Abstract
The paper presents the assessment of social and economic situation in the republics of the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation in the perspective of existing trends in the labor market of the macroregion and existing features of social and demographic processes. It gives the analysis of prerequisites to the problems in labor market in the subjects of North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation. This study is based on statistical analysis of dynamics of various parameters characterizing social, economic and demographic processes in the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation. The empirical data obtained during the study are synthesized at their theoretical generalization. The study resulted in the assessment of social and economic trends in the region regarding employment, unemployment, reproduction of population and workforce. The tendency towards the reduction of the difference in workforce reproduction between territories of the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation and the average Russian level in general is revealed on the basis of the labor replacement coefficient. It is shown that the employment within territories of the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation is the result of long-term social, economic and demographic factors. This period is also characterized by unregulated gradual delay of workforce reproduction and replacement dynamics, which might be the natural reason for the labor market strains in North Caucasian regions of Russia in the medium- and long-term perspective.
Keywords: EmploymentunemploymentNorth Caucasusworkforcereproduction of the population
Introduction
These days North Caucasus represents a tangle of complex and at times even insoluble problems related, first of all, to economic transformations in the Russian Federation over the past three decades. At the same time economic problems are closely linked to the development of the social sphere of constituent territories of the North Caucasian Federal District, level and trends of their social development. The consequences of poorly operating economic mechanism were particularly difficult for social and labor sphere. The income of over 1 million people in the region is below the poverty line, high youth unemployment is typical for the region, level and profile of staff training does not correspond to real requirements of the economy and the industry, there is no efficient personnel policy, and the income inequality of the society is quite high (Abdulmanapov & Abasova, 2009; Abdulmanapov et al., 2011; Sagidov, & Denevizyuk, 2014).
The problems in social and labor sphere are somehow caused by certain social, economic, political, cultural, national, geographical, demographic and geopolitical factors. The constituent territories of the North Caucasian Federal District need qualified regulation due to the variety of tools, social importance of workforce management and efficient labor market performance. First, they shall rely on the evidence-based idea on factors and features of workforce reproduction and trends of demographic development of the population in the regions.
Problem Statement
The majority of socio-economic indexes of the North Caucasus lag behind the average indicators in Russia. High unemployment rates of the population in comparison with other regions of Russia are typical for these regions. The North Caucasian Federal District is included into the group of subjects of Russia with a critical situation in labor market and its position among the last ten Russian regions.
Thus, for example, Dagestan takes the 76th place regarding the employment rate of the working population. In 2016 the unemployment rate in the Republic of Ingushetia made 30.2%. Such regions as the Chechen Republic, the Karachay-Cherkess Republic and the Republic of Dagestan are also characterized by relatively low employment rate of economically active population (Figure
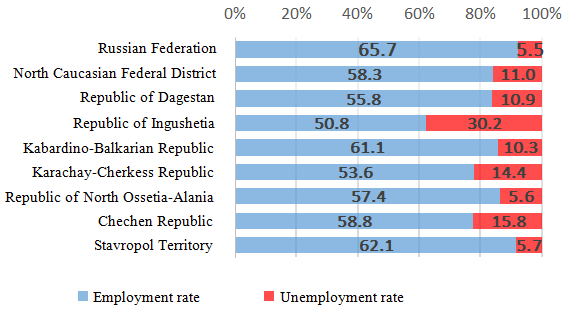
Unemployment in the North Caucasian Federal District is still extremely high. However, in 2016 the unemployment rate decreased in comparison with 2014 and made about half a million people, which is 11.1% of the total number of economically active population. As of the end of December 2016 the public employment agencies registered nearly 4% of economically active population as the unemployed. At the same time in general across the Russian Federation the number of the unemployed made 4 243 thousand people in 2016.
The following features characterizing the development of labor market and economy in general are typical for the subjects of the North Caucasian Federal District: surplus of human resources; large number of unoccupied population; high growth rates of human resources; low level of social facilities and services; low level of tax revenues and high level of subsidized budget; low investment attractiveness.
