Professional Interaction Of Educational Organizations Managers In Context Of Knowledge Management Methodology
Abstract
In this paper, we present the analysis of existing learning needs and motivations of educational organizations in the realities of the contemporary systemic changes in the educational environment of the Russian Federation. The theoretical basis of the research was the work of researchers of the concepts of knowledge management (knowledge management), human resources management (human resources management), organization theory and management practices, as well as sociology. The methodological and instrumental base was the mathematical analysis of sociological data processing, one-dimensional and two-dimensional descriptive analysis with the use of regression, factor and cluster analysis, which allowed to obtain five factors of qualification deficiencies and three groups of motives for the formation of educational requests. The results of the research work were the identification of weak and strong current competencies of managers of educational organizations. Identified educational programs meet the identified learning needs of managers. The main aim of this paper is to solve the problem of management accounting and the effectiveness of professional interaction of managers in the transition to project activities in order to obtain additional resources for the development of the educational organization.
Keywords: Knowledge managementresearch activitiesprofessional trainingproject management
Introduction
The systemic changes taking place in the field of education management are related, first of all, to the introduction of principles and mechanisms of project management (Res. No. 1242; Res. No. 1642), which means that the role of project activities (both "external" and" internal") is increasing dramatically. In fact, the development and implementation of University development projects becomes an important activity of University managers, but for this they need qualifications based on relevant competencies. First of all, these are competencies expressed through communicative labor actions, the methodological basis of which is the process of knowledge exchange, their processing and consolidation at the level of subjects of the management process. On this basis professional interactions of managers of modern University are built. It turns out that project management and project management is the management of professional knowledge of managers. In addition, the management of a modern Russian University is characterized by the following contexts:
it's a merger of universities. Universities are expanding, in the regions of the country there are large Federal universities and supporting universities;
a cluster of globally successful research universities is being formed;
there is a gradual "globalization" of Russian University education, the activities of Russian universities show international trends in development ("bolonization", "digitalization" and the increasing role of online education, the formation of universities as centers of innovative research and development, internationalization and growth of the "export" potential of Russian higher education, the development of "network" and the entry of Russian universities into international University corporations and other associations, etc.);
the emergence of a number of strategic projects for the development of Russian universities, aimed at strengthening their global positions (project "5 in 100"), the transformation of universities into drivers of innovative development of regions, the digital economy and new information culture in General (project "supporting universities", University development Projects in the Concept of "Twelve solutions for new education"). These initiatives are supported by the state and University communities (Kuzminov & Frumina, 2018);
standardization of professional activity in Russian higher education is a manifestation of global and national trends characteristic of society and the economy as a whole. The introduction of the professional standard regulates the professional activities of the faculty (Order No.608n) and University leaders (conclusion of the discussion of the professional standard "head of the educational organization").
Problem Statement
All of the above contributed to the development of strategic planning for the development of the educational organization of the University management system and is reflected in many programs of development of universities and their communities. An example is the development program of St. Petersburg state University. The development of action plans, project activities aimed at achieving strategic goals and obtaining effective results, today is not so much the responsibility of management as a vital necessity, because in the context of the ideology of project management gives the opportunity to participate in various competitions to attract additional resources (primarily financial) held within the framework of the state program "development of education in the Russian Federation" for 2018 – 2025 (Res. No. 1642).
Naturally, in the context of the above situation, the organization of teamwork within the project management ideology is the main goal of diversification of management and reengineering of organizational business processes.
The basis of the design and functional management structure consists of highly qualified employees capable of implementing long-term, comprehensive projects. Thus, the high competence of specialists is the basis for the effective and efficient functioning of the educational organization, which reduces the risks of erroneous management decisions, duplication of management functions and expands the possibilities of operational management of organizations.
At the same time, it should be noted that the concomitant expansion of information and communication links leads to the complication of professional interactions, which can reduce personal responsibility and lack of unity of teamwork, respectively, the loss of productivity of the project and the main functional activities of University leaders.
Attempts to standardize the activities of the University staff, in particular management categories, in the short and medium term are related to the optimization of the organizational structure and diversification of management, management and economic activities. The management faces new challenges, such as management accounting for the effectiveness of professional interaction of managers to obtain additional resources for the development of the University on this basis.
