Abstract
The article reflects the results of the studies of forming an effective institutional mechanism for restoring business activity of regional socio-economic systems. The main parameters of the institutional mechanism for business recovery are defined: the purpose of implementation, the application area, the functional content and the costs of the functioning. It has been revealed that the institutional mechanism of interaction between the state and economic entities should be differentiated by the level of socio-economic development of the regional socio-economic systems. The functional filling of the institutional mechanism should be based primarily on a comprehensive analysis of the business activity of the regions taking into account all its components: production, investment and innovation activity. This approach will reveal specific problems in the regional development, which should be addressed by the regional authorities in the first place. In order to better identify the problems hindering the recovery of the business activity in the regions, it is necessary to determine the nature of their manifestation: the insufficient level of development capacity in the region or the low efficiency of its use. In order to improve the efficiency of the institutional mechanism functioning, it is proposed to use a certain set of assessment indicators of the region economic potential and efficiency use as targets for the state regional business recovery programs. It is noted that the main condition for the effectiveness of the institutional mechanism is the study of the transmission mechanism to stimulate business activity of the economic agents of the regional systems.
Keywords: Business activityinstitutionalisminstitutional mechanismregional economy
Introduction
T. Veblen is considered to be the founder of institutional theory in the scientific community. His writings were published at the beginning of the 20th century, but the heyday of the institutionalism as an economic theory falls to the second half of the twentieth century and is associated with the research of J. Buchanan, R. Cowes and D. North, as well as their followers L. Hurwitz and O. Williamson. D. North formulated, a definition of institutions as the “rules of the game” in society, it became classic in our time (North, 1990). The existence of economic institutions is conditioned by the need to develop and then comply with the rules that would lead to the desired result of the activities of the subjects of socio-economic systems. According to the research of Japanese economics professor Shinji Teraji (2017), in the theory of institutions two main approaches can be distinguished: institutions as rules and institutions as balance. In accordance with the first approach, institutions are seen as the rules that are followed by the subjects of agents involved in socio-economic interaction. From the point of view of the second approach, institutions are considered as behavior patterns (Teraji, 2017).
Nobel laureate Hurwicz (1994) identifies the concept of institution and economic mechanism. The economic mechanism, according to the scientist, specifies a lot of choices of economic actors and results related to each of these elections. The mechanism itself is determined as the interaction between economic agents and the regulatory center that consists of three stages: each subject sends a message to the center, the center receives the message, calculates the expected result and develops management decisions on the basis of the received information.
According to many scientists, the market as a mechanism of economic interaction is not always able to reconcile information and incentives for the optimal result (Furton & Martin, 2019). Accordingly, there are problems of institutional inconsistency where the rules governing interaction are not appropriate for the problems faced by economic agents. Therefore, the formation of an institutional mechanism for the restoration of business activity of regional socio-economic systems should be based on an analysis of common factors for the national economy and specific factors for a particular region, defining its development.
The representatives of institutionalism highlight various ways of “tuning” of the economic mechanism, including a conscious influence on the part of the state, which can have a regulatory impact on the market. According to the opinion of a number of foreign scientists, the state's presence in the economic life of society is felt the more strongly, the lower the quality of its institutions is. At the same time, the high quality of established institutions has a positive impact on the level of socio-economic development of the territories and contributes to the reduction of state interference in the economy (Afonso & Jalles, 2016). National scientists also note that the quality of institutions affects the level of economic activity in the Russian regions, that is, the subjects of the Russian Federation with a higher level of institutional capacity produce a higher amount of GRP per person (Kaneva & Untura, 2017). At the same time, Shvetsov (2017) in his work on the effectiveness of state incentives for the development of the territories proves that the orientation of public policy in the field of spatial development only on the creation of preferential business regimes (special economic zones, territorial development zones and territories of advanced development) is not only ineffective, but also counterproductive. According to Bufetova (2017), the state policy of stimulating business activity of developed regions will only increase the polarization of spatial development. We agree with the scientist's conclusions that in today's environment it is necessary to focus on overcoming interregional imbalances and inequalities (Bufetova, 2017). The analysis of the experience of the development, adoption and implementation of the strategies of socio-economic development of the Federation subjects and the evaluation of their effectiveness was carried out in the studies of Budaeva and Klimanov (2016). However, the most interesting is the article by Alekseev (2015), where the organizational features of Russian regional development programs are examined. The author notes that in most cases it is difficult to assess the success of regional development strategies realization, as the conclusion is based only on whether the target indicators have been achieved or not.
