Abstract
As a central part of territory sustainable development concept – people, standards of living and environment conditions can be considered, it is vital to understand the factors that influence customer satisfaction of the living place and those, that compose the customer value of each particular territory. At the same time human resources is one of the core factors of the territory sustainable development and it is important to study the factors creating extra value for the people and having an impact on their choice of living place. Thus, knowledge of the value creation factors of the territory is of high relevance nowadays due to wider range of opportunities open for people and high competition between the territories. Such surveys have even more importance in regard of young people, who are less conservative and more willing to move and find a better place for living. Therefore, the paper is focused on the exploration of customer value of the territory for youth. The report comprises the general goal of determining the most significant factors of the attractiveness of the territory and disclosing the level of customer satisfaction with these factors in relation to the residence of Saint-Petersburg. To achieve this purpose an empirical research has been conducted with sample size 283 respondents. The target audience of the survey is youth living in Saint-Petersburg.
Keywords: Attractiveness factorscustomer value of the territorySaint-Petersburgsustainable development of the territoryyoung people
Introduction
Stable development of the territory is based on three main aspects: economic, social and ecological. Economic factors can be considered as a core instrument of different regions fight to attract investors, entrepreneurs, tourists, labor, etc., which, in turn, are providers of funds to the regional budget and contribute to improving the well-being of the population. Social stability, infrastructure and relevant living level are vital conditions of development and at the same time satisfaction of people. Besides, there is high attention to ecological problems and need and search for better ecological environment from the people. So it is argued that sustainable development factors come both, as a bases for territory improvement and value of the territory for citizens, considering the interdependence of them. These ideas match to the value chain theory.
All the authors, who analyze the value chain (Uldasheva & Mescherikov, 2011; Baccarini, Cassia, Rossato, & Cavalio, 2019), point out human resources to be a very important part of it in addition to infrastructure, technology development and supply chains. The same way, citizens and human potential, together with industrial production, research and development, city infrastructure and trade development and their combination make the city economy. Insufficient quantity of human resources and aging of the population of the city can influence significantly all the other factors and slow down development of city economy. Aging of population, divergence between supply and demand in labor market, existence of weak communications between educational institutions and the enterprises and also with outflow of highly qualified personnel to other cities and the countries are vital problems for city development that come particularly acute in our days for many Russian cities as well as many cities in Europe and other countries.
Different aspect of territory value can be considered and have different power of influence when discussing different age groups of people. And if elder people are more conservative, younger people travel very actively and can easier move to different region for living. (Different sources consider people aging from 14-16 to 29-30 to youth, and sometimes and up to 35, years. Most of sociologists define an age framework from 16 to 29 years for youth.) So it comes that studying the factors of young people territory value is highly important to provide the stable development of the territory.
Problem Statement
In spite Saint-Petersburg gets tourists from Russia and abroad on regular bases, the population dynamic is not very positive: population is getting old and many high professional specialists move to Moscow or abroad searching for better salaries prospects or better conditions. This shows that the question of increasing the customer value is highly important for Saint-Petersburg and many other Russian cities as well. Thus, value creation of territory is a key element of its attractiveness (Baccarini, Cassia, Rossato, & Cavalio, 2019).
According to the fact that numerous scholars periodically examine factors of territory attractiveness (Kim, Kim, & King, 2019; Charushina, 2014; Budnikevych & Gavrysh, 2017), different aspects of territory development (Voronkova, Iakimova, Frolova, Shafranskaya, Kamolov, & Prodanova, 2019; Arutyunova, Smirnova, Isakova, Zelik, & Kozin, 2017; Lazhentsev, 2015; Uldasheva & Mescherikov, 2011; Navarro, Aranguren, & Magro, 2012), region competitiveness (Shtanchaeva, Zjablova, & Denmukhametov, 2015; Claver-Cortés, Marco-Lajara, Seva-Larrosa, & Ruiz-Fernández, 2019) etc., but there is a lack of studies related to the structure of territory value. Besides, at the moment there is no systematized approach to assessment of satisfaction and value of the territory for youth.
Research Questions
The current research sets as the ultimate goal obtaining answers to the following questions:
What factors determine territory value for youth audience?
As far as the youth is satisfied with these factors within their activity in St. Petersburg?
What corresponding factors are of the greatest value for youth of St. Petersburg?
