Abstract
The aim of this research was to develop instructional materials to teach descriptive text material in the form of bilingual pictorial dialogue for the 8th grade students of State Junior High School (SMPN) 6 Mengkuang Kabupaten Bungo Jambi Province. The design of this research is research and development (R and D). This research was conducted by using 4-D models which consists of 3 steps, namely define step, design step, and develop step. The product was validated by three validators. Two validators are lecturers at English Education Program Faculty of Education and Teacher Training the State Islamic University Sulthan Thaha Saifuddin Jambi and the other validator was the English teacher of SMPN 6 Mengkuang Bungo Regency. To get the data about the practicality of the product, the questionnaire was distributed to the English teacher and 34 students. Then the data of questionnaire was analysed. The validity score was (95%) which is categorized strongly valid. The results of questionnaire from the teacher showed that the practicality of the product was (95%) which is categorized strongly practical, while from the students the score was (87%) which is categorized practical. The module was categorized strongly valid and practical. It means that the module is easy to use, effective and efficient. The teacher and students can use this module as an instructional material in teaching and learning descriptive text.
Keywords: Moduledescriptive textbilingual pictorial dialogue
Introduction
Sadiman (2009) stated that learning process is essentially a process of communication, namely the process of delivering a message from the message source via a specific channel or media to the receiver of the message. In this case the teacher is as a messenger and student is the receiver of the message. In delivering the messages, the teacher often fails because of some challenges and obstacles which make the communication become ineffective. Therefore, Lufri (2010) stated, “the skill of a teacher is required in order to create an effective learning process to develop the potential of students. One of the skills which are needed by the teacher are the ability to develop and use instructional materials” (p. 73).
Ahmadi (2011) explained that iinstructional materials are all kinds of materials that are used to help teachers as instructors in carrying out the teaching and learning activities in the classroom. The materials in question can be written material or unwritten material. Teachers need to have or use appropriate teaching materials which is in line with the curriculum, target characteristics, demands troubleshooting learn some vital lessons.
The availability of various instructional materials help the students to get many benefits, such as the learning activities become more attractive and interesting, the students will get more opportunity to learn independently and the teacher-centred style in learning can be minimized. In line with learning independently and minimizing teacher-centred style, Prasojo et al. (2017) revealed in his research finding that the advantages of Social Network Services (SNS) use in writing courses. He stated that some advantages found through the focus group discussions are offering possibility of peer review, independence from time and location, perceived progress in vocabulary, and grammatical improvement. For language learning itself, some studies have found association between SNS use and improvement in new literacies and language skills in language class (Lee, 2011; Mills, 2011), and others have focused on nonstandard uses of language in online interactions (Lee, 2011). Stevenson and Liu (2010), Mills (2011), and Lee (2011) reported that users of SNS in language learning achieve the following advantages: 1) perceived progress in vocabulary or vocabulary acquisition, 2) increase confidence in using the target language, 3) fostered an interactive community for communication, interaction, and discussions, 4) L2 learners’ participation on SNS appeared to have a positive impact on their oral proficiency, and 5) syntactical complexity or grammatical improvement. For all finding showed that the advantages of using SNS contributed to vocabulary building and grammar improvement. Furthermore, students will also be easy to learn the competence to be mastered in learning writing.
Nwike (2013) in his research revealed that those students who are taught by using various instructional materials performed better than those who are not taught by using various kinds of instructional materials. This finding is in line with Olagunju’s study (2000) found out that there was a remarkable difference in the achievement scores between the students who are taught by using various instructional materials and those who are not exposed to the various kinds of instructional materials. Therefore, a general consensus that instructional materials enhance teaching & learning, and it leads to better students’ achievement. (as cited in Nwike, 2013).
