Abstract
In our study we consider that the physical training with and without the ball in football can developed the motion capacity and also the effort capacity, adapted to the principal technical and tactical components of the football game. Physical preparation is realized with different movements who try to developed and improve the physical qualities requested by the particularities of the football game. Our idea is to obtained a superior physical training, a request of our game conception and is made only with a multilateral physical training and the harmonious combining of the general physical training to the specific one. In this study we try to develops and improve the physical qualities requested by the technique and tactics requested by the game. From this point of view, we try to build programs to improve physical qualities and to made a good preparation for the football game. Our conclusion for this study is a new type of training, during practice in all the training periods, the specific physical training programs to the level of B youth footballers, dosed and programmed appropriately to the preparing period, aiming, by this process, at the optimization of the specific physical training, all this things can lead increase technical and tactical game capacity.
Keywords: Experimentinginstructionfootballphysical training
Introduction
Physical preparation is realized by the aspects of better specialization; this is why in our study we try to use selective exercises, when analytical type is predominant, in pre competion period which the effort load is dosed depending on the motion quality aimed at (Cernăianu, 200).
The reason of this selection are among the basic and specific technical methods, combining the objectives of the technical advancement to those of the manifestation to maximum level of the motion qualities required in any of the executions performed (Neţa, 2008). It does not replace the effects and the effectiveness of the general physical training, nor does it exclude it (Neţa, 2005).
The specific physical training is characterized by movements developing and improving the physical qualities requested by the particularities of the football game technique and tactics (Rădulescu, 2007). Assuring a superior physical training, a request of our game conception, is made only if at its basis stands the multilateral physical training and the harmonious combining of the general physical training to the specific one (Apolzan, 1999).
In football, performance is strictly determined by the level of development of a complex set of motion qualities, (Trapattoni, & Cecchini, 2005). Specific physical training is made by strictly specialized means which develop the combinations of qualities, primarily determined by the particularities of football, by the muscle groups employed to effort, by the strain, etc. Suspension training exercises may help adjacent muscle groups to work together in a synergistic fashion, or as a single unit.
This is one of the primary focal points of any type of functional training. Suspension training exercises may help adjacent muscle groups to work together in a synergistic fashion, or as a single unit. This is one of the primary focal points of any type of functional training (Curitianu, & Catanescu, 2016). The football players’ yield is determined by the relation between the two types of physical training. In order to carry out the physical training to a superior level, supplementary factors are used, such as the recovery methods of vitaminization, nutrition, practices at an average or high altitude and adequate equipment (simulators, etc) (Bompa, 2002). For the professional football players, there may be planned both separate lessons of general physical training, and specific physical training (Stancu, 2009).
Model of microcycle applied weekly to B junior team of FC Arges (Leonte Ianovschi) in the National Junior Championship (competition period 2017/2018) The pre-competition period – Defence Area
O.1. – Develop general and specific capacity to move in the field in a direct or indirect relation to the ball.
O.2. – Develop ability to lead the ball under specific game conditions with the semi active and active opponents.
O.3. – Improving the capacity to adapted to own teammates having an intensity specific to the official match (Table
Problem Statement
In the first phase we realized a documenting to a national level and after we realized a comparation with reference to the international level on the practices’ patterns and the manner of approach of the actual practices, it results that, nationally, we are outrun by the great football academies and schools in Europe, this phenomenon being tested by use of practical performances.
Our idea was how it s better to use and administering in the practice of C, B, A youth footballers adapted programs with and without the ball during all the training periods programmed and dosed correspondingly to the respective period of time, and after we build the programs it was important for us to test in practice at a national level, the application of the specific physical training programs with and without the ball, so that, in the end of the practical experiment, we bring real, tested arguments that it is worth implementing the use of the specific physical training programs with and without the ball, including in B category of youth players (14 – 16 years old).
Research Questions
For us was a challenge to realize a different projection of the programs and planning to the level of B youth players within the national football, by implementing the adapted physical training programs with and without the ball will have a favourable impact on the optimization of the technical tactical play capacity at this age, increasing the general performance level and the promotion of youth players even from 14 -17 years old.
