Abstract
The rapid propagation of the internet has been accompanied with a wide growth of e-commerce market. This growth was however restricted due to the avalanche of information available to users from various e-commerce websites. There is a huge challenge in the aspect of decision making most especially when a buyer has to visit quite a number of e-commerce sites to make comparisons amongst prices of different products to purchase. Nevertheless, Purchase intention has been identified as a concept which gives the service providers of e-commerce systems the indication of the actual buying behavior. Therefore, this study aims to review and analyze the factors that improve and affect e-commerce customers’ purchase intention. This subject has been rarely touched in literature and needs more focus regarding its importance for both customers and service providers. This study however highlights information on patterns in e-commerce purchase intention research by analyzing the publications over the last seven years, and establishes insights and future guidance for researchers towards improving customers purchase intention.
Keywords: Purchase IntentionE-commerceLiterature Review
Introduction
Electronic commerce (often known as e-commerce) is defined as an online trade which includes different kinds of business activities such as banking, investment, rentals and retail shopping. E-commerce involves baying, selling products or services through an electronic medium without using any paper document (Niranjanamurthy, Kavyashree, 2013). The development of e-commerce has changed the traditional way of business thinking. In traditional commerce, customers were trapped to geographical and social boundaries without the chance to compare prices and products. People need to go to the marketplace to transact which usually available in specific places and times. The potential market size is limited to the region where the customers live in. E-commerce can break the old traditional boundaries and enable the users to access high quality products easily with convenience which help them to save the time and money by viewing more products and comparing prices through different and diverse websites. The activity of e-commerce can be classified into five types according to the type of business transactions: The first one is Business to Business (B2B) which refers to sales or purchase services among firms or companies. Examples of business to business e-commerce are: Alibaba, Zebra Imaging and New Town Group. Secondly, another type is business to government e-commerce which is understood as a business model that refers to trading which involves sales of products, information or services to the government parastatals. In other words, business firms can bid on government products and government organizations can purchase the products or the services. Thirdly, consumer to consumer e-commerce (sometimes can be called as customer to customer e-commerce) refers to the direct transactions between consumers usually through a third party. Examples of consumer to consumer e-commerce are: eBay and Etsy. Fourthly, business to costumer refers to business companies selling products to individuals. An example of the business to customer e-commerce is the famous Amazon website. Finally, customer to business e-commerce is the type in which customers offer a project and the budget online and the firms bid on the project then the customer chooses the company after reviewing the bids (Kang, Jang, & Park, 2016). An example of this is Elane.
Online providers are interested in understanding the factors that can improve customers’ purchase intention because of the expected profits that they will get. Purchase intention refers to the user’s plans to purchase a certain product or service. Actual user behavior can be predicted through customer intention. Customer intention provides the best determinant of a person’s behavior. This intention then helps to provide an understanding of a customer’s actual behavior (Eid, 2011).
Problem Statement
Generally, identifying factors affecting IT user adoption and acceptance has been considered a very important issue most especially in the context of e-commerce systems and many theories which originally came from the field of sociology and psychology have been propounded to explain the attributes that make a prospective user to make a decision to use new technological innovations (Venkatesh, 2012). In the previous studies on e-commerce adoption, it was mentioned that there is a significant relationship between a user’s attitude and his intention to buy a product or service using e-commerce platform (Bakar, Bidin, Syuhaidi, Bakar, & Bidin, 2014). Nevertheless, the actual behavior can also be measured by the prospective user’s intention since user’s intention is considered a determinant of a user’s behavior. However, to fully understand the user’s actual behavior, it becomes very important to firstly focus on the user’s intention (Eid, 2011).In this context, purchase intention is described as the user’s decision to buy products or services using e-commerce platforms and this attribute was considered a very crucial indicator of user IT adoption in e-commerce systems (Mansouri et al., 2012).Over the last decade, researchers have studied the factors that improve e-commerce customers purchase intention to increase the service provider’s profits. In this research, the articles which were published in an academic journal on e-commerce purchase intention since 2010 were reviewed and classified.
Research Questions
To achieve the objectives of this research we propose two main research questions. The research is expected to answer these questions which we believe will help the researchers to understand the factors that can convert the e-commerce user from browser to buyer and to gain an overall understanding of the IS theories adopted in the studies. The research questions of this study are:
What are the dominant IS theories in the studies of e-commerce purchase intention context?
