Abstract
The economic nature and features of the changes of the agricultural and industrial production determine the need for legislative and financial strengthening for the small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) strides, it implies intensive state regulation processes in this area. Improving communications in the public administration system will enhance the SMEs activity in the agricultural and industrial production of Russia. The positive dynamics of our country agro-industrial complex’s functioning is revealed, the shift of agro-industrial production from the processes of import substitution to the processes ensuring the intensification of agricultural exports is recorded. The article defines the need for government intervention, the main trends and components of state regulation of SMEs changes at various levels of government are presented. The formation of a multilevel system of state regulation of SMEs adjustment for the agricultural sector should be implemented at all levels (federal, regional and municipal) of government. The presented targeted solutions lead to further strengthen the food security of our country and focus on the growth of agricultural exports. Optimization of agroindustrial production will make it possible to achieve its steady state, create conditions for the implementation of innovative processes, shift the emphasis from import substitution processes to processes that ensure the intensification of agricultural exports.
Keywords: Communicative impactcommunication strategysmall and medium businessstate regulationagricultural and industrial production
Introduction
The relevance of research on issues of state communications in managing the SMEs progress for agricultural sector
The potential for intensifying the sphere of agricultural production is far from exhausted for the Russian economy. Improvement of state communication at all levels of government (federal, regional, municipal) can be specified as the main direction. Each of the levels is characterized by peculiar features of functioning, technologies and methods of interaction among the subjects of the communication process.
Taking into account the results achieved and previous experience, it is important to refine and improve the mechanisms of state support and regulation ( Vilenskii & Lylova, 2016). According to a survey conducted by the “Agrovestnik magazine” news portal among the businessmen and government officials, their assessments of the Russian agro-industrial complex prospects in 2019 are somewhat different (Dmitriev, 2018). Business representatives are cautiously optimistic and consider strengthening the positions achieved as a priority. Representatives of the authorities are primarily focused on state regulation, which involves state support, innovative planning. The positions of both sides do not contradict each other, but rather create the prerequisites for accelerating the improvements of the agricultural and industrial production of the Russian economy.
Problem Statement
The problem of the study is to consider possible ways for improving the communicative strategy in the practice of public administration aimed at activating small business in the development of the agricultural and industrial production of the Russian economy. A communicative strategy, in this case, is a specific strategic plan on the part of state and municipal authorities for such target audience as representatives of SMEs in the promotion of the agricultural and industrial production of the Russian economy. The communicative impact will enhance the processes of formation and sustainable progress of small enterprises in agribusiness.
Research Questions
Purpose of the Study
The objective of this research was to overlook the current trends and possible directions for improving communications in the field of public administration of the small and medium-sized businesses development for the agricultural and industrial production of Russia. The tasks are set: to determine the schemes and the main components of the processes of state regulation of small and medium-sized businesses activities in agricultural production at all levels of government: federal, regional, municipal.
The object of the study is the state regulatory processes of creation and progress of small business enterprises in the agricultural and industrial production for the Russian economy. The study period includes 2013-2018.
Research Methods
The study is based on a combination of general scientific methods, such as analysis and synthesis, deduction and induction, as well as a statistical method that allows identifying emerging patterns. Official data of the RF Government site, significant information data presented in public media and on the Internet are the informational and empirical base of the article.
Findings
In the medium term, progressive dynamics in agricultural and industrial production is forecasted. The main factors stimulating this process are:
Climatic;
Sanctions and countermeasures;
Increased demand for food;
A change in macroeconomic proportions in foreign and domestic markets;
Intensification of agricultural products export;
Single economic space.
An important area of 2019 is the development of an updated industry support program. Considerable attention has been paid to financing export activity, which will be strengthened by government support. The influence of such external factors as geopolitical decisions and macroeconomic indicators minimizes the impact on the dynamics of behavior and the degree of investment attractiveness of the industry.
