Abstract
The determining factor in the development of the agro-industrial complex (AIC) in Russia is the attraction of a sufficient amount of investment; however, despite considerable attention to this issue, the agricultural sector remains unattractive to investors. To determine the feasibility of investing in the agricultural sector of a particular region, it is necessary to take into account many conditions and factors ensuring the comfort of doing business, determining the financial condition, level of development of production, technical base, institutional environment, innovative activity, possible risks and potential investment efficiency, growth prospects etc. However, the existing scientific, methodological and practical measures to increase the investment attractiveness of regional agribusiness, taking into account its features and the specifics of socio-economic development, remain poorly understood and require a comprehensive and integrated review in order to develop additional tools. An objective assessment of the impact of the totality of determining factors will allow us to adjust the direction of investment in the agricultural sector of the region and ensure long-term sustainability of its development. To assess the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region, it was proposed to use a combination of the method of point and expert estimates, coefficients and development in dynamics. The indicators characterizing the level of investment attractiveness of the regional agribusiness are combined into ten groups reflecting the state of investment activity, economic and geographical factors, staffing, level of innovative development, infrastructure, production, financial, institutional conditions, consumer and social constrain.
Keywords: Agricultureinvestmentsmethodology for assessing investment attractiveness
Introduction
Effective functioning and development of any sector of the economy, including agriculture, is impossible without investment. However, with the growth of investment in fixed assets in the sector, agriculture, forestry, hunting, fishing and fish farming in the whole economy of the Russian Federation from 524.3 billion rubles in 2014 up to 777 billion rubles in 2018, the share of investments in the structure of investments by type of activity remains low (4.2%). Despite the obvious need to diversify the national economy, the desire to reduce its raw material orientation, solving the problems of import substitution and ensuring food security in Russia, as well as the social importance of the agricultural sectors, it remains unattractive for investors in comparison with activities such as mining minerals, attracting 24% of all investments in fixed assets, or activity on operations with real estate, which accounts for 7.1% of investments. This problem is widely discussed both in the world and domestic scientific community, and in the framework of government meetings.
Problem Statement
The task of increasing the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex cannot be solved without an accessible and transparent methodology for investors to assess the investment attractiveness and investment potential of the agro-industrial complex using a balanced scorecard.
Research Questions
Assessing of the investment potential of the agricultural sector in the region should help the investor comprehensively consider the features of doing business, compare possible risks and potential investment efficiency, growth prospects. An analysis of studies on the problem of assessing the level of investment attractiveness of regional agribusiness shows a high degree of scientific interest in this issue, since the set of conditions that encourage investors to invest resources is very diverse (Tereshkina, Mottaeva, & Andreeva, 2017; Zheltenkov, Syuzeva, & Vasilyeva, 2017; Fuluc, & Akulenko, 2018; Tahumova, Semenova, & Fursov, 2018).