What are the factors that influence consumers’ purchase intention in e-commerce context?
Purpose of the Study
The main purpose of this article is to explore the studies that have been published in the context of e-commerce purchase intention in the time between 2010 to 2016 focusing on the factors that can improve the purchase intention. This study aims to understand the trends of e-commerce purchase intention research by examining the published articles, and to provide a practitioners and academics with insight and future direction.
Research Methods
The researches of e-commerce purchase intention can be organized under diverse research disciplines which includes the field of IS, IT, computer science, management and marketing. After a deep search in the literature we have noticed that there is an increasing and diverse number of research papers in this area but there is a lack of comprehensive literature review studies in e-commerce customers’ purchase intention which is rarely touched in the literature. The purpose of this study is to understand the factors that improve customers’ purchase intention in e-commerce websites by examining the published articles in some of the well-recognized electronic journals and to provide the researchers in this area with future direction on the trends in this topic. The research methodology we followed is presented in Figure
First, description of the research methodology that is used in this research.
Second, classification of the research papers of e-commerce purchase intention according to the presented criteria’s.
Third, analysis of the results of the classification process.
Fourth, presenting the conclusion and discussion of the results. Paragraph text/Figures etc.
Classification Method
The classification processes started by a deep search in the electronic databases to find and download the papers that have a related topic. After that, the authors review the papers one by one to classify each one based on the classification framework. The selected papers were analysed and categorized according to the proposed framework adopted for this study. The classification process followed the deep electronic database search. After that classification results were discussed and verified by the authors. The papers were classified regarding to the: year of publication, journal and conference or information system theory.
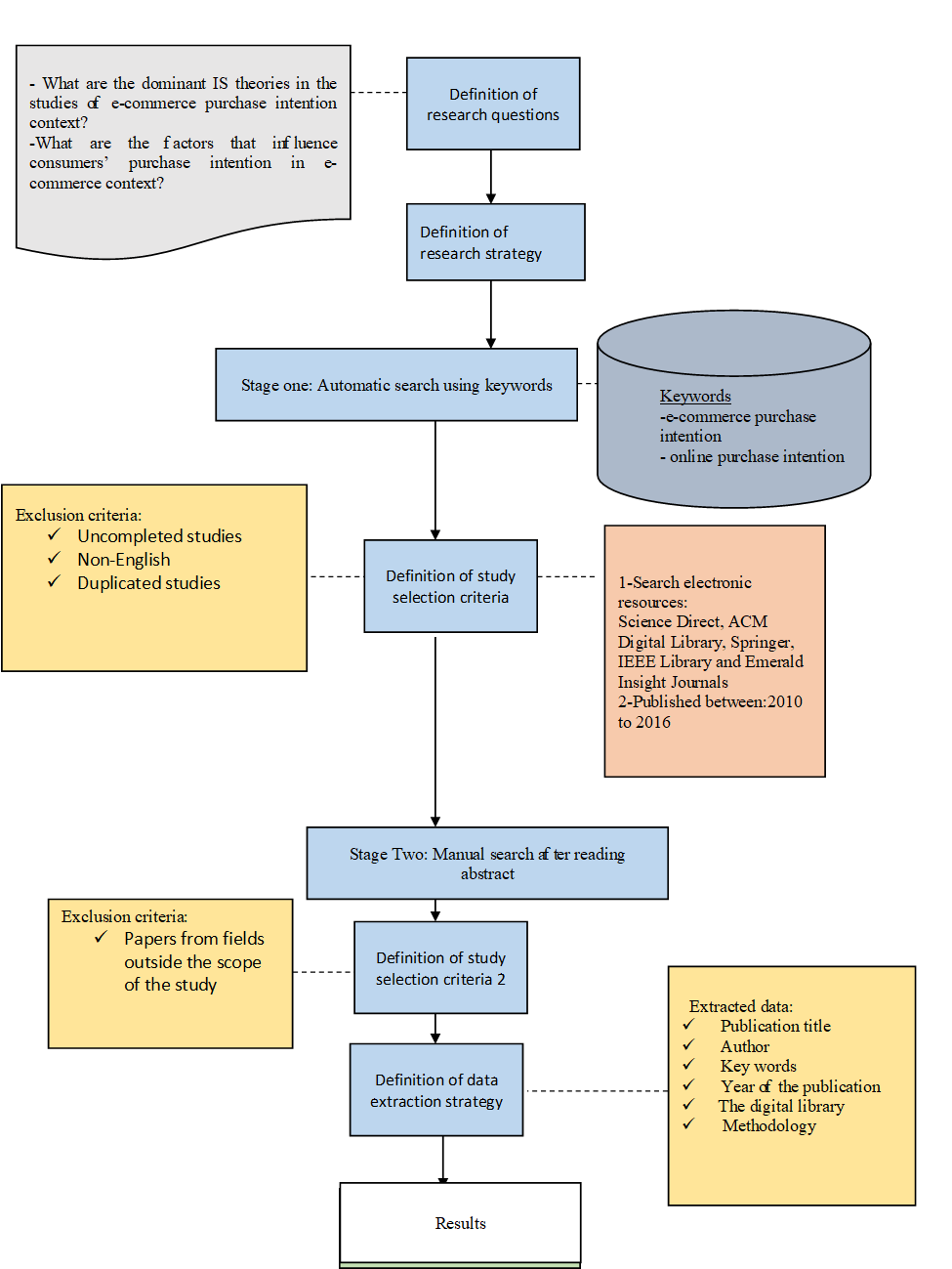
Classification method by the electronic resources
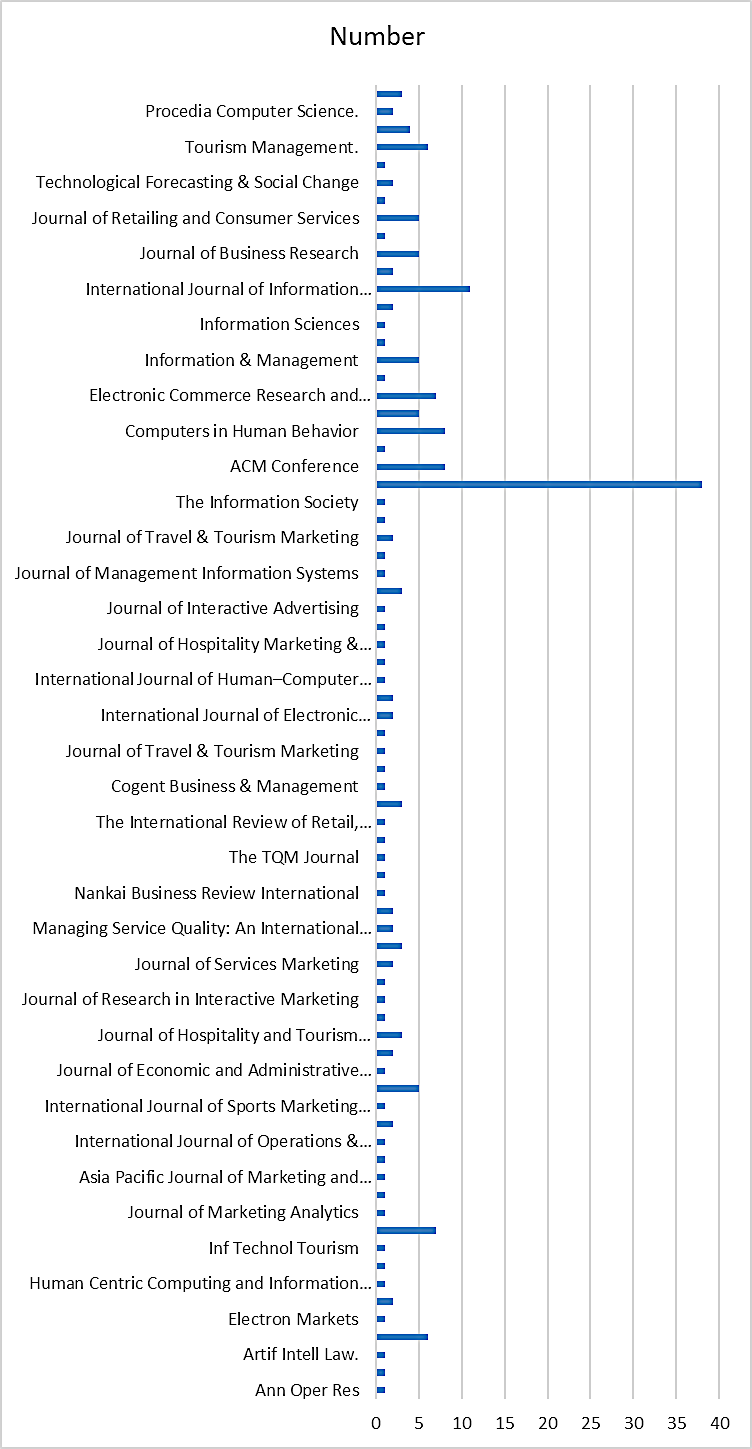
A total number of 203 research articles were selected from six main databases which include 72 journals and 41 conferences. Research papers proportion by the electronic resources is highlighted in Figure
