Abstract
The growth of Indonesian mass media shows a significant number, the increasing number of journalists in Indonesia follows it. Journalists as the spearhead of the mass media must have a good performance in order to compete with other media. Journalist’s job performance is a significant determinant of mass media quality. Journalist’s job performance consists of task performance and contextual performance. The individual factors of journalists such as motivation, extraversion, and self-efficacy are important factors in the competition of mass media in order to generate news and strategies in obtaining advertising and increase journalists job performance. This study using SmartPLS 3.0 to examine the importance of performance-matrix analysis (IPMA) from antecedents of individual variable factors as endogenous variables. Search data using questionnaires to local newspaper journalists who gathering news in politics and government newsdesk. In conclusion, it is known that extraversion not to important compared with motivation and self-efficacy to improve Indonesian Journalist Job Performance.
Keywords: Motivationextraversionself-efficacyjournalists job performance
Introduction
In Indonesia, the era of press freedom has been reborn after more than 40 years of disappearance, and it occurred at the end of the New Order government in 1998 and was replaced by the Order of reform.
Press freedom consists of the First structure (freedom from) where the freedom of the press is understood as a condition accepted by the media as a result of a certain structure. The state is called free press when there is no censorship, free from pressure on journalists, independence from the influence of the economic environment including ownership, no rule of law that curbs freedom of the press and free from social and political pressures (Hutagalung, 2013).
Press freedom consists of the First structure (freedom from) where the freedom of the press is understood as a condition accepted by the media as a result of a certain structure. The state is called free when there is no censorship, free from pressure on journalists, independent of the influence of the economic environment including ownership, no rule of law that curbs freedom of the press, free from social and political pressures. The second is performance (freedom to) where the freedom of the press is also measured by how the press use the independence. For example, whether media coverage has been honest and fair, disclosing the truth and defending the public interest.
Press freedom is proven to have the ease of obtaining business licenses for Publishing Press, then the ease to set up community newspapers, magazines, and tabloids. Freedom of the press in Indonesia in recent years has encouraged the increase number of media: print media, electronic and cyber media, as can be seen in table
The development of mass media in Indonesia can be seen in the increase number of News online specifically 112 in 2013, 180 in 2014, 223 in 2015, 251 in 2016 and 295 in 2017. In terms of radio stations on the other hand, the number has increased from 500 in 2013, 600 in 2014, 613 in 2015, 642 in 2016 and 674 in 2017.Television stations has also showed an increase from 200 in 2013, 223 in 2014, 250 in 2015, 275 in 2016 and 300 in 2017. Due to the increasing number of mass media used in Indonesia, the number of print media has showed a slight decrease from 567 print media in 2013, to 425 in 2014, 321 in 2015, 311 in 2016 and 293 in 2017.
The era of the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) demanded quality of natural resources (HR) is reliable. Therefore, Indonesia as part of the AEC should improve the quality of human resources. Indonesia's competitiveness in the labor market efficiency pillar was ranked 115th out of 140 countries and is the lowest among ASEAN countries ( Schwab, & Sala-i-Martín, 2016).
Journalists in the era of the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), journalists need to improve Job performance, because Foreign media companies can establish a media company in the city, or even in the area, for it is expected that the entire journalists also should be prepared, especially by continuing to hone his skills and professionalism. Journalist organizations and organizations press can realize the importance of competence to deal with the open competition (Astro, 2013).
Problem Statement
Base on interview with the Chief Editor local newspapers Radar Bandung ("Azzam interview", 2017) the reason of poor job performance among Indonesian journalists may be due to the lack of support by the management facilities, salaries and training. Other professions in Indonesia, such as teachers and lecturers are supported by good salaries, especially when they already have a certification of competency. Unfortunately, when a journalist got their certificate of competence, they are not paid
Indonesian journalism suffers from a bigger problem – lack of well- trained journalists who see their work as a service to the public (Ristiani, 2017). It is a challenge for the press media in providing support towards the journalists. According to (Pintak & Setiyono, 2011), Indonesian reporters and editors see their own lack of professionalism and poor journalistic ethics as the greatest challenges in their industry.
The journalist's profession does not adhere to a specified working hours. Therefore, it is stated that the working hours of reporters are 24 hours. The job of reporters is to cover all current and actual events. Moreover, these events can happen any time within a day, so the profession of journalists has became a profession that is rarely been given a holiday (Waldyazkia & Pramadewi, 2017). In addition, the expectation from the journalist job performance is high, because the journalists are required to meet the daily deadline, which makes the journalists under pressure ("Azzam interview", 2017). The challenge is in keeping the journalists to constantly be motivated and result-oriented to achieve the best performance. Past researches studied about factors that affect the work of journalists; most researches were based on a conceptualization of influences on journalism in terms of their objective effects. Individual factors influencing journalist performance still needs to be explored (Melissa, 2015).