Considering the features of investing in the agro-industrial complex, it is impossible to bypass the large domestic scientists who have been engaged in this issue for a long time. In the works of Nechaev N. G., Ternovih K. S., etc. the theoretical and methodological aspects of the functioning of the agro-industrial complex are widely covered, the features of the agro-industrial complex of the Central Black Earth regions of Russia that determine their condition are revealed, promising directions, as well as methods and mechanisms for their development, are developed and proposed (Ternovich et al., 2013). As noted by Golovetsky and Terekhova (2015)"... the issue of attracting investment in agriculture remains one of the key in the development of the economy. Investments in agriculture have their own characteristics. They are manifested in the fact that, along with the investment of capital in objects, the results of human labor, as in other sectors of the economy they are also carried out in nature objects in agriculture. In all other things being equal, it makes their activities more capital-intensive with a long payback period and high risks, because nature lives according to its own laws, which today are either impossible or expensive to manage" (Golovetsky & Terekhova, 2015). The research of Tahumova, Semenova and Fursova (2018) is of great interest to consider investment promotion as a combination of organizational, financial, economic, regulatory and some other elements of an interconnected system (Tahumova, 2018). Safiullin and Gubaidullina (2018) argue the dependence of investment attractiveness on the dynamic interaction of subjective and objective factors, which represent a system of indicators of the socio-economic situation of the region, which is the basis for the development of a methodology for its assessment. At the same time, some researchers, despite the active position of state and regional authorities in shaping the investment attractiveness of the region, note the shortcomings of the institutional environment. Therefore, Nikitskaya and Valishvili (2016) note that more than half of the Russian regions offer tax incentives to investors, state guarantees for attracting loans and investment tax credit as incentive measures, while about half of the regions offer the possibility of subsidizing interest rates on loans. However, according to the results of the studies, it was found that from the list of the most common measures of state incentives, only tax preferences cause active interest, otherwise investors focus on conditions and factors that are not considered in investment legislation (Nikitskaya, & Valishvili, 2016). A number of researchers focused on the need to create conditions for new production, the formation of infrastructure factors, the socio-economic development of territories (Kursky, Zubkov, & Shapovalova, 2018).
In this regard, despite a fairly wide range of existing studies in the field of investment in the agricultural sector, many aspects of scientific, methodological and practical measures to increase the investment attractiveness of the regional agricultural sector, taking into account its features and the specifics of socio-economic development, capable of becoming a catalyst for the investment process remain poorly understood and require a comprehensive and integrated review in order to develop additional tools. An objective assessment of the impact of the whole complex of determining factors will allow us to adjust the direction of investment in the agricultural sector of the region and ensure long-term sustainability of its development.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the study is to develop and test a methodology for assessing the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex in the region (using a balanced scorecard), as well as to offer, on the basis of a comprehensive analytical study of existing scientific and methodological developments in the field of investment analysis, as well as the current state of investment processes in the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region, practical recommendations designed to help optimize the structure and parameters of the investment portfolio and increase and investment attractiveness of this sector of the regional economy.
Research Methods
The considered methods for assessing the investment potential of the agro-industrial complex are based on assessing the totality of quantitative and qualitative indicators that directly or indirectly characterize the condition and development potential of the complex. In order to determine the ranking position of a regional agro-industrial complex, its development potential and attractiveness for investors, it is necessary to take into account the values of indicators characterizing its financial condition, level of development of production, social sphere, infrastructure, technical base, institutional environment, innovative activity and a number of others. Development prospects may be constrained by consumer and social constraints, as the interests of the investor must meet the interests of potential consumers. The declining purchasing power of the region’s inhabitants, aggravated population decline, active urbanization processes, accompanied by the outflow of active working population from the village, and many other unfavorable political, demographic, social, environmental, and economic factors can negatively affect the volume of investments. As the Mayor of Moscow S. Sobyanin noted On June 7, 2019, at the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum, explaining Moscow’s leadership in the national rating of the investment climate among Russian regions in 2018, “... business goes where people go ...“.
To assess the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region, it was proposed to use a combination of the method of point estimates, expert estimates, the method of coefficients and development in dynamics.
Factors characterizing the level of investment attractiveness of regional agribusiness are grouped into ten groups.
1) The current state of investment activity is determined with the volume of investments in fixed assets in absolute terms and per capita of the region, the share of own investments, the volume of attracted investments in fixed assets of the agro-industrial complex, the volume of foreign direct investment, as well as the level of return on investment in the form of manufactured products.
2) The potential of the agro-industrial complex is characterized by the size of the region’s territory, sown areas, the share of rural settlements in the total number of municipalities, and the population.
3) The group of indicators of staffing includes such indicators as the average annual number of people employed in agriculture, the share of the rural population in the total population, the level of labor productivity in agriculture, the average monthly nominal wage in agriculture, the share of the employed population with higher education, migration rate.
4) Production factors are estimated with the value of fixed assets, the degree of their depreciation, the level of capital productivity.
