Abstract
Introduction: Stable and dynamic parameters of speech production associated with aggressive behavior as well as the intensity of emotional background of multimodal communication are rarely investigated. The aim of the research is to characterize discrete discursive units associated with aggressive behavior and to contribute to the knowledge of auditory and visual perception on the basis of aggressive behavior in relation to different degrees of the emotional intensity of communication. Methods: perceptual-auditory and perceptual-visual analysis. Participants: 31 females aged 18-22. Stimuli: two discursive situations in Russian language, produced by males, taken out of the original database of multimodal content evaluated as aggressive behavior. The experiment was conducted in two sessions: 1) visual perception (facial expressions and body movements), 2) auditory perception (verbal and prosodic). Statistical reliability of the results obtained was measures using ANOVA. Findings: The majority of participants perceived the stimuli as aggressive behavior. They estimated emotional intensity of communication lower when perceived through the visual channel, than when perceived through the auditory channel. Nominations of emotions mentioned by recipients in perceptual-visual and perceptual-auditory sessions correlate with each other and relate to the complex of emotional states associated with aggressive behavior. The most stable parameters during auditory perception were voice pitch, voice intensity, speech tempo; during visual perception – movements of eyes and eyelids, eyebrows and forehead muscles, movements of arms.
Keywords: Visual perceptionauditory perceptionemotionsaggressive behaviorprosodyfacial expressionsgesticulation
Introduction
“This paper is a part of a project aimed at a cross-disciplinary study of influence of aggressive Internet environment in multimodal polycode social network communication upon transformation of psychophysiological and cognitive features of Internet user personality (with regard to adolescent and young adult Internet users). According to the research hypothesis, multimodal polycode communication in modern social networks has a number of features causing its negative influence over recipients” (Potapova, Potapov, Komalova, & Dzhunkovskiy, 2019). “The detrimental effects of this environment are compared to the effects of acoustic noise”. We focus on the consequences of such noise impact on “the functional status of the subjects based on psychophysiological personality features”, on the one hand, and “cognitive deterioration under the influence of such stressors as different types of noise”, on the other hand (Potapova & Potapov, 2017).
We consider polycodedness as “a result of interaction between codes of different semiotic systems and discourses”. A polycode text crossroads “interaction of different codes, i.e. symbols, systems of symbols, signs and rules of their combinations with each other for the transmission, processing and storage of information in the form most adapted thereto. This term describes the phenomenon of textual heterogeneity at the level of form achieved through a mix of different semiotic systems, such as verbal and visual” (Dmitrichenkova, Dolzhich, & Popova, 2017). The literature argues that “polycode text usage changes categorial realia of communication through information perception management resulting in modification of recipients’ value orientation” (Vashunina, Ryabova, & Egorova, 2018).
The “research field has collectively been called ‘multimodality’, where ‘multimodal’ typically refers to the multiple modes (e.g. spoken, written, printed and digital media, embodied action, and 3-D material objects and sites) through which social semiosis takes place” (O’Halloran, 2010, p. 3). “According to social semiotics, language covers only a part of human expression, understanding, and meaning making. Other modes of expression, like visuals and sound, are equally relevant in human communication processes” (Zamparini & Lurati, 2017).
“During emotive spoken communication, listeners use multiple sources of information spanning from verbal content to prosodic modulation, pragmatic context, facial expression, and gestures” (Filippi et al., 2017). “Research has shown that when emotional stimuli are conveyed only in one channel, emotion recognition is more accurate in the visual modality than in the auditory modality” (Paulmann & Pell, 2011). “However, in emotion communication, multiple channels can also strongly reinforce each other” (Grandjean, Baenziger, & Scherer, 2006; Paulmann & Pell, 2011; Wilson & Wharton 2006). Studies have shown that “the integration of facial expression and prosody guides the perception of the speaker’s emotional state” (Belin, Fecteau, & Bédard, 2004; Campanella & Belin, 2007; Massaro & Egan, 1996). “The integration of different sources of information in emotion comprehension has a relevant social function, as multiple emotional cues can be employed as appeals to appropriate behaviors, and ultimately, to regulate interpersonal interactions” (Fischer & Roseman, 2007; van Kleef, De Dreu, & Manstead, 2004).