The main hypotheses are:
The level of overall satisfaction with the territory for young people depends on the level of satisfaction of this target audience with specific factors related to living in the territory
Important factors when choosing a territory for young people are the level of educational services provided and the availability of career opportunities.
Purpose of the Study
Purpose of the study is to determine the factors that have the greatest value for the youth audience when choosing a city for permanent residence and to determine the level of satisfaction of these factors with the residents of St. Petersburg.
Research Methods
On the basis of the studied theoretical background on customer value and territory development and various ratings of territories attractiveness analyzed, a survey questionnaire was compiled for young people living in St. Petersburg. The main hypotheses were determined, and subsequently, a corresponding survey was conducted. Next, the data was processed in Microsoft Excel and IBM SPSS Statistics, as a result of which the proposed hypotheses were tested. Based on the data obtained, the authors proposed a structure of the consumer value of the territory for young people living in St. Petersburg.
For the study a questionnaire was compiled of 16 questions, which was distributed online on the Internet. More than 300 people answered the questionnaire. However, in order for the sample to be representative, as a result of processing the obtained data, the sample size was reduced to 283 people due to the discrepancy between retired age criteria (age from 15 to 29 years). The second reason for the reduction of the sample was the lack of direct affiliation of respondents to the city of St. Petersburg, since they do not live on its territory at the moment or did not live in it for the last 5 years, and, accordingly, can assess various current nuances biasedly.
Of course, given the fact that the general population of the studied audience is about 1 million people, we can note the insufficiently large sample size as a drawback of the research being conducted. On the other hand, all members of the sample meet all the necessary age criteria, live on the territory of St. Petersburg for quite a long time, face in varying degrees with the solution of the same tasks and function, for the most part, in the same environment. All of the above arguments allow the respondents to be regarded as experts, from which it can be concluded that the sample is representative.
As for the demographic component of the respondents, most of them were female. 68% of the sample were women, and 32% were men. The average age of respondents was 23 years.
It is necessary to indicate that in questions on assessing the level of satisfaction, as well as in the question of ranking factors by degree of importance, 15 factors were used that were identified as the most significant in assessing the area by young people. Relevant factors were chosen based on the literature review on consumer value of the territory. The factors used in the compilation of the territory ratings were also taken into account.
Pilot studies were conducted to generate a pool of questions and determine the optimal response scale. Initially, the questionnaire was sent to 20 respondents, some of whom originally lived in St. Petersburg, but in the last couple of years they went abroad to get a master’s degree or to undergo an internship in an international company; another part arrived in St. Petersburg for various reasons for permanent residence from other cities of Russia; for the rest of the respondents, St. Petersburg was a hometown, and they lived there on the date of the research. Then, detailed feedback was received from the respondents, on the basis of which some question and answer details were adjusted.
As a result of a careful analysis of scientific works to determine the structure of the consumer value of a territory, as well as studying key ratings of the attractiveness of territories, 15 factors were formulated that may affect the attractiveness of the territory of such a consumer group as the local population, or rather, the youth (see Table
For these 15 criteria a correlation analysis was performed. The analysis showed that the majority of the criteria are completely or practically absent, since the correlation coefficients are low (<0.3). This suggests that each of the criteria for the attractiveness of the territory has the right to exist.
Next was a factor analysis. The main purpose of factor analysis was to reduce the number of variables, determine the relationships between them, and create new variables (factors). Before extracting factors, it was necessary to conduct several tests to assess the suitability of the data for factor analysis. To assess the reliability of the calculations, the variables were tested using the Kaiser-Meier-Olkin sample adequacy measure (KMO).
KMO measure value = 0.744, which indicates the suitability of variables for analysis, since G. Kaiser notes that the minimum suitable value should be at least 0.5, values of 0.7-0.8 are acceptable, and values higher than 0.9 – great.
There are several ways to extract factors and conduct factor analysis. However, in order to determine the factors with the maximum degree of importance and, as a consequence, the factor structure, it is usually customary to use the principal component method. It is the only mathematically sound method of factor analysis, the main task of which is to form from a large group of variables only a few factors independent of each other, within which the criteria have a stronger relationship with each other than with criteria from other factor groups. To determine the number of factors, the Kaiser criterion was used, according to which the number of factors corresponds to the number of components whose eigenvalues are greater than 1. As a result, the cumulative percentage of variance is 61.88% and highlights a total of 5 factors whose eigenvalues are greater than one. The resulting factors were rotated to maximize the relationship between variables and certain factors. The rotation of the varimax allows maximizing the variance. This method also allows you to simplify the description of the columns of the factor matrix (see Table
It should be noted that a limitation was established - the table shows the values of only those variables whose weight is greater than 0.6. After rejecting the factors with minor loads, 5 end factors were extracted. The rotation converged in 16 iterations.