5) The innovative development opportunities of the agro-industrial complex are determined with the number of personnel engaged in research and development, the volume of internal research and development costs, the number of advanced technologies used, the share of innovation-active organizations, the share of innovative products shipped, and the number of high-productivity jobs in agriculture.
6) The group of infrastructural factors of the investment process includes indicators of the density of public railways, the share of public roads that meet regulatory requirements, the volume of freight transport by rail, freight turnover of motor transport, the level of energy supply, the number of credit organizations and branches, the number of sources of heat supply to rural settlements , the number of non-gasified settlements.
7) The financial conditions for investment are determined with the level of income of the consolidated budget of the region per capita, the average size of the bank deposit of individuals, the level of credit debt of commercial organizations, the share of unprofitable commercial organizations, indicators of the financial results of organizations, including in the crop and livestock sectors, profitability sold goods, products (works, services) of organizations in the fields of crop production and livestock.
8) The institutional conditions for making investments are assessed with the degree of development of small business, the number of small enterprises per 10,000 people, the number of jobs replaced at small enterprises, the number of enterprises and organizations by type of economic activity “agriculture”, “forestry”, “hunting”, “fishing and fish farming”, the state of the legislative framework and the impact on business activity.
9) Consumer restrictions are determined by the level of average per capita income, consumer spending on average per capita per month, as well as the share of the population with incomes above the subsistence level.
10) Social restrictions reflect the incidence of the population, the number of recorded crimes, the amount of overdue arrears in the payment of wages, mortality of the working age population and the amount of need for workers declared by employers to the employment service authorities.
The values of these indicators are compared with their average values for all regions of the Central Federal District (CFD), on the basis of which the indicator for a particular study region is assigned points as follows: if regional indicators are significantly lower than average then 1 point is assigned, if they are at the average level 2 points are assigned, if they are better than average 3 points are assigned.
At the same time, to determine the level of investment attractiveness of the regional agro-industrial complex, it is not enough to evaluate indicators that have developed at a certain moment (as a rule, statistics are late with data reflection), therefore, we believe that it is necessary to show the dynamics of the indicators so that investors can predict the development of the situation in the region.
Findings
When applying the proposed methodology for calculating the values of the above indicators for assessing the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region, first, official statistical materials were used for the period from 2010 to 2018, which allowed us to determine their dynamics and outline the general trend in the investment situation in the region.
To express an expert assessment, a number of coefficients were used to determine the degree of influence of individual conditions on the volume of attracted investments. For example, the effectiveness of normative legal acts adopted in the region to aim at promoting the development of the business environment, in addition to the above indicators, was estimated using the density coefficient of interregional ties, determined by the ratio of the number of entities with which the studied region concluded agreements on the supply of agricultural products to the total number of Russian entities Federation. An assessment of the level of development of production was supplemented by an analysis of the equipment of agricultural machinery, taking into account the number of machinery and equipment per 1000 hectares of arable land in relation to standard indicators. An important information source was an expert assessment of the effectiveness of investment projects implemented in the region on the basis of calculating the ratio of average profit to investment. The average values for the Central Federal District were taken as criteria, they were assigned a level of 2 points. The use of the ball method made it possible to identify strengths and weaknesses in the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region. The study showed that only in four groups of indicators does the region exceed or correspond to the values accepted as criteria (average for the Central Federal District).
So the indicator “financial investment conditions” received with the maximum value of 3 points. Favorable territorial location, relative proximity to large markets for products and developed infrastructure are attractive for potential investors when choosing a region for the organization of production. The agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region is developing on the basis of competitive advantages (black soil, favorable geographical location, transport infrastructure) and cheap labor (the level of the average monthly nominal accrued wages of workers for a full circle of organizations in the Lipetsk region is 41.6% behind the average for the Central Federal District, and 27.2% from the level of the Russian Federation) and demonstrates steady positive dynamics. The results of doing business in the agricultural sector justify attracting investment. The profitability of products sold by manufacturers in the Lipetsk region in the crop sector (15.7%) is higher than the average data for the Central Federal District by 2.7%, in the livestock sector (20.3%) - by 4.1%. Balanced financial results have a steady positive trend. The volume of agricultural production for the period from 2010 to 2018 increased by 3.3 times, amounting to 115,268.9 million rubles, which is 1.5 times higher than the average for the Central Federal District.
