Abstract
The relevance of this research is conditioned by the ongoing development of the concept of strategic human resource management at the stage of maturity. In this connection, this paper is aimed at addressing the issues of efficiency of different human resource management systems at the territorial and institution level. The author considers it necessary to complement the measured types of effects (economic, technological, and social) with the effect of prevention of risks that are possible in the activity of any organization: commercial, financial, operational, and personal risk factors. All the noted types of effects have an immediate impact on each other. The leading approach to researching the issue of management efficiency is a complex of various theoretical and empirical methods that allows to consider human resource management through structuring as a type of such management. The analysis of the structural levels of human resource management clearly illustrates that it is only possible to influence the qualitative characteristics of individual human resource management at the regional level. The paper describes the situation in the area of reproduction of human resources in Ulyanovsk Oblast on the basis of calculation of individual indicators. The materials of this study have practical value for human resources service specialists and heads of organizations and can be useful for territorial human resource management institutions as well as present scientific interest to researchers of the strategic management of human resources
Keywords:
Introduction
Market environment has radically changed the planning practices in every organization, especially the planning of labor indicators. People, as the main asset, are the core of all organizations. Human resource costs become the base for planning the performance and social indicators of the organization's efficiency. The appropriate staffing of an organization by personnel possessing the necessary knowledge and skills, and along with it their performance efficiency, are highly important to increase the organization's overall performance. A manager in any organization always faces the issue of how to efficiently invest in the staff and achieve their maximum performance. For this reason, currently important is the interest of the market players to objective and accurate information about the state of the enterprise's workforce, as well as to their assessment. One of the ways of obtaining such information is analyzing the organization's human resources for the management to make optimal decisions and to increase the efficiency of using the workforce. In the conditions of a market, performance of any organization is affected by a substantial number of various factors of the external and internal environment. The search for criteria that would allow to most precisely and objectively establish an organization's performance efficiency dates back to the early 20th century. Still, up to the present date the researchers have not been able to shape a shared approach to determining the economic efficiency of an organization, its indicators and structural elements, as well as its individual employees. Analyzing the available research of the issue of the efficiency of various human resource management systems allowed to distinguish two key concepts (Braverman & Saulin, 1998). The first concept is based on economic psychology where personnel management is not included in production efficiency. The second concept, on the other hand, defines the input of a personnel management system in the efficiency of production. Researchers (Gibson, Ivantsevich, & Donnelly, 2000) analyze the term "efficiency" in terms of several aspects: efficiency through achieving the organization's goals, alignment of interests, flexibility, survival, adapting to the macro environment. Efficiency according to Vilfredo Pareto is considered as a limiting result in the from of a manufacturing system's output without causing damage to anyone else. Pareto optimality is such state of an economic system or such allocation of resources, under which improvement in one parameter is impossible without degradation in another (Shchegortsov & Taran, 2014).
Problem Statement
Proceeding from the analysis of the main concepts of efficiency, assessment of human resource management efficiency should be carried out in two directions: the process of managing human resources and their use. .
Research Questions
The author organized the main methods of assessment of the efficiency of human resource management into groups (Table
This research's author considers it necessary to complement the traditionally measured types of effects (economic, technical, social) with the effects of risk prevention that are possible in the operation of every organization: the commercial, financial, production, and personal risk factors. All the noted types of effects have an immediate impact on each other.In managing an organization, assessment of efficiency represents one of the principal components of human resource management. A flowchart of efficiency assessment in a human resource management system is shown in (Figure
Demographics. 2. Socioeconomics. 3. Natural resources.
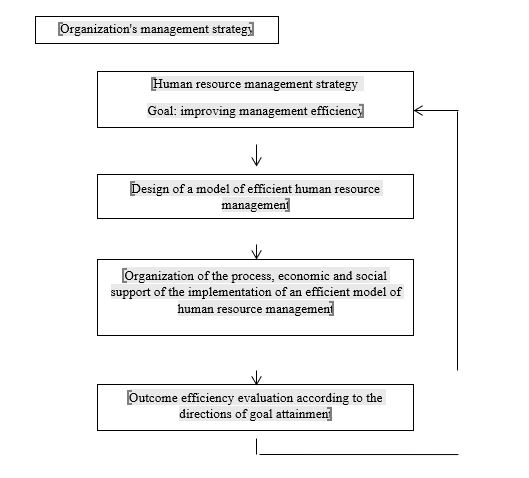
It is the functioning of each component and their interoperation that determine a region's HRM system.