In 2018 a shift of agricultural production from import substitution processes to processes ensuring the activation of exports was indicated. The food embargo which has been in force since August 2014 was prolonged. Pursuant to the Decree of the Head of our state Putin (2018) “On the National Intentions and Strategic Tasks of the Propulsion of the Russian Federation for the time up to 2024”, the strategic goal was set, that is to double the volume of agricultural exports. The passport of the National Project “International Cooperation and Export” was developed. The Federal Project “Export of agricultural products” is a priority component of it. The main indicators of the project determined the increase of agricultural products export up to $ 45 billion by 2024 ( Passport of the Federal project “Export of agricultural products”, 2018) The State Program “Agricultural Development and Regulation of Markets of Agricultural Goods, Raw Materials and Foodstuffs for 2013-2020” was extended until 2025 (Order of the Administration of the Russian Federation No. 98, 2019). The indicator of agriculture gross value added shows a positive dynamics in the period 2013-2018 (Table
It should be noted that only 89% of the planned values for 2018 were fulfilled. The labor productivity index in relation to the previous period is reduced, which is determined by various factors. For example, in 2018, the reduction of this very indicator by 3 percentage points (p.p.) is primarily due to the instability of the macroeconomic situation, difficult weather conditions, and the prolonged sowing campaign. The value of agricultural products exports is growing at a faster pace. In 2018, the actual implementation of this indicator was 119.3% compared to the planned 106.5%.
Foreign trade in agricultural products and food is characterized by a negative trade balance. We note the positive changes: in the last two years the indicator of foreign trade increased by 9.9% or by $ 4,979.7 million; export growth rates significantly exceed import growth rates, respectively, 119.3% and 102.8% (Table
The share of agricultural products in the export structure of the Russian Federation is insufficient – 5,5%. Grain crops (40.7%), fish and seafood (19.9%), vegetable oils (9.3%) are the key positions in the agricultural commodity exports structure. The growth of cereals and legumes, wheat or wheat-rye flour, pork and pork offal, poultry meat, pastries and confectionery was shown among the exported products in 2018. At the same time, there was a significant decrease in exports of sunflower seeds, white sugar, rice, and tobacco products.
In 2018 the share of imported food products and agricultural raw materials in the import structure of the Russian Federation amounted to 12.4%, i.e. it significantly, more than 2 times, exceeds the share of exports. Import priority is given to fruits and nuts, alcoholic and soft drinks, processed meat, vegetables, dairy products. In the import structure there has been a reduction in the supply of pork meat, sunflower and corn seeds, milk and dairy products, and grapes. At the same time the volumes of live cattle, sugar, palm oil, other supplies are increasing. Based on data to the Ministry of Agriculture, world prices for agricultural raw materials and food in 2019 will exceed the values of 2018, as a result, one can predict an increase in ruble prices. A slowdown in development and relative stagnation are expected in the poultry and sugar industries (Order of the Administration of the Russian Federation No.1352-r, 2019).
The economic nature and peculiar development of agriculture need for state regulation ( Aimurzina et al., 2017). Targeted decisions to ensure further strengthening of the food security of our country by the state authorities can be implemented in the following areas:
Legislative and financial support for small-sized business;
Domestic seed industry and pedigree farming base recovery;
Regulation in the field of aquaculture (fish farming);
Improving the management system of socio-economic development of rural areas;
Formation of the modern production potential of agricultural machinery;
Creation of the material opportunities and facilities of agricultural production based on the introduction of innovative technologies;
Attracting young specialists to the agricultural sector, creating conditions for increasing the level of their professional training.
The implementation of the first relevant area – help for SMEs - involves the activation of state regulation processes in this area.
The need for state intervention in the processes of formation of small business in agriculture is determined by the following objectives ( Koptseva & Kirko, 2016; Mironenko, 2016):
Stability of economic growth;
Sustainable financial performance;
Lower inflationary expectations;
Providing a high level of employment for the able-bodied population;
Equity in income distribution.
The goals are based on the consistent solution of the following tasks: the introduction of the legal framework for the effective functioning of agricultural sector; formation of a competitive environment; stimulation of entrepreneurial activity of small-sized businesses; formation of entrepreneurial infrastructure. The presented goals and tasks can be reached through measures of state regulation for small business in the agricultural sector. The following measures can be referred to these ones:
Support for the types of businesses identified as a priority for the development of the domestic economy;
Developing a rational tariff and pricing policy, an effective tax system;
Redistribution of limited resources;
Protection of consumer rights, creating a competitive environment and restriction of monopolistic activity;
Creation of a legal basis for entrepreneurial activity.
