Abstract
The article discusses the characteristics of the socio-cultural situation in conditions of instability of the development of society and digitalization. The contradictions and complexities of this process for a teenager are determined, including changes in the psychological characteristics of schoolchildren, a decrease in the significance and influence of the family. Emphasis is placed on the consideration of the virtual space as a significant factor of secondary socialization. The vocational guidance was assigned to the leading factors of socialization, and its effectiveness was assessed. In the cited results of monitoring the views of parents of schoolchildren, it is concluded that, despite the development of digital technologies and their influence on the formation of the value system of schoolchildren, parents are diagnosed with a very high level of their trust in school as the leading factor in the socialization of students. As a result, a system of pedagogical education and vocational guidance of schoolchildren in the format of project pedagogical shifts during the year, implemented within the university cluster, is presented. The multifunctionality of the activity of pedagogical shifts is determined, the main of which is the function of creating an emotionally saturated communicative space that provides meaningful life orientation of schoolchildren.
Keywords: Socializationvocational guidancedigitalizationprojectcommunicationmediation
Introduction
In a society that is transforming in the conditions of digitalization, a whole set of additional conditions arises that make it difficult to become a harmoniously socialized person (Gergen, 1997). One of the reasons for the emergence of these conditions is a significant transformation of the sociocultural environment, on the one hand, as a result of a change in the value system, on the other hand, with the advent of a new type of information and communication space. At the same time, social (sociocultural) space is considered as a product of interaction determined by human activity and experience, since man is a subject of space, constituting spatial characteristics in the reality surrounding him (Remm, 2015). In this situation, the study of socialization results becomes a subject of study for sociologists, and psychologists, and teachers, since the socio-humanitarian implications of the functioning of new information technologies are extremely diverse: and they change the nature human activity, its social connections, organizational forms and content of social interactions, etc. (Shakurova, Dyuzhakova, & Akulova, 2017). Recognizing the alternativeness of a social process means constructing a social reality from the standpoint of the existence of not only alternatives that are most likely to be realized in the future, but also the reasons related to transitional periods and unstable situations within a transforming society.
The task of socializing the student's personality is one of the leaders in the education system. And in a transforming society, this task is updated in such a way that when new philosophical ideas emerge in the course of changes in the educational space, reflecting changes in the cultural stratum of society, its intellectual state, the essence of professional activity, its competence characteristics, ways of professional activity and the list popular in the socio-economic situation specialties (Zanina, Kirik, Bondarev, & Zashchitina, 2017).
Problem Statement
It should be emphasized that in the conditions of digitalization, the structure of socialization becomes more complex: virtual reality from the element of socialization becomes a powerful agent of secondary socialization, including not only online space, but also off-line reality, having a significant impact on the functioning of the real society in which a person lives. The studies of psychologists and pedagogues of recent years deal with a whole generation of children born “with gadgets in their hands,” and that the Internet is considered as a new cultural tool that influences not only the socialization of the student’s personality, but also the development of his higher mental processes, because Higher mental processes, traditionally developing in the process of communication between the student and adults and peers, in the current situation are largely developed in the process of his interaction with the gadget, and / or through Internet and so forth. (Savchenko, 2011; Zanina & Kirik, 2018). As a result of changes in the system of values and life priorities, the importance of parents, family traditions and the importance of classmates compared to virtual friends is reduced by several times.
Another problem in the conditions of digitalization is changes in the professional preferences of young people, which are a consequence of the socio-economic and socio-cultural transformations of the Russian reality. As a result, young people often make professional choices not in favor of specialties that correspond to personal needs and abilities, but in favor of those determined by parents' opinion about the need for higher education, the possibility of free tuition at a higher education institution, and the greater likelihood of obtaining “prestigious” work in the future. The difficulties of choosing and realizing the professional preferences of young people are largely related to the fact that professional self-determination occurs too late or is perceived as forced. The current situation leads to negative consequences both for the individual and for society as a whole. It may be assumed that as a result of digitalization, schoolchildren receive additional information about the prospects for professional online activities (which confirms the importance of virtual space as a factor of secondary socialization). And one of the results of the emergence of this situation is the devaluation of the role of the school, family and extracurricular activities of students. All of the above actualizes significance in the conditions of digitalization, when there are virtually no well-founded holistic models and technologies to counter the emergence of risks and threats of loss of spirituality by young people, finding ways and ways to counter such threats (Miroshnichenko, 2009). The solution of this problem cannot be realized by the efforts of only one structure or organization (state, public, research): it is necessary to integrate the efforts of science, education, the parent community.
