Abstract
The paper studies the role of an individual value system in interrelation with the mechanisms of psychic self-regulation of behavior in the context of the communicative environment expansion within the modern information society. The relevance of the analysis of internal value behavioral regulators is connected with the declaration of freedom of thought and action as a priority guideline for self-assertion of youth in the modern society. However, the implementation of thought and action freedom in social life causes an internal psychoemotional tension, as a young person evidently or non-evidently is forced to correlate her objectives with the boundaries and the traditions of one or another field of activity. The purpose of this study is to compare youth terminal values and to assess their role in a life position shaping during social adaptation to professional, educational, family fields of activity. The methodology of the study is based on the activity theory of personality. The empirical research used the method of standardized self-reports and psychological testings. The results of the comparative research between different age groups of young people showed that value orientations, which determine the objectives, play a key role in constructing life strategies. Values priorities in different age groups of young people revealed the importance of terminal values for planning adaptive behaviour in difference social and communicative environments.
Keywords: Personalitylifeworldgoal setterminal valuesself-regulationsocial and communicative fields
Introduction
The human lifeworld in the digital age is changing dynamically and radically. Global, regional and local levels of transformation in economics, politics, and social relations affect different sides of interaction between subjects, directly or indirectly connected with conscious and subconscious systems of social orientation and behavior regulation. Social influence acquires an implicit character and is exercised through internal mental mechanisms that determine the specificity of behavior and activity of people in different social situations and at different levels of social reality.
Today's young generation has many priorities to address in various areas of life. The country's development, as well as preservation and transfer of basic values to the next generation depend on these decisions. In forming a personality, value orientations belong to the system of motivation and self-regulation of behavior. It is values that underlie a person's comprehension and evaluation of social objects and situations and, consequently, serve as the basis for cognition and construction of a holistic image of the social world. The system of values, which is formed at the subconscious level of everyone's mentality, has a significant impact on direction and content of any form of social activity, on formation of a person's civic position, on a person's actions and behavior in everyday and critical situations, on general perception of the world and attitude towards it.
Value systems are the basis for the life strategies construction. In psychology, a value system is regarded as one of the central personal entities that form and express a person's conscious attitude to social reality and in this capacity defines a broad motivation for their behavior, having a significant impact on all aspects of their activities. These are ideal, symbolically mediated entities that go beyond the limits of a person's consciousness; they are implemented into practical life activities as guidelines and priorities within the social adaptation.
Traditionally, there has been a distinction between systems of terminal values and instrumental values. The established belief in the priority of a certain final goal (meaning) of an individual existence from personal or public point of view is connected with the system of terminal values that motivate the direction of life orientations at the level of subconscious mental mechanisms. The established belief about the preferred way of thinking and acting is connected with instrumental values (Rokeach, 1973). To understand how the modern youth's value orientations are formed and to identify value priorities in different age groups is an urgent task of social adaptation and communication. We correlate the level of personal terminal values expression with the communicative potential that provides natural self-regulation of behavior in the lifeworld's social sphere.
Problem Statement
The communicative problem of preservation, transmission and assertion of basic values correlates with ethical and psychological problems of life-affirming mindset formation among young generation, based on corresponding conceptual understanding of value priorities.
The value system offered to young people by their culture often leads to social tension and frustration manifested in various forms of marginal behaviour. Various forms of autonomy and isolationism in the social and spiritual spheres and in various youth subcultures are emerging in society.
The question of forming a system of values among youth has been raised in sociology (Ritzer, 2002), psychology (Rokeach, 1973; Sheldon & Gunz, 2009), philosophy (Ilyin, 2005; Matveev, 2017). At present, this issue is being discussed by scientists in various fields of knowledge: from management and business ethics to religious studies and happiness studies (Lee, 2019; Wruk, Oberg, & Klutt, 2019; Bergmann & Todd, 2019; Bucher, Neubauer, Voss, & Oetzbach, 2019; Stavrova & Haarmann, 2019). The "scanning" of value systems using proven psychological techniques continues to play an important role in these studies (Kern, Waters, Adler, & White, 2015; Liu, Tov, Kosinski, Stillwell, & Qiu, 2015; Neubauer & Voss, 2018; Hodges & Gore, 2019).
Research Questions
Our study aims to identify the content of a youth value system. This attitude implies the characterization of terminal values and their expression in different age groups and in the application to different communicative spheres of the lifeworld.