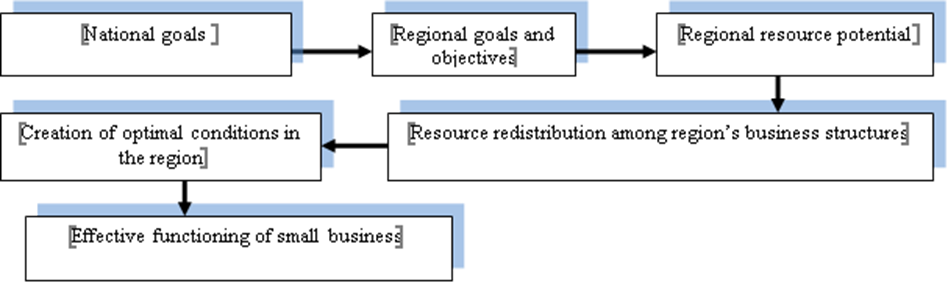
An appropriate organizational mechanism for small-sized business must be created at all levels: national, regional and local. State regulation of small business development for all the members of the Federation specifies requirements, delegates authority, determines competencies, compliance with the legislative framework of the Russian Federation, takes into account regional conditions and features ( Kozhakhmetov & Rakhimgulova, 2017; Regionalization…, 2019). Schematically, Figure
National goals are specified taking into account the characteristics of the region;
Regional goals and objectives aim the promotion of small-sized business;
Creation of the resource potential of the region is focused on solving regional problems;
Redistribution of resources, taking into account the identified priorities and region’s resource potential limits among business entities;
Creation of optimal conditions in the regional environment for the effective functioning of the small business production structures.
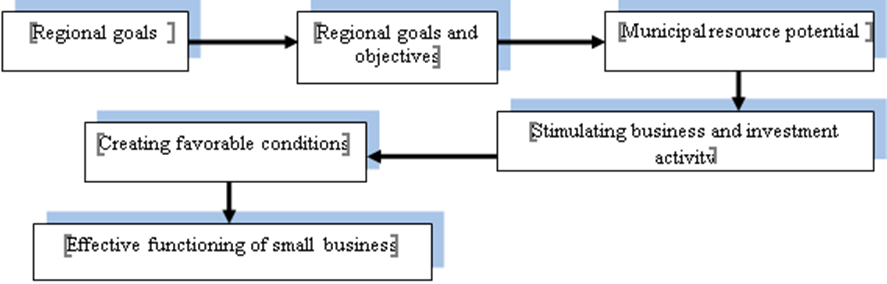
The main stages of managing the small business regulation process at the local government level are determined by the composition and structure of the municipality. The scheme (Figure
Setting municipal economy goals and objectives is focused on the priority of small business development;
The resource potential of the municipality is distributed between small businesses through economic mechanisms: municipal order, priorities and restrictions;
Development of the municipal territorial-production complex on the basis of business and investment activity of small and medium-sized business enterprises;
Creating favorable conditions for the establishment of small and medium-sized businesses entrepreneurial structures.
The formation of a multi-level state regulation system of creating and development of SMEs in the agricultural sector allows us to increase the rate of economic progress of our state.
Conclusion
We believe that the following components are most relevant while forming a state regulated multi-level system for creating and development of small-sized business structures in the agricultural sector
Countering illegal entrepreneurial activity and unfair competition is the most important component of the small business state regulation system in the Russian Federation ( Vilenskii, 2014). A set of conditions stimulating business representatives to “come out of the shadows” should be created, including criminal prosecution of illegal business activities as well as encouraging the best small business taxpayers.
Legal regulation of land relations on the basis of a roadmap approved by the government in November 2018, which includes: a set of measures that determine the rules for the use and protection of farmland; providing a special legal regime for the most valuable lands. Boundaries of these areas are to be defined clearly and traced on the map, besides the quality of supervision over the use and turnover of land should be improved.