It was a real process to administer into the instruction process adapted physical training programs with and without the ball to the level of B youth footballers, rethought over the way of conceiving and their content achieved by modern quality processes with the help of the Soccer Tutor Tactics Manager 3D Software, especially conceived for the football coaches, but especially, key moments of their introducing to the planning at this age, dosed correspondingly in the training periods, will contribute effectively and efficiently to the improvement of the technical tactical play capacity and implicitly to the increase of performances;
We think it is useful to implement the specific physical training programs with and without the ball in the instruction process in all the training periods, conceived and dosed depending on the period, this aspect being helped by the way of modern conceiving, having at its fundament the Soccer Tutor Tactics Manager 3D Software, which is a real source of inspiration for the academies and children and youth players facilities, legally approved by the International Commissions of youth players from UEFA agreement
Purpose of the Study
This experiment is a new point of view of previous experiment, following which the tests and trials have been filtered, emphasizing the quality of the specific physical training programs with and without the ball, which is beneficial to B youth footballers’ instruction process, lied at the basis of the carry out of the experimental process undergone during two seasons, in the Junior Footballers National championship, approximately 2 years, carried out within the experiment that we chose, more exactly, within the “Dănuţ Coman” ASC Football Club. I make the mention that, by obtaining the consent in writing of B youth player groups aged 14 -16 years old, within the ,,Dănuţ Coman” ASC Football Club I have had the opportunity of carrying out the practical experimental process under real, official conditions for obtaining sports performances, with quality material and human values nationally, but also at a European level by the finite products that they have records.
Research Methods
The national and international specialty literature study method: The observation method; The modern method of conception and presentation of the training themes by use of the Soccer software; Tutor – Tactics Manager; Tests and measurements’ method; Statistical- mathematical method; Experimental method; Graphical and tabular method.
B).
C).
Findings
We realize some contributions to accomplishing the planning of the programs experimented into practice (Table
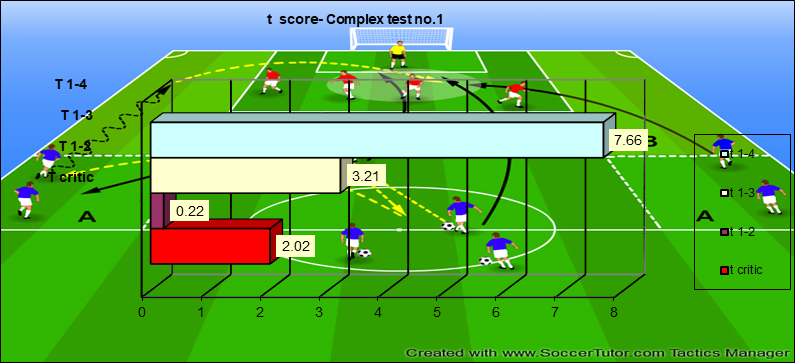
Analysis, processing and interpretation of the data issued upon the completion of the practical experiment - Test – Complex test no. 1
In the
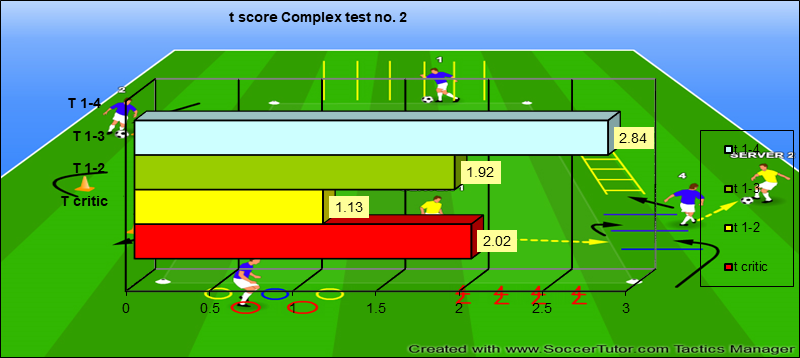
Test – Complex test no. 2
For complex test no. 2 we may interpret that upon the processing of the results between the first two testing, the means’ difference does not show us a significant increase of the results, the t calculated having a score of 1,13 inferior to the t critical for the threshold of 0,05 that we determined. This fact that we are ascertaining may be due to the content of the programs we proposed, which did not aim primarily at this parameter in the first part of the proposed. We may notice that in between testing 1- 3 as well is seen an insignificant increasing tendency of the initial level with a significance of the thresholds registered of 0,07, respectively which shows that in this period the content of the programs we proposed did not register a higher effectiveness like the first period (Figure
Conclusion
After the experimental part, finally we have some conclusions about this subject:
From our point of view is important to develop physical training programs with and without the ball, with a new design of projection documents: (annual plan, regular training plan, weekly microstructure of training and specific physical training programs in the four periods, preparing, pre competition, competition and off transition)
We consider that It is necessary to have specific physical training programs who contribute to improve the technical aspects and also tactical play capacity, the level of the technical executions, a specific objective of the game and implicitly of the performance related objectives.