Research Questions
Based on the discussion above, this study attempts to address the following underlying research questions:
Purpose of the Study
This research will be contributing to the journalist practices on Indonesian job performance. Through this research will also contribute to the influence of factors (motivation, extraversion and self-efficacy) in the environment journalist work as individual influences.
Research Methods
This study adopts a quantitative research design to answers the research questions and to fulfill the objectives of the study. According to Polit and Beck (2008), research design is researcher’s reflection on the plan for obtaining answers to the research question and to fulfill the research objectives. It is the strategies that the researcher plans to adopt in order to develop information that is accurate and interpretable (Wagner, 2013). Population on this study is Indonesian Journalist newspaper with the criteria permanent employee and journalists who gathering on the political and government news desk.
Table
It can be seen in Table
In conclusion, the journalist respondents are made up with almost equal number of male and female, the same with their marital status. Mostly, the respondents are from productive age group, those aged 20 to 40. Their annual income varied from IDR 500.001 to IDR 5.000.000. Most of the respondents’ education is Bachelor Degree, followed by Master Degree.
Hypothesis Development
The motivation schemes are satisfactory, relevant and good for journalists, and thus they fulfill the needs of the journalists to make them perform well if they are not satisfactory. The motivation schemes tend to diminish the morale of employees or journalists to perform well (Janerose, 2014). The employee motivation is obviously important. In fact, it is one of the most important and essential factors for the achievement of employees, and ultimately the organizational targets and goals (Berman, Bowman, West, & Wart, 2010). Ekerman (2006) asserts that motivation to work, whether intrinsic or extrinsic, are essential in the lives of workers because they form the fundamental reason for working in life. Motivation increases the job involvement by making the work more meaningful and interesting as well as the fact that it keeps the employees more productive and improves their subsequent job performance.
Hypothesis 1a: Motivation is positively related to Journalist Job Performance.
Extraversion has positively influenced job performance because the main characteristics of extraversion are sociable, assertive and active. People with these characteristics are energetic in direct participation, confident in putting forward their views and not conflicted with the others; therefore, they could produce good job performance (Yang & Hwang, 2014). Personality traits such as extraversion could have a positive association with job performance (Binti Rusbadrol, Mahmud, Suriani, & Arif, 2015).
Hypothesis 1b: extraversion is positively related to Journalist Job Performance.
Creative self-efficacy has a significant and positive relationship with job performance (Nicolae & Wagner, 2011). Vancouver, Thompson & Williams (2001) argued that the effect of creative self-efficacy on performance is due to the influence of past performance on self-efficacy, self-efficacy is defined as individuals’ beliefs about their capabilities to produce designated levels of performance (Bandura, 1994). The performance of the employees is positively influenced by the overall self-efficacy. It is also proved that the organizational behavior of the skeptical practicing professionals is usually influenced by a significant amount of confidence (Cherian & Jacob, 2013).
Hypothesis 1c: Creative self - efficacy is positively related to Journalist Job Performance.
Findings
The relationships of the direct paths among the exogenous variables and endogenous variables are presented in the structural model. Bootstrap analysis was conducted to assess the statistical significance of the path coefficients after computing the path estimates. To determine the significance of the path coefficients, a nonparametric bootstrapping method was applied to obtain the t-values (with 500 resamples and 218 cases). According to Chin (1998), 500 resamples is the usual recommendation when conducting the bootstrapping procedure. This section discuss of hypotheses were tested with the corresponding statistical analyses. Based on PLS path analysis by using SmartPLS 3.7, the empirical result of this work encompasses the assessment of hypothesized main effect, in direct effect is a one-way hypothesis, was declared or significance if the t – test value is > 2.33 (α=1%) and the path coefficient value is positive. Direct effect in this study tested 3 hypothesis and the t-values from the hypothesis testing result calculation are shown below (see table
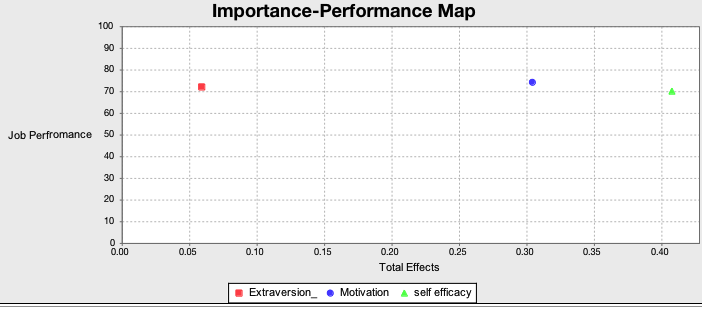
Asessment Importance Performance Map (IPMA)
The IPMAwas carried out using smartPLS 3 software by taking the performance of each exogenous latent variable into account. IPMA results in a priority map for management-oriented presentations (see figure
Conclusion
This study aimed to investigate the direct relationship of individual factors in journalist job performance on Indonesia. The individual factors are motivation, extraversion and self-efficacy. This study found that motivation (t=3.15) and self-efficacy (t=3.67) had significantly and positively relationship with journalists’ job performance, extraversion (t=0.66) had no significantly and positively relationship with journalists’ job performance.