The research questions related to the definition of the terminal values communicative potential imply the identification of personal positions with regard to the target values priority and clarification of the terminal values representation in specific social areas, such as: professional field, educational processes, family life. From this perspective, we consider terminal values to be the target values represented by the following personal positions:
own prestige;
high financial standing;
creativity;
active social contacts;
self-development;
achievements;
moral satisfaction;
personal identity preservation.
Purpose of the Study
Purpose of the study is to assess the priorities of terminal values in different age groups of young people, to identify the importance of terminal values in social adaptation by comparing value priorities and targets for entering different fields of activity (professional, educational, family, public).
Research Methods
Theoretical basis of the study is the activity theory of personality. Comparative and systematic methods of analysis are used in this work. Empirical research is based on the method of standardized self-reports and psychological testing.
To study the special aspects of the hierarchy within a personal values system the questionnaire "Terminal values (TQ)" (Senin, 1991) was used. It allows to estimate the expression of eight terminal values (life goals): own prestige, high financial standing, creativity, active social contacts, self-development, achievements, moral satisfaction, personal identity preservation, as well as their representation in different spheres of life (professional activity, training and education, family life, social life, hobbies). The test results are expressed in the form of an individual profile, separately for terminal value scales and life spheres.
The selected methods are aimed at identifying priority targets among youth and correlating them with adaptation to the basic social fields of human activity.
An empirical study to clarify the special aspects of the terminal values hierarchy involved 64 respondents aged 15-17 years.
Findings
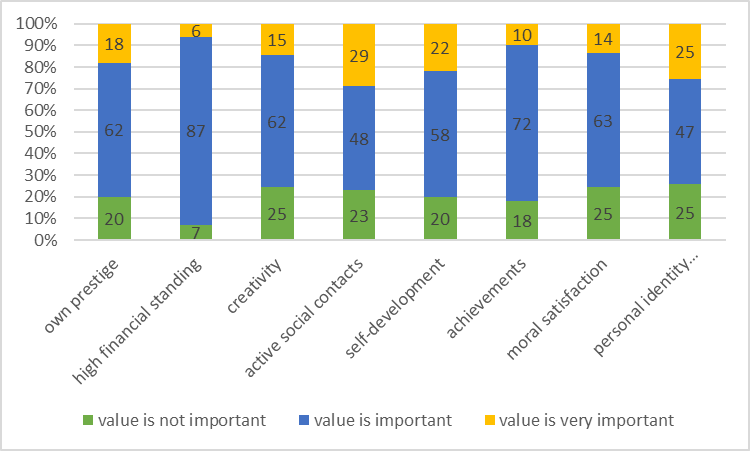
The research of terminal values expression by means of psychological testing allowed to reveal a vivid picture for average indicators of the survey participants' value priorities concerning specific communicative area of social adaptation (Figure
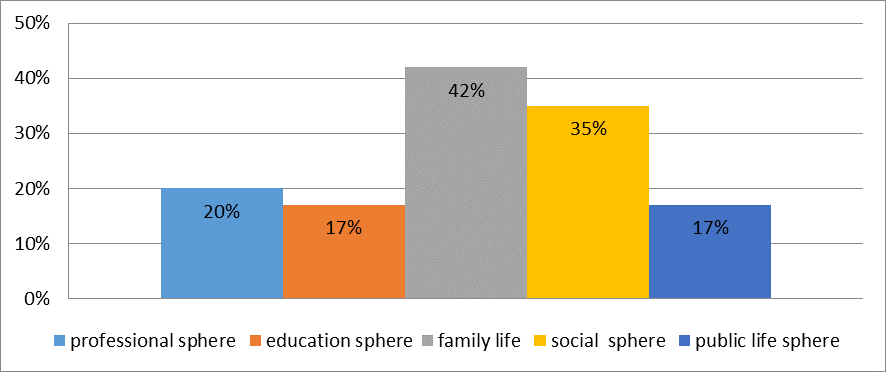
Young people named family life as the most important social and communication sphere (42%). It is in this sphere (in comparison with other ones) that they consider to be the most important such values as: self-development - knowledge of one's own individual features; achievements - setting and solving certain life tasks as the main life factors; moral satisfaction - being guided by moral principles, prevalence of spiritual needs over material ones; own prestige - gaining recognition in society by following certain social requirements.
The professional sphere was named the main one by 20% of young people. Along with family life, this sphere is most often associated with such values as: achievements, moral satisfaction, active social contacts - the establishment of favorable relations in various areas of social interaction, the expansion of one's interpersonal connections, the implementation of one's social role. The hobbies sphere is important for 20% of respondents. The value of creativity - implementation of one's creative abilities, desire to change the surrounding reality - and the active social contacts value are associated with it first of all.