Professional standard is the characteristic of qualification of the worker for implementation of a certain type of professional activity including such signs as competence of the worker, namely level of knowledge, skills, motivational factors, personal qualities, situational intentions and qualification [nspkrf.ru], i.e. readiness of the worker for high-quality accomplishment of specific functions within a certain type of labor activity.
Accordingly, the term "skills gap" refers to the difference ("Delta") between the skills required and those currently possessed by the staff member. Thus, the qualification demands means formulation of need of acquisition of missing practical experience, self-education and advanced training for improvement of qualification level that includes substitution of deficit of concrete knowledge as bases of competences and attributes of qualification level of the worker.
Information and knowledge are cumulative, and the infrastructure of their transfer through the levels of hierarchy of the University horizontally and vertically oriented, i.e. linearly between departments and from subordinates to managers. Thus, the depth of professional knowledge and experience of each employee, the peculiarities of the University of management have a great impact on the final result (Butrova, 2008), as the knowledge of top managers generalization of knowledge managers, and those, in turn, to generalize the knowledge of specialists, etc.
Updating of competences, subordinates and heads at all levels, depending on the level of qualification, carry out professional development through training on short-and medium-term professional and technical programs, as well as training of scientific and pedagogical personnel in postgraduate, residency and postgraduate, which, in turn, are identified with the titles, professions and qualifications contained in the unified qualification reference book of positions of managers, specialists and employees and professional standards.
Thus, we will continue to talk about research work to identify existing qualifications shortcomings and the nature of their occurrence, the educational needs of middle managers of the modern University, as well as the motives of their occurrence in order to determine the educational programs in accordance with the "weak" current level of competence and to determine the "strong" relevant competencies, which promote formation of specificity of professional interaction of heads of the educational organization of the higher education in the main directions of activity of University.
The category of middle-level managers (heads and Deputy heads of departments, departments and other departments of the University management infrastructure) is chosen by us as the subject of research for several reasons: first, middle-level managers are more accessible due to their status and position in the educational organization to participate in the second research process; , their representatives in this category are easier to form a valid sample; thirdly, in the situation of project management, the degree of their independence in the preparation of management information of a strategic nature increases, as they traditionally lead the formation and actual activities of the project teams of the University, implementing both "external" and "internal" strategic projects, where representatives of senior management traditionally use the memory of the function and function of external motivation.
Research Questions
What is the most effective way to manage professional interaction of the project managers tasked with obtaining additional resources for the development of the educational organization?
Purpose of the Study
The main aim of this paper is to solve the problem of management accounting and the effectiveness of professional interaction of managers in the transition to project activities in order to obtain additional resources for the development of the educational organization.
Research Methods
Theoretical and methodological basis of the research are the works of researchers in the field of sociology and social research, the concept of knowledge management (knowledge management) and personnel management (human resources management), the Basics of management theory, Organization and practice in the field of management.
The collection and analysis of primary statistical, normative, administrative and managerial data was carried out on the basis of the study of periodicals, information and legal portals and systems that publish the texts of normative legal acts, official information and scientific research.
The study was conducted in three stages. The first stage consisted of a survey of 310 respondents from 8 Federal districts of the Russian Federation, 12 profiles of higher education institutions, including 21%–from the Republican scientific and Federal support of higher education institutions and 79% - from regional, which included specialists, middle and senior managers, as well as teaching staff. Age, gender, socio-professional composition of the examined subjects and their spatial localization with restrictions on the professional qualification structure were the program requirements for achieving representativeness of the sample.
The second stage is data processing, analysis of results and their interpretation. The reliability of the results of the sample of the research is determined with the usual precision (confidence level 95%) of generalizations, i.e., errors (uncertainty) in the sample of 4,32% (confidence interval distributions at the level of 0,03—0,1), with 79% of the responses received, with a random error of representativeness of the sample to 6% In the General population sample of over 5000.
Third-conducting 2 focus surveys in academic circles on the basis of the Higher school of management of St. Petersburg state University with the participation of 5 expert respondents, 4 respondents–participants to interpret the results and interview 10 experts–heads of universities to obtain expert evaluation of the results.
The analysis of primary questionnaire data was carried out using one-dimensional, two-dimensional descriptive analysis of mathematical statistics, the results were processed using regression, factor and cluster analysis of survey data using computer software packages SPSS, Microsoft Office, and on some open questions we conducted quantitative content analysis using the software Qda Miner and Wordstat Lite.
