Abstract
The idea of initiating an educational programme concerning the development of communication skills of future teachers is based on our proffesional experience in students’ teaching practice activities. During these activities, we have noticed that students have difficulties in effective communication with preschoolers and primary school pupils. Lesson observation and teaching activities are not enough for this, so, this is the reason why we initiated a study in which we involved 98 undergraduated students, future teachers for primary school and preschool education, which attended the Faculty of Psychology and Education Sciences. For identifing the major problems in this area of study we administrated a questionnaire concerning the communication abilities (speaking, writing and reading) and the mentors (kindergarten educators and primary school teachers) filled in a communication grid during the teaching practice activities of each student. After analyzing the results, for developing students’ communication skills, we initiated an educational programme based on communication skills, which aim was to increase their level of development. The subjects of this programme concerned: oral communication skills, written communication skills, empathy, active listening, questioning and nonverbal communication.
Keywords: Educational programmefuture teacherscommunication skillsprimary schoolpreschool
Introduction
Communicative competence is one of the most important competencies that teachers need to form and develop during their training. If teachers own communication skills, they can cooperate efficiently with their students and be able to convey the proper information in their lessons. Referring to future teachers for primary and preschool education, we consider that communication skills have to be developed on a high level. We consider that all these reasons are enough for studying this problem (Catalano, 2015).
The argument that prompted the development of this study involves understanding the communication difficulties encountered by students enrolled in Primary and Preschool Pedagogy Education specialty while involved in didactic activities. Thus, in order to identify efficient strategies that contribute to the development of the communication skills of future teachers for primary and preschool education, a psycho-pedagogical intervention program was initiated for this purpose.
We started the study from the hypothesis that the implementation of a programme which consists in interactional experiences based on: oral and written communication, active listening, empathy, nonverbal communication and collaborative learning in teaching practice activities and organised communication workshops contributes to the development of communication skills.
Problem Statement
School represents an area of professionalism and responsibility, in which the teacher shows pedagogical qualities through which it leads the student to success. The overall skills for the teaching career include the professional (general and specific) skills, the transversal and the specialized ones, supported on a wide and flexible theoretical purview, as well as on the research skills of the educational phenomenon. The communication skills is one of the most important skills in the series of professional ones that ensure the efficiency of the didactic act and the success of the entire instructive-educational process.
In specialized literature (Pânişoară, 2008; Şoitu, 1997; Dospinescu, 1998; Cucoş, 1998; Prutianu, 2005) aspects of didactic communication and communication skills proved to be very relevant to our investigative approach. The data provided by the cited authors has been an important starting point in the design and implementation of our psycho-pedagogical intervention program.
In terms of studying this phenomenon, it is worth noting the works of Erbay, Ömeroğlu &Çağdaş (2012) and Bakić-Tomić, Dvorski &Kirinić (2015), which constituted an important starting point in conceiving the experimental approach.
Research Questions
Is it possible to develop communicative competence through teaching practice activities? Is it necessary to develop an educational program to develop this competence?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study was to identify the extent to which the interventional program meant to develop future teachers’ communication skills can raise the level of communicative competence.
Research Methods
In order to identify the main obstacles and barriers in the pathway towards effective communication, the study began with the application of the Communication Skills Analysis Grid, completed by students regarding their own communication behavior. As a result of the analysis of the obtained data, the themes of the intervention program were established. Thus, the research-action suggested by us was based on a methodological system whose components also include: the psycho-pedagogical experiment, the observation method and the activity products analysis.
The collective psycho-pedagogical experiment, carried out in the natural environment in which students deploy their activity was the basic method used in research. It took place during the first and second semesters, beginning in October 2016 and finalizing in April 2017. Through the experiment, the main objective was to increase the level of development of the communication skills of practising students, focusing on the development of their communication abilities.
Throughout the program, the students were engaged in direct observation of teacher trainers communication behaviour as well as of their fellow practising students during the test and final lessons. The investigative tools within the observation took the form of grids, analysis sheets, observation logs, and reflection logs. The activity products analysis referred to the study of the products of the activity organized in the learning portfolios of the subjects involved in the investigative approach. Students involved in the research were asked to review the learning processes and products at the end of each lesson, completing the reflection journal. The portfolio included all the materials used in the program.
In conducting the study we started from the following hypothesis: the implementation of a psycho-pedagogical intervention program focused on the communication needs of the practicing students during teaching practice and the analysis and self-analysis sessions of the communicative behavior contributes significantly to the increase of the level of communication skills development.
The sample of subjects was made up of 48 students of Primary and Preschool Pedagogy Education specialty. The themes of the activities were circumscribed to the communication skills and implicitly to the communication skills approached at the theoretical, methodological and practical level. It was considered useful to introduce activities related to the role of cooperative learning, drama art, outdoor communication and emotional communication in the development of communication skills, as contemporary pedagogy emphasizes their importance in developing the teacher's skills. These themes constituted novelty elements for students, due to their theoretical approach presented, but especially to the practical approaches initiated. Students have been very involved in the organized activities, proving creativity, empathy, emotional communication and adaptability to unpredictable situations.
In order to identify the increasing level of communication skills of students involved in the intervention program, the initial grid was reapplied.
Findings
In order to assess the extent to which the introduction into the program of learning activities centered on communication skills has significant positive effects on the level of communication skills development, quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed. As a result of completing the instruments from the stage of the formative experiment, a constant increase in them was noted during the intervention.