References
- Annual Report Indonesian Press Council (2018). Retrieved from https://dewanpers.or.id
- Astro M. M. (2013, December 14). PWI Tekankan Pentingnya Profesionalisme dan Kompetensi Jurnalis. Retrieved from http://www.antarajatim.com/lihat/berita/123222/pwi-tekankan-pentingnya-profesionalism-dan-kompetensi-jurnalis
- Azzam interview (2017). Permasalahan Wartawan Media Cetak di Indonesia. Bandung Indonesia.
- Bandura, A. (1994). Self-efficacy. In V. S. Ramachaudran (Ed.), Encyclopedia of human behavior (Vol. 4, pp. 71-81). New York: Academic Press. (Reprinted in H. Friedman [Ed.], Encyclopedia of mental health. San Diego: Academic Press, 1998).
- Berman, E. M., Bowman, J. S., West, J. P., & Wart, M. R. V. (2010). Motivation: Possible, Probable or Impossible? Human Resource Management in Public Service: Paradoxes, Processesand Problems (pp. 180). California: SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Binti Rusbadrol, N., Mahmud, N., Suriani, L., & Arif, M. (2015). Association between Personality Traits and Job Performance among Secondary School Teachers. International Academic
- Cherian, J., & Jacob, J. (2013). Impact of Self Efficacy on Motivation and Performance of Employees. International Journal of Business and Management, 8(14), 80–88.
- Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In G. A. Marcoulides (Ed.), Methodology for business and management. Modern methods for business research (pp. 295-336). Mahwah, NJ, US: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
- Ekerman, G. (2006). Job Enrichment and Staff Motivation. Human Resource Management (pp. 183-191). Cape Town: Maskew Miller Longman (Pvt) Ltd.
- Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance. Long range planning, 46(1-2), 1-12.
- Hutagalung, I. (2013). Dinamika Sistem Pers di Indonesia. Interaksi: Jurnal Ilmu Komunikasi, 2(2).
- Janerose, R. (2014). The Impact of Motivation on Journalists’ Performance. A case of Citizen and The Guardian newspapers in Tanzania. ST.Augustine Universty Of Tanzania.
- Melissa, K. (2015). The Internal and External Influences on Individual Journalists. California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo.
- Nicolae, O., & Wagner, G. (2011). Towards simulation of organizational norms. Proceedings - Winter Simulation Conference, (1), 3104–3115.
- Pintak, L., & Setiyono, B. (2011). The Mission of Indonesian Journalism: Balancing Democracy, Development, and Islamic Values. The International Journal of Press/Politics, 16(1), 185–209
- Polit, D. F., & Beck, C. T. (2008). Nursing research: Generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Ristiani, R. (2017). Profesionalisme Wartawan dalam Peliputan Berita Radio di Rri Pekanbaru. Jurnal Online Mahasiswa Fakultas Ilmu Sosial dan Ilmu Politik Universitas Riau, 5(1), 1-15.
- Schwab, K., & Sala-i-Martín, X. (2016, April). The global competitiveness report 2013–2014: Full data edition. World Economic Forum.
- Vancouver, J. B., Thompson, C. M., & Williams, A. A. (2001). The changing signs in the relationships among self-efficacy, personal goals, and performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(4), 605-620. DOI:
- Wagner, J. D. (2013). Communication satisfaction of professional nurses working in selected public health care services in the city of Johannesburg (Unpublished master thesis). University of South Africa.
- Waldyazkia, A., & Pramadewi, A. (2017). Pengaruh Lingkungan Kerja Dan Karakteristik Individu Terhadap Stres Kerja Wartawan PT Serambi Media Press di Kota Padang. Jurnal Online Mahasiswa Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Riau, 4(1), 562-574.
- Yang, C. L., & Hwang, M. (2014). Personality traits and simultaneous reciprocal influences between job performance and job satisfaction. Chinese Management Studies, 8(1), 6-26. https://doi.org/10.1108/CMS-09-2011-0079
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
02 August 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-064-8
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
65
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-749
Subjects
Business, innovation, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues
Cite this article as:
Nuraeni, R., Tan, C., & Azmawati, A. A. (2019). The Influence of Individual Factors on the Indonesian Journalists Job Performance. In C. Tze Haw, C. Richardson, & F. Johara (Eds.), Business Sustainability and Innovation, vol 65. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 742-749). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.08.75