Smirnyagin (2017) proposes to adapt regional policy to the diversity of Russian regions. It is intended to classify the subjects of the federation, based on the processing of statistics on their development indicators, grouped into four blocks: resources, population, economy and finance. The author makes recommendations on a specific type of regional policy on the basis of the above classification (Smirnyagin, 2017). We propose a different approach to the regional economic policy formation. In our opinion, the effectiveness of the economic development programs primarily depends on the competent identification of the existing social and economic problems in a particular region.
Problem Statement
Current economic development programs for individual Federation actors are largely similar and do not reflect the specific characteristics of the regions. Accordingly, the economic policy implemented in most regions of Russia is ineffective, declarative and does not contribute to the improvement of the level of socio-economic development of the territories. The formation of an institutional mechanism for business recovery based on a comprehensive study of the regional development potentials and their actual Implementation should facilitate the overcoming of the imbalances in the regional development.
Research Questions
The study involves finding answers to the following questions:
Determining the basic parameters of the institutional mechanism for restoring business activity in the regions.
Finding ways to improve the effectiveness of the institutional mechanism for restoring business activity in the regional socio-economic systems.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the study is to identify approaches to forming an effective institutional mechanism for the restoration of business activity in regional socio-economic systems.
The objectives of the study are to identify the parameters that characterize the institutional mechanism for the restoration of business activity in the Russian Federation subjects as well as to find ways to improve the effectiveness of this mechanism on the basis of systemic business activity research. The proposed analysis scheme should help to identify areas of economic life in the region where regional authorities need to concentrate on restoring business activity.