Structured hierarchical models of the strategic HRM system within the scope of the Russian Federation factoring in the regional level have been proposed by many researchers. This way, Ozernikova and Berkovich (2009) suggested a three-level hierarchical structure of an HR management system. This model points out the strategic, management, and tactical levels. The strategic level is represented by the managing entity: the Government of the Russian Federation and its respective bodies. Management entities at the level of regions, municipal entities, as well as large corporations represent the management level. But strategic plans are only implemented at the tactical level. The tactical level is represented by all HR services of organizations, as well as human resources themselves.
According to Fedorov (2013), depending on the level of the socioeconomic system, it is possible to determine the levels of strategic management and, respectively, the HRM levels. This researcher points out three directions: strategic management of the state, of a company, and the strategic management of personal development. At the state management level, the goal of the HRM is creating the conditions to increase the social capital as a factor of the development of society. At the company management level, it is the maximum engagement of a company's human potential to achieve the desired goal within the framework of the selected strategy. At the level of personal development, it is the maximum use of an employee's labor potential.
Mirolyubova and Chuchulina (2011) suggested a model of the formation of a region's human potential that factors in an individual's human potential based on the existing social, ecological, and economic situation and the crime rate in the region.
Based on the information above and the author's own experience, it can be concluded that the problem of managing the HRM system in the scope of the Russian Federation remains unsolved due to the absence of a universal HRM model and, correspondingly, absence of an efficient mechanism of managing the entire HRM system.
In our study, the object of the region-level HRM are the region's government agencies and organizations' top management. The object of management are the region's human resources. The main goal of HRM is shaping and developing the region's human resources.
Completing the following list of tasks will allow to achieve the desired goal in HRM:
Eliminating the misalignment between the subject and object of management.
Identifying the special features of the HRM.
Developing the region's HRM mechanism.
Selecting the HRM methods that match the stated goals.
The region's territory houses not only the working-age population, which means that it is important to cover the entire human life cycle (birth, upbringing, education, and further socialization) for every person living in this territory. In this respect, HRM mechanisms must ensure the cooperation of all components of life of the region's HR.
Application of the mechanisms of self-regulation and self-reproduction is also acceptable in the process of managing the formation, development, and reproduction of HR.
Purpose of the Study
It is important to note that the key goal of all changes implemented in the region without exception is, without question, creating the conditions for ensuring the high living standards for the population. To do this, when designing a program for a region's long-term development, it is first of all necessary to channel all efforts to solving the key problems of the region that impede its development, while only engaging own resources and using the available potential with maximum efficiency and improving upon the available strengths. In order to identify a region's major problems, they need to be categorized, i.e. the structure of their problems must be identified by their significance based on specific criteria.
Research Methods
There are different approaches to evaluating the existing problems in human resource management in a region. The first approach allows to characterize the situation in the area of HR reproduction to estimate the amount of HR of a specific age that will be demanded in the region in the future. This approach is based on demographic and socioeconomic calculations. The second approach is based on calculating the quality of life index (based on the calculation of individual indicators).
To describe the situation in the area of reproduction of human resources in Ulyanovsk Oblast, let us use the following indicators (Horvach & Partners, 2008):
Index of viability.
Population health index.
Marriage to divorce ratio, divorces per 1000 marriages.
Population migration index.
Estimation of the proportion of population with higher, secondary, and vocational education, as well as those with no professional education in the total working population.
Level of female economic activity.
Measuring the population's income level. This index is calculated as the ratio of change in the population's real monetary income (income index) to the level of prices (price index).
Findings
Let us calculate and analyze the dynamics of these indices for Ulyanovsk Oblast for the ten-year term from 2005 to 2016 (Regions of Russia, 2015). The results of the calculations are presented in the tables below (Table
In the period from 2005 to 2016, the number of divorces per 1000 marriages remains unchanged on average, from 591 in 2005 to 590 in 2016, with a sharp rise in 2013, 2014, and 2016. This indicates that there are additional problems in the region that will require further research. The low birth rate may also be the consequence of this situation.