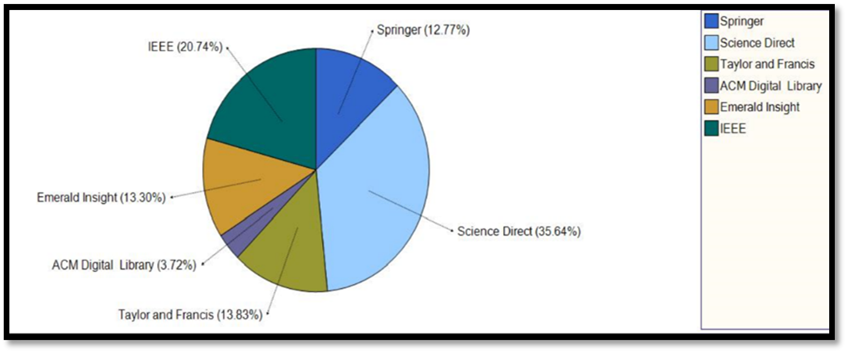
Classification method by the related IS theory
The chosen classification framework consists of the related IS theory. We classified the research papers after the review stage into 17 categories of IS based theories. The classification framework is presented in Figure
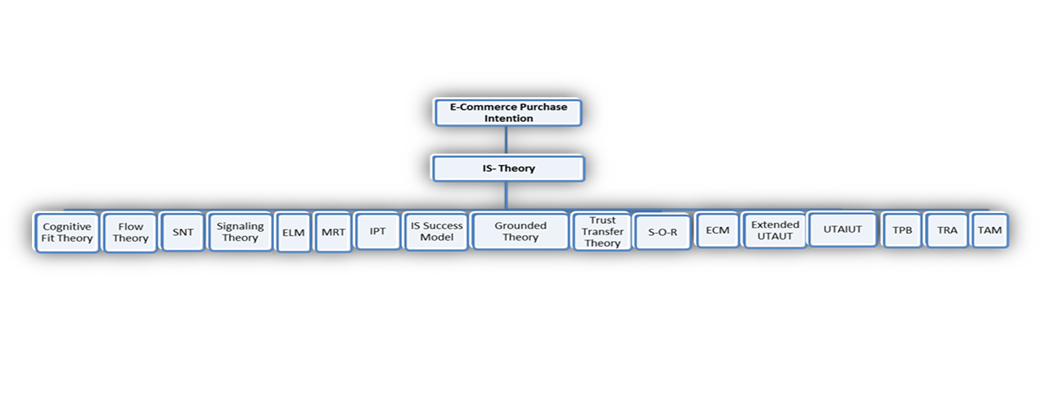
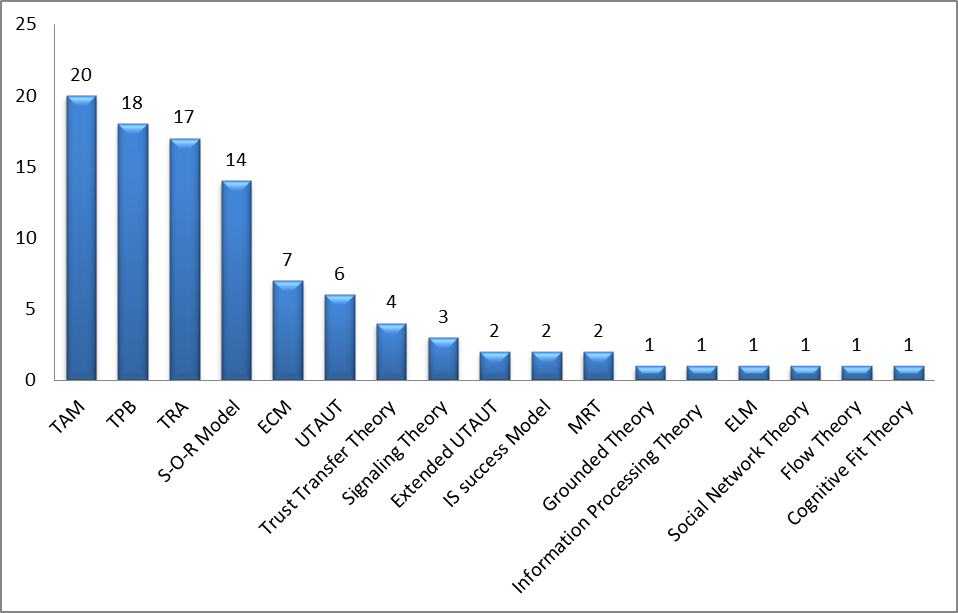
The papers which were collected and reviewed were classified according to the related IS theories. The IS theories which were founded as a base of the reviewed papers were almost about 50 IS theory. The most used theories were chosen as a base of the classification framework of this research. We classified the IS theories into the following 17 IS theories: Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB), Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), Extended Unified Theory of Acceptance and use of Technology (UTAUT2), Expectation confirmation Model (ECM), Stimulus–Organism–Response Model (SOR),Trust Transfer Theory, Grounded Theory, IS Success Model, Information Processing Theory, Media Richness Theory (MRT), Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM), Signalling Theory, Social Network Theory, Flow Theory and Cognitive Fit Theory.