A strategic approach to the SMEs changes in the national economy, which involves: creating favorable conditions for maintaining market relations; the availability of investment resources and the identification of opportunities for their rational implementation; formation of a consistent legislative framework; involvement of qualified personnel in entrepreneurial activity, staff training and retraining; development of an effective tax and investment policy. Creating a strategy for a sustainable small business development implies favorable external conditions not only now, but also in the perspective, correspondence with the goals and objectives of the country, regional entities, and large businesses. Measures to support and develop small businesses should include: identifying key priorities and development goals, principles and methods of creating a system of regulatory measures, an assessment of the organization’s external environment, analysis of production potential, and complex target programs (CTP).
A programmatic approach to small business support. Federal programs are specified at the regional level. For example, the Ministry of Economic Development has been consistently introducing a complex target program, according to which subsidies are provided from the federal budget to provide state support to small and medium-sized enterprises at the regional level. Also, in the framework of the state project “Economic Development and Innovation Economy”, introduced in 2014, the subproject “Advancement of Small and Medium Enterprises” is being implemented. It gives priority to measures aimed at changing the activity of a network of organizations that form a service infrastructure model for providing state support. Loans are provided to entrepreneurs operating in priority-recognized industries, including agriculture. Small business can obtain loans at a reduced rate of not more than 8.5% per annum for investment purposes up to about 2 billion. rub. for up to ten years as well as for working capital replenishment up to 500 million rubles for a three-year period ( Order of the Administration of the Russian Federation, 2018; Prudskiy, Demin, Oshchepkov, & Gershanok, 2017; Sharapova & Vlasova, 2018). According to the passport of the national project “Small and Medium-sized Enterprises and Support of Individual Entrepreneurship Initiatives”, the Ministry of Economic Development suggests the formation of a system of support for farmers, the popularization of entrepreneurship, and the development of rural cooperation ( Passport of the National Project…, 2018). The presented national project combined the following five federal projects: improving the business environment, expanding access for SMEs to financial resources, including concessional funding, accelerating SMEs, creating a system of farmers support, development of rural cooperation, and promoting entrepreneurship. Within the framework of the national project, the Ministry of Agriculture believes that the amount of funds aimed at farming support and rural cooperation development will be up to 37.4 billion rubles by 2024, and 7.4 billion rubles in 2019 ( Passport of the Federal Project…, 2018).
Digitalization of the agro-industrial complex. The agricultural sector digitalization involves adapting digital technologies and platform solutions for the Russian agricultural sector. The project "Digital Agriculture" will be implemented in 2019-2024. Surely, this activity will ensure the efficient use of labor potential in farms and other small forms of management ( Amirova et al., 2018).
The quality and safety of agricultural products and food. There is a need to prepare a new edition of the Food Security Doctrine of the RF (2010-2020). The project submitted by the Ministry of Agriculture introduced a new methodology for calculating food safety indicators, indicators have been added that reflect food availability for the population (both economic and physical). In 2019 a legislative amendments concerning updated definition of the concept of “quality of healthy nutrition” is to be introduced, also the responsibility of unscrupulous producers for the production of surrogate products is to be determined. Businesses focused on agricultural products and food production meeting all the specified quality characteristics can count on state support (Gordeev, 2019; Polushkina, Akimova, & Kochetkova, 2016). Importance is given to the development of ecological agricultural production. Support at the regional level for local organic producers is relevant for small businesses.
The significance of the presented components leads to the conclusion that implementation of a multilevel system of state regulation of small businesses promotion in the agricultural sector is vital
In accordance with federal guidelines, legal, political, economic, social, informational, consulting, educational, organizational measures of state authorities and local self-government influence are combined to achieve the main goals and principles of small and medium-sized businesses activity in the agricultural and industrial production sphere of the Russian economy. Successful SMEs development is determined by the degree of state support, creation of proper political, legal, social and economic conditions. The management team of small and medium-sized agroindustrial business structures notes the distribution of state support in favor of large holdings. In accordance with the “May Decrees” of the Head of our state V.V. Putin the proposed amendments to agricultural legislation are made, a market-oriented planning scheme is being introduced, strategic priorities in this sector of the economy have been identified, one of them being the SMEs strides. In the medium term this particular business segment is likely to lead to rational use of agricultural land, complex development of rural areas, and agricultural products and food quality improvement. The progress of small and medium-sized business structure, creating a competitive environment in the agricultural sector, provokes an increase in the volume and change in the structure of export of agricultural products and food for the Russian Federation.