Considering the importance of teaching materials explained above, the researcher is interested in ddeveloping iinstructional material to teach ddescriptive text. Since the students still have many difficulties in identifying the main idea of the text, the students are also difficult to construct the sentences properly they tend to ignore the text organization such as the generic structure. Most of students still do not understand the generic structure of descriptive text well because the materials provided by the teacher are not suit the students need. Therefore, the students become demotivated in learning the text. It is indicated by (70%) the results of the students’ test were still confused about the generic structure of descriptive text. Based on the phenomenon above, the researcher assumed that it is important to develop an interesting material to teach Descriptive Text. In order to match the materials with the students’ need, the researcher has distributed questionnaire to the student to analyse the student’s need. From the results of the questionnaire, the researcher obtained that 85% of students agreed that the instructional materials will be presented in the form of modules that is nuanced on bilingual pictorial dialogue.
Problem Statement
This research used 4-D model which consists of three main steps namely Define Step (Preliminary Analysis, Curriculum Analysis, and Media Analysis), Design Step and Develop Step (The Validity and Practicality of the Product).After developing the product, the researcher tried out the product to the students in order to get the data about the effectiveness of the product.
Research Questions
In developing the instructional module that is nuanced on bilingual pictorial dialogue to teach descriptive text for the 8th grade students of SMPN 6 Mengkuang Kabupaten Bungo Jambi Province, It designed for students to learn independently (self-instruction). The first step of developing the module is creating or drawing the character of the dialogue then the character will be edited by using Photoshop. The next step is collecting the pictures that are relevant to the descriptive text. This module arranged base on the School-based Curriculum (SBC), in Indonesia we call Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) curriculum.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this research is to develop the instructional module that is nuanced on bilingual pictorial dialogue to teach descriptive text for the 8th grade students of SMPN 6 Mengkuang Kabupaten Bungo. In addition, the results of this research are expected to give contribution to the teachers, students, and further for other researcher. For the teacher, as an alternative instructional materials to help students understand the subject matter. For the students, as a learning resource that help to make easier to understand the material, especially descriptive text. Then for the other researchers, as a reference source and the example of developing module and others advanced research.
Research Methods
This research used Research and Development (R&D) method since the objective of the research was to develop an instructional material. The subject of the research was the eighth grade students of
Findings
Define Step Preliminary Analysis
The researcher gave the questionnaire to 20 students as the representative of the 8th grade SMPN 6 Mengkuang. The questionnaire was used to know the problems of the students in using the module used by the teacher. The questionnaire was also used to know the students’ needs in the development of instructional materials. The results of questionnaire showed that (65%) of students stated that the existing instructional materials are not interesting. Therefore, the instructional materials in the form of modules need to be developed to fulfil the students’ need and interest and found. Moreover, the researcher found that (85%) of the students were interested.
Curriculum Analysis
Curriculum analysis cannot be eliminated in designing and developing the modules in order to match the contents of the module with the curriculum. After analysing the curriculum, the contents fo the module were then developed based on Standard of Competence (SK) and Basic of Competence (KD). SMPN 6 Limbur Lubuk Mengkuang uses SBC (KTSP) curriculum.
Students’ Analysis
The data was obtained by interviewing the English teacher. The results showed that most of students at 8th grade have different ability in understanding the material. Some of them were quick to understand and some of them were slow. Several students still had difficulties to understand the material. Therefore, one of the alternative ways to solve the problem is by developing more interesting instructional materials for the students. An interesting module will increase the motivation of the students to learn.
Media Analysis
From the result of interviewed and observation, the researcher found that the teacher rarely used module in the learning process because the teacher had not developed the instructional materials in the form of interesting module. Therefore, the researchers were interested in developing a module that nuanced on bilingual pictorial dialogue.
Design Step Preparing the Components of the Module
The design of the module was begun by searching the characters and pictures that are relevant to the material such as animals, things, person, places and emoticons. After selecting the pictures, then the researcher began to set up the pages by using Microsoft office publisher 2010. There were some points that the researcher did in this stage included an adjustment of layout, margin, font size, font type and space that used in designing the modules. The arrangement of layout was designed to make the readers interested in. The margin used was moderate type which the entire border was 1. 27 cm. The paper was A5 portrait with the size 14.8 cm x 21 cm. The font used was Comic Sans. This module was set up with 1.5 cm line spacing. It was based on general requirements of formal writing.