Research Methods
The methodology of this study is based on the fundamentals of the regional and spatial economy and the applied aspects of system analysis theory. The work implemented a systematic approach based on the methodology of theoretical generalization and analysis.
We conducted an assessment of the level of business activity of the regions in the Central Federal District of Russia, with the exception of Moscow and the Moscow region, as on these territories most of the macro-region economic potential is concentrated, that causes significant distortions in the assessment of other regions is concentrated. The study of the business activity level of regional socio-economic systems used the two groups of indicators outlined above.
The results of the comprehensive analysis are presented on the diagram of Figure
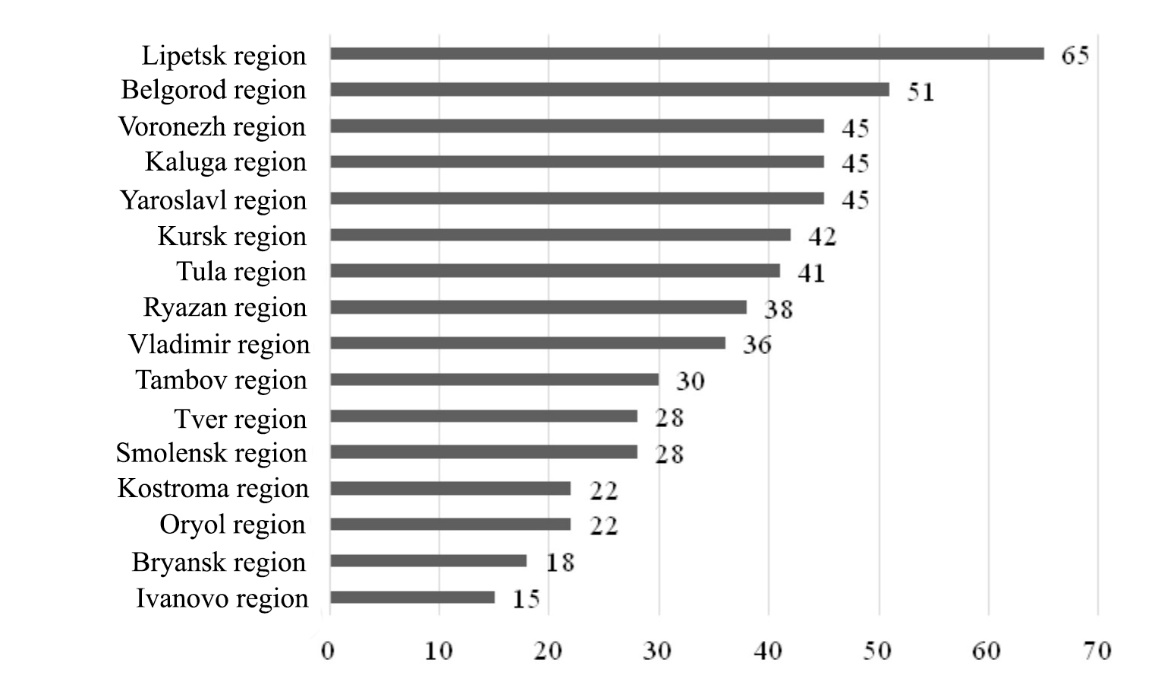
The data of the calculations show a significant differentiation in the level of business activity of the CFD regions from 15 points in the Ivanovo region to 65 in the Lipetsk region. In order to identify the causes of this disproportion in the development of the regions of the Central Federal District of Russia we have compiled ratings based on the components included in the assessment of the level of business activity: manufacturing, investment and innovation. The results are presented in Figure
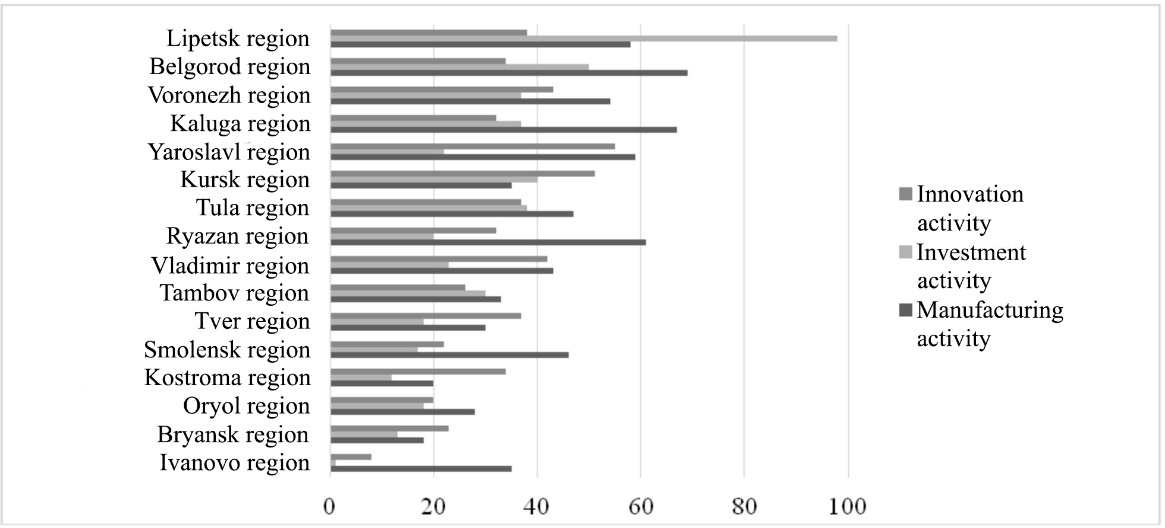
The figures show that in most regions of the CFD there is low investment activity, except in the Lipetsk region, which according to statistical reports is among the leaders in attracting foreign investment not only within the borders of its macro-region but also in the country as a whole. The explanation for this situation is the following: the main shareholder of the largest in the region of the Novolipetsky steelworks is “Fletcher Group Holdings Ltd.”, is registered in Cyprus. Low investment activity in 2017 was recorded in Ivanovo, Kostroma, Bryansk, Oryol and Smolensk regions. Consequently, in these subjects, the policy is not conducive to increasing investment in the region economy.
Component analysis of the level of business activity reveals those areas of economic life in the region that need the support of state institutions of power.