At the total population of 9 776 thousand people the workforce or economically active population is 4 535 thousand people, i.e. about 46% of the population in the region. At the same time, the population growth is observed in regions of the North Caucasus throughout a long period – the number the born in the region exceeds the number of the dead. Thus, the total birth rate in 2016 made 15.9 (in 2010 – 17.5). The mortality rate in 2016 was 7.8 (2011 – 8.5). In general, the natural increase rate in the North Caucasian Federal District in relation to quite average Russian level is high and makes 8.1 per 1 000 people, whereas the same indicator across the Russian Federation is only 0.2.
Research Questions
Due to social importance of the workforce reproduction and development of their quality there is also the need to increase the efficiency of labor market performance within the subjects of the North Caucasian Federal District. The most acute problem in the region is the sociodemographic justification of measures related to labor management. (Poggi, & Nicolini, 2016) The workforce supply in the labor market directly depends on the demographic situation, including the birth rate of the population. High natural population growth rates in most subjects of North Caucasus at low workforce demand cause problems of functioning and development of the labor market in this region. The existing problems in labor market management become the major deterioration factor in the field of employment, uncertainty of unemployment issues and strengthening of migration activity of the population. (Aliyeva, Gimbatov, Eldarov, & Efendiyev, 2004) For this reason, the purpose of this study is to reveal regional features and factors influencing the workforce reproduction. The understanding of objective social and demographic processes in this field can form the scientific base for effective measures of state policy in the sphere of regulation and development of regional labor market. In turn, successful implementation of these measures in general ensures the economic growth of the region in the medium term perspective. (Dokholyan, Petrosyants, & Sadykova, 2013).
Purpose of the Study
Considering the above, the tendency towards demographic development, and as a result, the age distribution dynamics of the population living in the North Caucasian Federal District is important for the formation of the workforce potential in the region. The present sociodemographic structure of the population in the region is estimated as relatively “young”, i.e. with high share of youth and low ratio of the population above the working-age. Such ratio in age distribution led to the growth of supply in the regional labor market in recent decades.
With regard to the existing situation in the sphere of employment within territories of the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation the paper presents the analysis of prerequisites for labor market problems in the region and evaluates social and economic situation in the republics of the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation concerning the existing labor market trends in the macroregion and the existing demographic features.
Research Methods
It is critical to consider the removability of the working generations in the analysis of the social and demographic situation in the labor market.
In some republics of the North Caucasus the number of people under the working-age reaches 30% considering the fact that the all-Russian level only makes 18%. In general, about 24% of the population in the North Caucasian Federal District are people under the working age. This ratio remains stable over the past ten years. Besides, the indicators characterizing the number of people above the working age are quite different from the figures for Russia – about 18% in the subjects of the North Caucasian Federal District and nearly 25% across the Russian Federation in general. The Chechen Republic, the Republic of Dagestan and Ingushetia have the smallest share of persons above the working age. At the same time, the share of the able-bodied (working) population slightly differs from the all-Russian level (57.4% across Russia in general and 58.7% in the region) (Table
The demographic situation is characterized by relative stability, increase in birth rate and decline in mortality, as well as mass migration in the region (Gimbatov, 2008; Gimbatov, 2009).
Thus, from 2005 to 2015 the population of the region increased by almost 800 thousand people. In 2016 the natural population growth in the national republics of the North Caucasus made 8.1 people per 10 000 population of the North Caucasian Federal District (this is the highest level among the federal districts of the Russian Federation) considering that on average in the country this indicator reaches 0.2. Besides, the North Caucasus has the lowest death rate across Russia (Regions of Russia …, 2017).
The renovation of the working population and its labor replacement may be expressed through the potential replacement coefficient, which is expressed by the attitude of the young population pre-working age) against the able-bodied population in the total share of people withdrawn from this category due to their age and death (Efimova, 2011). The workforce replacement coefficient (RC) is calculated by the following formula 1:
(1)
where
Findings
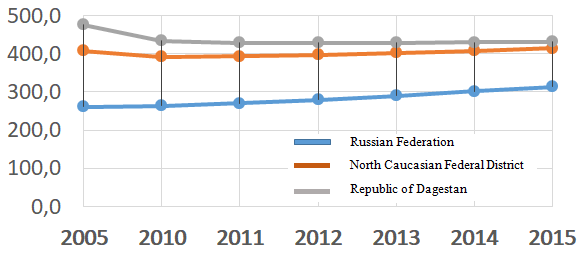
Figure
It is particularly seen in the Republic of Dagestan. Here the coefficient is dynamically reduced throughout the considered period. This trend is also typical for general demographic indicators, such as the total fertility rate (Regions of Russia…, 2017). Despite considerable difference in the demographic situation in the North Caucasus there is a gradual reduction of the workforce reproduction.
