Abstract
Aerobics and fitness lessons are activities which stimulate the mentality in forming the emotion as a motivational force of expression. The body must synchronise with the human personality in order to develop self-esteem. Knowing the efficiency of aerobics and fitness activities carried out during the hours allocated by the faculty determined us to implement a specific set of programs, contributing to the development of both theoretical and practical knowledge, giving the experts from this line of business information and practical activities which will help the educational process of the students. To exercise means to release the suppressed emotions, which leads to the possibility of relaxation. This process is known as the catharsis effect. We can safely say that a systematic program of physical exercises leads to harmony in our lives, a balanced personality and develops a particular set of skills which will help us, from a professional point of view. The current students, who are going to become the next generation of economists, think that good physical condition and a good set of physical activities lead to a more balanced relation between body and mind, to efficiency and a good method of socialising. Aerobic and fitness activities can be found at the core of each person’s physical, social and mental condition. Our activities have the following beneficial effects: they can develop team spirit, cooperation with other human beings, can satisfy social needs and can develop the spirit of fair-play.
Keywords: Shapephysical conditionmental toneself-image
Introduction
As specialists in aesthetics, we have always been interested in aerobics and fitness, their nature, form and effects. These physical activities have some distinct advantages compared to other disciplines, offering favourable conditions to develop basic and specific motor skills, both being methods of shaping the mind and body as well. This holistic approach is also an efficient method to educate students for a healthy lifestyle. Furthermore, aerobics and fitness have many benefits: prophylactic, healing, strengthening, boosting, relaxing effects etc., all of them combining with basic, medical, respiratory and articular gymnastics.
The prophylactic purpose of being physically active is underpinned by Tüdös (2000), who says that physical and mental health through sport is the only strategy with equal opportunities to reduce the negative effects of the informational drug (television), of usual drugs (alcohol, tobacco, coffee, sweets) and strong drugs (heroin etc.).
Youngsters are naturally drawn by this kind of physical exercising which, accompanied by music, becomes even more appealing. Music generates higher emotions, enriching the life of those who practice aerobics and contributing to the joy of movement.
The increasing number of students who practice aerobics and fitness find a biological and psychological motivation in contributing to their own well-being, as well as improving or building-up their body aesthetics, both to levels as close to the optimum as possible.
We consider that this type of movement in the university environments “is increasingly raising the awareness in regulating health, getting the desired body and changing the sedentary way of life” (Nae, 2011).
Knowing the efficiency of aerobics and fitness activities carried out during the lessons for college students determined us to implement a specific set of programs. Their aim was to contribute to the development of both theoretical and practical knowledge, giving the future economists information and practical abilities which will help them not only in the educational process, but for a lifetime as well.
“Self-esteem can also be improved, in 29.3% of cases, by physical education. It is known that the most commonly mentioned physical education objectives are improving the state of health and harmonious physical development” (Ciomag & Pop, 2014, p. 739).
Glasser (2000) states that exercise induces a form of positive dependence, followed by symptoms of depression on subjects that have suddenly stopped exercising. The euphoric state, “self-abandonment” and feeling good are explained by the rising of endorphin level, with opiate similar effects. They are found in nerve cells located in the hypothalamus and anterior lobe of the pituitary glands.
Listening to music during exercise educates the rhythm, contributes to musical education by enriching the musical culture. This has an impact not only on the movement, but also on the whole activity of a person, inspiring optimism (Grigore, 2001).
In parallel, exercising is associated with emotional release or catharsis (a therapeutic effect by releasing a supressed emotion) and the possibility of relaxation. We can deduce that systematic exercise influences personality balance, sense of joy of life and qualities that facilitate professional performance.
Problem Statement
A diagnostic research related to the physical activity of student population from the Bucharest University of Economic Studies was undertaken. The main research goal was to gather students’ opinions about how physical education (PE) complemented their future professional activity. Opinions about the efficiency and benefits of aerobics and fitness programs specially designed for body aesthetics, high physical tone, stress release and emotional control, as revealed by the questionnaire items, were of particular interest to us.
Aerobics and fitness are accessible forms of exercising on a regular basis. Most female students experience a deep focus on movement as a way to reach their inner consciousness, which can, in turn, ease the mind, clarify the thoughts and align day-to-day activities with psychological aspects. These kinds of exercises are also a way to help the inner balance restoration and a mean of boosting self-awareness and self-esteem.
Research Questions
The main questions this research puts forward are related to the role and scope of physical education content in the students’ daily lives and their future professional activity. This study was designed to evaluate college students’ awareness of their professional physical and psychological challenges and how physical education skills and knowledge could help them overcome these challenges.
Purpose of the Study
As specialists in aesthetics, we want to prove that there is a strong bond, dialectical interdependence between individual physical development and student ability to assimilate and exploit their knowledge. Practicing aerobics and fitness or any other kind of movements strengthening their body and health, the youth create the essential conditions required by a fruitful and intense intellectual activity. A study was conducted at the Bucharest University of Economic Studies on a sample of 560 female students. They enrolled voluntarily, being randomly chosen among students in the first and second years, who were attending physical education classes. The identity of participants in the study was kept anonymous, respecting the data confidentiality.