Findings
Representatives of national research (51%), Federal (45%) and supporting (4%) higher education institutions make up 25% of all respondents, 84% of which from multi-profile higher education institutions of the millionaire cities (57%) of the Central and Volga Federal districts (60%) are predominantly women (84%). 45% of managers aged 25-39 years (43%) and 45-59 years (39%) with University experience of more than 8 years (67%) have PhD degree, although 49% did not consider it necessary to answer this question. 75% of the respondents have a total teaching experience of more than 10 years and are currently engaged in teaching activities (67%) under the "effective" contract (55%) in combination with administrative activities (63%) as heads of various administrative levels (76%). 80% of the respondents of this category took advanced training courses, 49% of them studied on the profile of their main activity during the last 3 years, and 43% could not remember the name of the educational program or did not find it necessary to answer this question.
Regional universities represented 75% of all respondents, 65 % of whom were from multi – disciplinary and technical universities in the millionaire cities (54,4 %) of the Central and North-Western Federal districts (55%), mostly women (66 %). 60% of managers aged 35-49 years with University experience more than 8 years (64%), 30% have a doctoral degree, although 60% did not consider it necessary to answer this question. 75% of the respondents have a total teaching experience of more than 10 years and are currently engaged in teaching activities (72%) under the "effective" contract (53%) in combination with administrative activities (72%) as heads of various administrative levels (87%). Over the past 3 years, 85% of respondents in this category have completed advanced training courses, 38% of them studied on the profile of their main activity, and 51% could not remember the name of the educational program or did not find it necessary to answer this question.
One of the tasks of the questionnaire data analysis was to determine the demands for the necessary educational programs from the point of view of University managers. Also, the task of identifying the causes of their occurrence was performed. So, 10 programs were allocated in the main directions of requirements to managers of any level: management theory, marketing, office work, work with information management systems, in particular with information automated systems, psychology, conflict management, business and inter-ethnic communication, social networks and career guidance. However, these preferences were noted only in 50% of respondents, so the focus of the search for reasons switched to the analysis of answers about the shortcomings of qualifications, which are noted by respondents at the management, at home and at their subordinates. As a result, 60% of respondents were allocated to 7 directions, which did not coincide with the previously demanded 10 programs. According to the results of the survey on the existing deficiencies in the skills of managers selected 7 programs to overcome them: management theory, which includes strategic knowledge about the functioning of the organization, including monitoring, information analysis, psychology, self-management, including time management, decision-making, change Management.
To identify the reasons for the occurrence of qualification deficits, a factor analysis was conducted, the method of which in the analysis of 28 questions on the semantic differential scale " has not changed-not much-is very noticeable-it is difficult for me to answer (do not do)."
As a result 5 factors statistically reliable result (1> p > 0,5, p=0,712) correlate with conceptual level of knowledge and the direction of professional activity of the head are allocated the first factor is connected with strategic management of external development of the educational organization, the second – with Strategic management of internal development, and on the third – organizational processes, the fourth – from production, the fifth – from the analysis of professional activity of the Manager (Blackler, 1995; Foss, 2005; Wiig, 1997).
Further, the calculation of the factors values for each Respondent by age, experience, type and level of position, profile of professional activity, status and profile of the University. Calculations revealed both "weak" and "strong" knowledge of University leaders.
When calculating the values of coefficients, it is found that the shortcomings in the qualification of University leaders during the interrogation are not related either to the profile of professional activity, nor the type and level of their position, nor the status of the University, as well as related to their age and experience, as well as the profile of the University. Thus in each of the allocated 5 directions of professional activity there are certain ranges of formation of lack of knowledge:
in the strategic management of external development of the organization involved managers with experience of 8-12 years or the legal profile of the University;
in strategic management of internal development of the organization-at the age of 60-64 years or with the experience of 3-8 years;
in organizational processes-at the age of 50-54 years, either with 1-3 years of experience, or from legal, socio-economic profiles of universities;
in production processes-at the age of 40-44, 60-64 years, or with experience up to 1 year, or from legal, creative profiles of universities;
in the analysis of professional activities-at the age of 25-29, 40-44 years, or with experience up to 1 year, or from socio-economic profile of universities.
Thus, the received factorial values allow to allocate the directions of development of educational programs.