TAM (Technology Acceptance Model): was developed by Davis (1985) to explain users’ acceptance of the technology. According to Davis the two-main construct affects users’ acceptance of the technology are: perceived usefulness (PU) and perceived ease of use (PEOU) (Junadi & Sfenrianto, 2015).
TRA (The theory of reasoned action): was developed by Ajzen & Fishbein (1980). This model suggests that customers’ behaviour is determined according to subjective norm and attitude towards the behaviour which affects directly customer’s behavioural intention (Hasbullah et al., 2016).
TPB (Theory of Planned Behavior): was developed by Ajzen (1991) to predict human behavioural in various fields. According to the author there are three constructs of: attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioural control which affects directly into intention(Sara et al., 2014) .
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT). A model established by Venkatesh et al. (2003). Venkatesh mentioned that performance expectancy, effort expectancy, facilitating condition and social influence are determinants of prospective users IT adoption.
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT2) an extension to original UTAUT model established by Venkatesh (2012).
Expectation confirmation model (ECM): this model was developed based on expectation confirmation theory to predict IS customers continues usage and customers’ satisfaction by Oliver (1980). The model contains three main constructs which are: expectations, perceived performance, and disconfirmation of beliefs (Hozhabri et al., 2014).
Stimulus–Organism–Response Model (SOR): the model was proposed by Mehrabian & Russell (1974). In SOR model environmental stimuli (S) affects consumer internal states (O) and influences consumers' overall responses (Liu et al., 2016).
Trust transfer theory: According to Stewart (2003) trust can be transferred to new target if this target related to trusted source (Lee et al., 2011)
. The Grounded Theory method was developed by Glaser & Strauss (1967)Grounded theory is considered as a research methodology which involves developing a theory through the data analysis (Ong & Teh, 2016).
Information System Success Model: was developed by Petter, DeLone & McLean (2008) to measure the success of an information system. According to it, the quality of the information system affects users’ acceptance and adoption of it (Gao, Waechter, & Bai, 2015).
Information processing theory: Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) developed the stage theory which is the base of information processing theory. In this theory, human brain processes the information like the computer.
Media Richness Theory (MRT): developed by Daft & Lengel (1986). Basically, this theory is about how the organization reduces the uncertainty and equivocality by processing the information.
Elaboration likelihood Model (ELM): developed by Petty & Cacioppo(1984). It is a “dual-process” theory that explains the persuasion’s process.
Signaling theory: developed by Spence (1973). The main idea behind signaling theory is about two parties and how one part conveys information to the other.
Social Network Theory: it was originated by Milgram (1967) . This theory presents the social network as nodes and ties. Nodes are the actors in the network and ties are the relationships between the actors in the network.
Flow Theory: it was proposed by Csikszentmihalyi et al. (1975). This theory describes the positive experiences of enjoyment and the positive affect on individuals.
Cognitive Fit Theory: developed by Vessey (1991), this theory describes how matching between the task and the format of the presentation will result to effective problem solving.