The solution of the problem, in our opinion, may consist in the early vocational guidance of schoolchildren and the revision of the content of their extracurricular activities, orienting them to the professional competencies demanded in the future and new areas of professional activity. In the current situation in the domestic socio-cultural situation, the greatest difficulty for school teachers, in our opinion, is the design of the content of early career guidance activities of a pedagogical orientation (Piskunova, 2011).
Research Questions
Determine the degree of parental confidence in the Russian school system and, on the basis of the results obtained, determine methods for early professionalization of schoolchildren Theoretically substantiate the content of early professional pedagogical orientation of schoolchildren in the conditions of digitalization.
Purpose of the Study
After analyzing the results of a sociological study, determine the position of parents in relation to the school system. Based on the data obtained, determine the directions of the collaboration between the university and the school in modeling the conditions of early vocational guidance of schoolchildren to pedagogical specialties, taking into account.
Peculiarities of orientation of schoolchildren in conditions of digitalization.
Research Methods
To study the identified problem, we used the monitoring of the results of the project “Development of normative-methodical proposals for the formalization of non-formal additional education of children” Institute of Social Technologies LLC; method of modeling project thematic shifts of schoolchildren, implemented in the framework of the Educational Cluster of FSAEI HE Southern Federal University.
Findings
During the monitoring of the research results of the project “Development of normative-methodical proposals for the formalization of non-formal additional education for children”, we obtained data confirming the opinion of a number of researchers (Sorokoumova, 2015). They believe that at the current stage (despite increased requirements and attention to the school’s activities), in Russian society there is a rapprochement between the family and the school.
Thus, as a result of a survey of parents, 1,375 schoolchildren included in extracurricular activities in 9 districts of Russia.
As a result of monitoring, it was found out that in the system of out-of-school education, pupils of graduating classes make up 13.3%, grades 5-9 - 32.8 (Figure
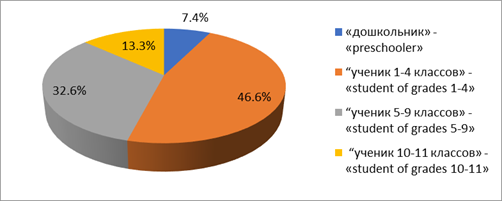
Almost 70% of parents surveyed believe that a traditional school with a class-less system is capable of educating socially active and potentially successful citizens. This high parental confidence was confirmed in the results of the analysis of questions about how often students participate in extracurricular activities organized in school or out-of-school institutions (Figure
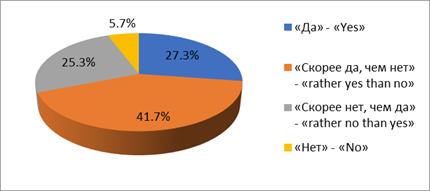
The overwhelming majority of parents (73.5%) believe that, first of all, the child should perform school tasks, and then - be included in extracurricular activities (Figure
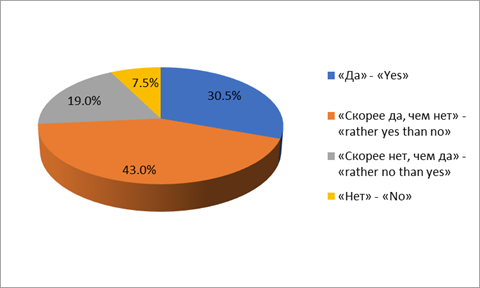
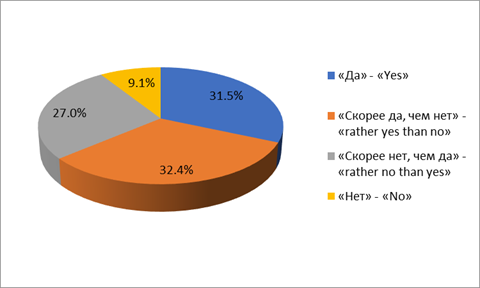
At the same time, 60% consider extracurricular activities as a “ladder to heaven”, which allows them to develop personal qualities that are in demand: opening up the maximum of the child’s individual abilities (62%), building faith in one’s own strength and capabilities, responsibility for one’s actions and actions ( 56%), the formation of autonomy and critical thinking (50%), the formation of communication skills (60%), the preparation of a child for independent life and work activity (42%) (Figure