The effectiveness of the intervention program activities was observed at the end of each activity in terms of observable indicators as a result of its continuous assessment: enriching knowledge on the topics covered, developing practical and intellectual skills, increasing the level of skills development, changing attitudes towards learning, pedagogical practice and pupils. The evaluation was conducted through oral questionnaire, written examination and alternative portfolio method. The latter were conscientiously drawn by students, being an important source of information on practical ways of developing communication and relational competence.
For statistical analysis of research data, SPSS for Windows version 11 was used.
In order to analyze scores representing the level of communication skills development through specific abilities (oral communication, nonverbal communication, paraverbal communication, active listening, questioning, empathy, written communication), the t test for independent samples was used.
Thus, it was found that the average of the level of self-assessed communication skills by the students in the experimental group in the posttest (Average=78,06, AS=6,17) is significantly higher (t=-6,434, p<0,01) than the pretest average (Average=66,21, AS=6,17) . Figure
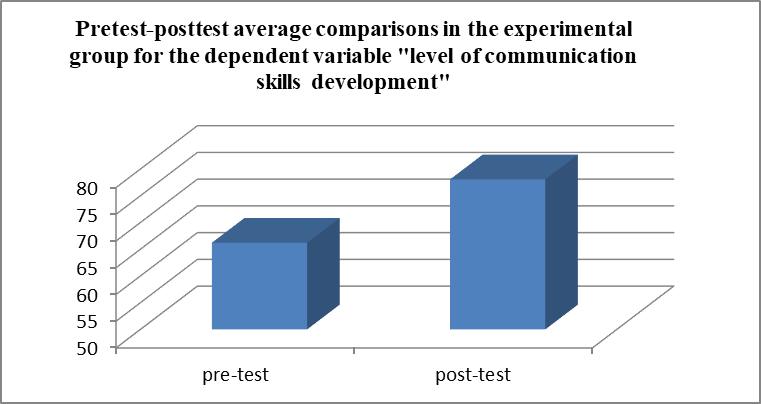
Table
The data shows a significant increase in the level of development of the students' communication
skills:
The number of students with a high level of communication skills development has increased from 5 to 32.
The number of students with a good level of communication skills development has dropped from 22 to 16. This decrease is due to the increase in the number of high-level skills students and climbing up one level in students with average skills.
The number of students with average, poor and very poor communication skills development level is non-existent.
Beyond the statistical validation of the hypothesis, the implementation of the communication skills development program has shown that the activities of the program have also contributed to the development of team work skills. Cooperative learning has been a good exercise to support the views of the group, to fight ideas, but also to support one's own opinions. The debate of reasoning and the construction of group cohesion have been considered as effective exercises for cooperation.
Conclusion
The overall conclusion is that during the experimental process, amid the practice of communication skills in the pedagogical practice activities, but also in the activities carried out within the experimental workshops, there has been a significant development of communication skills. Thus, by analyzing the results obtained during the formative intervention, as well as by the comparative pretest and posttest analysis at the level of the experimental group, the hypotheses of the research are validated.
In the category of the strengths of research, we can find the following aspects:
1. Introduction of activities related to the role of cooperative learning, drama art, outdoor communication and emotional communication in the development of communication skills promotes principles of contemporary pedagogy that contribute to the development of the teacher's skills. These themes constituted elements of novelty for students, due to their theoretical approach, but especially to the practical approaches initiated. Students have been very involved in organized activities, proving creativity, empathy, emotional communication, and adaptability to unpredictable situations.
2.The quantitative and qualitative analysis of the data in order to evaluate the extent to which the introduction into the curriculum of learning activities centered on communication skills has significant positive effects on the level of communication skills development has been recorded as a constant increase during the formative intervention. The data thus obtained during these analyzes was extremely relevant to supporting the validity of the first specific hypothesis formulated.
In addressing such a research topic, errors may frequently occur among the investigated subjects considered to be research boundaries:
providing responses comprised within the limits of social desirability, influenced by what is accepted and desired by the researcher;
the phenomenon of reactivity, which makes a person who is conscious of being observed to adopt behaviour different from the normal one.
References
- Bakić-Tomić, L., Dvorski,J. &Kirinić, A. (2015). Elements of Teacher Communication Competence: An Examination of Skills and Knowledge to Communicate, International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 157-166.
- Catalano H. & Catalano, C. (2015). The Contribution of Pedagogical Teaching Practice Activities on the Development of Communicative Competence of the Students Future Teachers for Preschool and Primary School-Ascertaining Study, International conference, Education, Reflection, Development, ERD 2015, ProcediaSocial and Behavioral Sciences, doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.11.265, 109-115
- Cucoş, C. (1998). Pedagogie. Iaşi: Editura Polirom,
- Dospinescu, V. (1998). Semiotică și discurs didactic. București: Didactica Publishing House.
- Erbay, F., Ömeroğlu & E. Çağdaş (2012), A Development and Validity-Reliability Study of a Teacher-Child Communication Scale, in Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice-Special Issue Autumn, Educational Consultancy and Research Center, 3165-3162.
- Pânişoară, I.O. (2008). Comunicarea eficientă. Ediţia a III-a, revăzută şi adăugită. Iaşi: Editura Polirom.
- Prutianu, St. (2005). Antrenamentul abilităților de comunicare. Iași: Polirom.
- Şoitu, L. (1997). Pedagogia comunicării. București: Didactica Publishing House.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
28 June 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-040-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
41
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-889
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques, special education, children with special needs
Cite this article as:
Catalano, C., & Catalano, H. (2018). Opportunities Of A Programme For Development Of Communication Skills Of Future Teachers. In V. Chis, & I. Albulescu (Eds.), Education, Reflection, Development – ERD 2017, vol 41. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 118-123). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.06.14