The multi-level system of state regulation and support business of small-sized business in the agricultural and industrial production of the Russian economy requires rational use of resources and opportunities at all levels: federal, regional, municipal, which allows us to increase the socio-economic rate of our state. Practical adaptation of measures ensuring the strides of the small-sized business segment, creates conditions for private entrepreneurial initiative, contributes economic development potential, ensures control and support for the development of small business on the basis of reforming the legislative, regulatory and tax base, it also regulates administrative activity of economic entities with the help of innovative and credit and financial state support.
Despite the active state support (development and implementation of federal programs, creation of a favorable economic climate), small and medium-sized businesses have not fully shown their capabilities in the agricultural sector.
The content of the article proves that it is necessary to intensify the processes of the communicative impact of state authorities on small and medium-sized businesses in agro-industrial production.
References
- Amirova, E. F., Voronkova, O. Yu., Pyurveeva, K. A., Shatalov, M. A., Panteleeva, T. A., & Sorokina, O. A. (2018). Functioning of Agroindustrial Complex in the Conditions of Digital Economy, International, Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 9(13), 586–594. https://doi.org/IJMET_09_13_061
- Aimurzina, B., Gulzhan, A., Dauletova, A., Kamenova, M., Omarova, A., & Beisengaliyev, B. (2017). State Regulation of the Agro-Industrial Complex as the Most Important Component for Sustainable Development, Journal of Environmental Management and Tourism, 5(21), 1086-1091. https://doi.org/10.14505/jemt.v8.5(21).14
- Dmitriev, M. (2018, December 28). Chto ozhidayut agrarii ot 2019 goda [What agrarians expect from 2019]. “Agrovestnik magazine” news portal. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from: agrovesti.net›news... zhdut-agrarii-ot-2019-goda.html
- Gordeev, A. V. (2019 January 29). Changes in laws will help improve the quality of products and increase responsibility for falsification. [in Rus.]. KVEDOMOSTI.RU. Retrieved from http://kvedomosti.ru/nbews/gordeev-uluchshit-kachestvo-produktov-i-otvetstvennost-za-falsifikat-pomogut-izmeneniya-v-zakony.html
- Koptseva, N. P., & Kirko, V. I. (2016). Development of the Russian Economy’s Agricultur Sector under the Conditions of Food Sanctions (2015-2016). Journal of Environmental Management and Tourism, 2(10), 105-113. https://doi.org/10.14505/jemt.v5.2(10).01
- Kozhakhmetov, G., & Rakhimgulova, M. (2017). Provisions for Effective Development of Regional Agricultural Systems in Russia’s Economy, Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 2(24), 485–489 https://doi.org/10.14505/jarle.v8.2(24).26
- Mironenko, N. V. (2016). Gosudarstvennoye regulirovaniye regional'nogo agropromyshlennogo kompleksa. Razvitiye: voprosy otsenki i ratsionalizatsii. [State Regulation of the Regional Agricultural Complex. Development: Assessment and Rationalization Issues]. Journal of Economic and Social Change: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 5(41), 118-132. [in Rus.]. https://doi.org/10.15838/esc/2015.5.41.8
- Order of the Administration of the Russian Federation No. 1764-r, (2018, December 30). “Ob utverzhdenii Pravil predostavleniya subsidiy iz federal'nogo byudzheta rossiyskim kreditnym organizatsiyam na vozmeshcheniye nedopoluchennykh imi dokhodov po kreditam, vydannym v 2019 - 2024 godakh sub"yektam malogo i srednego” [“About approval of procedure for the provision of federal budget subsidies to Russian credit organizations for refunding of their lost income on loans issued to small and medium-sized enterprises at a preferential rate in 2019-2024”]. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from mcx.ru
- Order of the Administration of the Russian Federation No. 98 (2019, February 08). “O vnesenii izmeneniy v postanovleniye Pravitel'stva RF No.717 (2012.Iyul'.14)” [“On Amending the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No.717 (2012, July 14)”]. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from mcx.ru