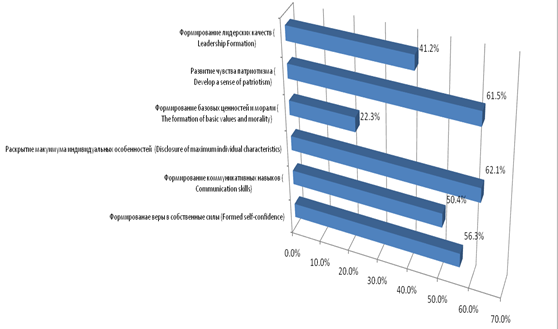
The analysis made it possible for us to design the content of pedagogical project shifts for schoolchildren implemented in the framework of the SFD Educational Cluster on the basis of the Southern Federal University. Pedagogical project shifts are held for pupils of schools in the city of Rostov-on-Don on the basis of the SFU and for pupils of rural schools on the basis of the Children's and Schoolchildren Creativity Centers with the participation of the SFU faculty. The experience of three years of activity shows that the peculiarity of pedagogical project shifts, as opposed to subject-related ones, is that the participation of schoolchildren in this kind of activity ensures the humanization of the educational space of the region and each individual school. The content of each project shift is adjusted on the basis of the received “feedback” with students and taking into account the current scientific research of psychologists and teachers of the Academy of Psychology and Pedagogy of the University. Moreover, school teachers also take part in project shifts. Thus, the project change of schoolchildren performs an educational function on the one hand and is a development space for the actual professional competencies of schoolchildren. On the other hand, it is a platform for research by university scientists and professional development of teachers.
The concept of project pedagogical project change of schoolchildren “Pedagogical mediation” is based on the definition of mediation in education as 1) the direction of education, 2) as an element of preventive work in an educational organization, 3) as an innovative method of resolving disputes and preventing conflicts between participants in the educational process.
The complexity of the current socio-economic and socio-cultural situation of transformations of Russian reality in terms of digitalization is that young people often make a professional choice not in favor of specialties that correspond to personal needs and abilities, not in favor of specialties oriented to future demands of the professions market, but in favor of those professions that are determined by the opinion of the parents about the need for higher education, the possibility of free education in high school , More likely to produce "prestigious" in the future. In this situation, the teaching activity acquires an additional function, involving the resolution of conflicts, difficult communicative and preventive situations (Zaidman & Mozheykina, 2007; Chistyakov, 2006). The organization of the school mediation process requires the integration of several areas of research: legal, psychological and educational.
The goal of the pedagogical project change of schoolchildren “Pedagogical mediation”: on the basis of mediation technologies and methodology, the formation of promising professional competencies: communication, collaboration, critical thinking and creativity, which are the competences of “tomorrow”.
The tasks of the pedagogical project change of schoolchildren are: 1) to form among the participants a change of stable ideas about the mediation component of the teacher’s professional activities; 2) the formation of the participants in the change of experience of the mediative activity (or its individual elements) in educational and professional situations, structured on the basis of the model of the activity of the mediator .; 3) formation of the project basis change participants of the technological foundations of the organization of a system for monitoring the effectiveness of the mediative activities of the volunteer unit.