In order to better identify the problems hindering the recovery of the business activity in the regions, it is necessary to determine the nature of their manifestation: the insufficient level of development capacity in the region or the low efficiency of its use. We conducted an analysis of business activity in this aspect and the results are presented in the Figure
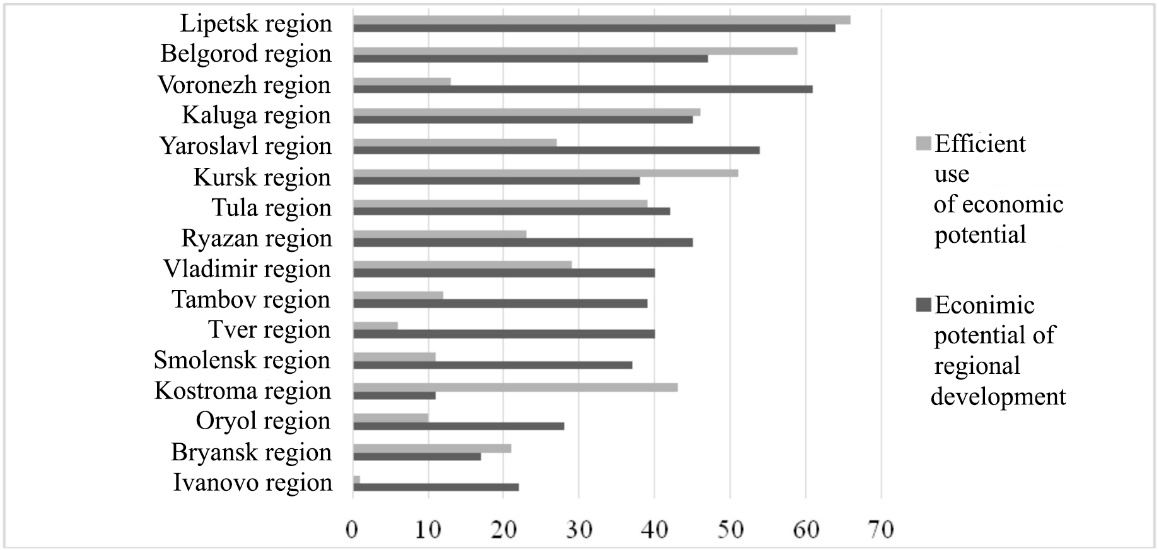
According to statistical reports low performance indicators according to statistical reports were recorded in Ivanovo, Tver, Oryol, Smolensk regions as well as Voronezh region. Moreover, if the first four regions have relatively low economic potential, the potential of the Voronezh region is comparable to the leader of the rating – Lipetsk region.
Findings
The basics of forming an institutional mechanism for restoring business activity in the regions
Taking into account the purpose of our research under the institutional mechanism, we will understand the reaction of economic agents of regional systems to the incentives generated by the state government as a specific institution of economic interaction. The institutional mechanism is characterized by the following parameters: the purpose of existence, the scope of the application, the functional content and the costs of functioning. Let us consider the main parameters of the institutional mechanism for restoring business activity of regional socio-economic systems.
The existing significant differentiation in the socio-economic situation of the regions does not allow the Russian economy to reach the trajectory of sustainable economic growth, even under favorable external and internal development conditions. In our opinion, the main condition for increasing the level of economic and social well-being in the regions is the restoration of business activity of economic actors. Consequently, the purpose of the regional institutional mechanism should be to create the conditions for increasing business activity. The institutional mechanism of interaction between the state as a specific subject of economic relations and economic entities in the regional economy should be differentiated according to the level of socio-economic development of regional socio-economic systems. Accordingly, the scope of the application of the analyzed institutional mechanism should be a specific territory with its specific natural-climatic, demographic and cultural-historical characteristics. Functional filling of the institutional mechanism for restoring the business activity of the regions should be based primarily on a comprehensive analysis of this characteristic, taking into account all components: production, investment and innovation and the region's competitive advantage as growth points, as well as the problematic areas on maintaining and developing of which regional authorities should focus on. The costs of an institutional mechanism directed to the alignment of the development level of the regions must be justified. Russian practice shows that many development programs implemented at the regional level are considered ineffective and the indicators identified in them are not attainable due to an insufficiently reasonable transmission mechanism that stimulates economic growth.
The nature of the institutional mechanism is the implementation and compliance with the rules and regulations of any kind of activity. Regional economic policies are implemented in the form of government policies, programs and development programs. The institutional changes that have been made must be understood and accepted by economic agents. Only then the incentives, that will move the regional socio-economic system in a given direction, will appear if the institutional mechanism is to work effectively, the proposed rules and regulations must be sustainable. The unsustainable institution does not inspire confidence on the part of business entities and ceases to perform its functions. However, there are more often situations where existing institutions are sufficiently stable but ineffective.
In our opinion, the main condition for the effectiveness of the institutional mechanism is the study of the transmission mechanism to stimulate business activity of economic agents of regional systems.
The basics of forming an institutional mechanism for restoring business activity in the regions
Taking into account the purpose of our research under the institutional mechanism, we will understand the reaction of economic agents of regional systems to the incentives generated by the state government as a specific institution of economic interaction. The institutional mechanism is characterized by the following parameters: the purpose of existence, the scope of the application, the functional content and the costs of functioning. Let us consider the main parameters of the institutional mechanism for restoring business activity of regional socio-economic systems.