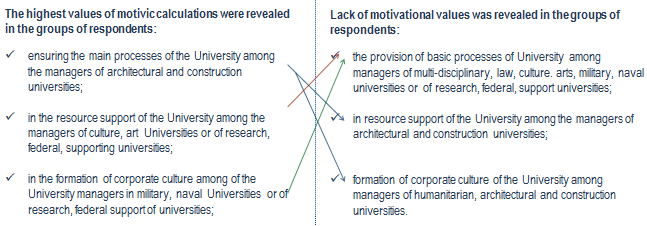
To determine the motives of the lack of knowledge on the basis of the obtained values of factors, a cluster analysis was carried out by the method of analysis of cluster centers. As a result, 3 groups of respondents were identified, the reasons for the formation of which are the provision of basic processes of the University, resource support activities and the formation of corporate culture.
By means of the received data the calculation and the analysis of accessory of the allocated motives to each Respondent was carried out.
Informative are the values calculated on the basis of data characterizing the profile of activity and the status of the University, see Figure
Conclusion
It is possible to state, the received values allow to formulate not only directions of development of educational programs, but also to define their target audience. As noted above, systemic changes in the work of Russian universities contributed to the formation of project management in determining and implementing the objectives of their strategic development. Therefore, in the professional activities of University leaders there is a need to combine project activities aimed at development with the implementation of the tasks, the solution of which provides the functioning of the organization.
Thus, professional interaction of managers is now formed on the basis of design and functional interactions, and high productivity of specialists in this field is the basis of the effective functioning of the University.
However, the effectiveness of the project largely depends on how the project teams will be formed and work productively: on the basis of certain skills, experience or specialization?
We believe that the project team should be formed on the basis of previously identified "strong" knowledge of managers. Based on this, it makes sense to allocate roles within the team. Thus, it is necessary to introduce a division of inter-and intra-institutional projects of the University.
Within the framework of the in-house project, as well as inter-organizational, teams can be formed on the basis of their activities: external and internal development, organizational and production support, as well as analytical activities based on the calculations of the above "strong" relevant knowledge based on age characteristics and experience, see Figure
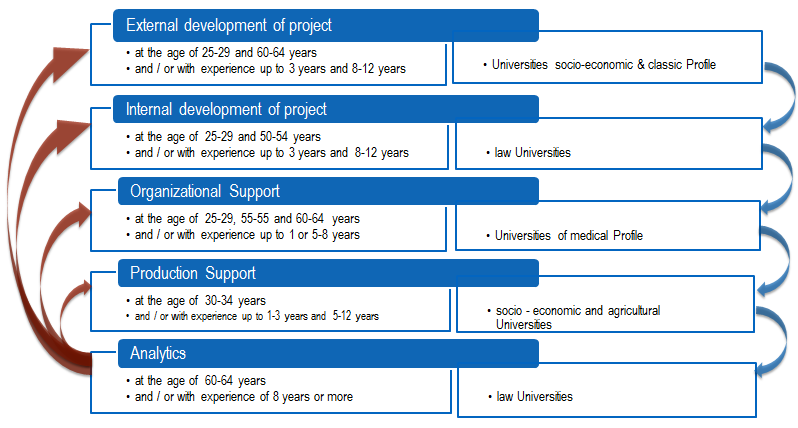
The interaction of such project teams occurs at different stages of preparation and implementation of the project, they can be divided up to 7, which are associated with the processes of accumulation and exchange of information and knowledge within the positions and professional activities of managers in the organizational structure of the University.
For example, in the implementation of the strategic development project of the University analysis, preparation and implementation are the main stages of the project teams.
At the stage of project analysis of the external strategic development of the University formed a team with competencies in the field of formation of values and" strong " knowledge of higher education, missions, goals, capabilities of systems and schemes of their operation, as well as methods and new approaches to decision-making. Such a team may consist not only of managers, but also highly specialized specialists from different fields.
At the next stage, the analysis of external changes is carried out and the results correlate with the strategic goals of the University, the problematic issues are formed and at the next stage there is interaction with the internal team of developers, which implements the analysis of the external and internal development of the project.
At the stages of the project it is necessary to form teams with the competence of structuring and systematization of work, work with changes.
At the next stage, the analysis of the project implementation, ways of further development and transfer of the acquired knowledge to the third team for organizational support of the project is carried out, which, in turn, compares the analytical data and conducts the establishment of organizational processes. The tasks of the fourth team includes the organization of production processes.