The basic principles of modeling the project change of schoolchildren “Pedagogical mediation”:
- the principle of integrity and consistency, the implementation of which includes: prevention and rehabilitation as components of the mediation process, which, in turn, imply a whole complex of integration of co-educational and supporting educational opportunities of an educational institution, society, family, law enforcement agencies, etc .; the interaction of which will ensure the implementation of a “recovery approach” in the mediation process with children and adolescents, including in the resolution of disputes and conflicts and after the commission of offenses; skills and abilities aimed at comprehensive restoration of relations, trust, material and moral damage, etc .;
- The principle of social design, based on the conceptual approaches of the theory of "positive majority" (Zykov, 2010);
- the principle of axiology - the formation in children and adolescents of values of a morally healthy lifestyle, law-abiding, respect for the person, patriotism, etc .;
- The principle of legitimacy - the availability of the necessary legal framework for preventive activities.
- The principle of pedagogical support (tutoring, coaching), the implementation of which, unlike the traditional interpretation of crime as a violation
behavioral norms and laws of the state and society, is carried out on the understanding of juvenile crime as a consequence of the lack of positive skills of adolescents out of the current conflict situation, how their inability to find appropriate ways to meet their needs, on the one hand, and the lack of an effective system of socio-psychological and social -pedagogical aid stumbled, on the other. This approach allows us to consider conflict situations in various spheres of vital activity of minor adolescents as the basis for organizing the process of their recovery in society. The essence of pedagogical mediation is to carry out activities aimed at reducing violent methods of resolving conflicts and precluding the use of restrictive-punitive measures against the violator (Ovchinnikova, 2007; Ulyanova, 2019).
The result of the project shift is the creation of two types of volunteer mediation programs: intraschool and regional.
Conclusion
Considering the problems of socialization of schoolchildren in the conditions of digitalization, we proceeded from the fact that, on the one hand, the real processes of market modernization of the economy determine the need to form an economically active population with a qualitatively new thinking, high competitiveness, social mobility and formed basic values that together provide optimal professional self-determination of graduates at the stage of general education. On the other hand, there is no effective model for managing the process of personal orientation of a person as a complex set of necessary knowledge, skills and abilities, a broad outlook, moral principles characterizing the concept of "profession". On the one hand, digitalization contributes to the expansion of schoolchildren’s perception of professional activities. On the other hand, the prospects for professional activity are determined by parents, who, according to psychologists, are becoming more and more distant in the hierarchy of significant “others” for adolescents.
The study showed a high level of parental confidence in the activities of the education system and out-of-school education in the socialization of schoolchildren. That allowed us to put forward a hypothesis and test it in practice that the career guidance activities of the school should be supported by parents. And the results of monitoring of surveys of parents that we received confirmed this. Knowing the specifics of the psychology of modern adolescents, the content of the project pedagogical shift is modeled as a space with a high emotional component, based on a positive attitude of teacher-student, student-student, teacher-parent, student-parent.
Therefore, the mission of the university in this case is not only to prepare students for admission to a particular university, but also to promote the self-realization of schoolchildren in extracurricular activities. These tasks are solved by pedagogical project (profile) changes of schoolchildren, which are carried out modularly during school holidays, and between vacations - during extra-curricular time. The emphasis in the activity of pedagogical changes in schoolchildren, in addition to vocational guidance, is made on the formation of 4K competencies: communication, collaboration, critical and creative thinking, which are defined as the most demanded competences in the future. And a significant component in the content of vocational orientation project pedagogical shifts of schoolchildren, taking into account the risks and threats of digitalization, is their media orientation.
As a result of the participation of university scientists in the organization of project pedagogical shifts of schoolchildren, it becomes possible to use scientific and methodical features of modern social and technical conditions in which young people enter life (new for schoolchildren’s parents and some teachers). Thus, the pedagogical project change of schoolchildren acquires the function of schoolchildren’s life-conscious orientation, since it is modeled with consideration of the countering risks and threats to their livelihoods resulting from the expansion of the vertical space of secondary socialization (trolling, bullying, aggression, etc.).
References
- Chistyakov, A.V. (2006). Sochializaciya lichnosti v Internet- kommunikacii: sochiokulturnii analiz [Socialization of the individual in the society of Internet communications: a socio-cultural analysis] (Doctoral Dissertation). Rostov-on-Don [in Rus.].
- Gergen, K. J. (1997). Social psychology as social construction: The emerging vision. In C. McCarty & A. Haslam (Eds.), The message of social psychology: Perspectives on mind in society (pp. 113-128). Oxford: Blackwell.