Assessment of investment attractiveness, investment potential and innovative susceptibility of agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region showed that investments in this sector of the regional economy have a very significant share, having reached 19.3% of the total investment in fixed assets, while this indicator on average in the Russian Federation is only 4.2 %, and the central federal district is 6.4%. Such indicators are achieved thanks to a wide range of regulatory documents and government programs aimed at the development of investment processes, including in the agricultural sector of the region. As a result, the value of the “state of investment activity” indicator in the Lipetsk Region turned out to be higher than the average for the Central Federal District.
Two more groups of indicators – “infrastructural conditions” and “social constraints”, generally correspond to criteria. At the same time, the mortality rate of the working-age population in the region is also higher than the average for the Central Federal District by 15%. The need for workers declared by employers in the employment services of the Lipetsk region is 2.2 times lower than in neighboring regions. The totality of the above conditions that form the socio-economic environment in the region explains the negative values of the migration growth rate (-6 per 10,000 people in 2017, -3.6 in 2018) observed at the last several years with high positive values of this indicator in the Central Federal District on average (in 2018, it amounted to 46.7 per 10,000 people).
In addition, a comprehensive assessment of the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex in the region revealed a number of negative aspects that could negatively affect the development of the complex and its attractiveness for investors in the future (see Figure
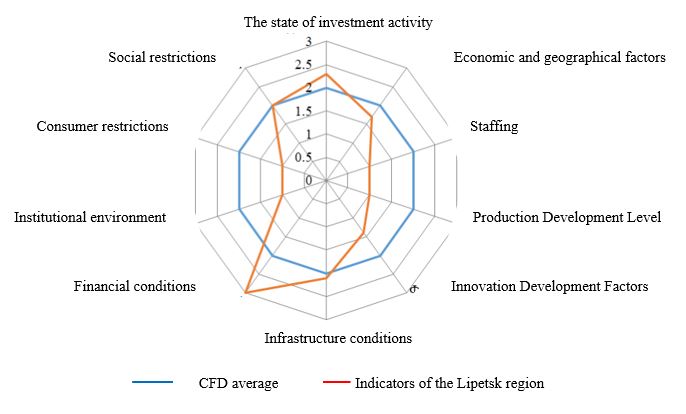
Despite the slightly higher level of attracting investment in the agricultural sector in 2018 compared to other regions, provided mainly with favorable financial and infrastructural conditions, the investment attractiveness of the complex is constrained with economic and geographical conditions, a low personnel component, insufficient levels of production development, creation and the use of innovation, institutional environment, social and consumer constraints.
The creation and implementation of innovations is constrained with the low level of internal costs for research and development. While maintaining the prevailing policy of copying foreign technologies, the predominance of raw materials exports and a low share of processing of manufactured products, the Lipetsk Region risks to lose its position in the rating of investment-attractive regions. Dependence on imported means of production, technology, seed material remains. The study revealed that, despite the increase in production intensification and the active involvement of investors in the development of the agricultural sector in the region, the areas of investment activity are not focused on creating innovations.
In the Lipetsk region, the number of highly productive jobs in agriculture is higher than the average value in the Central Federal District, but there is a negative trend. For the study period (2010-2018), the value of this indicator decreased by 24%. The share of shipped innovative products varies over the years, but there is a general trend towards its reduction.