“In conditions of one channel perception of negative emotional-modal states of an interlocutor the significance of visual / auditory perception fluctuates in dependence with the current emotional-modal state (EMS) of a recipient. The subjects with higher current EMS tend to rely more on the results of the auditory perception, and the subjects with low current EMS are more likely to rely on the visual type of perception” (Komalova, 2017; Potapova & Komalova, 2016).
In general, “emotion expression is most ambiguous in terms of vocal expression and most clear based on multimodal audio-visual expressions. Various modalities show advantages in representing different emotions. For example, people need longer time to perceive emotion via vocal expression in general, while they have similar faster response speed for facial and audio-visual expressions on average. This suggests that involving of vocal expression may help to increase the speed of perception in some cases” (Cao et al., 2014).
Problem Statement
Despite the fact that modern literature provides background for identification of separate emotions (such as, for example, anger, hatred, disgust, etc.), describes gender characteristics of emotions’ perception, taking into account that numerous scholars do researches aimed at aggressive behavior speech recognition in various linguacultures, a multimodal content associated with aggressive behavior is rarely analyzed. Even less often, stable and dynamic parameters of speech production associated with aggressive behavior, as well as the intensity of the emotional background of communication, are investigated in the deployment of a discursive situation.
Research Question
In this paper, we are trying to answer the following research questions. What are the vocal and prosodic parameters in perceptual-auditory analysis and what are the parameters of facial expressions, gesticulations, body movements in visual perception that act as reference points for the characterization of aggressive behavior? Do these parameters persist in perceiving the emotional background of communication of different intensity?
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the research is to characterize discrete (auditory and visual) monological discursive units associated with aggressive behavior (auditory: verbal and prosodic, and visual: facial expressions and body movements) and to contribute to the knowledge of auditory and visual perception on the basis of aggressive behavior (which is understood as a complex of emotional / emotional-modal states, all together perceived as aggression) in relation to different degrees of the emotional intensity of communication.
Research Method
In total, 31 females aged 18-22 participated in the research. All recipients were Russians, full-time students (third year, humanities). Recipients considered themselves pertaining to the middle class population. Previously, all participants were informed about the ongoing research, the possibility of leaving it at any time, and also signed an informed consent.
To identify the evaluations provided by recipients with respect to behavior associated with aggression, proven perceptual-auditory and perceptual-visual analysis techniques were applied (Potapova & Potapov, 2017). We extracted the stimuli (two discursive situations in Russian language, produced by males) out of the original database of multimodal content evaluated as aggressive behavior. As well as in many European cultures, in Russian linguaculture people lean on a stereotypical notion that, compared with females males are characterized by more aggressive biologically-related behavior, while females often play the role of victims (Araya, 2017; Capezza, D’Intino, Flynn, & Arriaga, 2017; Ermer, Roach, Coleman, & Ganong, 2017; Hammock, Richardson, Lamm, Taylor, & Verlaque, 2017; Krahé et al., 2015; Lepeltier & Fontaine, 2018; Orpinas, Mcnicholas, & Nahapetyan, 2015; Sharma, Kishore, Sharma, & Duggal, 2017; Teranishi, 2015; Turchik, Hebenstreit, & Judson, 2015; Walker, Ashby, Gredecki, & Tarpey, 2018; Valeeva, Litvinova, & Kulesza, 2016). We completed our test group out of females, and asked them to analyze aggressive behavior produced by males, supposing that by triggering the effect of stereotyping perception we would achieve more unambiguous evaluations of the stimuli.
The experiment was conducted in two sessions. During the first session, the recipients evaluated the stimuli transmitted through the visual channel (the audio track was removed). During the second session, which was held a week later, the recipients evaluated the same stimuli but that time transmitted through the auditory channel (prosody, verbal content; video was deleted). The stimuli did not consist of musical background. After viewing / listening to each discursive situation the recipients were asked to evaluate the emotional intensity of communication using 10 points Likert scale, where values from 0 to 3 corresponded to a low emotional intensity of communication, from 4 to 6 – to medium emotional intensity, from 7 to 10 – to high intensity). After the first session the recipients characterized facial expressions, gesticulation, body movements, distance between interlocutors; after the second session – communicant’s voice and speech features (pitch and intensity of voice, speech melodic pattern, speech tempo, duration of speech pauses, speech rhythm and speech breathing). To confirm that the recipients associated the stimuli with aggressive behavior, an additional task was introduced: recipients were to indicate the dominant emotional background of communication (to say whether it is neutral, jolly or aggressive) and, if possible, name dominant emotion. Statistical reliability of the results obtained was measures using analysis of variance for incoherent samples (ANOVA).