The education sphere was identified as important by 17% of young people. It is associated with such values as high financial standing, i.e. the factors of material well-being are seen as the main meaning of existence in this sphere, and achievements. The public life sphere is significant for 17% of respondents. Such values as moral satisfaction, personal identity preservation - i.e., predominance of one's own opinions, views, convictions over the common ones, protection of one's uniqueness and independence, - and active social contacts are highlighted first of all in this sphere.
Communicative potential of respondents' terminal values in the family life sphere
Youth views on the value structure in the family life system are presented in Figure
33% of people in the survey consider
30% of young people believe that
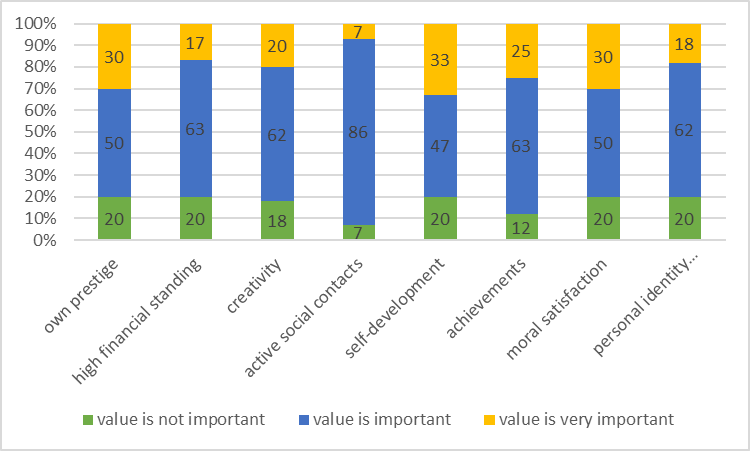
All of these values are reinforced with age, as evidenced by the significant differences in age groups among young people (Table
In addition, older boys see such values as
Table
Communicative potential of the respondents' terminal values for adaptation to professional activity
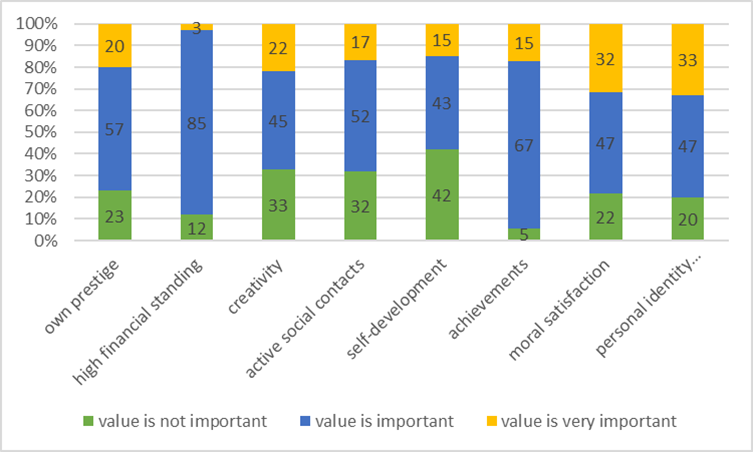
Young people consider
Comparative analysis of terminal values in professional sphere for different age groups of young people
A comparison of the results of 15-16 and 17-year-olds shows that the importance of such professional values as
Communicative potential of the respondents' terminal values for hobbies
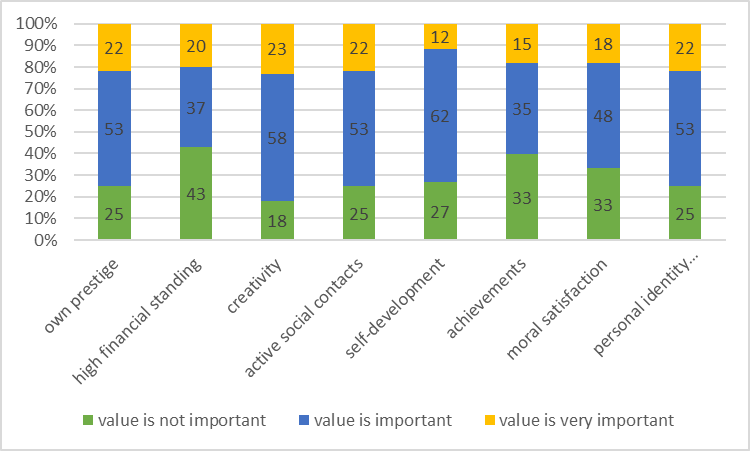
20% of respondents consider values in this sphere very important for themselves.