The existing significant differentiation in the socio-economic situation of the regions does not allow the Russian economy to reach the trajectory of sustainable economic growth, even under favorable external and internal development conditions. In our opinion, the main condition for increasing the level of economic and social well-being in the regions is the restoration of business activity of economic actors. Consequently, the purpose of the regional institutional mechanism should be to create the conditions for increasing business activity. The institutional mechanism of interaction between the state as a specific subject of economic relations and economic entities in the regional economy should be differentiated according to the level of socio-economic development of regional socio-economic systems. Accordingly, the scope of the application of the analyzed institutional mechanism should be a specific territory with its specific natural-climatic, demographic and cultural-historical characteristics. Functional filling of the institutional mechanism for restoring the business activity of the regions should be based primarily on a comprehensive analysis of this characteristic, taking into account all components: production, investment and innovation and the region's competitive advantage as growth points, as well as the problematic areas on maintaining and developing of which regional authorities should focus on. The costs of an institutional mechanism directed to the alignment of the development level of the regions must be justified. Russian practice shows that many development programs implemented at the regional level are considered ineffective and the indicators identified in them are not attainable due to an insufficiently reasonable transmission mechanism that stimulates economic growth.
The nature of the institutional mechanism is the implementation and compliance with the rules and regulations of any kind of activity. Regional economic policies are implemented in the form of government policies, programs and development programs. The institutional changes that have been made must be understood and accepted by economic agents. Only then the incentives, that will move the regional socio-economic system in a given direction, will appear If the institutional mechanism is to work effectively, the proposed rules and regulations must be sustainable. The unsustainable institution does not inspire confidence on the part of business entities and ceases to perform its functions. However, there are more often situations where existing institutions are sufficiently stable but ineffective.
In our opinion, the main condition for the effectiveness of the institutional mechanism is the study of the transmission mechanism to stimulate business activity of economic agents of regional systems.
Conclusion
As a result of our research, we have defined the concept of the institutional mechanism in the context of the restoration of business activity of regional socio-economic systems, the parameters of its functioning are outlined. The need to form an institutional mechanism for business recovery based on a comprehensive study of the potentials of economic development in the regions and their actual implementation is justified
Acknowledgments
The article was prepared with the financial support of the Russian Fund for Fundamental Research (Scientific Project 18-010-01011 A).
References
- Afonso, A., & Jalles, J. T. (2016). Economic performance, government size, and institutional quality. Empirica, 43(1), 83-109.
- Alekseev, A. V. (2015). State programs as regional development tools. Regional Research of Russia, 5(4), 362-366.
- Budaeva, K. V., & Klimanov, V. V. (2016). Content and retrospective analysis of regional strategizing in Russia. Regional Research of Russia, 6(2), 175-183.
- Bufetova, A. N. (2017) Trends in the concentration of economic activity and disparities in Russia’s spatial development. Regional Research of Russia, 7(2), 120-126.
- Furton, G., & Martin, A. (2019). Beyond market failure and government failure. Public Choice, 178(1-2), 197-216.
- Hurwicz, L. (1994). Economic design, adjustment processes, mechanisms, and institutions Econ. Des. 1(1), 1-14.
- Kaneva, M., & Untura, G. (2017). Innovation indicators and regional growth in Russia. Econ Change Restruct, 50(2), 133-159.
- North, D. (1990). Institutions, Institutional Change and Economic Performance. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Shvetsov, A. N. (2017). Growth points or black holes: How efficient are state stimulation tools for territorial development? Regional Research of Russia, 7(2), 108-119.
- Smirnyagin, L. V. (2017) Regional policy of Russia as a geographic task. Regional Research of Russia, 7(2), 97-107.
- Teraji, S. (2017). Understanding coevolution of mind and society: institutions-as-rules and institutions-as-equilibria. Mind & Society, 16(1-2), 95-112.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-076-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
77
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1056
Subjects
Industry, industrial studies, project management, sustainability, business, innovation
Cite this article as:
Ilyukhina, I. B., & Ilminskaya*, S. A. (2019). Institutional Mechanism For The Restoring Of The Reginal Business Activity. In I. O. Petrovna (Ed.), Project Management in the Regions of Russia, vol 77. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 308-315). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.05.37