- Order of the Administration of the Russian Federation No. 1352-r, (2019, June 22). Natsional'nyy doklad o khode i realizatsii v 2018 godu Gosudarstvennoy programmy razvitiya sel'skogo khozyaystva i regulirovaniya rynkov sel'skokhozyaystvennoy produktsii, syr'ya i prodovol'stviya [The National Report on the Progress and Implementation of the State Program for Agriculture Development and Regulation of Markets of Agricultural Goods, Raw Materials and Foodstuffs in 2018]. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from mcx.ru
- Passport of the Federal project was approved by the National Project “International Cooperation and Export” meeting minutes No.5 (2018, December 14). “Eksport produktsii APK” [“Export of agricultural products”] [in Rus.]. Retrieved from mcx.ru
- Passport of the Federal Project (2018, December 11). “Sozdaniye sistemy podderzhki fermerov i razvitiye sel'skoy kooperatsii” [“Creating a system for supporting farmers and developing rural cooperation”]. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from altsmb.ru ›images / docs ... FP Agricultural cooperation.pdf
- Passport of the National Project (2018, December 24). “Maloye i sredneye predprinimatel'stvo i podderzhka individual'noy predprinimatel'skoy initsiativy” [“Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises and Support for Individual Entrepreneurial Initiatives”]. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from government.ru ›info / 35563 /
- Polushkina, T. M., Akimova, Y. A., & Kochetkova, S. A. (2016). State Regulation of Organic Agriculture Development, Journal of Environmental Management and Tourism, 7(3), 429-438. [in Rus.]. Retrieved from: https://journals.aserspublishing.eu/jemt/article/view/352
- Prudskiy, V. G., Demin, G. A., Oshchepkov, & Gershanok, A. A. (2017). Improvement of AssessmentMechanism of Agricultural Enterprises Creditworthiness in Conditions of National Specificity, Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 2(24), 570–585. https://doi.org/10.14505/jarle.v8.2(24).26
- Regionalization will give an additional incentive to the development of agribusiness of the subjects. Kazan, (2019, February 22). Visiting meeting of the leadership of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation with the regional governing bodies of the agro-industrial complex. Retrieved from http://mcx.ru/press-service/news/regionalizatsiya-pridast-dopolnitelnyy-stimel-razvitiya-apk-subektov//
- Sharapova, V. M., & Vlasova, A. S. (2018). Problemy rossiyskikh proizvoditeley sel'khozproduktsii pri poluchenii subsidirovannogo kredita [Problems of Russian agricultural producers in obtaining a subsidized loan]. Russian Journal of Entrepreneurship, 19(7), 2021-2018. [in Rus.]. https://doi.org/10.18334/гр. 19.7.39237
- Vilenskii, A. V. (2014). Features of small and medium-sized enterprises in Russia. Economics: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow, 6-7, 26-45. Retrieved from http://www.publishing-vak.ru/archive/ economy.htm
- Vilenskii, A. V., & Lylova, O. V. (2016). Specificity of the territory of small business and its state support in Russia. Economics: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow, 3, 186-197. Retrieved from http://www. publishing-vak.ru/archive/economy.htm
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
12 March 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-079-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
80
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-483
Subjects
Information technology, communication studies, artificial intelligence
Cite this article as:
Surzhikov, M. A., Saltanova*, T. A., Mikhnenko, T. N., & Chlysheva, E. A. (2020). Organizational Communications In Small Business Management In The Agro-Industrial Sector. In O. D. Shipunova, V. N. Volkova, A. Nordmann, & L. Moccozet (Eds.), Communicative Strategies of Information Society, vol 80. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 291-301). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.03.02.34