The factors were named by the authors as follows: 1 – Health and activity, 2 – Living conditions, 3 – Culture and entertainment, 4 – Climate and location, 5 – Professional development. The names of these factors are directly related to the variables included in each factor. Interpretation of factors is a subjective and theoretical process. However, as Hanson and Roberts note, the designation of factors ultimately depends on the definition of the researcher.
Findings
According to the survey results, the overall level of satisfaction with living in St. Petersburg is 4.06 points out of 5. In other words, in general, young people are satisfied with their lives in the city of St. Petersburg. However, very often just satisfaction, unlike full satisfaction, does not guarantee absolute loyalty.
Two consumer groups were compared in regards to satisfaction level: 1 – originally from St. Petersburg, 2 – moved to St. Petersburg (see Figure
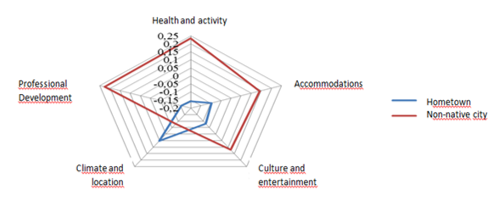
It can be concluded that for young people who moved to St. Petersburg, the level of satisfaction is much higher than for residents who were born and raised in this city. Most of those who moved to St. Petersburg came from various cities of Russia. All these cities are inferior in size to St. Petersburg, and, with a high probability, have a less developed infrastructure. Moreover, some people noted that moving to St. Petersburg was their childhood dream. These reasons may explain the higher level of satisfaction for the relevant group of people.
Another interesting finding is the difference in satisfaction levels for different age groups of young people. The youth audience was divided into 2 groups according to age: 1 group – from 15 to 23 years, 2 group – from 24 to 29 years. The corresponding results are presented in Figure
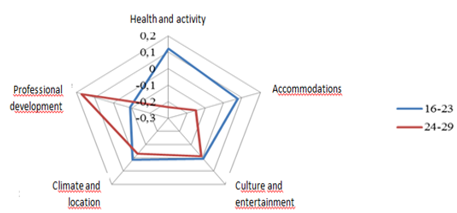
While satisfaction with the factors of climate and location and culture and entertainment is about the same level, other results show significant differences between the two groups. In general, group 1 is more satisfied with all factors except professional development, since most of it’s members have not yet begun their career path. Moreover, with age the cost and conditions of accommodation become more and more important, and people also begin to care more for their health that forces them to think of quality of the provided services and development of infrastructure more deeply.
For testing of the first hypothesis the regression analysis in the IBM SPSS Statistics program was carried out. Before the analysis, it was ensured that all the main assumptions of the regression analysis were satisfied: a normal distribution of data and no correlation between the independent variables. As a dependent variable, total satisfaction was chosen with accommodation in St. Petersburg. As independent variables, 5 factors generated by factor analysis were identified. The results are presented in Table
R-square shows the degree of accuracy of the description of the model of the main process. The value of this indicator lies in the range from 0 to 1. The closer its value is to 1, the more accurately the model describes the main process. In this study, R-squared = 0.251. Based on this value, we can conclude that this model explains only 25% of the variation of the dependent variable. Thus, the first hypothesis is refuted. However, the model in question is significant because the significance level (0.000n) is significantly less than the maximum allowable value of 0.05.
The reason for such results may be a relatively small sample size relative to the general population. However, if we consider the results of answering a question related to determining the level of youth satisfaction with various factors related to living in St. Petersburg, we can conclude that the level of satisfaction with many specific factors is below the overall level of satisfaction.
According to the survey, for the youth audience of St. Petersburg, the most important factors when choosing a territory for a place of residence are: vacancies and career opportunities, cost of living, housing and communal conditions, accessibility and quality of the education system, security level, developed health care system, cultural and entertainment infrastructure of the city. Thus, we can assume that the second hypothesis is proved.