The index of migration gain indicates the reduction in migration numbers. It can be concluded that the region is not attractive for migration and its migration policies are not successful. But there also is a positive aspect, which is manifested the absence of conflicts between immigrants and the indigenous population, decrease in ethnic crime rate, etc.
the next indicator is the share of people with different level of professional education in the total working population. Table
The value of the female economic activity index has a virtually constant value with a small rise from 2011 to 2013. This can not be expressly explained.
The level of the population's income varies from 0.98 in 2005 to 1.01 in 2012, which indicates the stability of the income level relative to the rise in prices. A sharp decrease in the population's level of income is seen after 2014. There are possible negative consequences that can influence the reproduction of HR in Ulyanovsk Oblast.
Conclusion
The obtained indicators show that there is a number of problems in the system of human resource reproduction and usage in Ulyanovsk Oblast, above of all in healthcare, access to professional education, and the lack of growth in the real income of the population. The identified problems result in the natural decline in the region's population. It can lead to the lack of HR, contraction of the gross regional product, and, naturally, a decrease in the welfare of the region's HR. All of this clearly indicates that the priorities of the region should include the issues of healthcare, education, and increasing the living standards of HR.
Certain structural changes in the region's strategic HRM are also necessary.
References
- Braverman, A., & Saulin, A. (1998). Integrated assessment of effectiveness of the enterprises. Economy questions, 6, 108-121. Retrieved from: http://economy-lib.com/sovershenstvovanie-sistemy-upravleniya-personalom-v-holdinge#ixzz44e6uz0dD
- Dedov, O.A. (2008). Metodologiya of controlling and practice of management of the large industrial enterprise. Moscow, М: Alpina Business of Axle boxes.
- Fedorov, M.V. (2013). Strategic management of human resources. Theory of management, UEKS, 59, 29. Retrieved from: http://uecs.ru/marketing/item/2506-2013-11-07-06-38-18
- Gibson, D.L., Ivantsevich, D., & Donnelly, D.H. (2000). Оf the Organization: Behavior. Structure. Processes. (The lane with English). Moscow, М: INFRA.
- Horvach & Partners (2008). Introduction of the balanced indicators. Retrieved from: http://files.alpinabook.ru/iblock/af6/af6dbf5ddd755528104c051ae6d6f3b1.pdf
- Kartashova, L.V. (2013) Management of human resources. Moscow, М: INFRA-M.
- Kucherov, D.G. (2015). Strategic management of human resources: development of the concept at a maturity stage. Тhe Bulletin of the St. Petersburg university. Management series, 2, 124-151. Retrieved from: https://readera.ru/vestnik-management-spbu/2015-2
- Mirolyubova, T.V., & Chuchulina, E.V. (2011). Regional model of human potential. Bulletin of the Perm University, 3(10), 65-73. Retrieved from: http://econom.psu.ru/upload/iblock/067/mirolyubova-t.v._-chuchulina-e.v.-regionalnaya-model-chelovecheskogo-potentsiala.pdf
- Ozernikova, T. G., & Berkovich, T.A. (2009). Use of system approach to management of human resources of the region. News of the Irkutsk state economic academy, 3, 42-45. Retrieved from: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/ispolzovanie-sistemnogo-podhoda-k-upravleniyu-chelovecheskimi-resursami-regiona
- Regions of Russia. (2015). Socio-economic indexes: statistical collection. Rosstat, Moscow, Russia.
- Tuktarova, F.K. (2008). Comparative tactical analysis of economic development of the organizations: Monograph / Tuktarova F.K. Penza:The Penza state university.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 December 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-049-5
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
50
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1464
Subjects
Social sciences, modern society,innovation, social science and technology, organizational behaviour, organizational theory
Cite this article as:
Smolkin, V., & Svetunkov, M. (2018). Conditions And Directions Of Increasing The Efficiency Of Human Resource Management. In I. B. Ardashkin, B. Vladimir Iosifovich, & N. V. Martyushev (Eds.), Research Paradigms Transformation in Social Sciences, vol 50. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1115-1123). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.136