Findings
It was found that the majority of participants perceived the stimuli as aggressive behavior (Table
In
Evaluations of the first and second discursive situations formulated after the first and second sessions differ. The recipients estimated emotional intensity of communication lower when perceived through the visual channel, than when perceived through the auditory channel (Table
At the next step of the experiment we the selected groups of evaluations which characterized the stimuli emotional intensity (low / medium / high). The distribution of the evaluations obtained during perceptual-visual analysis is presented in Tables
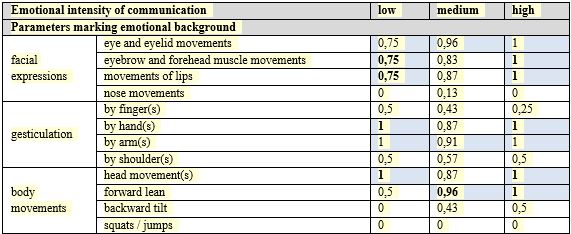
As it is shown on Table
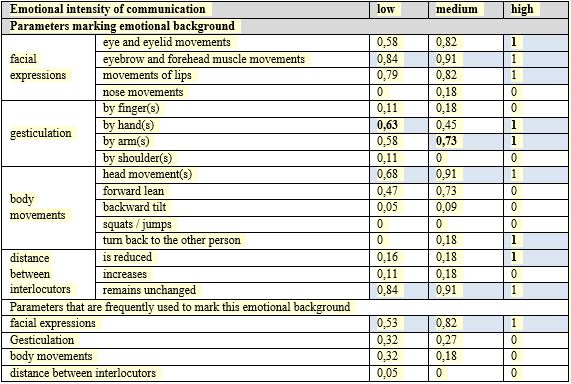
While evaluating the second discursive situation the recipients noted that high emotional intensity of communication is decoded relying on eyes and eyelid movements, lips movements; when a person turns his / her back to the other person; it is noted by reduction of the distance between interlocutors during communication. Validation of the data obtained showed that the patterns found were statistically significant at ρ < 0,05 (the
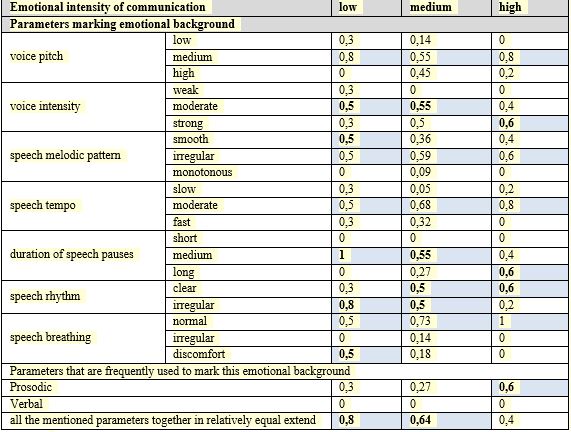
In perceptual-auditory analysis of the first discursive situation differences in the level of emotional intensity of communication are manifested in the following patterns:
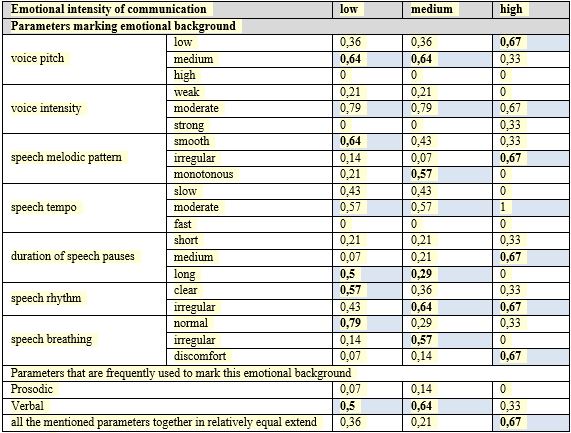
During the analysis of the second discursive situation it was revealed that the
Conclusion
Summarizing the obtained results, it can be noted that, in general, while evaluating communication associated with aggressive behavior through
The limitation of the research is a small number of participants, which, in turn, did not allow differentiating the evaluations on the basis of the “influence of stable personality traits and individual psychological characteristics of the recipients on the stimuli perception results”. Moreover, “current emotional-model state (EMS) of the participants was not taken into consideration. According to the results of our previous research” (Potapova & Komalova, 2016), EMS can make certain adjustments to the evaluation results of behavior based on auditory and visual perceptions.