The research revealed the students’ needs and preferences and the effects obtained on the somatic, functional, motor and psychological levels. Results obtained by applying the questionnaire were processed and qualitative analysis was used to point out details and group features.
Research Methods
We designed an opinion questionnaire and applied it to 560 students with economic specialties. The first part of the questionnaire consisted in seven items related to students’ involvement in everyday formal and informal physical activities and focused on the types of professional demands.
The second part of the questionnaire consisted of 13 items referring to the contribution and potential beneficial effect of physical activity in relation to the chosen specialisation.
Following the research purpose regarding professional requirements of different economics branches, the following objectives were set:
making a synthesis of professional requirements in commerce activities; accounting and IT accounting; international economics; finances; general, theoretical and applied economy;
understanding students’ opinions regarding physical exercising and its importance for the chosen specialisation.
Qualitative approach was done using a 4-point Likert scale. The four options corresponded to the following responses: 1 - nothing, 2 - little, 3 - a lot, 4 - very much. The neutral response option was deliberately avoided.
Findings
According to the research objectives (purpose), we found interesting results, as follows (Table
The results obtained were graphically represented as follows (Figures
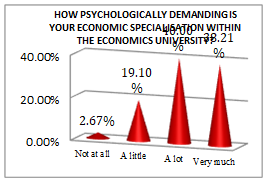
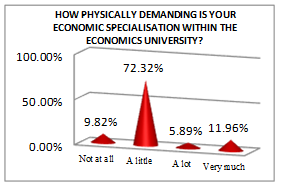
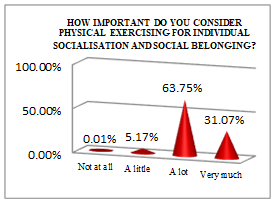
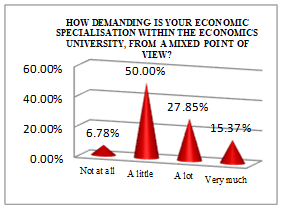
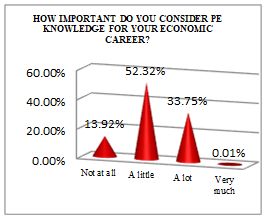
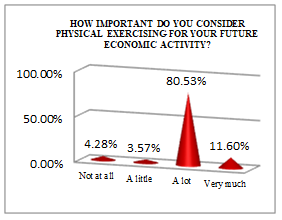
The economist student profile, according to the processed data presented in Table
Of all students, a high percentage (72.32%) think that their physical effort is at a medium level, while 40% of them consider their psychological effort quite high.
50% of students consider that the effort required by their specialisation is significant.
A high percentage of students (63.75%) consider sport as a means of socialisation and integration, whilst 31.07% acknowledge this particular trait of PE.
Although many of the subjects think that PE knowledge is almost useless (13.92% - not at all, 52.32% - a little), there is a high percentage, of almost 34%, who consider it very useful.
Most questioned subjects consider that psychological effort must alternate with physical effort (aerobics and fitness). Half of the female students (52.14%) consider that this mixture is necessary, while 35.17% think that it is an absolute must.
The results reflecting the importance of physical exercising on a personal and professional scale (for performing day-to-day activities) are portrayed below (Table
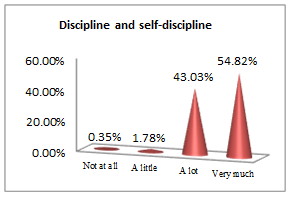
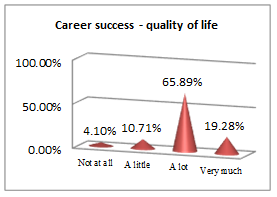
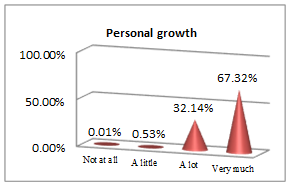
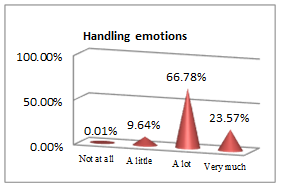
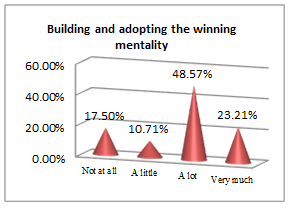

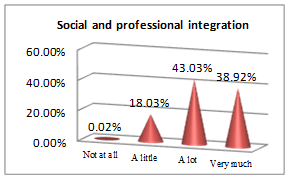
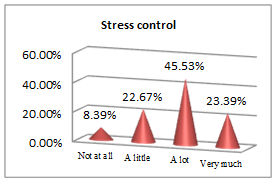
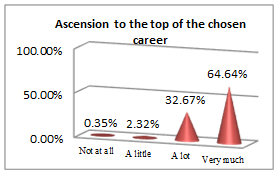
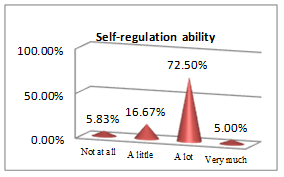
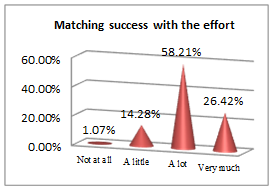
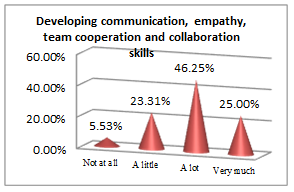
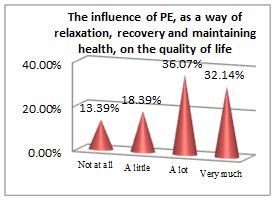
The above set of questions aim at underlining the features that lead an economist to a successful career.