The aims of tis specific training at the age of B youth footballers (14 -16 years old) have been created for adapted programs, when every period of the time was determined, so that the reason to realize a superior quality standards in order to favour its manifestation under optimum conditions in the competition period.
For us, the assessment system of B youth players in football, can close the entire experimental process because allows us to made a functional feedback of the activity of planning – administering- assessing, having as a result the improvement of the technical tactical game capacity and implicitly, the entire activity.
To have a exactly estimation of the level of the athletes capacity evaluated in this experiment, there have been administered control tests for the segments involved in the carry out of the specific movements: lower limbs (genuflections, long jump, vertical jump – détente, sprint running specific to football, maintaining the ball in place, maintaining the ball from movement, complex test 1 and 2) , upper limbs (push ups, pull ups in the arms, the specific test for goalkeepers 1 and 2) Also, there have been administered control tests for the estimation of the functional capacity ( recumbent position Pulse and orthostatism, blood pressure, Ruffer Test, the Sergent test) and of the somatic capacity;
Like a final conclusion we can say about the performance in football game for each position, the comparison of the level in the beginning and at the final of the experimental program, as well as upon the administering of the training programs, the exact determination of the dosing of the actuating systems.
References
- Apolzan, D. (1999). Fotbal 2010 [Football 2010], Bucureşti: F.R.F.
- Bompa, T. (2002). Teoria si metodologia antrenamentului sportiv – Periodizarea, [Theory and methodology of training. Periodization], Constanta: Ex Ponto.
- Curitianu I., & Catanescu A., (2016). The Effect of Six-Week TRX Suspension Training on Physical Skills in Female Skier Students, The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences EpSBS, 1456-1460, DOI: 10.15405/epsbs.2017.05.02.178
- Cernăianu, C. (2002). Football The professional coach’s manual, Bucuresti: Rotehpro Publishing House,
- Neţa, Gh. (2005). Fundamentele jocului de fotbal, [Fundaments of the football game], Cluj-Napoca: Risoprint.
- Neţa, Gh. (2008). Strategia performantei in fotbal [Performance strategy in football], Cluj-Napoca: Dacia Publishing House.
- Rădulescu, M., (2007). Tehnica – factor prioritar [Technique as a priority factor], Bucuresti: Răzeşu Publishing House.
- Stancu, M., (2009). Bio-periodicity and its influence on the football results obtained by the student teams during the “university spring” sport competition, Citius, Altius, Fortius 9 (4), 115-118.
- Trapattoni, G., & Cecchini, E., (2005). Konzeption und Etwicklung der Taktik im Fussball, Germany: Prhontos.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
15 August 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-066-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
67
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2235
Subjects
Educational strategies,teacher education, educational policy, organization of education, management of education, teacher training
Cite this article as:
Cojanu*, F., & Visan, P. F. (2019). Optimizing Phases Of Attack With Specific Physical Training Programs With The Ball. In E. Soare, & C. Langa (Eds.), Education Facing Contemporary World Issues, vol 67. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 2109-2116). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.08.03.262