The share of rural settlements in the total number of municipalities in the Lipetsk Region is 91.7%, which is higher than the average for the Central Federal District by 15.9%, while the staffing of potential investment projects in the countryside leaves much to be desired. The average annual number of people employed in the agricultural sector is steadily declining. Despite the fact that in the region the average monthly nominal wage of agricultural workers, which amounted to 30,243 rubles in 2018, is 2,676 rubles. higher than the district average, the general low level of income in the region makes young people and the active part of the population look for more decent work, and often in neighboring regions. The average monthly salary of employees of organizations in the Lipetsk region in 2018 was 31,835 rubles, while the average for the Central Federal District was 54,470 rubles. Low incomes hold back the purchasing power of the population: consumer spending in the Lipetsk region is 28% lower than the average for the Central Federal District. The number of operating enterprises in the Lipetsk region is less than in neighboring regions, from 2010 to 2018, their number increased by only 383 enterprises, or 1.7%, and in agriculture - decreased by 151, or 13.7%. Small business development is significantly lower than the average for the Central Federal District, in the region in 2018, there were only 1.4 thousand units (without microenterprises), while the corresponding average value in the district was 4.8 thousand units. The number of non-gasified settlements remains too high, which hinders the development of entrepreneurial activity in the countryside, and, consequently, the attraction of investments.
Conclusion
The agricultural sector is capital-intensive, its level of development is determined with compliance with modern requirements of technologies used in production, for which continuous attraction of investments is necessary. Their volumes and directions of investments depend on the attractiveness of investment areas. In choosing a region for placing a business, the investor is guided by personal experience, expert opinions, and existing ratings. Often, judgments can be the opposite, because they are based on the selection of various criteria. Therefore, a balanced methodology is needed that takes into account the totality of indicators, which allows to evaluate the widest possible range of conditions that affect the decision-making of investors, which is not cumbersome and does not cause difficulties in obtaining information.
The application of a systematic approach to assessing the investment attractiveness of the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region made it possible to identify strengths and existing problems, the solution of which will contribute to increasing investment activity in the agro-industrial complex of the region. Monitoring of the indicators proposed in the described methodology, combined into ten enlarged groups and a comparative analysis of the dynamics of the current state of the Lipetsk region and the regions of the Central Federal District, as a whole, showed that the Lipetsk region in a number of indicators relates to the economically developed regions of Russia: the increase in agricultural production and the volumes of attracted investments are higher than in neighboring regions.
At the same time, negative aspects in the development of the agro-industrial complex were also established.
In terms of the indicator, the internal costs of research and development in agriculture, the Lipetsk Region is inferior to neighboring regions. It is substantiated that increasing investment in science and creating forms of interaction between researchers and farmers, guaranteeing support and consultation on the introduction of new varieties, crosses, technologies from the beginning of the production process to obtaining the final result, will create a stable platform for the effective breakthrough development of the agro-industrial complex.
It has been established that in the agro-industrial complex of the Lipetsk region, an increase in the share of processing agricultural products is necessary. Improving the material and technical support for the storage of regional agricultural products will allow agrarians of the Lipetsk region to compete with domestic and foreign manufacturers, be less dependent on weather conditions, and satisfy growing customer requirements. The agricultural products market is developing dynamically. Demand for off-season products, i.e. fresh vegetables and fruits should be on sale year-round, there is a proposal for new processed products; consumers seek to improve their quality of life by consuming more environmentally friendly natural products. Therefore, the priority areas of investment should be storage, processing and logistics operations with wide territorial localization, which will not only solve the food security problem, but also relieve social tension and reduce significant differentiation in both income and quality of life between urban and rural population .
The uneven level of development of the infrastructure of municipalities, the localization of production in large settlements upset spatial balance, strengthen the socio-economic stratification of rural and urban areas of the region. Therefore, it is advisable to develop production cooperation with the processing and marketing of agricultural products, as well as the socio-economic development of the entire territory of the region, and not just the regional and some district centers.