In the future, it is planned to conduct an experimental research applying the same design described in this paper, involving a group of male recipients. We also plan to develop a research design with the aim to identify the correlation between the results of perceptual-auditory and perceptual-visual types of analysis of the stimuli associated with aggressive behavior. Achieving this goal will allow to address the issue of the impact of auditory (sounding speech, musical accompaniment) and visual (motor activity of interlocutors, spatial movements of communicants, as well as reading verbal content, perception of static and moving images) content on the recipient in certain discursive situations, mediated by technical devices (computer interface, mobile devices) and technological tools (Internet applications, social networks).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from Russian Science Foundation (RSF) according to the research project № 18-18-00477.
References
- Araya, M. (2017). Gender based violence and its consequences in Ethiopia: A systematic review. Ethiopian Medical Journal, 55(3), 243-250.
- Belin, P., Fecteau, S., & Bédard, C. (2004). Thinking the voice: Neural correlates of voice perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 129-135.
- Campanella, S., & Belin, P. (2007). Integrating face and voice in person perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11, 535-543.
- Cao, H., Cooper, D. G., Keutmann, M. K., Gur, R. C., Nenkova, A., & Verma, R. (2014). CREMA-D: Crowd-sourced emotional multimodal actors dataset. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 5(4), 377-390. DOI: 10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2336244. http://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC4313618&blobtype=pdf
- Capezza, N. M., D’Intino, L. A., Flynn, M. A., & Arriaga, X. B. (2017). Perceptions of psychological abuse: The role of perpetrator gender, victim’s response, and sexism. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, Article in Press. DOI:
- Dmitrichenkova, S. V., Dolzhich, A. E., & Popova, T. G. (2017). Cognitive & pragmatic aspects of polycodedness of a scientific text, a case study of the Spanish language. International Journal of Applied Linguistics and English Literature, 6(1), 128-135. https://journals.aiac.org.au/index.php/IJALEL/article/view/2721
- Ermer, A. E., Roach, A. L., Coleman, M., & Ganong, L. (2017). Deconstructing attitudes about intimate partner violence and bystander intervention: The roles of perpetrator gender and severity of aggression. Journal of Interpersonal Violence. DOI: 10.1177/0886260517737556
- Filippi, P., Ocklenburg, S., Bowling, D. L., Heege, L., Güntürkün, O., Newen, A.,…& de Boer, B. (2017). More than words (and faces): evidence for a Stroop effect of prosody in emotion word processing. Cognition and Emotion, 31(5), 879-891. DOI:
- Fischer, A. H., & Roseman, I. J. (2007). Beat them or ban them: The characteristics and social functions of anger and contempt. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 103-115.
- Grandjean, D., Baenziger, T., & Scherer, K. R. (2006). Intonation as an interference between language and affect. Progress in Brain Research, 156, 1-13.
- Hammock, G. S., Richardson, D. S., Lamm, K. B., Taylor, E., & Verlaque, L. (2017). The effect of gender of perpetrator and victim on perceptions of psychological and physical intimate partner aggression. Journal of Family Violence, 32(3), 357-365. DOI:
- Komalova, L. R. (2017). Aggressogen discourse: The multilingual aggression verbalization typology [Aggressogennyj diskurs: Tipologiya mul’tilingval’noj verbalizatsii agressii]. Sputnik+, Moscow. http://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=28993951 [in Russian].
- Krahé, B., Berger, A., Vanwesenbeeck, I., Bianchi, G., Chliaoutakis, J., Fernández-Fuertes, A. A., …& Zygadło, A. (2015). Prevalence and correlates of young people’s sexual aggression perpetration and victimisation in 10 European countries: A multi-level analysis. Culture, Health and Sexuality, 17(6), 682-699. DOI: 10.1080/13691058.2014.989265
- Lepeltier, S., & Fontaine, R. (2018). Integration of gender of the aggressor – victim pair and of socio-emotional context of the aggression on judgment of blame: A developmental approach. Psychologie Francaise, Article in Press. DOI: 10.1016/j.psfr.2018.04.001
- Massaro, D. W., & Egan, P. B. (1996). Perceiving affect from the voice and the face. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 3, 215-221.