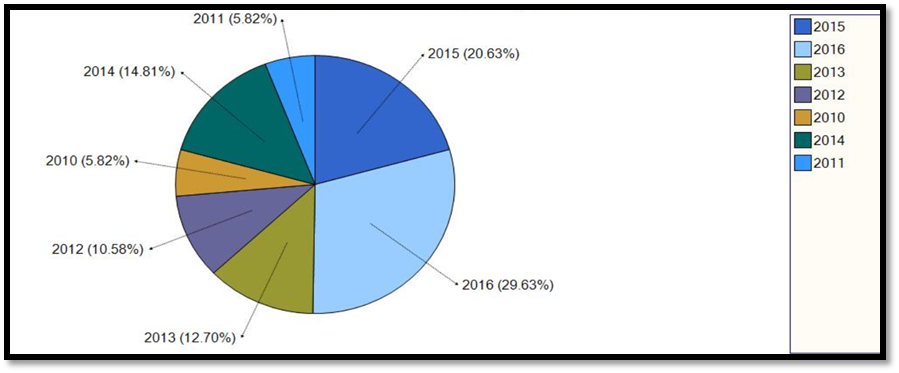
Research papers distribution by year of publications.
The research papers in this study were chosen according to the publication year between 2010 and 2016. According to the analysis of the selected papers, it appears that the publications related to e-commerce purchase intention increase steadily between 2011 and 2016. The research papers distribution by year of publication is highlighted in Figure
Findings
Research papers distribution by information system theory
Among the 203 papers 20 papers adopted TAM model or extended it in e-commerce purchase intention context. This shows that TAM model is still popular among researchers and it is still widely used in e-commerce studies. TPB model was adopted in 18 papers in the chosen frame work, followed by TRA model which was adopted in 17 papers. S-O-R model was used in 14 papers. Classifications of research papers according to Information system theories were highlighted in Figure
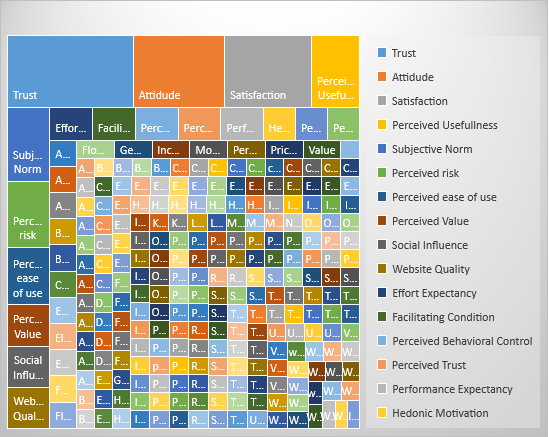
Distribution of research papers by factors affecting customers purchase intention
The main purpose of this study is to investigate the factors affects customers purchase intention in e-commerce. As this issue is very important for both researchers and service providers, this topic gained the interest of researchers from different areas. The research showed that trust plays an important role in improving customers purchase intention. Trust appeared in 29 of the selected research papers as an influence factor that can derive customers purchase intention. Attitude and satisfaction were studied as some determinants of customers purchase intention in 19,18 studies respectively. Other factors such as: perceived usefulness, perceived risk, perceived value, perceived ease of use and subjective norm were investigated as important drivers of consumers purchase intention. Figure
With the increasing demands of e-markets and the furious competition from several rivals, firms are eager to maintain their customers by gaining their satisfaction and trust. The trust issue have been investigated in several researches in the context of e-commerce, information system, market and recommender systems fields (Nilashi et al., 2016). Trust formation theories were inspected deeply in the literature and identified by several processes such as: cognition, knowledge, transference and calculation. Mayer, Davis, & Schoorman (1995) defined the trust as the “willingness to be vulnerable”. Trust is positively associated with customers’ intention to purchase a product, transact and return to the website (Pu & Chen, 2007).
Satisfaction on the other hand is defined as the pleasurable fulfillment accumulated over multiple transaction experiences, which comes from overall evaluation of the online retailer. Researchers have made great efforts to understand antecedents and consequences of customers satisfaction.
As mentioned before, TRA model was adopted in 17 papers from the surveyed papers. TRA model assumes that the actual behavior is predicted by the behavioral intention. On the other hand, it proposes that subjective norm and attitude determine the customer behavior. There is a clear relationship between consumer attitude and their intention to buy products or the services using e-commerce (Bakar et al., 2014).