- Miroshnichenko, A.V. (2009). Psikhologicheskie issledovaniya informacionnoy kulyuri i osobennosty chennostno-smaslovoy sfery studentov, rabotaushih s informacionnima technologiyami [Psycchological studies of information culture and peculiarities of value-value sphere among students working with information technologies]. North-Caucasian Psychological Journal, 3, 38. [in Rus.].
- Ovchinnikova, T.S. (2007). Pedagogicheskoe posrednichestvo v uregolirovanii konfliktov s uchastiem deviantnih podrostkov [Pedagogical mediation in conflict resolution with the participation of deviant adolescents] (Doctoral Dissertation). Tyumen. [in Rus.].
- Piskunova, V.E. (2011). Buducheee v pedagogicheskom obrazovanii v Rossii: kto budet uchit’ homo innovaticus [The future of pedagogical education in Russia: who will teach homo innovaticus]. Universum: Bulletin of Herzen University, 6. [in Rus.].
- Remm, T. (2015). Sociocultural Space: Spatial Modelling and the Sociocultural World. Tartu: University of Tartu Press.
- Savchenko, T.A. (2011). Vzaimodeistvie sem’I I shkoly v otechestvennoy pedagogike vtoroy poloviny XVШ – end ХХ kak sochiokulturnoe yavleniye [The interaction of family and school in the national pedagogy of the second half of the XVIIIth - the end of the twentieth centuries as a socio-cultural phenomenon] (Doctoral Dissertation). Moscow [in Rus.].
- Shakurova, M.V., Dyuzhakova, M.V., & Akulova, L.N. (2017). Diagnostics of educational space: to the problem of determining criteria. In Educational space in the information age (EEIA -2017). Collection of scientific papers of the international scientific-practical conference (pp. 182-189). [in Rus.].
- Sorokoumova, E.A. (2015). Pokolenie Z v prochesse samopoznaniya. Sochialnyy komp’uting: technologii razvitiya, sochialno-gumanitarnii [Generation Z. In the process of self-knowledge]. In Social computing: fundamentals, technologies of development, social and humanitarian effects. Materials of the fourth International Scientific and Practical Conference (p. 52). Moscow: Moscow State Pedagogical University. [in Rus.].
- Ulyanova, I.V. (2019). Aktualmost’ I sushnostnie charakteristiki pedagogiki smis. Ozhisnennich orientacii kak nauchnogo napravleniya [Relevance and essential characteristics of pedagogy of life meaning orientations as a scientific direction]. Modern problems of science and education, 1. [in Rus.].
- Zaidman, I.N., & Mozheykina, L.B. (2007). Tehnologiya terapevticheskoi didaktiki v aspekte formirovaniya tolerantnosti podrostkov [Technology therapeutic didactics in the aspect of the formation of tolerance of adolescents]. Psychological science and education, 2, 50-59. [in Rus.].
- Zanina, L.V., & Kirik V.A. (2018). Tendencii vishsey shkoly I economicheskoy situacii [Trends in the development of higher education in the current economic situation]. Problems of modern education, 2, 72-78. [in Rus.].
- Zanina, L.V., Kirik, V.A., Bondarev, M.G., & Zashchitina, E.K. (2017). Federal university public department as an instrument of higher education quality assessment by professional community.. Science. Education. Innovations, 6, 205-207.
- Zykov, O.V. (Ed.). (2010). Profilaktika patologicheskih form povedeniya “v treh tomah [Prevention of pathological forms of addictive behavior "in three volumes]. In Vol. I. Positive majority: technologies influencing personal choice. Primary prevention (p. 342). Moscow: RBF NAS [in Rus.].
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 September 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-068-6
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
69
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1054
Subjects
Education, educational equipment, educational technology, computer-aided learning (CAL), Study skills, learning skills, ICT
Cite this article as:
Zanina, L. V., & Miroshnichenko*, A. V. (2019). Collaboration Of High School And School In Ensuring Socialization Of Students. In S. K. Lo (Ed.), Education Environment for the Information Age, vol 69. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1008-1017). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.09.02.114