As for the fifth team – analysts, they can be highly specialized representatives of different directions and form the "core" of the project participants, the purpose of which is to conduct an audit and examination of the project at any stage.
Data analysis of sociological research of management environment of educational institutions of higher professional education showed that, in the opinion of respondents, the most significant changes in professional activity of Russian universities has occurred in the internal organizational work, increased the number of external and internal reporting changed a lot of software and methodical work and training activities, increased vertical coordination subordination in decision-making and reduced network interaction, with the qualification requirements for experts, researchers and managers have not changed much. It is possible to interpret this conclusion in the sense that the middle Manager, despite the fact that objectively, as we pointed out above, is included in the deep processes of significant changes, is forced to react in everyday professional activities rather to external evidence of changes that do not always adequately reflect their essence.
Also, as a result of the study, data on the active involvement of middle managers of the University in the above-mentioned profound changes in the nature of management. This is evidenced, first of all, by the change in the nature of their professional interactions and the growing trend of “managerial”, that is, the strengthening of the role of the head in the implementation of strategic management strategies and procedures, which are characterized, at the same time, by the restructuring of the functions of management levels, departments and divisions, the introduction of a system of strategic and targeted planning on the basis of formalized quantitative and qualitative performance criteria.
The formation of the phenomenon of "managerial" in the system of University management was also determined by a number of indicators: statistical and functional dependence between the indicators of age, length of service and teaching activities, that is, the younger the Manager, the less experience of his work, the less likely that he conducts teaching activities.
In the process of noticeable consolidation of universities within the territorial arrangement, the management system and organizational structure tend to become more complicated. The forms and types of University management structures depend on the category, status, profile of professional activity, diversity and complexity of tasks, especially in large universities, which may include research institutes and other separate research units, as well as research laboratories that are part of departments in addition to faculties, departments and institutes.
The development and strengthening of competition, the introduction of market incentives and mechanisms in the market of educational services of higher education leads to the formation of new types of special management, which can be conditionally designated as scientific, educational, administrative and managerial Management in the field of educational services.
The exhaustive list of positions of the administrative and managerial personnel entering into group, and heads of the educational organizations of the higher education relating to the field of the higher education does not exist now, however there are mechanisms of regulation of pedagogical, administrative and professional activity in the field of education by introduction of compliance of positions to the qualification requirements specified in qualification reference books and (or) professional standards.
Change of the organizational-economic bases of the rules of functioning of the education system and the implementation of educational activities, the transition to effective project work, the complexity of information and communication environment contributes to the formation of the qualification deficiencies related to insufficient qualification of professional activity of heads of educational institutions of higher professional education.
It should be noted that in the innovation and information era, knowledge management has become an integral part of the strategic management of the organization. In order to ensure the cooperation of staff and related entities as a single management system, communication channels are needed to transmit information or knowledge to each other as a basis for the development of skills gaps or an inherent lack of information or knowledge.
References
- Blackler, F. (1995). Knowledge, knowledge work and organizations: An overview and interpretation. Organization studies, 16(6), 1021-1046.
- Butrova, O. (2008). Nacional'naja ramka kvalifikacij Rossijskoj Federacii [The national frame of qualifications of the Russian Federation]. Moscow: Federal Institute of Education Development.
- Foss, N. J. (2005). Strategy, economic organization, and the knowledge economy: the coordination of firms and resources. Oxford University Press.
- Kuzminov, Y., & Frumina, I. (2018). Twelve solutions for new education: the report of the Centre for strategic research and Higher School of Economics. Moscow: Research University Higher school of Economics Press.
- Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1242 of 12.10.2017 (On the development, implementation and evaluation of the effectiveness of certain state programs of the Russian Federation).
- Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1642 of 26.12.2017 (On approval of the state program of the Russian Federation ‘development of education’).
- The Order of the Ministry of the Russian Federation from 08.09.2015 No.608n (On approval of professional standard ‘Teacher of vocational training, professional education and additional professional education’).
- Wiig, K. M. (1997). Knowledge management: Where did it come from and where will it go?. Expert systems with applications, 13(1), 1-14.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
05 September 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-044-0
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
45
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-993
Subjects
Teacher training, teacher, teaching skills, teaching techniques
Cite this article as:
Verkhovskaia, I., & Prikot, O. (2018). Professional Interaction Of Educational Organizations Managers In Context Of Knowledge Management Methodology. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education - IFTE 2018, vol 45. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 544-553). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.09.62