- O’Halloran, K. L. (2010). Multimodal analysis and digital technology. In A. Baldry, E. Montagna (eds.) Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Multimodality: Theory and Practice. Campobasso: Palladino. http://multimodal-analysis-lab.org/_docs/Multimodal%20Analysis%20and%20Digital%20Technology.pdf
- Orpinas, P., Mcnicholas, C., & Nahapetyan, L. (2015). Gender differences in trajectories of relational aggression perpetration and victimization from middle to high school. Aggressive Behavior, 41(5), 401-412. DOI:
- Paulmann, S., & Pell, M. D. (2011). Is there an advantage for recognizing multi-modal emotional stimuli? Motivation and Emotion, 35(2), 192-201.
- Potapova, R., & Komalova, L. (2016). Multimodal perception of aggressive verbal behavior. In: Ronzhin, A., Potapova, R., Nemeth, G. (eds.) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2016, LNAI, vol. 9811, pp. 499-506. Springer, Switzerland. DOI:
- Potapova, R., & Potapov, V. (2017). Human as acmeologic entity in social network discourse (multidimensional approach). In: Karpov, A., Potapova, R., Mporas, I. (eds.) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2017. LNCS, vol. 10458, pp. 407-416. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-66429-3_40
- Potapova, R., Potapov, V., Komalova, L., & Dzhunkovskiy, A. (2019). Some peculiarities of Internet multimodal polycode corpora annotation. In: Salah, A., Karpov, A., Potapova, R. (eds.) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2019. LNCS, vol. 11658, pp. 392-400. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-26061-3_40
- Sharma, D., Kishore, J., Sharma, N., & Duggal, M. (2017). Aggression in schools: Cyberbullying and gender issues. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, 29, 142-145. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajp.2017.05.018
- Teranishi, M. C. (2015). Engendered expressions of aggression: The role of gender, proprietary behaviors, and jealousy in intimate partner violence. Violence and Gender, 2(2), 112-118. DOI:
- Turchik, J. A., Hebenstreit, C. L., & Judson, S. S. (2015). An examination of the gender inclusiveness of current theories of sexual violence in adulthood: Recognizing male victims, female perpetrators, and same-sex violence. Trauma, Violence, and Abuse, 17(2), 133-148. DOI:
- Valeeva, R. A., Litvinova, N. N., & Kulesza, E. M. (2016). Gender aspects in the victim behavior of adolescents. Specialusis Ugdymas, 35(2), 141-174. DOI: 10.21277/se.v1i35.278.
- van Kleef, G. A., De Dreu, C. K. W., & Manstead, A. S. R. (2004). The interpersonal effects of anger and happiness in negotiations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 86, 57-76.
- Vashunina, I. V., Ryabova, M. E., & Egorova, L. A. (2018). Polycode hypertext in polylingual discourse of intercultural communications. XLinguae, 11(2), 218-231. DOI:
- Walker, J., Ashby, J., Gredecki, N., & Tarpey, E. (2018). Gender representations of female perpetrators of intimate partner violence. Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research, 10(3), 170-180. DOI: 10.1108/JACPR-02-2017-0273
- Wilson, D., &, Wharton, T. (2006). Relevance and prosody. Journal of Pragmatics, 38, 1559–1579.
- Zamparini, A., & Lurati, F. (2017). Being different and being the same: Multimodal image projection strategies for a legitimate distinctive identity. Strategic Organization, 15(1), 6-39. https://doi.org/
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
12 December 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-073-0
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
74
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-419
Subjects
Society, culture, education
Cite this article as:
Potapov, V., Komalova*, L., & Potapova, R. (2019). Auditory-Visual Perception Analysis Of Multimodal Content Associated With Aggressive Behavior. In S. Ivanova, & I. Elkina (Eds.), Cognitive - Social, and Behavioural Sciences - icCSBs 2019, vol 74. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 267-276). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.12.02.32