It is the spatially balanced development of the region, improving the quality of social infrastructure, increasing the interest of authorities in opening new enterprises focused on the production of agricultural products of deep processing, the development of a scientific base, the creation of high-performance jobs will increase the level of income and the quality of life of rural areas, smooth out territorial separation. This is the key to the preservation and growth of labor resources and, at the same time, purchasing power. If a large business can organize production at some distance from the sales market, arranging storage and transportation, then small business, as a rule, develops in conditions of close relations with consumers. High-tech production in modern conditions is not labor-intensive and does not provide enough jobs that would remove the problem of rural employment, while small business is able to solve this problem. The experience of developed countries shows the logical effectiveness of the successful interaction of a large enterprise-leader and small enterprises on the basis of the complementarity of industrial, scientific, technological or commercial cooperation. A large competitive enterprise extends its influence to the production surrounding it, spreading ideas, technologies, communications, satisfying its own interests and increasing the profitability of partner enterprises. Mutually beneficial cooperation between large and small businesses gives a synergistic effect, which favorably affects the socio-economic development of the region.
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by the RFBR and the Administration of the Lipetsk Region as part of a scientific project № 18-410-480004.
References
- Fuluc, G., & Akulenko, K. (2018) Methodological principles of assessment of investment attractiveness of the enterprise. Baltic journal of economic research. 4(5), 387-395. [in Russ.].
- Golovetsky, N. I., & Terekhova, A. I. (2015). Investment attractiveness of the agricultural sector of the economy in terms of import substitution. Science of science, 7(5), 1-12. Retrieved from http://naukovedenie.ru/PDF/104EVN515.pdf [in Russ.].
- Kursky, R., Zubkov, R., & Shapovalova, I. (2018). Evaluation of the investment attractiveness of the region as a guarantee of leadership in the socio-economic development of the territory. The materials of the 2nd international conference on socio-economic and academic leadership, pp. 305-313.
- Nikitskaya, E. F., & Valishvili, M. A. (2016). Mechanisms of stimulation of investment and innovative activity at the regional level: socio-economic and legal aspects. Science of science, 8(6), 1-15. Retrieved from http://naukovedenie.ru/PDF/83EVN616.pdf
- Safiullin, A. R., & Gubaidullina, A. Y. (2018). Approach to risk assessment and investment attractiveness of Russia's regional economic activity. International transactional journal of engineering management and applied Sciences and technology, 9(5), 455-467.
- Tahumova, O. V., Loiko, V. I., & Baranovskaya, T. P. (2018). Development of methods of estimation of investment attractiveness of the regional system. Research journal of pharmaceutical biological and chemical Sciences, 9(5), 1661-1664. [in Russ.].
- Tahumova, O. V., Semenova, L. V., & Fursov, V. A. (2018). Тhe Creation and evaluation of investment attractiveness of agricultural enterprises. Research journal of pharmaceutical biological and chemical Sciences, 9(5), 1665-1670. [in Russ.].
- Ternovich, K. S., Nechaev, N. G., TheIzmalkov, A. A., Popkov, E. V., Gribanov, V. S., & Plakida, A. A. (2013). Agro-industrial integrated formations: state and prospects of development: monograph.
- Tereshkina, T., Mottaeva, A., & Andreeva, L. (2017). Social and economic mechanism of formation of favorable investment attractiveness of the region. Energy management of municipal transportation facilities and transport, 90, 1.
- Zheltenkov, A., Syuzeva, O., & Vasilyeva, E. (2017). Development of investment infrastructure as the factor of the increase in investment attractiveness of the region. Energy management of municipal transportation facilities and transport, 90, 20.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-076-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
77
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1056
Subjects
Industry, industrial studies, project management, sustainability, business, innovation
Cite this article as:
Stepanenkova, N. M., & Esina*, Y. L. (2019). Methodology For Assessing Investment Attractiveness Of Aic Of The Lipetsk Region. In I. O. Petrovna (Ed.), Project Management in the Regions of Russia, vol 77. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 162-171). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.05.20