Conclusion
E-commerce purchase intention has attracted the attention of researchers and academics in the last years and as we can conclude from the results, so many journals and conferences published about the research topic in the last six years. From the deep research, we came up with the following conclusions:
Among the 203 papers, 34 research papers are based on TAM model, TRA model or TPB model. These three models are still widely used in the researches related to user’s acceptance of the technology. Therefore, it is not surprising that these three models have been widely used in the e-commerce purchase intention context.
There are several models and theories which were used and applied to explain how the user accept an online product and convert from just browsing the website to purchase from it. Among these theories and models 17 theories appeared in the papers that were chosen from the literature.
After reviewing the previous publication rates, we can conclude that the interest in e-commerce purchase intention will increase in the future. This result is directly connected with the huge expansion of e-commerce and service providers’ interest of increasing the profits by knowing the factors that lead the customers to purchase from the website.
Our research is important because of the various journals and conferences that published e-commerce purchase intention researches. E-commerce purchase intentions researches have been published in MIS journals, business journals and CS journals. However, it is expected to see more publications in the research topic in the future. Published research articles dimension by journal/conference proceedings is highlighted in Figure
07 .The research highlighted the factors that have gained the interest of the researchers in the context of e-commerce purchase intention such as: trust, attitude, satisfaction, perceived usefulness, perceived risk, perceived value, perceived ease of use and subjective norm. Other factors such as: loyalty, emotion and e-word of mouth need more focus in the research.
This study classification framework is expected to provide researchers some insights for future research direction on e-commerce purchase intention. This research has some limitations which includes lack of time, limitations regarding researches’ year of publications and the search was limited to five top electronic databases. The results of the analysis could be different if this study was extended to cover more journals and conferences. The research was performed based on the following keyword: “e-commerce purchase intention”, “online purchase intention”. However, the results may change if different keywords like:”B2B purchase intention” or “C2C purchase intention”.
References
- Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
- Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1980). Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Prentice-Hall. Retrieved from https://catalog.hathitrust.org/Record/000039190
- Bakar, M. S. A., Bidin, R., Syuhaidi, M., Bakar, A., & Bidin, R. (2014). Technology Acceptance and Purchase Intention towards Movie Mobile Advertising among Youth in Malaysia. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 130, 558–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.065
- Csikszentmihalyi, I., Graef, R., Holcomb, J. H., Hendin, J., & Acaloon, J. M. (1975). BEYOND BOREDOM AND ANXIETY. Retrieved from http://psy2.ucsd.edu/~nchristenfeld/Happiness_Readings_files/Class 7 - Csikszentmihalyi 1975.pdf
- Daft, R. L., & Lengel, R. H. (1986). Organizational Information Requirements, Media Richness And Structure. Management Science, 32(5). Retrieved from https://blogs.commons.georgetown.edu/cctp-745-spring2010/files/organizational-information-requirements.pdf
- Davis, F. D. (1985). A Technology Acceptance Model for Empirically Testing New End-User Information Systems. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, (December 1985), 291.
- Eid, M. I. (2011). Determinants of e-commerce customer satisfaction, trust, and loyalty in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 12(1), 78–93. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
- Gao, L., Waechter, K. A., & Bai, X. (2015). Understanding consumersâ€TM continuance intention towards mobile purchase: A theoretical framework and empirical study – A case of China. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.014
- Glaser, & Strauss. (1967). The Discovery of Grounded Theory. Retrieved from http://www.sxf.uevora.pt/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Glaser_1967.pdf
- Hasbullah, N. A., Osman, A., Abdullah, S., Salahuddin, S. N., Ramlee, F., & Soha, H. M. (2016). ScienceDirect The Relationship of Attitude, Subjective Norm and Website Usability on Consumer Intention to Purchase Online: An Evidence of Malaysian Youth. Procedia Economics and Finance, 35(35), 493–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2212-5671(16)00061-7
- Hozhabri, A., Raeesi, R., Salimianrizi, H., & Tayebiniya, J. (2014). e- Trust e- Trust acceptance, (April).