Over half of the subjects consider important and very important discipline and self-discipline (a lot - 43.03%, very much - 54.82%) when it comes to their professions.
As a parenthesis, this is a necessary requirement in all activities; lack of coordination, discipline and self-discipline may have negative effects on one’s health and efficiency.
All students, future economists, consider physical education useful for implementing rules and guidelines (44.28% and 50%), personal growth (67.32%), managing emotions (66.78%) and getting a winning mentality, which contribute to building a successful career picture. The qualities an efficient economist must have and go further along with the results they must get: social and professional integration (43.03%) outcomes; but nothing would bring any success if pleasure and work satisfaction (58.21%) are not the ingredients to sustain it. In other words, results are obtained following sweat, patience and focus, which are all educated by consistently participating in PE classes.
A different noticeable aspect in students’ perception is that the quality-of-life level is directly related to career success, as 65.89% and 19.28% of them definitely agree with this statement. The interest and awareness of PE importance in college curricula were also confirmed by other studies on similar samples estimating the variance in levels of self-esteem and body image (Pop, 2016) or the effect of specially designed activities on students’ fitness level (Gorucu, Tokay, & Badau, 2017).
A worked-out body is less prone to disease, having better resistance to bacterial factors due to the biological adaptation to effort (translated through increased capability of the body). Equally, the connections between mind and body health should be analysed. It is well known that emotional imbalances come with organ failures, which, in turn, favour illness. The fact that exercising contribute to the emotional level of an individual allows us to appreciate that PE can help improve health by modifying mind patterns through self-respect, a positive and optimistic attitude.
Conclusion
Professions in the economic field are mostly mentally demanding, however 82% of our respondents have considered physical education as necessary for their future careers. Also, the majority of students have responded that fitness and aerobics are important means of socialising (95%) and improving the quality of life (87%).
Psychological balance, inner harmony and unity are bases for the effective development of our own success mechanisms. Attending physical education classes, in general, gives participants the choice of improving their health. Aerobics and fitness, via their beneficial effects on the body and mind, contribute to the young students’ harmonious development. By using aerobics and fitness, many of the hard problems in life can be tackled, shaping and reshaping self-balance: a person’s connection to the world and to him/herself through movement amplifies due to the movement-sound complexity, the body’s reception capability through bio-feedback.
The most favourable scores were obtained on items which correlated physical education with personal growth (99%), the effort oriented towards career success (97%) and the observance of rules and guidelines (94%).
Emotions generated by the environment in which classes take place (music, communication, aesthetics, a friendly climate) provide students with joy, enthusiasm, trust and a huge wish for success. Aerobic and fitness activities can be found at the core of each person’s physical, social and mental condition. Our activities have the following potential beneficial effects: they can develop team spirit and cooperation with other colleagues, can satisfy social needs and can develop the spirit of fair-play.
In conclusion, as revealed by the study, along with our satisfaction as teachers, the students have accumulated experience and shaped their character, preparing them for a healthy lifestyle and the future economist requirements.
References
- Ciomag, R. V., & Pop, C. L. (2014). The relationship between subjective parameters of well-being in a sample of young Romanian women. Procedia – Social and Behavioural Sciences, 149, 737-740. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.08.291
- Glasser, W. (2000). Reality therapy in action. New York: Harper Collins.
- Gorucu, A., Tokay, B., & Badau, A. (2017). The effects of three different types of exercises on aerobic and anaerobic power. Physical Education of Students, 21(4), 152-157.
- Grigore, V. (2001). Gimnastica artistică. Bazele teoretice ale antrenamentului sportiv. Bucureşti: Semne.
- Nae, I. C. (2011). Nou și divers în fitnessul pentru toți. Marathon, 3(1). Retrieved from http://www.marathon.ase.ro/pdf/vol3/1/IonelaCNae.pdf
- Pop, C. L. (2016). Self-esteem and body image perception in a sample of university students. Eurasian Journal of Educational Research, 64, 31-44.
- Tüdös, Ş. (2000). Criterii psihologice în fundamentarea şi structurarea pregătirii sportive, București: Padeia.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
16 February 2019
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-054-9
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
55
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-752
Subjects
Sports, sport science, physical education
Cite this article as:
Ciomag, R., & Filip, C. (2019). Physical And Health Education For Future Economists. In V. Grigore, M. Stănescu, M. Stoicescu, & L. Popescu (Eds.), Education and Sports Science in the 21st Century, vol 55. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 707-716). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2019.02.87