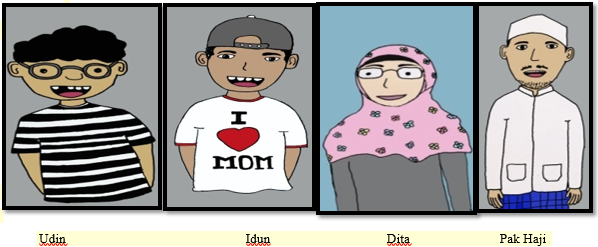
Creating the Characters of Module
In this step, the researcher created four characters for the dialog named Udin, Idun, Dita and Pak Haji. The characters were created by drawing the picture on a blank paper by using a pencil, and then the images were then scanned in order to insert the picture into computer. After that, the images were edited by using Photoshop application to give colour and make the character be attractive. Each of them has different characteristics. See the following pictures of the four characters (Figure
Designing the Cover of the Module
The cover was designed by using Photoshop application. The first step is designing and dominated by the yellow background of the cover with a retro model. The researcher chose retro shape because it simple, classic but it still becomes a trend style in this modern era. The combination between the circles will attract the reader’s attention. The cover contains the title of the module, the general description of the module, the level of the student, and some pictures that are representing the content of the material. After edited the cover, then it was inserted into the Microsoft Publisher 2010 to print it out.
Designing Preface of the Module
Preface of this module contains an overview of the contents of the module, stories of the characters in the dialog, consideration of the use of two languages (bilingual), an explanation of the additional contents in the module such as a smart dictionary, tips, and other general knowledge and also thanksgiving of the researcher (Figure

Designing Table of Contents of the Module
The table of contents contains the important points in the module such as Preface, instruction to use of the model,
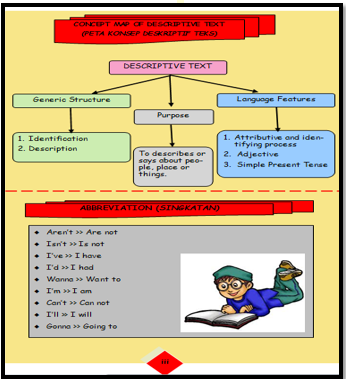
Designing the Concept Map of Descriptive Text
Concept map is the important part of the module. Concept map serves as a main instruction about the materials in the module. Displaying a concept map at the beginning part of the module will help the reader to be easy to understand the materials. The concept map was designed with different colour of each box. (Figure


Designing the Instruction to Use the Module
The first component of the module is the instructions to use the module. It contains the instructions how to use the module and the steps to learn materials. The researcher made two instructions for using the module for the teacher and students. The instructions were written in the box that contains some statements to guide the teacher and students in using the module.
Designing the Standard of Competence and Basic of Competence Descriptive
Standard of competence (SC), basic competence (BC), indicators, and learning objective for descriptive text were included in the module. They are used to know the purpose of the learning. Moreover, they are useful for the readers to know the achievements that must be obtained by the students (Figure


Designing the Introduction to the Characters of the Module
The researcher created 4 different characters of the dialog in the module they are
Design the Story Line and Material
In this step, the researcher wrote the storyline. The story is related to the materials that will be discussed in the module. Then, the materials were put in the dialog boxes in the module. The module was designed by using two languages Indonesia and English. The use of bilingual will make the students easier to comprehend the story. The pages on this module were designed with different colour of each background to make it interesting. The researcher displayed the materials in the form of dialogue. It aims at making the readers feel like reading a story book (Figure

esigning the Exercise of the Module
Exercises were presented with a picture that will facilitate the students in reconstructing the instruction to write the descriptive text. The exercises consist of blanks that should be filled by the students as an outline for writing descriptive text. The instructions of the exercises were also provided to guide the students. The picture facilitates the students to get their ideas in writing descriptive text.