Based on the results of the study, it is possible to make up the structure of the consumer value of the territory for young people living in St. Petersburg. This structure can be depicted as following from high to low priority:
1st level: Job vacancies and career opportunities, housing and communal conditions, cost of living, accessibility and quality of education;
2nd level: security level, health care, economic situation, cultural and entertainment infrastructure;
3rd level: natural and climatic conditions, geographical position, transport infrastructure development;
4th level: availability of monuments of architecture and cultural heritage, conditions for sports activity, ecological situation, political stability.
Of course, all factors play an important role in determining the attractiveness of the territory by young people. However, in this figure they are divided into several groups in order of importance to the target audience. The underlying factors of attractiveness of a territory are represented in the inner smallest circle of the diagram, which is the core of the value creation of a territory. The outer circumference of the diagram includes the factors that are of minimal value to young people when choosing a territory for permanent residence. The factors are grouped in accordance with the number of points as a result of their ranking by the respondents.
Conclusion
As a result of the study, the structure of consumer value of the territory for young people living in St. Petersburg was determined. The core of the structure were 4 fundamental factors, such as the availability of vacancies and career growth and development opportunities, the cost of living, housing and utilities, accessibility and quality of the educational system. It is these factors that, first of all, should be paid attention to in order to form the value of the territory and increase its attractiveness for the chosen target group.
It can be concluded that the modern youth of the city of St. Petersburg, above all, is driven by the desire for constant personal and professional development and self-realization, as well as the creation of favorable conditions for living. Such factors as geographical location, climatic conditions, rich cultural heritage, favorable conditions for sports activity and even the ecological situation in general are valuable for the target audience, but not fundamental in the choice of territory.
References
- Arutyunova, A. E., Smirnova, E. V., Isakova, Y. I., Zelik, V. A., & Kozin, M. N. (2017). Social and economic space of the territory: Development conditions, structure, evaluation criteria. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 15(23), 413-424.
- Baccarini, C., Cassia, F., Rossato, C., & Cavalio, D. (2019). Territory, firms and value co-creation synergies. Journal of Place Management and Development, 12(2), 197-208.
- Budnikevych, I., & Gavrysh, I. (2017). Modern marketing concepts as the basis for formation and increase of the attractiveness of cities and territories. Baltic Journal of Economic Studies, 1, 12-18.
- Charushina, E. I. (2014). Otsenka privlekatelnosti territorii. [Assessment of the attractiveness of the territory]. Vestnik NSUEI, 3(34), 99-109. [in Russ.].
- Claver-Cortés, E., Marco-Lajara, B., Seva-Larrosa, P., & Ruiz-Fernández, L. (2019). Competitive advantage and industrial district: A review of the empirical evidence about the district effect". Competitiveness Review: An International Business Journal, 29(3), 211-235. Retrieved from https://proxy.library.spbu.ru:2151/
- Kim, Seon, Kim, Sang, & King, B. (2019). Nostalgia film tourism and its potential for destination development. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 36(2), 236-252.
- Lazhentsev, V. N. (2015). Theoretical results of research on spatial and territorial development (on examples of the north of European Russia). Economy of Region, 4, 21-29.
- Navarro, M., Aranguren, M. J., & Magro, E. (2012). Smart specialization strategies: a territorial strategy for regions. Cuadernos de Gestión, 12, Especial Innovación, 27-49.
- Shtanchaeva, M. R., Zjablova, O. V., & Denmukhametov, R. R. (2015). The competitiveness potential of the regions of the European part of Russia as an important factor of the social-economic development of a state. International Business Management, 9(6), 1363-1366.
- Uldasheva, O. U., & Mescherikov, T. V. (2011). Institutsionalnaya kontseptsia upravlenia territorialnim marketingom. [Institutional concept of territorial marketing management]. Vestnik BFU im. I. Kanta, 3, 10-17. [in Russ.].
- Voronkova, O. Y., Iakimova, L. A., Frolova, I. I., Shafranskaya, C. I., Kamolov, S. G., & Prodanova, N. A. (2019). Sustainable development of territories based on the integrated use of industry, resource and environmental potential. International Journal of Economics and Business Administration, 7(2), 151-163.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-076-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
77
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1056
Subjects
Industry, industrial studies, project management, sustainability, business, innovation
Cite this article as:
Lizovskaya*, V. V., & Salikhova, Y. Y. (2019). Customer Value Of Saint-Petersburg For Young People. In I. O. Petrovna (Ed.), Project Management in the Regions of Russia, vol 77. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 423-430). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.05.51
