration? Sustainability, 10(12), 4499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124499
- Ortiz-Avram, D., Domnanovich, J., Kronenberg, C., & Scholz, M. (2018). Exploring the integration of corporate social responsibility into the strategies of small- and medium-sized enterprises: A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 201, 254-271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.011
- Pletnev, D., & Barkhatov, V. (2016). Business success of small and medium sized enterprises in Russia and social responsibility of managers. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 221, 185-193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.05.105
- Sizova, I. L., & Chilipenok, Yu. Yu. (2017). Social responsibility within labour relations among the employers in small and medium businesses. Journal of Social Policy Studies, 15(1), 67-80 [in Rus.].
- Zhikharev, K. L. (2008). Social responsibility of small-scale business. Russian Economic Online Journal, 4. Retrieved from: http://www.e-rej.ru/publications/117/?PAGEN_1=2 Accessed: 01.10.19. [in Rus.]
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
09 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-078-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
79
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1576
Subjects
Business, business ethics, social responsibility, innovation, ethical issues, scientific developments, technological developments
Cite this article as:
Andreeva*, S., Andreev, O., & Popova, E. (2020). On The Issue Of Social Responsibility Of Small Enterprises. In S. I. Ashmarina, & V. V. Mantulenko (Eds.), Global Challenges and Prospects of the Modern Economic Development, vol 79. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 739-745). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.106