Comparative analysis of terminal values in hobbies for different age groups of young men
All values emphasized by respondents in the sphere of hobbies - creativity, own prestige, active social contacts - acquire higher meaning with age (Table
There are no significant differences between young men and girls in this sphere.
Communicative potential of the respondents' terminal values for educational sphere
The values of young people are more evenly distributed in educational sphere (Figure
The biggest diversity of youth opinions is seen the
Comparative analysis of young men and girls' value priorities in education
The young men's educational goal set is focused on the possibility of achieving a
Comparative analysis of terminal values in education for different age groups of young men
A comparison of the results of 15-16 and 17-year-olds (Table
Conclusion
With the expansion of the modern society's information and communication environment, an individual's internal motivation and their life success are essentially determined by the priority of terminal values. The study showed that in different age groups of young people, the communicative potential of goal sets for planning adaptive behaviour in different fields of activity was revealed.
Young people identified family life as the most important social and communicative sphere. Comparative analysis has shown that terminal values - self-development, achievements, moral satisfaction and own prestige - are the most important in this sphere; they tend to gain foothold as young people grow older. Young men see
In the professional sphere, such values as
Such values as
References
- Bergmann, B. A. B., & Todd, N. R. (2019). Religious and Spiritual Beliefs Uniquely Predict Poverty Attributions. Social Justice Research, 32(4), 459-485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11211-019-00335-7
- Bucher, A., Neubauer, A. B., Voss, A., & Oetzbach, С. (2019). Together is Better: Higher Committed Relationships Increase Life Satisfaction and Reduce Loneliness. Journal of Happiness Studies, 20(8), 2445-2469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-018-0057-1
- Hodges, J. M., & Gore, J. S. (2019). Social Connections and Well-Being: With Whom Do You Identify and Why? Psychological Studies, 64(4), 436-446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-019-00506-1
- Ilyin, V. V. (2005). Aksiologiya [Axiology]. Мoscow: Moscow St. Univ. Publ. [in Rus.].
- Kern, M. L., Waters, L. E., Adler, A., & White, M. (2015). A multidimensional approach to measuring well-being in students: Application of the PERMA framework, The Journal of Positive Psychology, 10(3), 262-271, https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2014.936962
- Lee, M. T. (2019). Promoting Human Flourishing Beyond Foundational Concerns. Humanistic Management Journal, 1-3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41463-019-00065-7
- Liu, P., Tov, W., Kosinski, M., Stillwell, D. J., & Qiu, L. (2015). Do Facebook status updates reflect subjective well-being? Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 18(7), 373–379.
- Matveev, P. E. (2017). Aksiologiya v 2-kh chastyakh. CH.1. Istoriya aksiologii [Axiology in 2 parts. P.1. History of axiology], Vladimir: Vladimir St. Univ. Publ. [in Rus.].
- Neubauer, A. B., & Voss, A. (2018). The structure of need fulfillment: Separating need satisfaction and dissatisfaction on between- and within-person level. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 34, 220–228. https://doi.org/10.1027/1015-5759/a000326. (2000).
- Ritzer, G. (2002). Sovremennyye sotsiologicheskiye teorii [Modern sociological theories]. Saint-Petersburg: Piter. [in Rus.].
- Rokeach, M. (1973). The Nature of Human Values. New York: The Free Press.
- Senin, I. G. (1991). Anketa terminal'nykh tsennostey [Questionnaire of Terminal Values] - Yaroslavl: FGI "Assistance", 1991. [in Rus.].
- Sheldon, K. M., & Gunz, A. (2009). Psychological needs as basic motives, not just experiential requirements. Journal of Personality, 77(5), 1467–1492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.2009.00589
- Stavrova, O., & Haarmann, L. (2019). How to tell a happy person: Accuracy of subjective well-being perception from texts. Motivation and Emotion, 1-11, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-019-09815-4
- Wruk, D., Oberg, A., & Klutt, J. (2019). The Presentation of Self as Good and Right: How Value Propositions and Business Model Features are Linked in the Sharing Economy. Journal of Business Ethics, 159, 997–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04209-5
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
12 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-079-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
80
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-483
Subjects
Information technology, communication studies, artificial intelligence
Cite this article as:
Berezovskaya*, I. P., Kedich, S. I., Shipunova, O. D., & Gashkova, E. M. (2020). Youth Terminal Values In Modern Society's Communicative Field. In O. D. Shipunova, V. N. Volkova, A. Nordmann, & L. Moccozet (Eds.), Communicative Strategies of Information Society, vol 80. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 473-483). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.02.55