Conclusion
The state of the labor market in the North Caucasian Federal District is the most complicated among other territories of the Russian Federation. Tough economic situation and lack of skilled workforce was aggravated in recent years by high population growth in the region. The present days are characterized by the gradual delay in the reproduction of the population, which, in the near future, will reduce the labor strain in some territories of the North Caucasian Federal District of the Russian Federation.
Thus, high reproduction rates and the current demographic situation in general are key factors contributing to the formation and development of the labor market in the region. Therefore, efficient regulation of the workforce reproduction, their streamlining and optimization shall become the main direction of socioeconomic development strategy in the macroregion (Kutayev, 2014; Hampf, & Woessmann, 2017). It will decrease tensions in the social-labor sphere and the labor market.
Apparently, the solution of the above problems is based on the need to develop the following conditions, namely the creation of new jobs and active stimulation of youth entrepreneurial activity. This also requires continuous complex monitoring over the training system, labor market situation, migration, etc. Hence, there is a need for pragmatic approach and detailed strategic plans causing multiplicative effect and able to defuse social strain in the region.
Acknowledgments
The study is performed under financial support of the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project No. 17-02-00357a
References
- Abdulmanapov, P. G., Abasova, Kh. U. (2009). Features of demographic policy in the Republic of Dagestan. Issues of structurization of economy, 4, 20-22.
- Abdulmanapov, P. G., Kutayev, Sh. K., Bagomedov, M. A., Gimbatov, Sh. M., Sagidov, A. K., Khadzhalova, Kh. M. (2011). Social aspects of economic security of the region. Sh. K. Kutayev (Ed.). Makhachkala, Institute of Social and Economic Research of Dagestan Scientific Center RAS.
- Aliyeva, V. F., Gimbatov, Sh. M., Eldarov, E. M., Efendiyev, I. M. (2004). Modern migration processes in Dagestan. Regional aspects of social policy, 6, 84-95.
- Dokholyan, S. V., Petrosyants, V. Z. Sadykova, A. M. (2013). Methodological aspects of regional social and economic policy. Regional problems of transformation of economy, 3, 78-84.
- Efimova, M. P. (2011). General theory of statistics: textbook. Moscow: Infra-m, pp. 416.
- Gimbatov, Sh. M. (2009). Economic crisis and transformation of migration communications. Issues of structurization of economy, 2, 83-85.
- Gimbatov, Sh. M. (2008). Current trends of an otkhodnichestvo in the Republic of Dagestan. Issues of seasonal economy, 2, 167-172.
- Hampf, F., Woessmann, L. (2017). Vocational vs. General Education and Employment over the Life Cycle: New Evidence from PIAAC. CESifo Economic Studies, 63 (3), 255269.
- Kutayev, Sh. K. (2014). Problems of development of economy and human resource management of regions. Економiчний часопис – XXI, 5-6, 48-51.
- Poggi, A., Nicolini, R. (2016). Labor Market Reform and Rent-sharing, A Quasi-experiment Experience. Applied Economic Perspectives and Policy, 38 (4), 618-631.
- Regions of Russia. Socio-economic indexes (2017), Moscow: Rosstat. Rertieved from: http://www.gks.ru/wps/wcm/connect/rosstat_main/rosstat/ru/ statistics/wages/labour_force/# Date of address 23.09.2018
- Sagidov, Yu. N., Denevizyuk, D. A. (2014). Adaptive formation of industrial production. Regional problems of transformation of economy, 8 (46), pp. 81-87.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 March 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-057-0
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
58
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2787
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, science, technology, society
Cite this article as:
Gimbatov, S. M., Kutayev, S., & Gichiyev, N. (2019). Social And Demographic Aspects Of Regional Labor Market Development. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism, vol 58. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 2032-2038). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.03.02.236