Designing the Evaluation (Questions and Feedback)
The questions in the module used to know the student’s skills and comprehension of the materials. The function of feedback is to know the students mastery of the materials in the module (Figure


Designing the Answer Key
The answer key is used to help the teacher to check the students’ work. It will be more effective and efficient.
Writing References
References consist of the list of the sources of the materials included in the module (Figure


Development Step Module Validation
The module was validated by the lecturers of English Education Program Faculty of Education and Teacher Training UIN STS Jambi. The first validator was Dr. Faurina Anastasia, M.Hum and the second validator was Monalisa, S.Pd, M.Pd. the result of the validation is presented as follows Table
The results of questionnaire above show that the score of validity of the module is (95%) with the category strongly valid. It means that the module is valid in terms of content, language, presentation and the graphic. In the process of development, the module has been revised based on the suggestions and comments by validators.
Module Practicality.
Practicality test of instructional materials was conducted to 34 students of class VIII and 1 English teacher of
Conclusion
Even though the results of the research shows that the module is effective, but still the module has both strengths and weaknesses. The strengths of this module that the module is attractive for the students because the module was designed by using bilingual pictorial dialogue nuanced.
The use of two languages also facilitates the students to understand the material. For teachers, the use of this module in teaching will help the teacher explains the descriptive text effectively. Whereas, the weakness of the module is that the module only cover the materials for teaching descriptive text. Moreover, the module is only developed for writing skill.
Acknowledgments
Special Thanks to The Director of Islamic Higher Education, The Ministry of Religious Affairs Republic of Indonesia for all supports in providing a great opportunity through International Seminar for Islamic Higher Education (ISFI) cluster in participating and attending the EDU-WORLD conference to present the article paper from 9th – 10th November 2018 held by University of Pitesti and University of Bucharest Romania.
References
- Ahmadi, I., Khoiru. (2011). Strategi Pembelajaran Sekolah Terpadu. Jakarta: Prestasi Pustaka.
- Lee, L. (2011). Blogging: Promoting learner autonomy and intercultural competence through study abroad. Jurnal Language Learning & Technology, 3, 87-109. Retrieved from https://scholars.unh.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1144&context=lang_facpub
- Lufri. (2010). Strategi Pembelajaran Biologi. [Biology Learning Strategy], Padang: UNP Press.
- Mills, N. (2011). Situated learning through social networking communities: The development of joint enterprise, mutual engagement, and a shared repertoire. CALICO, 2, 345-368.
- Nwike, M. C., & Catherine, O. (2013). Effects of use of instructional materials on students cognitive achievement in agricultural science. Journal of Educational and Social Research, 3(5), 103.
- Prasojo, L. D., Habibi, A., Mukminin, A., Muhaimin, Ikhsan, Taridi, M., & Saudagar, F. (2017).
- Managing Digital Learning Environments: Student Teachers’ Perception on the Social Networking Services Use in Writing Courses in Teacher Education. The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology, 4, 42-55. Retrieved from http://www.tojet.net/articles/v16i4/1646.pdf
- Sadiman. A.S. (2009). Media Pendidikan, Pengertian, Pengembangan, dan Pemanfaatannya. Jakarta: Rajawali Press.
- Stevenson, M., & Liu, M. (2010). Learning a language with Web 2.0: Exploring the use of social networking features of foreign language learning websites. CALICO Journal, 7, 233-259. Retrieved from https://api.equinoxpub.com/articles/fulltext/23033
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
15 August 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-066-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
67
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2235
Subjects
Educational strategies,teacher education, educational policy, organization of education, management of education, teacher training
Cite this article as:
Taridi*, M., Rozal, E., & Sanjaya, M. E. (2019). Developing English Instructional Materials To Teach Descriptive Text. In E. Soare, & C. Langa (Eds.), Education Facing Contemporary World Issues, vol 67. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1972-1985). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.08.03.243