- Junadi, & Sfenrianto. (2015). ScienceDirect A Model of Factors Influencing Consumer’s Intention To Use E-Payment System in Indonesia. Procedia Computer Science, 59, 214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.557
- Kang, D., Jang, W., & Park, Y. (2016). Evaluation of e-commerce websites using fuzzy hierarchical TOPSIS based on E-S-QUAL. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 42, 53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.01.017
- Lee, J., Park, D., Han, I., & Park, D.-H. (2011). The different effects of online consumer reviews on consumers’ purchase intentions depending on trust in online shopping malls: An advertising perspective The different effects of online consumer reviews on consumers’ purchase intentions depending on trus. Internet Research Iss- Review, 21(1), 187–206. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1108/10662241111123766784
- Liu, H., Chu, H., Huang, Q., & Chen, X. (2016). Computers in Human Behavior Enhancing the fl ow experience of consumers in China through interpersonal interaction in social commerce. Computers in Human Behavior, 58, 306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.01.012
- Mayer, R. C., Davis, J. H., & Schoorman, F. D. (1995). An integrative model of organizational trust. Academy of management review, 20(3), 709-734.
- Mansouri, A., Amani, D., Karousli, B., Sarbaz Barazandeh, N., Mohammadi, F., Khoshghadam, N., & Nemati, H. (2012). The Impact Assessment of the Quality Factors of Different Brands of Machine-made Carpet in Increasing Costumer’s Satisfaction (A case study: machine –made carpet produced in Boukan). J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res, 2(6), 6128–6132. Retrieved from https://www.textroad.com/pdf/JBASR/J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 2(6)6128-6132, 2012.pdf
- Mehrabian, A., & Russell, J. A. (1974). An approach to environmental psychology. Cambridge Mass.: The Mit Press. Retrieved from http://www.worldcat.org/title/approach-to-environmental-psychology/oclc/318133343
- Niranjanamurthy, Kavyashree, S. J. D. C. (2013). Analysis of E-Commerce and M-Commerce: Advantages, Limitations and Security issues. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 2(6). Retrieved from www.ijarcce.com
- Oliver, R. L. (1980). A Cognitive Model of the Antecedents and Consequences of Satisfaction Decisions. Source Journal of Marketing Research, 17(4), 460–469. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/3150499
- Ong, C. E., & Teh, D. (2016). Redress procedures expected by consumers during a business-to- consumer e-commerce dispute. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2016.04.006
- Petter, S., DeLone, W., & McLean, E. (2008). Measuring information systems success: models, dimensions, measures, and interrelationships. European Journal of Information Systems, 17(3), 236–263. https://doi.org/10.1057/ejis.2008.15
- Petty, R. E., & Cacioppo, J. T. (1984). Source Factors And The Elaboration Likelihood Model Of Persuasion, 11(11), 668–672. Retrieved from http://www.communicationcache.com/uploads/1/0/8/8/10887248/source_factors_and_the_elaboration_likelihood_model_of_persuasion.pdf
- Pu, P., & Chen, L. (2007). Trust-inspiring explanation interfaces for recommender systems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 20(6), 542-556.
- Sara, N., Yunus, N. M., Edura, W., Rashid, W., Ariffin, N. M., & Rashid, N. M. (2014). Muslim’s Purchase Intention towards Non-Muslim’s Halal Packaged Food Manufacturer. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 130, 145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.018
- Spence, M. (1973). Job Market Signaling. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 87(3), 355–374. Retrieved from http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0033-5533%28197308%2987%3A3%3C355%3AJMS%3E2.0.CO%3B2-3
- Stanley Milgram. (1967). "The Small World Problem", Psychology Today, 1967, Vol. 2, 60-67 - DJJR Sociology. Retrieved August 11, 2017, from http://mills-soc116.wikidot.com/notes:milgram-small-world
- Stewart, K. J. (2003). Trust transfer on the world wide web. Organization Science, 14(1), 5-17.
- Venkatesh, V. (2012). C ONSUMER A CCEPTANCE AND U SE OF I NFORMATION T ECHNOLOGY : E XTENDING THE U NIFIED T HEORY, 36(1), 157–178.
- Vessey, I. (1991). Cognitive Fit: A Theory-Based Analysis of the Graphs Versus Tables Literature. Decision Sciences, 22(2), 219–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5915.1991.tb00344.x
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 May 2018
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-039-6
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
40
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1231
Subjects
Business, innovation, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues
Cite this article as:
Abumalloh, R. A., Ibrahim, O. B., Nilashi, M., & Abu-Ulbeh, W. (2018). A Literature Review On Purchase Intention Factors In E-Commerce. In M. Imran Qureshi (Ed.), Technology & Society: A Multidisciplinary Pathway for Sustainable Development, vol 40. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 386-398). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2018.05.31
